Case-Based Questions: Sources of Business Finance | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Faulad Steel Ltd. is a multi-product company, manufacturing steel pipes in wide range for wide spectrum of application. Recently the company received a big order from an MNC for which it requires additional funds. The finance manager reported that the company is not in a position to bear extra burden of explicit cost and equity shareholders insisted not to issue more shares as it can affect their control consideration. Now, the company has only one option, i.e., ploughing back of profit.
Q1: ‘Company is not in a position to bear extra burden of explicit cost.’ Identify the meaning of explicit cost in the context of equity shares.
(a) Dividend
(b) Interest
(c) Market value of shares
(d) Operating expenses
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Explicit cost in the context of equity shares refers to the direct financial obligation a company incurs. For equity, this is primarily the dividend, which is a portion of profits paid to shareholders. The finance manager's concern is that paying dividends would increase the financial burden on the company. Unlike interest on debt, dividends are not mandatory but are expected by shareholders. Issuing new equity could dilute ownership and control, thus dividends are considered a cost. Explicit costs are typical business costs that appear in the general ledger and have a direct impact on the profitability of a company. Examples of explicit costs include salaries, raw materials, utilities, lease payments, and other direct costs.
Q2: Right to control is enjoyed by which of the following sources of finance?
(a) Debentures
(b) Equity shares
(c) Retained earnings
(d) Preference shares
Correct Answer: Option (b)
Equity shares are long-term financing sources for any company. These shares are issued to the general public and are non-redeemable in nature. Investors in such shares hold the right to vote, share profits and claim assets of a company.
Q3: ’.............. can affect their control consideration.’ What is the meaning of control consideration in this context?
(a) Control over funds
(b) Control over management
(c) Control over risks
(d) Control over the activities of the company
Correct Answer: Option (d)
Control Consideration means the amount per Company Share to be received by Company Shareholders in connection with a Change of Control Transaction, with any non-cash consideration valued as determined by the value ascribed to such consideration by the parties to such transaction.
Q4: In the above case, which of the following sources of finance is most suitable?
(a) Shares
(b) Debentures
(c) Retained earnings
(d) Bank loans
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Retained earnings are funds generated from the company's profits, not distributed as dividends, and reinvested in the business. This source does not incur explicit costs like interest or dilute ownership, maintaining existing shareholder control. Ploughing back profits aligns with the company's situation, where external financing options, like issuing shares or taking on debt, are not viable. Using retained earnings is cost-effective and supports financial stability without affecting shareholder influence. Retained earnings (RE) is the amount of net income left over for the business after it has paid out dividends to its shareholders. The decision to retain the earnings or distribute them among the shareholders is usually left to the company management.
Case 2: Saksham Ltd.
Saksham Ltd., a firm manufacturing textiles, needs to finance its day-to-day expenses, like, wages, rent, maintain stock of raw material, etc. Other than this, the company also decides to set up a new plant at an estimated cost of ` 5 crores. The finance manager of the company, Mr. Ramakant was asked by the management to do the financial planning by identifying most suitable source of raising long-term funds for financing the investment decision and short-term sources for working capital decision. As per the suggestions of Mr. Ramakant, the company approached their raw material supplier to give them credit for three months, so that the company can get cloth for making garments without making immediate payment. For long-term investment, the company had issued equity and preference shares to meet its requirement. This decision resulted in payment of large amount of taxes to government as dividend on shares is not deducted from total income of the company before calculating income tax. But this situation could be avoided if company had chosen borrowed funds as a source of finance.
Q5: State the source of finance, suggested by Mr. Ramakant to finance working capital decision.
(a) Trade credit
(b) Public deposits
(c) Equity and Preference shares
(d) Retained earnings
Correct Answer: Option (a)
The source of finance suggested by Mr. Ramakant to finance the working capital decision is trade credit. Trade credit is an arrangement where suppliers allow the company to purchase goods or services and pay for them later, typically within 30 to 90 days. This method helps the company manage its cash flow efficiently by deferring payments, allowing it to use its available funds for other immediate expenses. Trade credit is a common short-term financing strategy for managing day-to-day operational costs.
Q6: State the factors which have not been kept in mind for selecting source of long-term finance.
(a) Risk involved
(b) Financial capacity of the firm
(c) Time period
(d) Tax benefits
Correct Answer: Option (d)
Long-term finance can be defined as any financial instrument with maturity exceeding one year (such as bank loans, bonds, leasing and other forms of debt finance), and public and private equity instruments. Equity, which has no final repayment date of a principal, can be seen as an instrument with non finite maturity.
Q7: State the source of finance which can give the benefit of tax saving.
(a) Equity Shares
(b) Debentures
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Correct Answer: Option (b)
Debentures are a debt instrument used by companies and government to issue the loan. Debentures are also known as a bond which serves as an IOU between issuers and purchaser. Companies use debentures when they need to borrow the money at a fixed rate of interest for its expansion.
Q8: Identify the fund needed for the day-to-day operations of business.
(a) Working capital
(b) Trading capital
(c) Equity capital
(d) Debt capital
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Working capital is the money used to cover all of a company's short-term expenses, which are due within one year. Working capital is the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities. Working capital is used to purchase inventory, pay short-term debt, and day-to-day operating expenses.
Q9: Equity shares are long term sources of Business Finance.
(a) True
(b) False
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Equity shares are one of the most important financial instruments to raise long-term funds needed for the incorporation, expansion, and growth of an organization. These shares are treated as the base for capital formation of the organization. Equity shareholders are considered as the real owners of the organization.
Q10: Match the Columns

Select the correct matching:
(a) 1-(b); (2)-(a); (3)-(c)
(b) 1-(b); (2)-(c); (3)-(a)
(c) 1-(a); (2)-(c); (3)-(b)
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer: Option (b)
1. Shareholder: A shareholder, also referred to as a stockholder, is a person, company, or institution that owns at least one share of a company's stock, which is known as equity. Because shareholders are essentially owners in a company, they reap the benefits of a business' success.
2. Commercial Bank: The term commercial bank refers to a financial institution that accepts deposits, offers checking account services, makes various loans, and offers basic financial products like certificates of deposit (CDs) and savings accounts to individuals and small businesses.
3. Debenture: A debenture is a bond issued with no collateral. Instead, investors rely upon the general creditworthiness and reputation of the issuing entity to obtain a return of their investment plus interest income. Examples of debentures are Treasury bonds and Treasury bills.
Q11: Match the Columns
(a) 1-(b); (2)-(a); (3)-(c)
(b) 1-(b); (2)-(c); (3)-(b)
(c) 1-(c); (2)-(b); (3)-(a)
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer: Option (c)
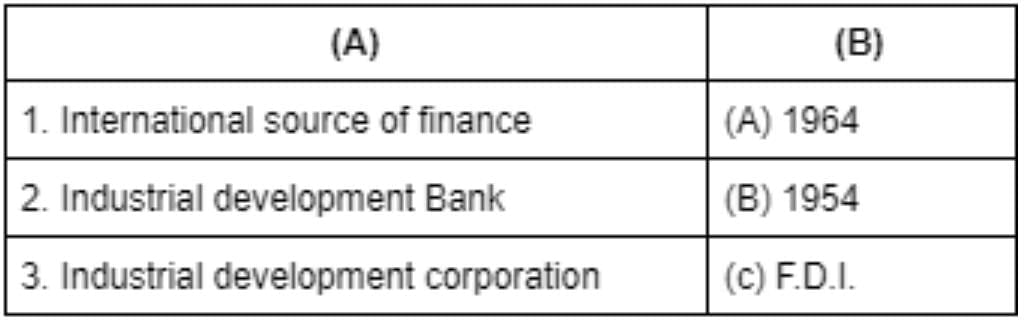
1. International source of finance: FDI has been an important source of finance for the LLDCs in terms of both the value of FDI stock as a percentage of GDP and the contribution of FDI to capital formation (GFCF).2. Industrial development Bank: Industrial Development Bank of India was established in 1964 by an act to provide credit and other financial facilities for the development of the fledgling Indian industry.3. Industrial development corporation: The National Industrial Development Corporation LTD is a Non-govt company, incorporated on 20 Oct, 1954. It's a public unlisted company and is classified as company limited by shares'.
Q12: Match the Columns
(a) 1-(b); (2)-(c); (3)-(a)
(b) 1-(b); (2)-(c); (3)-(b)
(c) 1-(a); (2)-(c); (3)-(b)
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer: Option (a)
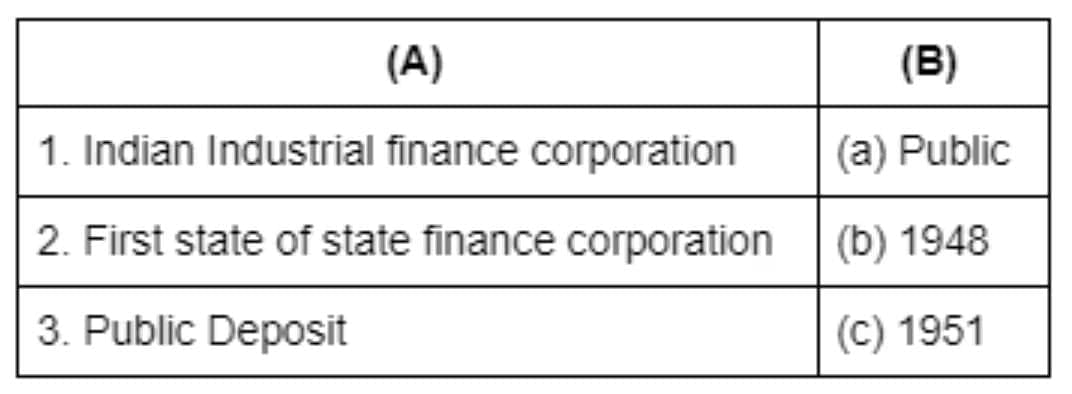
1. Indian Industrial finance corporation: IFCI, previously Industrial Finance Corporation of India, is a development finance institution under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. Established in 1948 as a statutory corporation, IFCI is currently a company listed on BSE and NSE.2. First state of state finance corporation: The State Financial Corporations Act, 1951, with the basic objective of promoting and developing small scale and medium scale industries in the State with a special focus on spreading industrial culture in the rural, semi-urban and backward areas of the State.3. Public Deposit: The deposits that are raised by organisations directly from the public are known as public deposits. Rates offered on public deposits are higher than of bank deposits. But, there is higher risk in public deposits. Public deposits cater to both short term and medium term finance requirements.
|
38 videos|264 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Case-Based Questions: Sources of Business Finance - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the primary sources of business finance? |  |
| 2. How does equity financing differ from debt financing? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using retained earnings as a source of finance? |  |
| 4. What role do venture capitalists play in business finance? |  |
| 5. What is trade credit, and how can it benefit businesses? |  |




















