Case-Based Questions: Small Business | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Carefully read the following case studies, which present real-world business scenarios, and answer the question(s) that follow each case to test your understanding and application of business studies concepts.
Case 1: Ramit is planning to start his business and wanted to know the related Acts and the years they were passed, applicable to his business. Help him in identification.
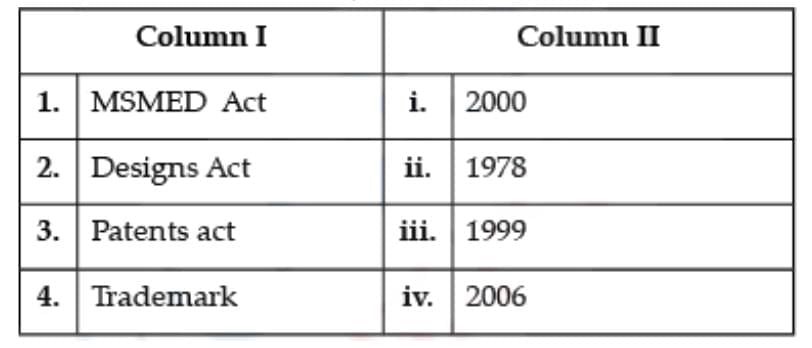
Question: Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (iv), 2. (i), 3. (ii), 4. (iii)
(b) 1. (i), 2. (ii), 3. (iii), 4. (iv)
(c) 1. (ii), 2. (iii), 3. (i), 4. (iv)
(d) 1. (i), 2. (ii), 3. (iv), 4. (iii)
Correct Answer: Option (a)
1. MSMED Act: The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development Act, 2006 aims at facilitating the promotion, development and enhancing the competitiveness of micro, small and medium enterprises and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.2. Designs Act: Designs Act 2000, a Design registration can now be obtained for new or original features of shape, configuration, pattern, ornamentation or composition of lines or colours as applied to an article, whether in two or three dimensions or both.
3. Patents act: The Patents Act 1970-1978 had a very limited scope of protection wherein the essential elements of invention were new, useful and manner of manufacture. The Act defines 'capable of industrial application' in relation to an invention as capable of being made or used in an industry.
4. Trademark: Indian trademark law statutorily protects trademarks as per the Trademark Act, 1999 and also under the common law remedy of passing off.
Case 2: Match the features given in column I with the suitable options of IPRs given in column II.
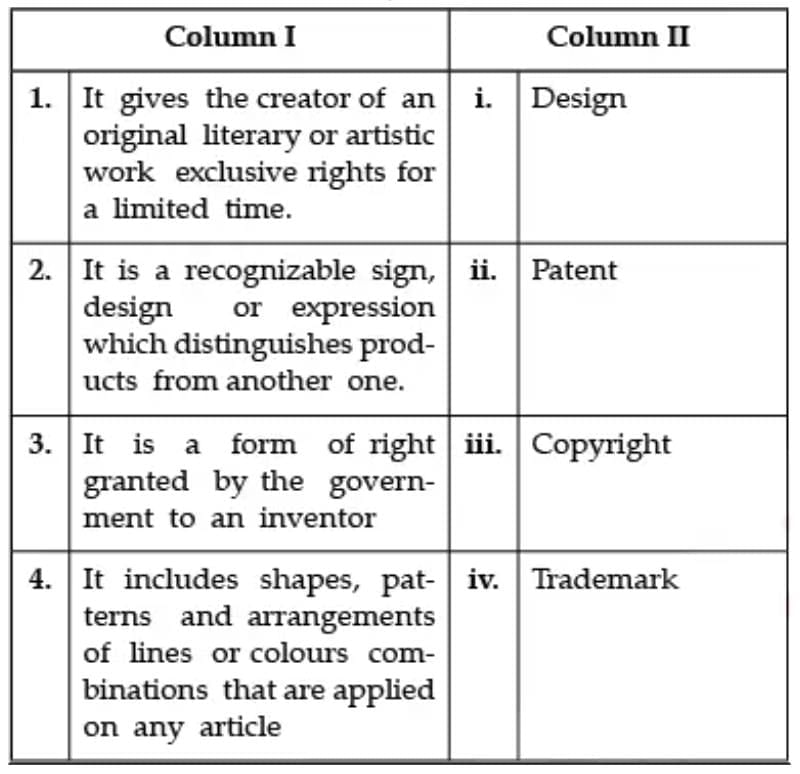
Question: Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (ii), 2. (iv), 3. (iii), 4. (i)
(b) 1. (iv), 2. (i), 3. (ii), 4. (iii)
(c) 1. (iii), 2. (iv), 3. (i), 4. (ii)
(d) 1. (iii), 2. (iv), 3. (ii), 4. (i)
Correct Answer: Option (a)
1. Patent: A patent is the granting of a property right by a sovereign authority to an inventor. This grant provides the inventor exclusive rights to the patented process, design, or invention for a designated period in exchange for a comprehensive disclosure of the invention. They are a form of incorporeal right.
2. Trademark: Trademark performs the following four functions. It identifies the product and its origin. It proposes to guarantee its quality. It advertises the product. It creates an image of the product in the minds of the public, particularly the consumers or the prospective consumers of such goods.
3. Copyright: Copyright restricts unauthorised use of any sort of work: Copyright gives the sole right to the owner to produce/reproduce the piece of their original work. Copyright protection is automatic: As of January 1, 1978, under US copyright law, a work is automatically protected by copyright when it is created.
4. Design: Design is not just about making objects pretty. Design is the process of deeply understanding customer/user needs and then creating a product or service physical, digital, or both—that addresses their unmet needs.
Case 3: Match the IPR given in column I with the suitable options given in column II.
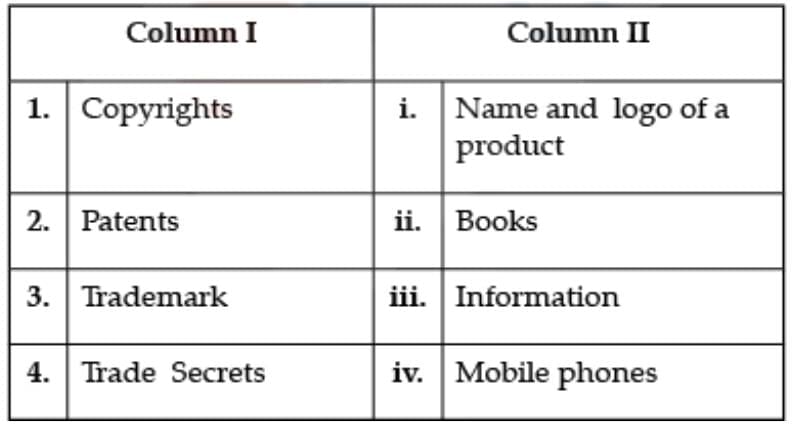
Question: Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (iv), 2. (i), 3. (ii), 4. (iii)
(b) 1. (ii), 2. (iv), 3. (iii), 4. (i)
(c) 1. (ii), 2. (iv), 3. (i), 4. (iii)
(d) 1. (iii), 2. (iv), 3. (i), 4. (ii)
Correct Answer: Option (c)
1. Copyright: Copyright law protects the owner of property rights in literary and artistic works against those who 'copy' or otherwise take and use the form in which the original work was expressed by the author. To qualify for copyright protection, a work must be original.2. Patents: A mobile phone consists of many different intellectual property rights, such as trademark, design, copyright and usually several thousand patents.
3. Trademark: A trademark is a visual symbol – a word, name, numbers, label, logo, a combination of colours, etc. It is a mark of uniqueness and helps the customers identify a particular brand or company. The Trademark Act, 1999, governs the laws related to trademarks and their registration.
4. Trade Secrets: A trade secret is any practice or process of a company that is generally not known outside of the company. Information considered a trade secret gives the company a competitive advantage over its competitors and is often a product of internal research and development.
Case 4: Matching Institutions and Objectives
Match the Institutions given in column I with their objectives given in column II.
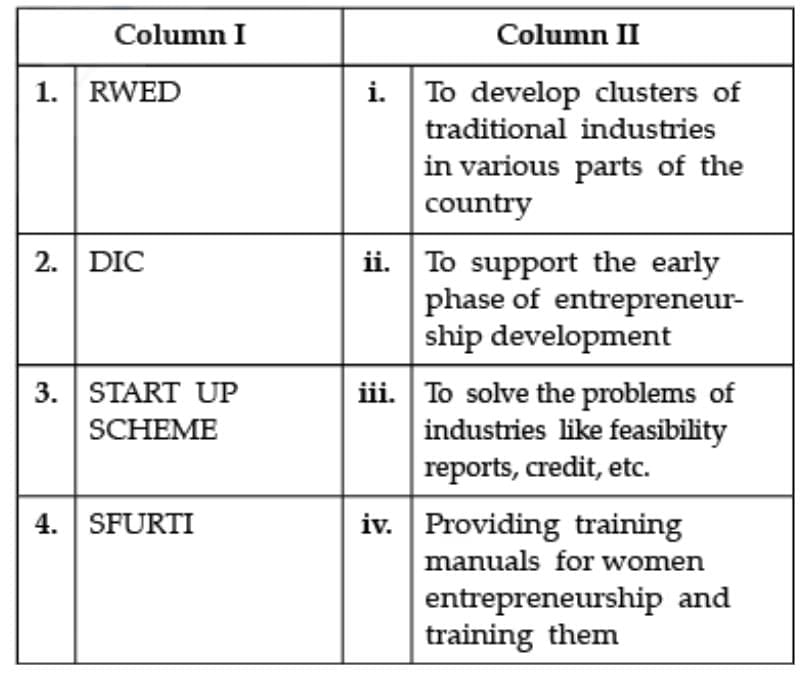
Question: Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (iv), 2. (iii), 3. (ii), 4. (i)
(b) 1. (ii), 2. (iii), 3. (iv), 4. (i)
(c) 1. (iii), 2. (ii), 3. (iv), 4. (i)
(d) 1. (iv), 2. (iii), 3. (i), 4. (ii)
Correct Answer: Option (a)
1. RWED: RWED stands for Rural and Women Entrepreneurship Development. RWED aims to promote female entrepreneurship in rural areas and improve women's professional qualifications in rural areas by organising a development program, i.e. through training on business matters, confidence and self-awareness of oneself and techniques related to the care of dependent elderly people.2. DIC: Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a serious disorder in which the proteins that control blood clotting become overactive.
3. Start Up scheme: Startup India Scheme is an initiative by the Government of India for the generation of employment and wealth creation. The goal of Startup India is the development and innovation of products and services, and increasing the employment rate in India.
4. SFURTI: SFURTI is a Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries. Ministry of MSME has launched this scheme in the year 2005 with the view to promote Cluster development. KVIC is the nodal Agency for the promotion of Cluster development for Khadi as well as for V.I. products.
Directions: Answer the next two questions based on the given passage.
Case 5: Neeru’s Pickle Business
Neeru was a daily wage labourer when she decided to be her own boss and transformed herself into a successful businesswoman. She started her small scale business of making Pickles using organic fruits and vegetables with a total investment of ₹ 10 lakhs, along with a few of her neighbours using their free time at home. She invested ₹ 2 lakhs by selling her jewellery and using personal savings, and ₹ 6 lakhs were contributed by her friends who are members of her business. They named their venture ‘Sakhi Aadhaar’. They launched their new range of pickles using aloe vera, turmeric, and other herbs, for boosting the immunity of the users. They were able to supply the entire district. One of the members suggested that they should make herbal candies too. The products made by them were well-liked and appreciated by the people.
Q1: Identify the quality of Neeru as an entrepreneur in the above case.
(a) Innovator
(b) Job provider
(c) Risk bearer
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer: Option (d)
Quality of Neeru as an entrepreneur are:
Innovator
Job provider
Risk bearer
Q2: Identify the essence of entrepreneurship in the light of the given statement. “…using organic fruits and vegetables with a total investment of ₹ 10 lakhs along with few of her neighbours using their free time at home. She invested ₹ 2 lakhs by selling her jewellery and using personal savings and ₹ 6 lakhs are contributed by her friends who are members of her business.”
(a) Arranging resources
(b) Risk-taking
(c) Vocational training
(d) Creating job opportunities
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Organizing involves assigning tasks, grouping tasks into departments, delegating authority, and allocating resources across the organisation. During the organizing process, managers coordinate employees, resources, policies, and procedures to facilitate the goals identified in the plan.
Case 6: Sensing the business opportunities in Food industry, Sagar Bagada, after completing his graduation in agricultural engineering, decided to open his own enterprise. His dream turned into reality when his enterprise, “Swaad Food Industries”, set up its food and beverages processing plant in ‘Mitrapura’’, one of the rural area of Rajasthan, under the Start-up India Scheme launched on 16th January, 2016. The enterprise opted for labour intensive technique, due to easy availability of labour at a lower cost. Within no time, he came on the list of successful entrepreneurs.
Q1: What is the process of creation of an enterprise known as?
(a) Venture
(b) Project
(c) Entrepreneurship
(d) Business idea
Correct Answer: Option (c)
The process of action, an entrepreneur undertakes to establish an enterprise is called entrepreneurship. It is the process of running, designing and launching a new company or business that is often a small business initially. The individuals who create these kinds of businesses or companies are called entrepreneurs.
Q2: “The enterprise opted for labour intensive technique, due to the easy availability of labour at a lower cost.” Identify the need for entrepreneurship satisfied in the given statement.
(a) Organisation of production
(b) Generation of employment
(c) Economic efficiency
(d) Generation of business opportunities for others
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Economic efficiency is when all goods and factors of production in an economy are distributed or allocated to their most valuable uses, and waste is eliminated or minimised.
|
38 videos|270 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Case-Based Questions: Small Business - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the primary benefits of using e-commerce for small businesses? |  |
| 2. How can small businesses effectively market their products online? |  |
| 3. What are the common challenges small businesses face in e-commerce? |  |
| 4. What payment options should small businesses offer on their e-commerce platforms? |  |
| 5. How can small businesses ensure customer trust in their online transactions? |  |





















