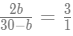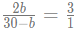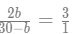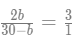CAT Previous Year Questions - Quantitative Reasoning | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) PDF Download
2022
Passage - 1
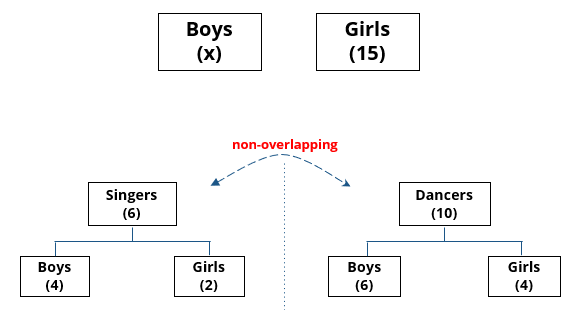
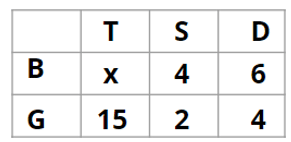
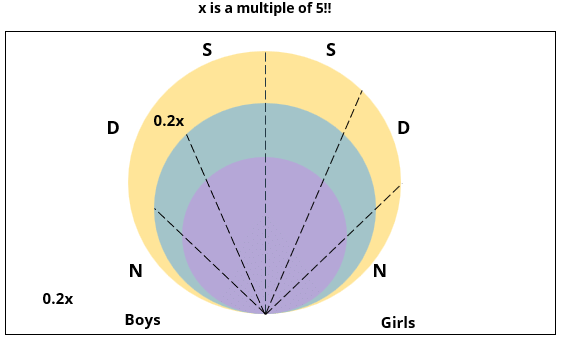
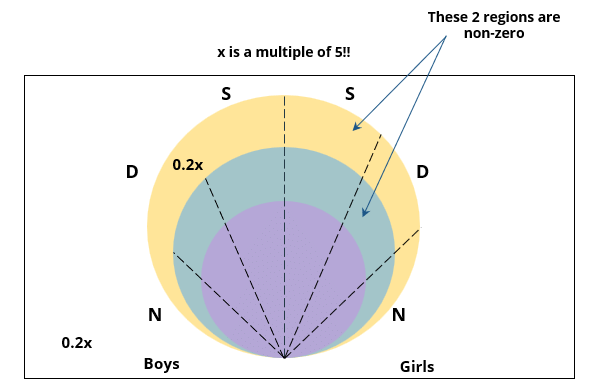
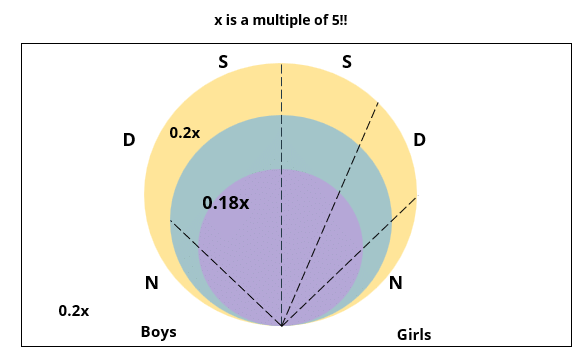
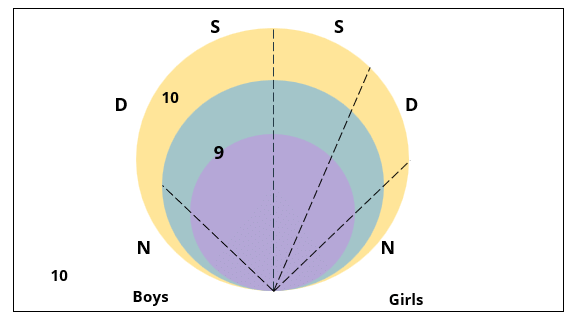
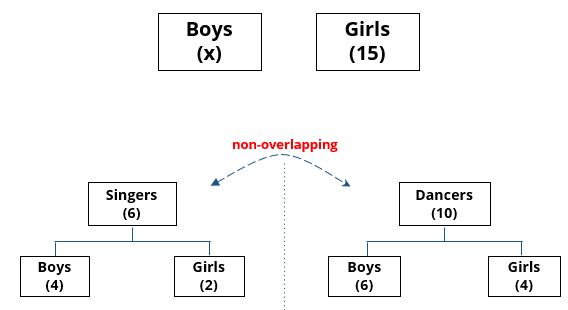
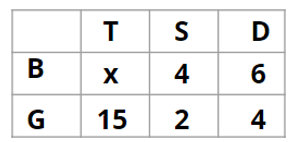
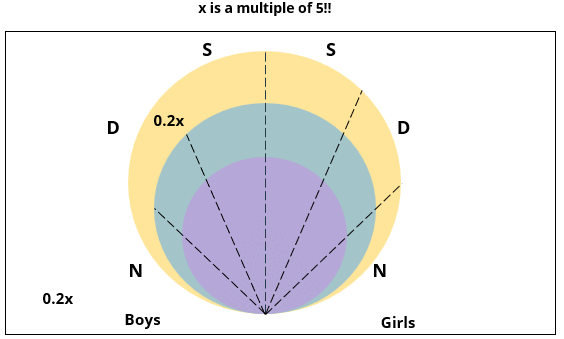
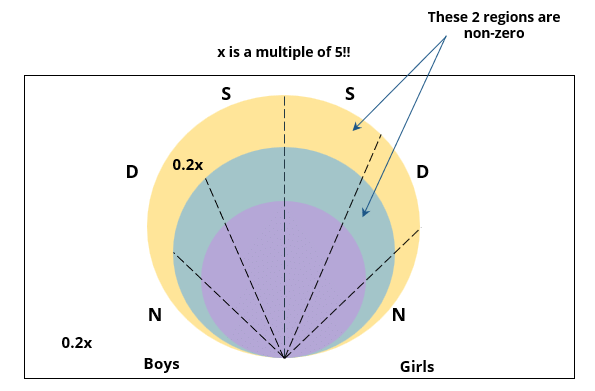
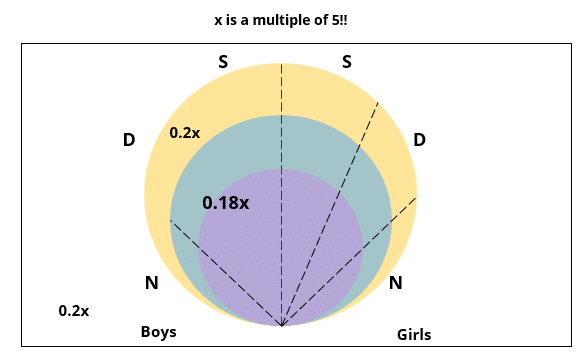
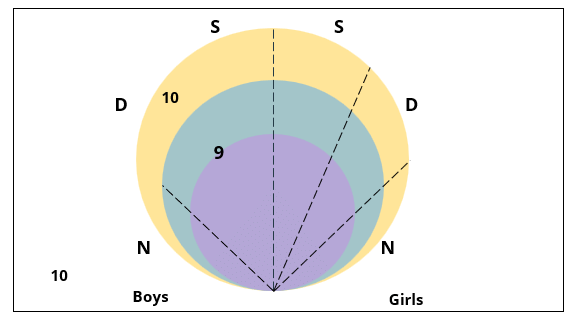
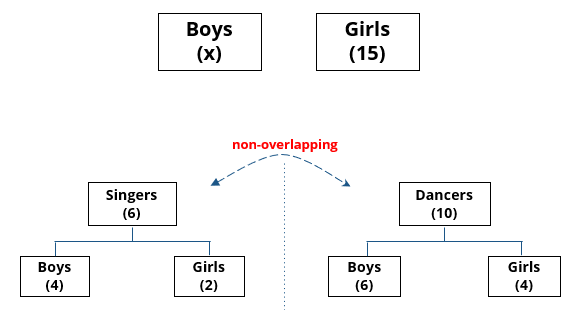
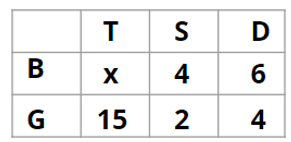
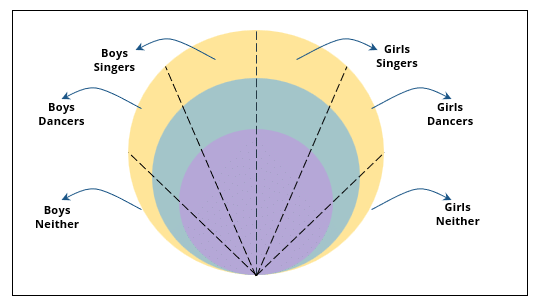
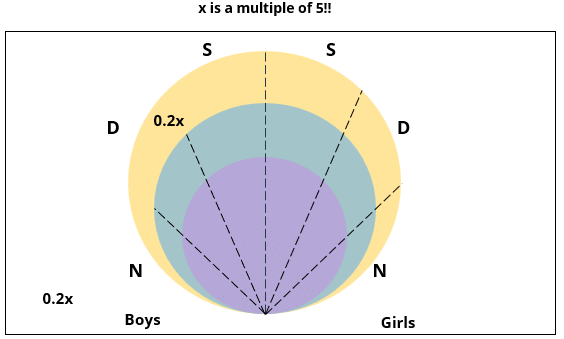
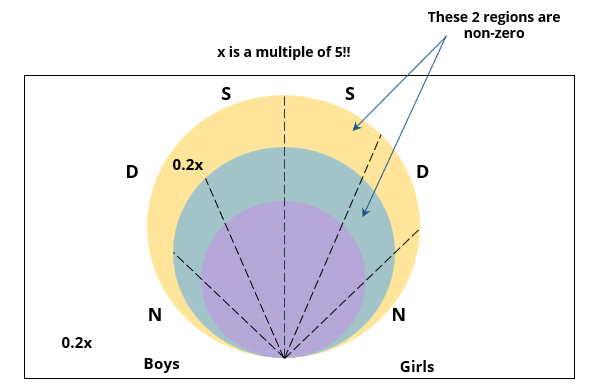
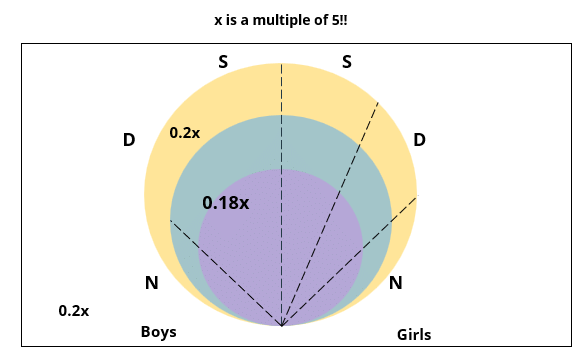
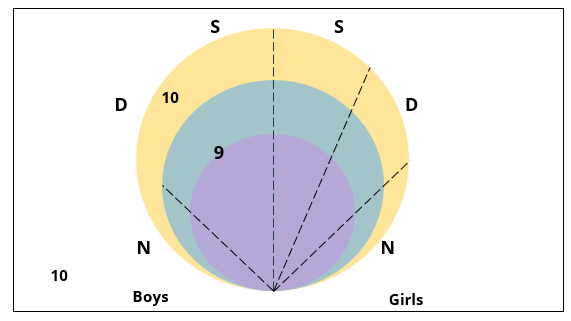
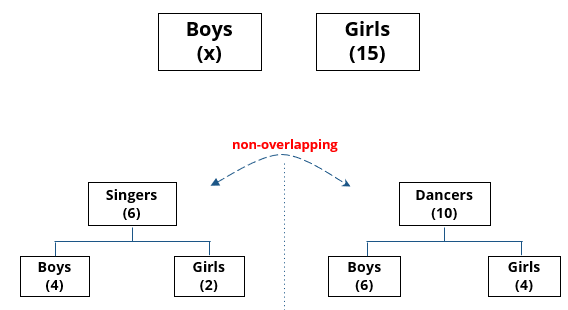
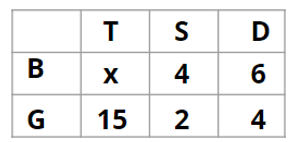
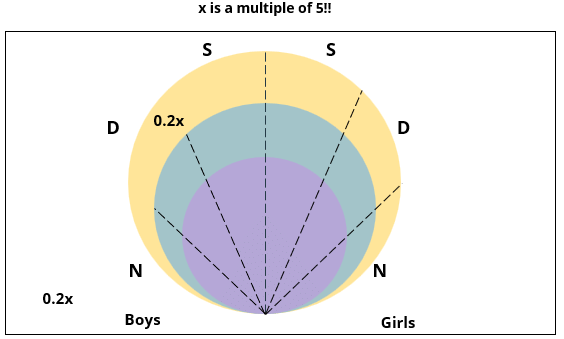
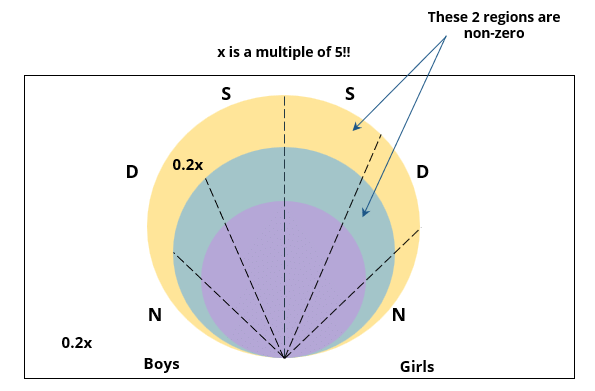
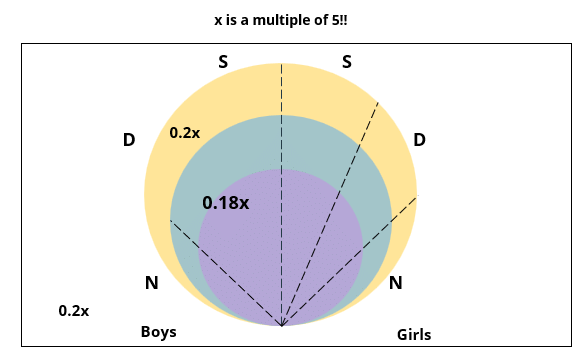
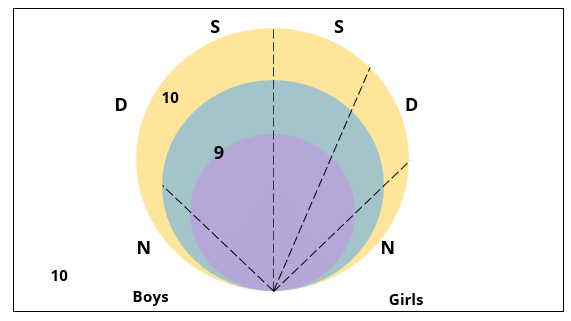
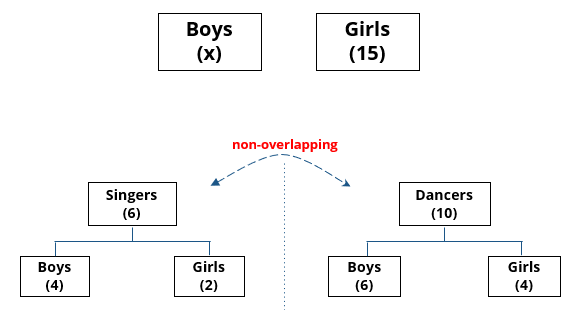
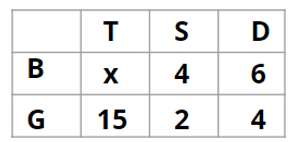
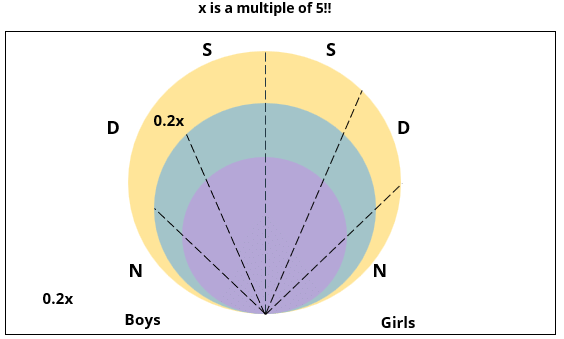
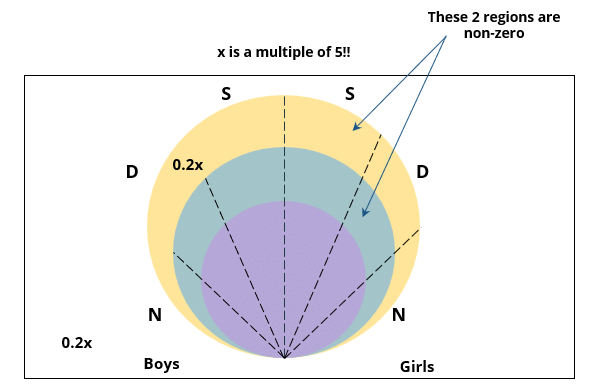
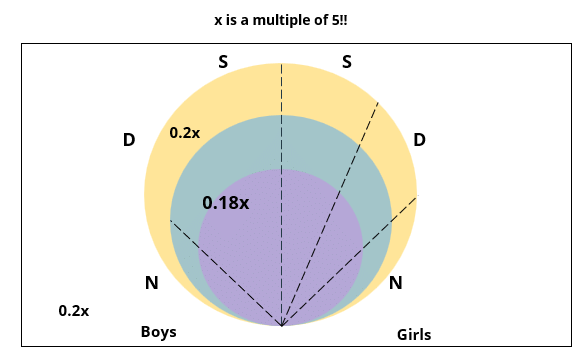
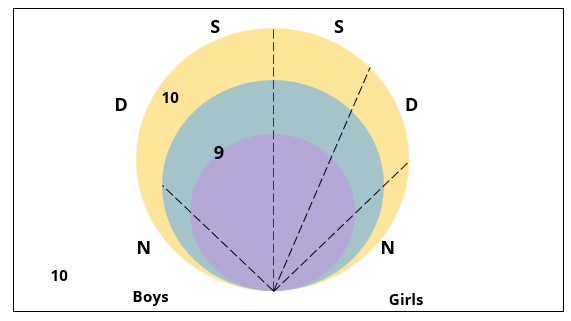
There are 15 girls and some boys among the graduating students in a class. They are planning a get-together, which can be either a 1-day event, or a 2-day event, or a 3-day event. There are 6 singers in the class, 4 of them are boys. There are 10 dancers in the class, 4 of them are girls. No dancer in the class is a singer.
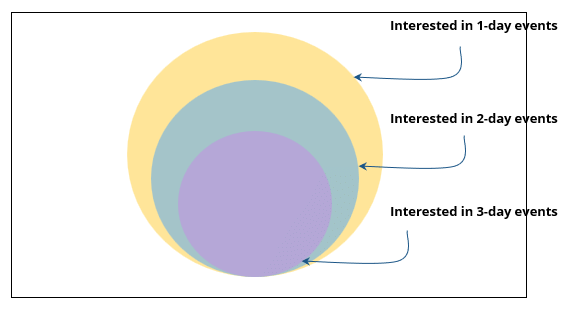
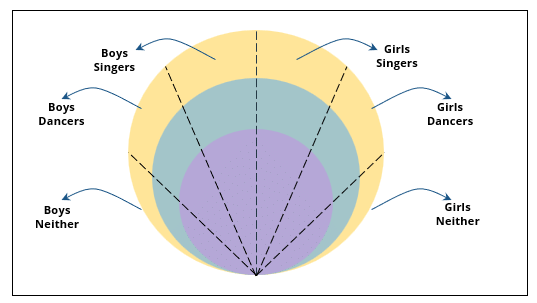
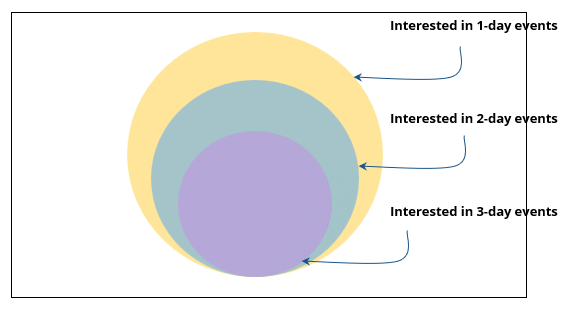
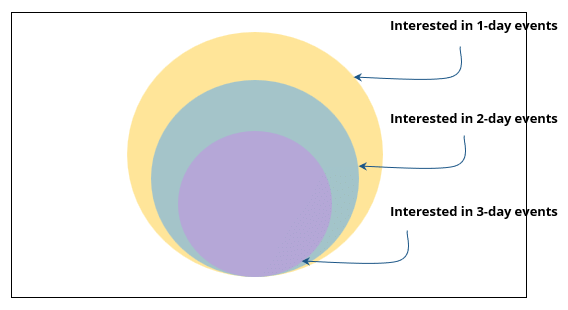
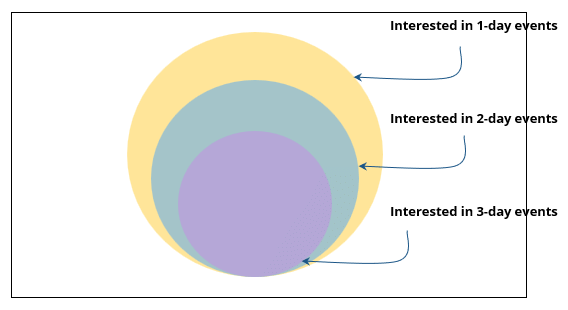
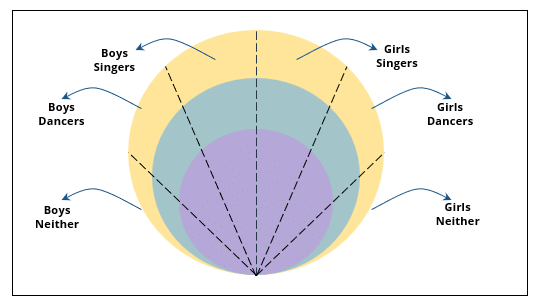
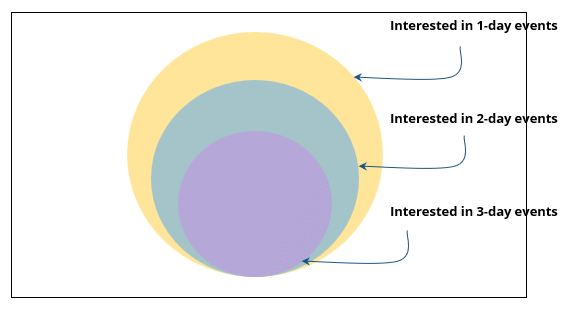
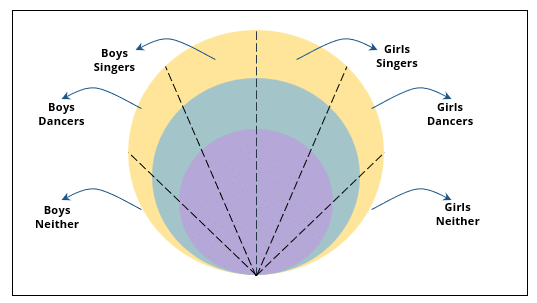
Some students are not interested in attending the get-together. Those students who are interested in attending a 3-day event are also interested in attending a 2-day event; those who are interested in attending a 2-day event are also interested in attending a 1-day event.
The following facts are also known:
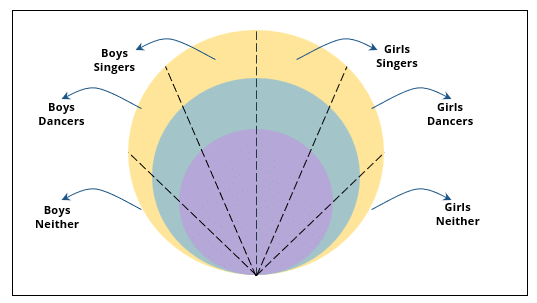
1. Some of the girls are interested in attending a 1-day event, but not a 2-day event; some of the other girls are interested in attending both.
2. 70% of the boys who are interested in attending a 2-day event are neither singers nor dancers. 60% of the girls who are interested in attending a 2-day event are neither singers nor dancers.
3. No girl is interested in attending a 3-day event. All male singers and 2 of the dancers are interested in attending a 3-day event.
4. The number of singers interested in attending a 2-day event is one more than the number of dancers interested in attending a 2-day event.
5. All the girls and 80% of the boys are interested in attending a 1-day event. 60% of the boys are interested in attending a 2-day event.
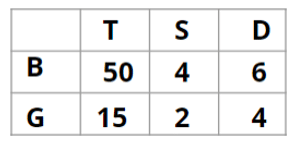
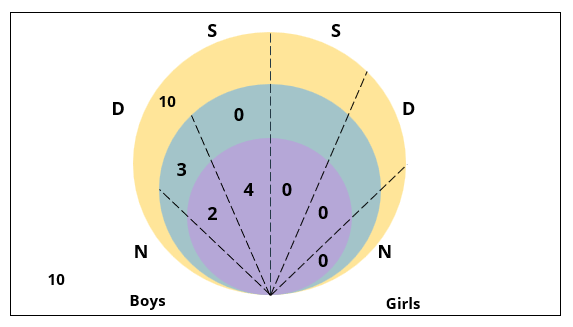
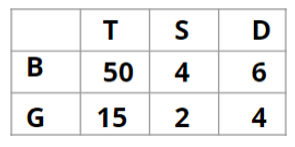
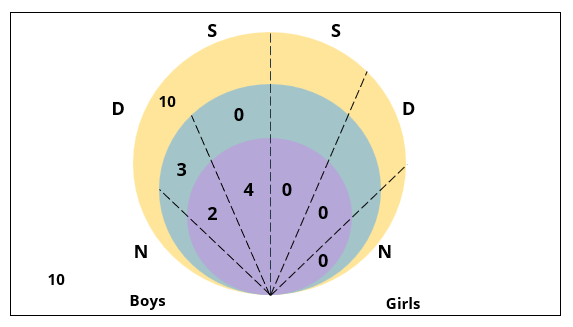
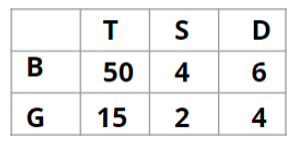
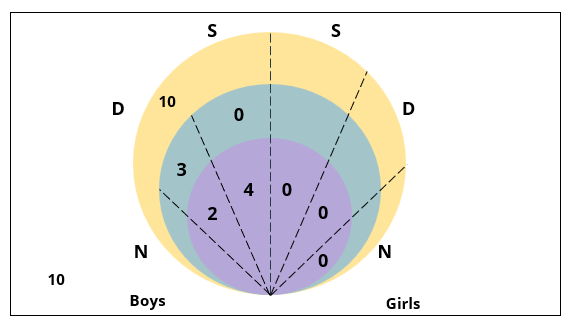
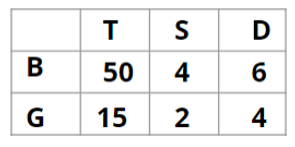
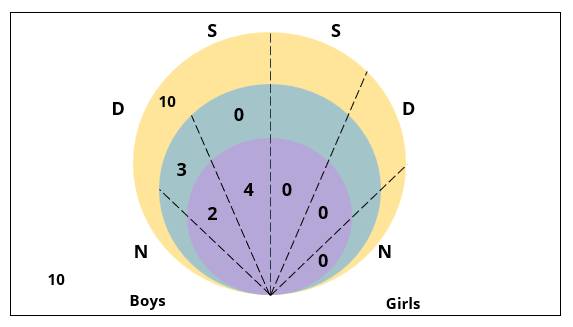
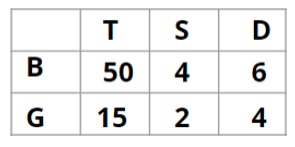
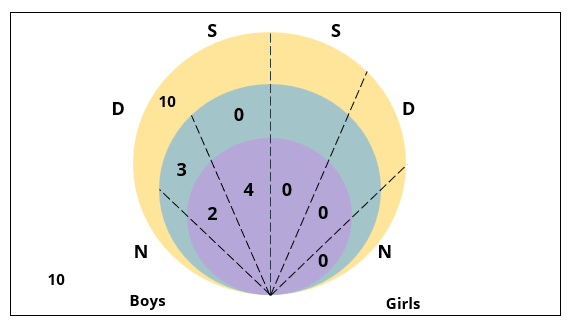
Q1: How many boys are there in the class?
Ans: 50
Sol:
Hence, the answer is '50'
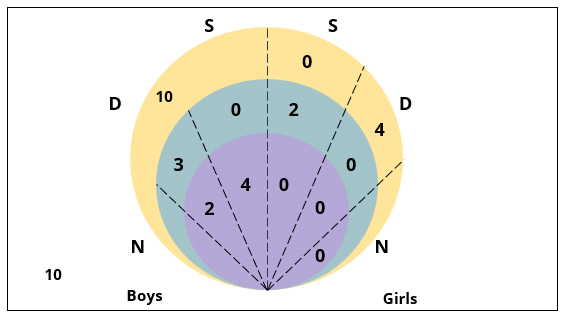
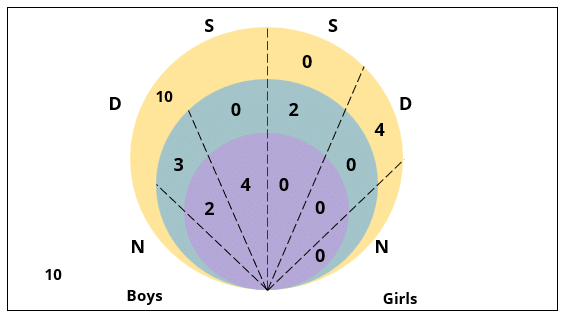
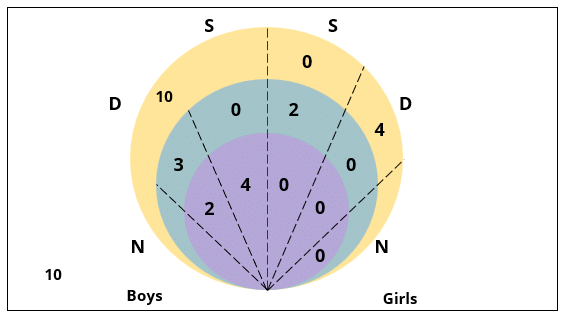
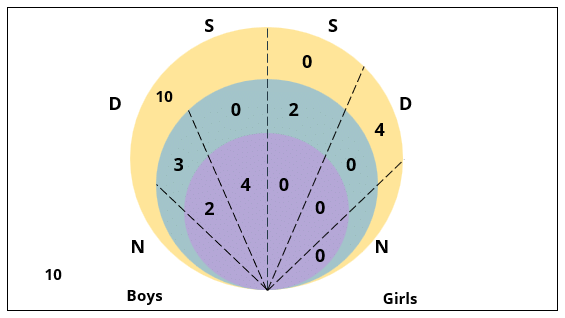
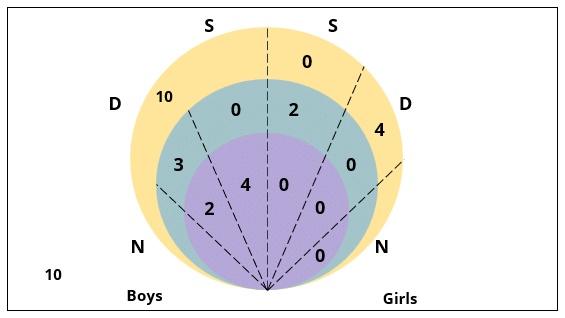
Q2: Which of the following can be determined from the given information?
I. The number of boys who are interested in attending a 1-day event and are neither dancers nor singers.
II. The number of female dancers who are interested in attending a 1-day event.
(a) Only I
(b) Neither I nor II
(c) Both I and II
(d) Only II
Ans: a
Sol:
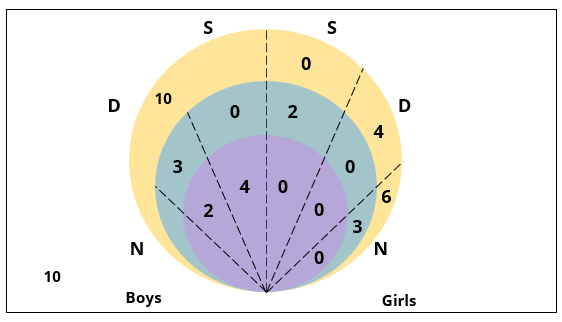
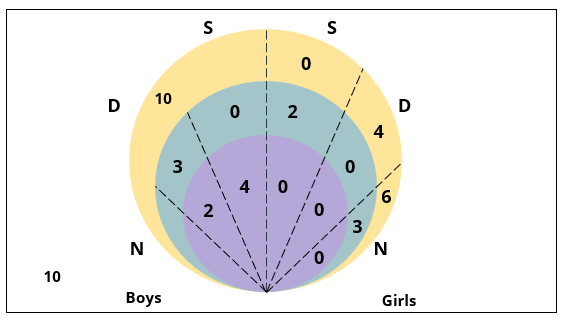
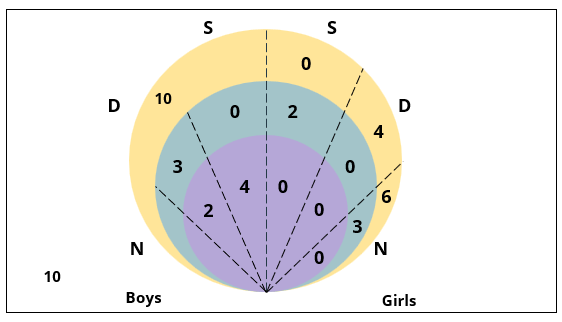
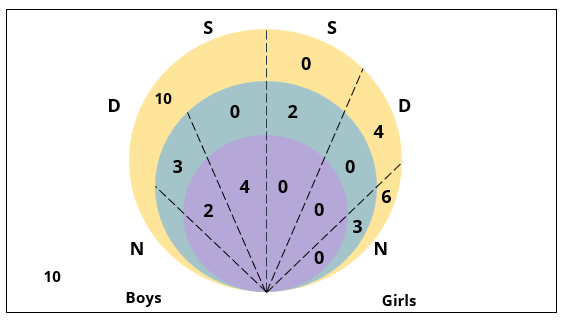
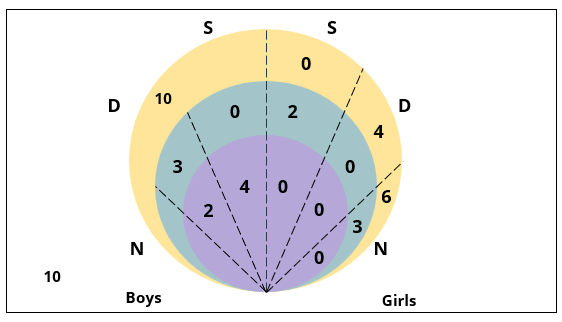
Q3: What fraction of the class are interested in attending a 2-day event?
(a) 7/10
(b) 2/3
(c) 9/13
(d) 7/13
Ans: d
Sol:
Q4: What BEST can be concluded about the number of male dancers who are interested in attending a 1-day event?
(a) 5 or 6
(b) 4 or 6
(c) 5
(d) 6
Ans: (a)
Sol:
Q5: How many female dancers are interested in attending a 2-day event?
(a) 1
(b) Cannot be determined
(c) 2
(d) 0
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Passage - 2
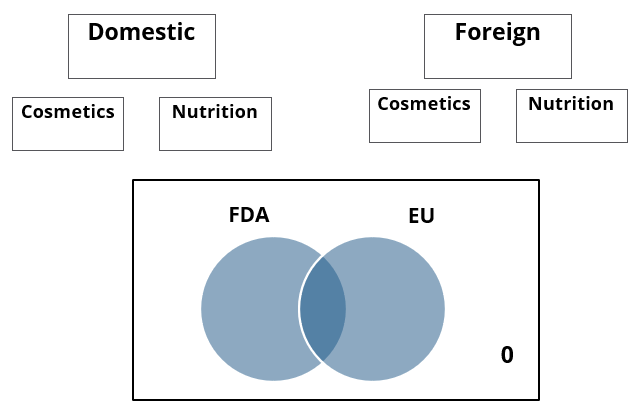
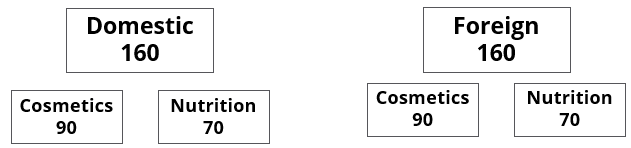
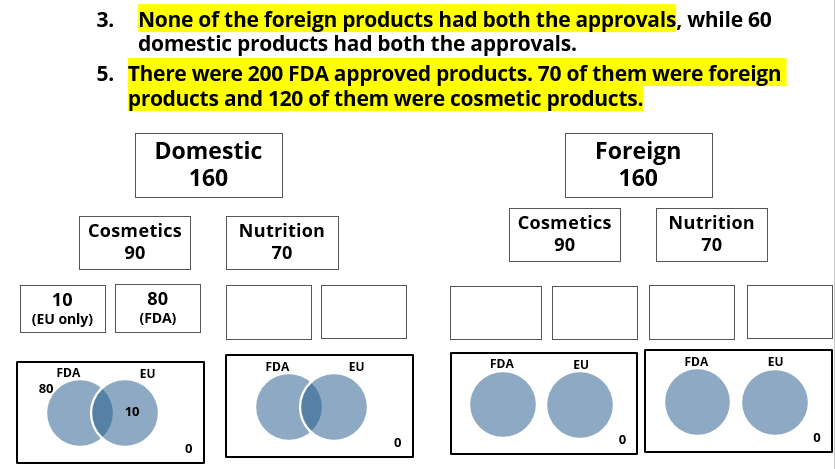
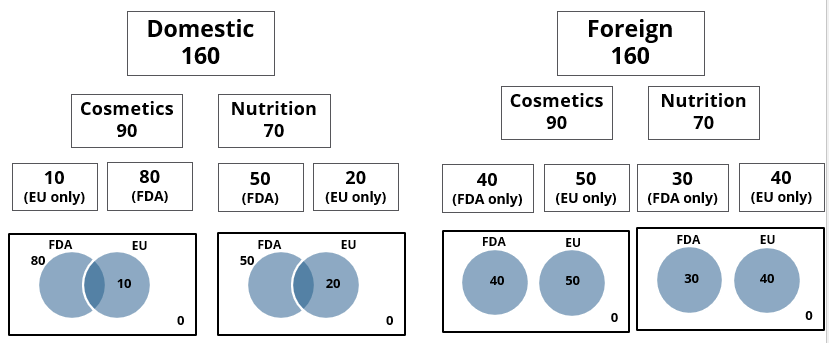
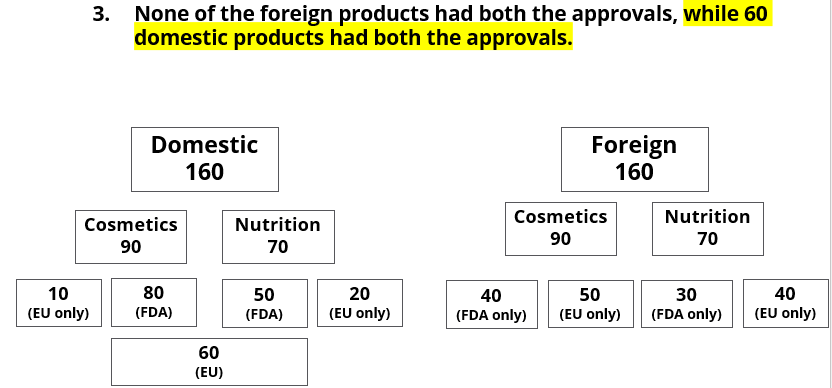
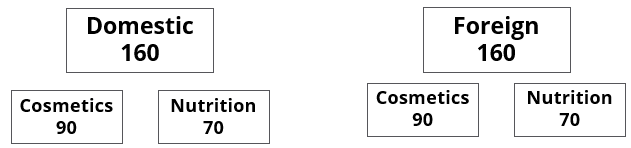
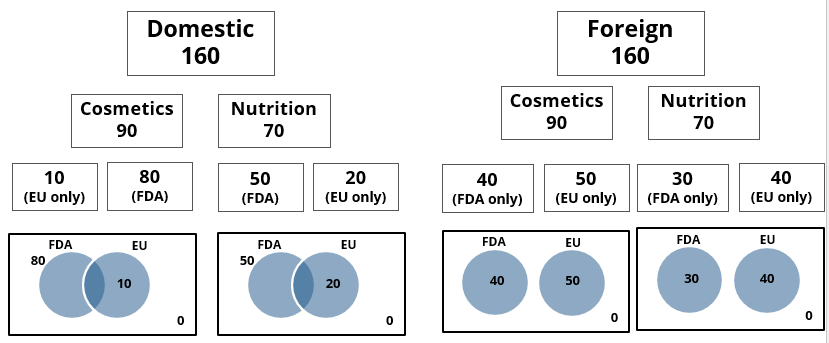
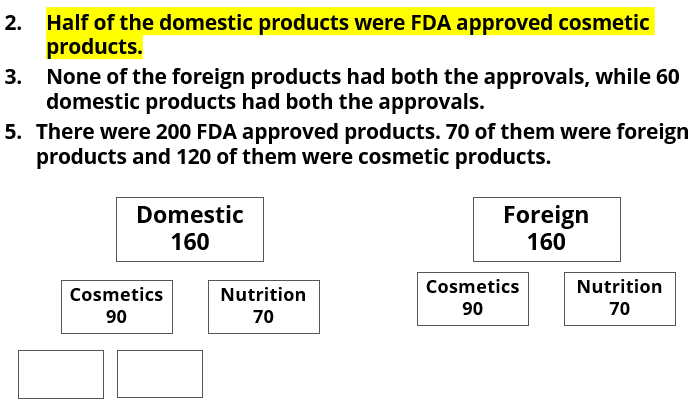
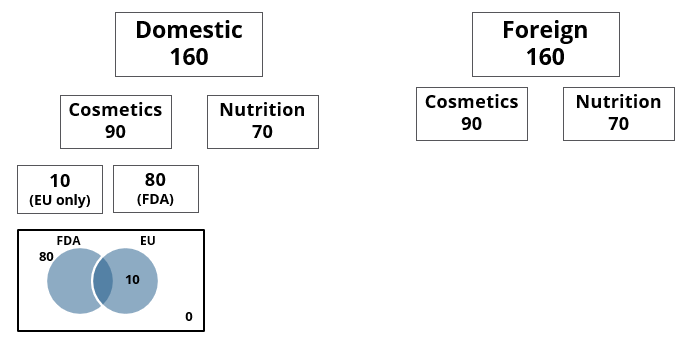
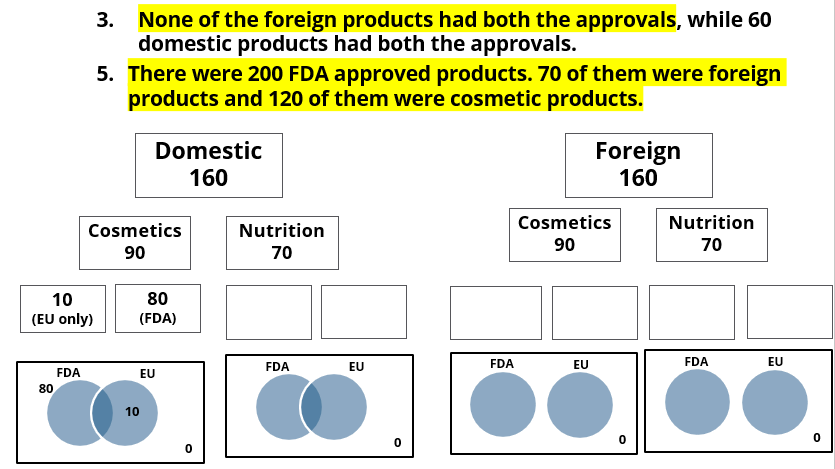
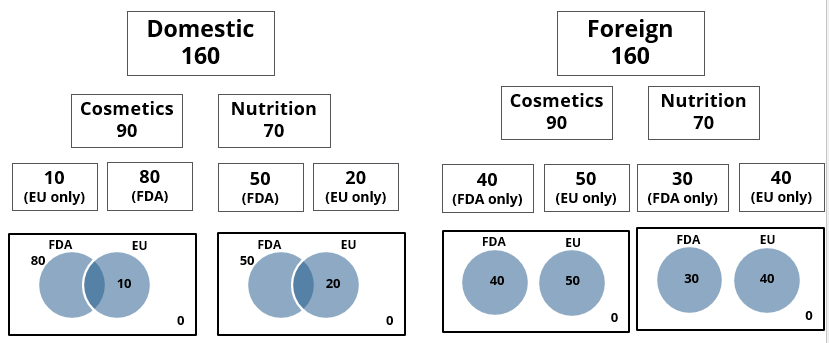
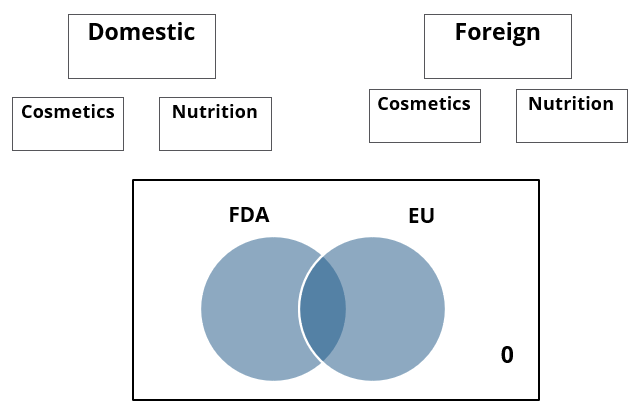
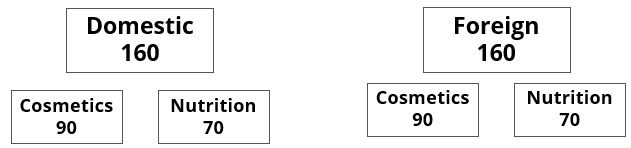
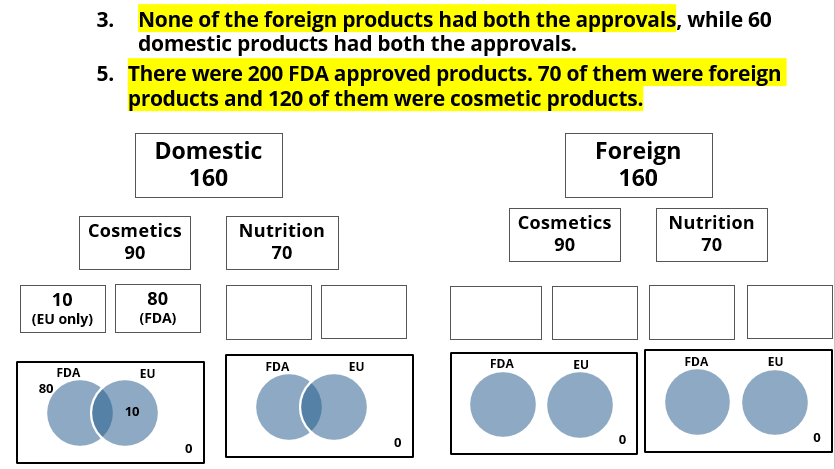
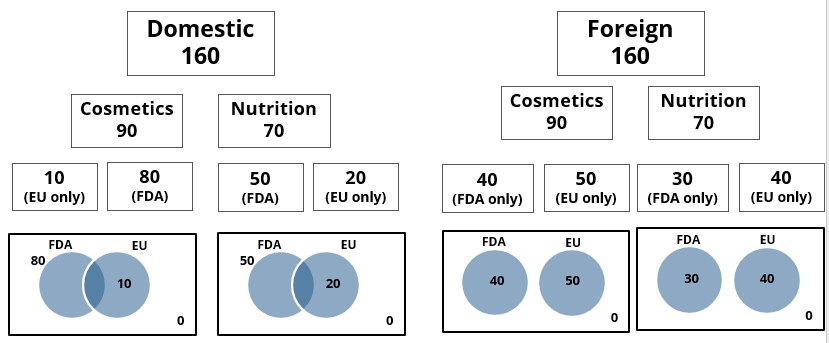
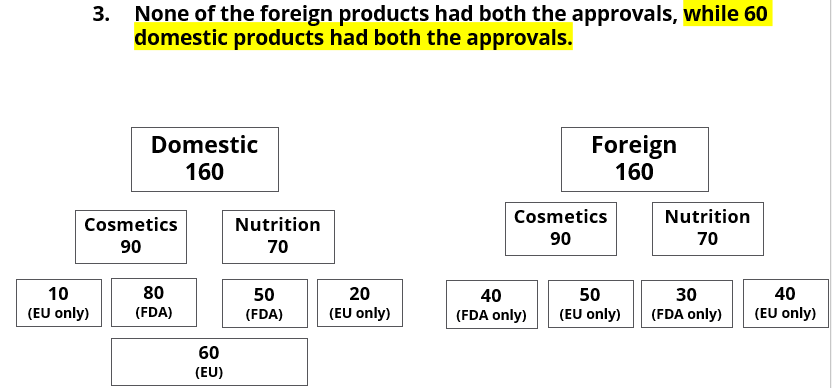
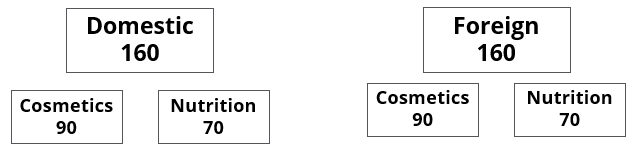
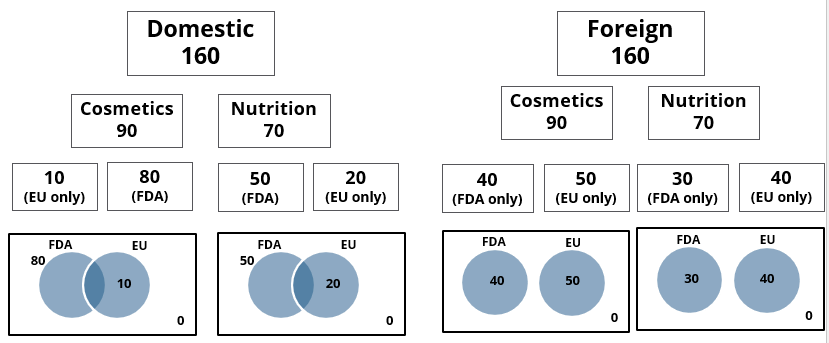
A speciality supermarket sells 320 products. Each of these products was either a cosmetic product or a nutrition product. Each of these products was also either a foreign product or a domestic product. Each of these products had at least one of the two approvals – FDA or EU.
The following facts are also known:
- There were equal numbers of domestic and foreign products.
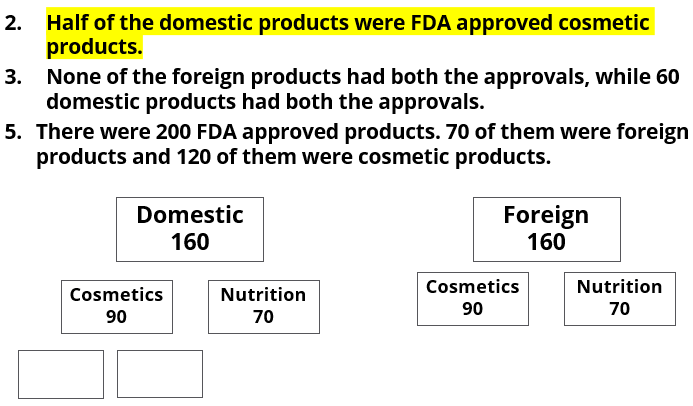
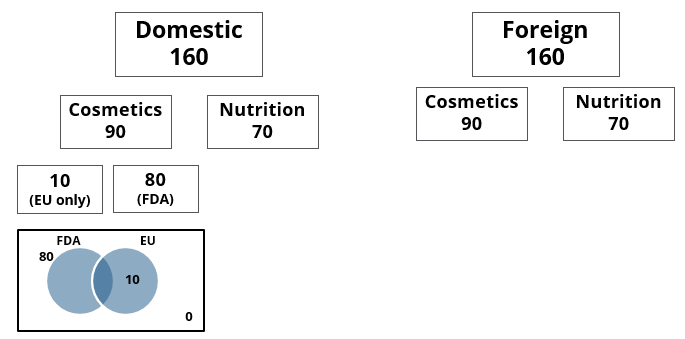
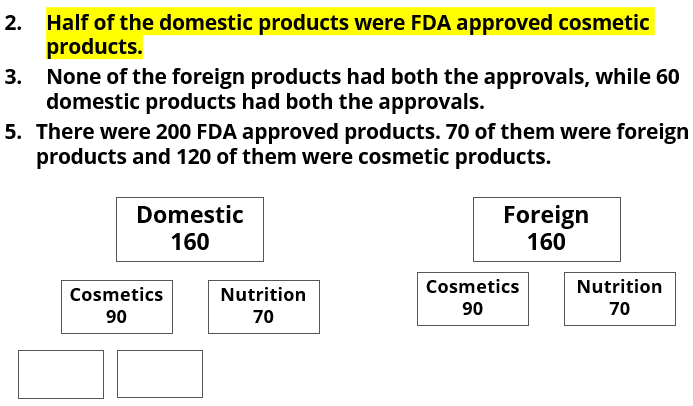
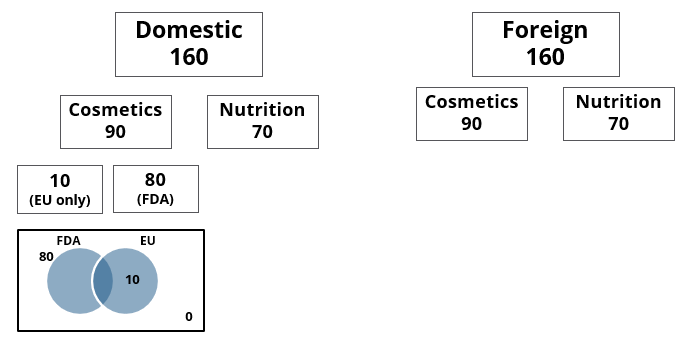
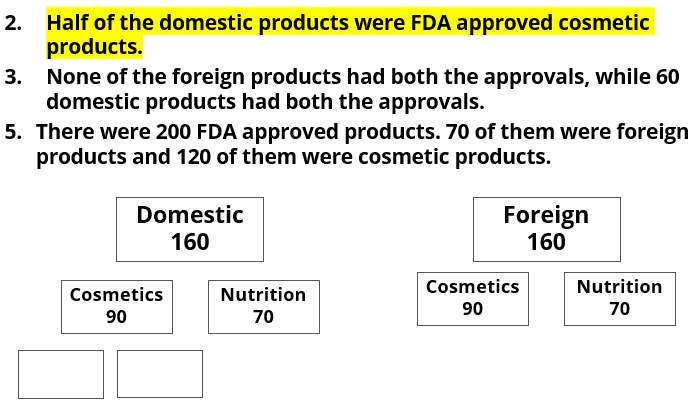
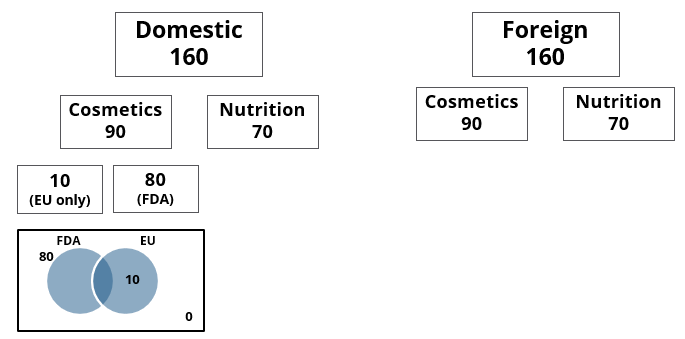
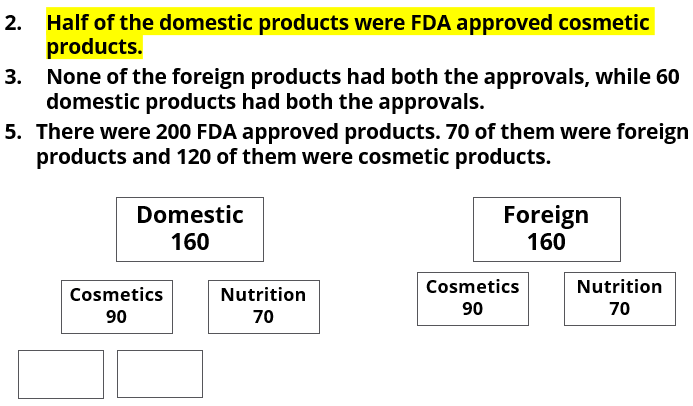
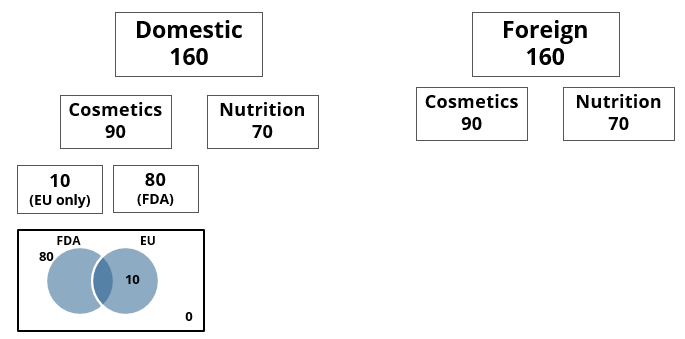
- Half of the domestic products were FDA approved cosmetic products.
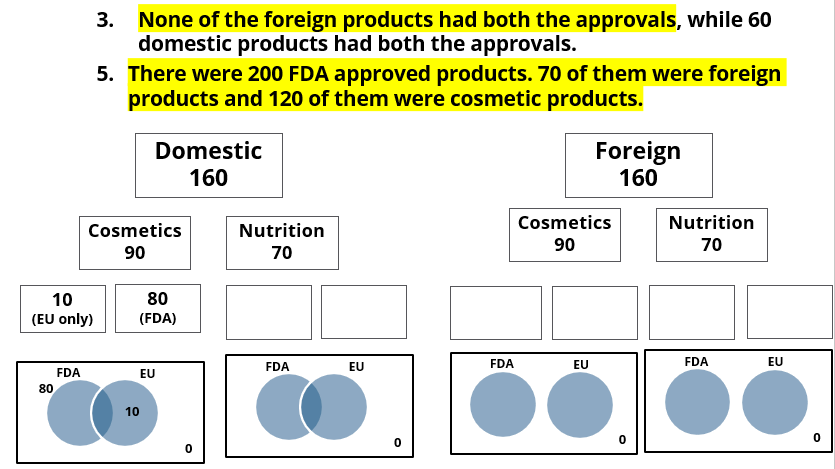
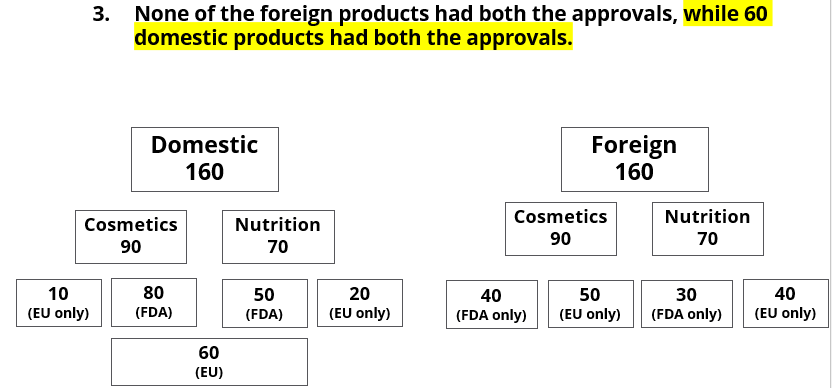
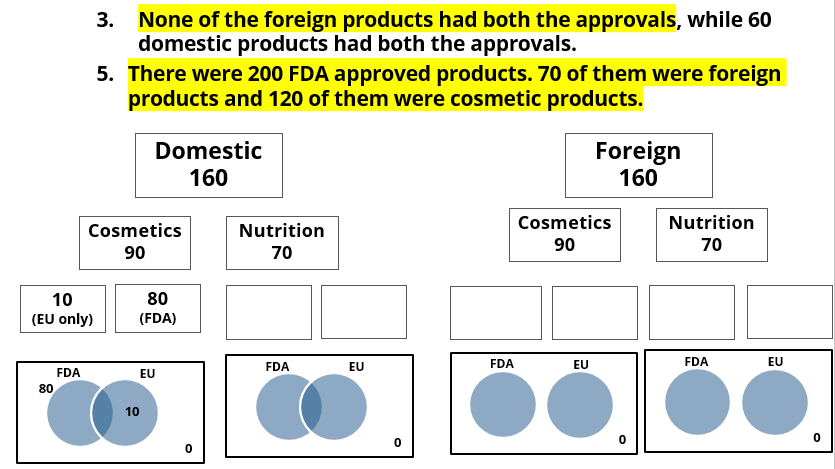
- None of the foreign products had both the approvals, while 60 domestic products had both the approvals.
- There were 140 nutrition products, half of them were foreign products.
- There were 200 FDA approved products. 70 of them were foreign products and 120 of them were cosmetic products.
Q1: How many foreign products were FDA approved cosmetic products?
Ans: 40
Sol:
Q2: How many cosmetic products did not have FDA approval?
(a) 10
(b) 60
(c) 50
(d) Cannot be determined
Ans: (b)
Sol:
Q3: Which among the following options best represents the number of domestic cosmetic products that had both the approvals?
(a) At least 10 and at most 80
(b) At least 20 and at most 70
(c) At least 20 and at most 50
(d) At least 10 and at most 60
Ans: d
Sol: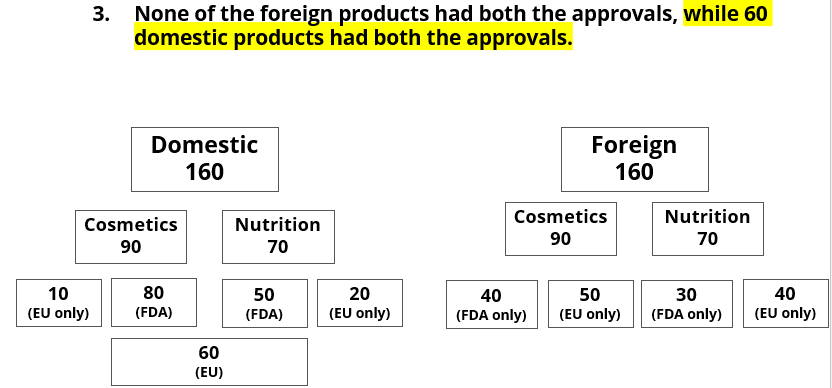
Q4: If 70 cosmetic products did not have EU approval, then how many nutrition products had both the approvals?
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 50
Ans: a
Sol:
Q5: If 50 nutrition products did not have EU approval, then how many domestic cosmetic products did not have EU approval?
Ans: 50
Sol: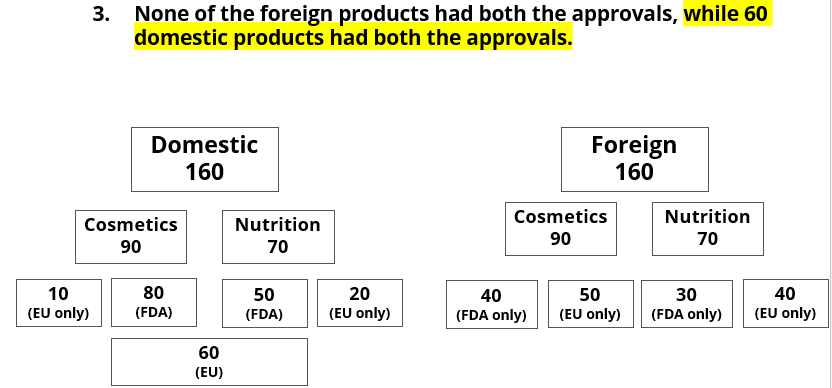
Passage - 3
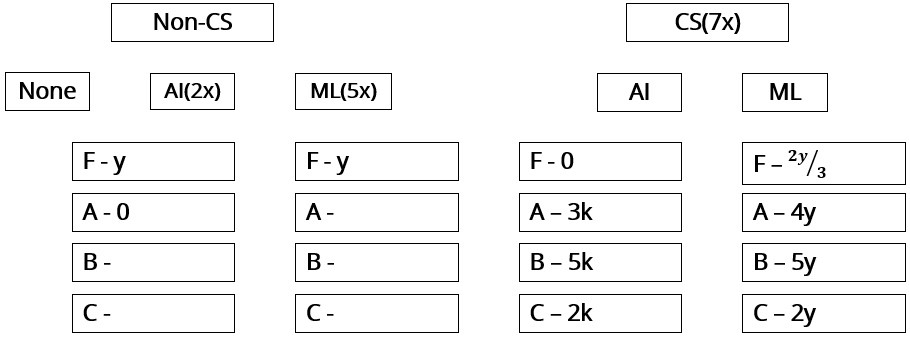
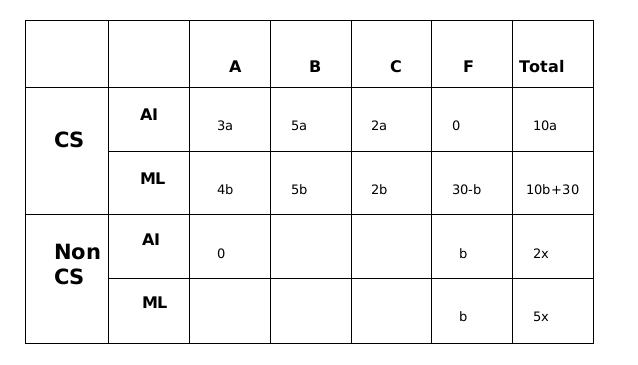
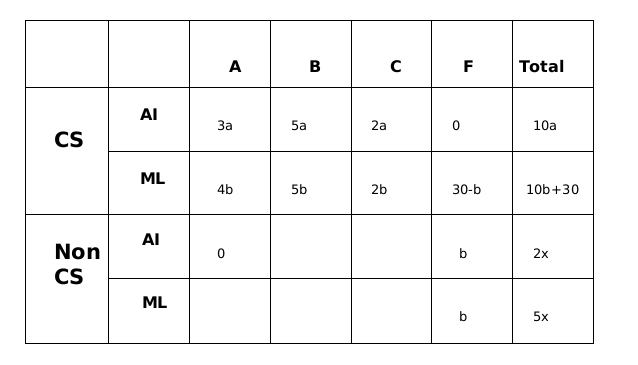
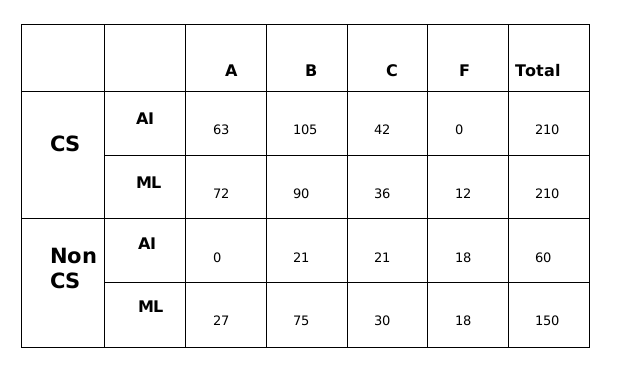
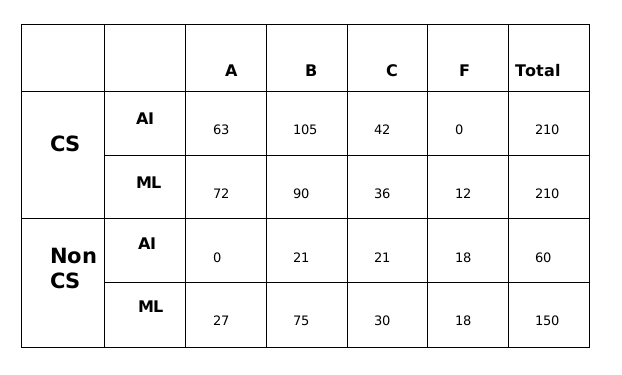
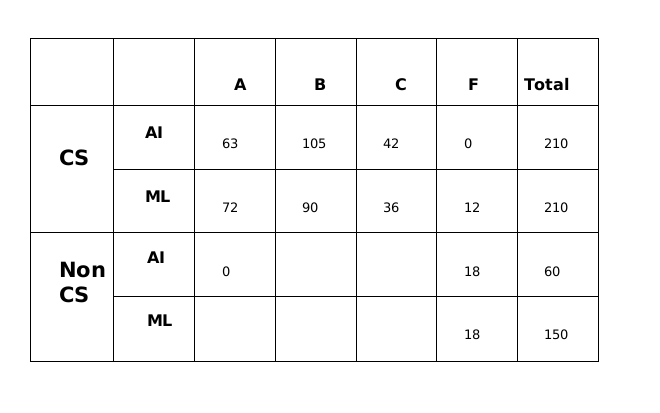
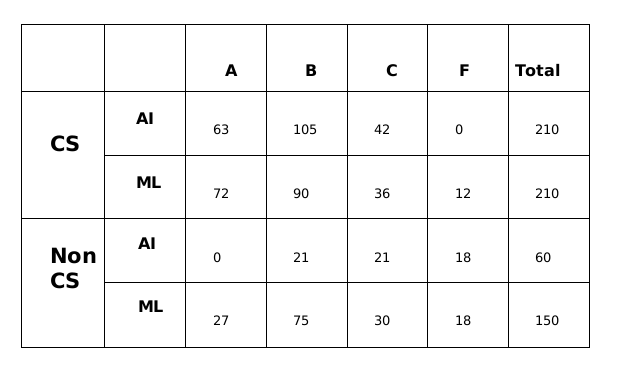
All the first-year students in the computer science (CS) department in a university take both the courses (i) AI and (ii) ML. Students from other departments (non-CS students) can also take one of these two courses, but not both. Students who fail in a course get an F grade; others pass and are awarded A or B or C grades depending on their performance. The following are some additional facts about the number of students who took these two courses this year and the grades they obtained.
- The numbers of non-CS students who took AI and ML were in the ratio 2 : 5.
- The number of non-CS students who took either AI or ML was equal to the number of CS students.
- The numbers of non-CS students who failed in the two courses were the same and their total is equal to the number of CS students who got a C grade in ML.
- In both the courses, 50% of the students who passed got a B grade. But, while the numbers of students who got A and C grades were the same for AI, they were in the ratio 3 : 2 for ML.
- No CS student failed in AI, while no non-CS student got an A grade in AI.
- The numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3 : 5 : 2, while in ML the ratio was 4 : 5 : 2.
- The ratio of the total number of non-CS students failing in one of the two courses to the number of CS students failing in one of the two courses was 3 : 1.
- 30 students failed in ML.
Q1: How many students took AI?
(a) 90
(b) 60
(c) 270
(d) 210
Ans: c
Sol:The numbers of non-CS students who took AI and ML were in the ratio 2 : 5.
The number of non-CS students who took either AI or ML was equal to the number of CS students.
The numbers of non-CS students who failed in the two courses were the same and their total is equal to the number of CS students who got a C grade in ML.
No CS student failed in AI, while no non-CS student got an A grade in AI.
The numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3 : 5 : 2, while in ML the ratio was 4 : 5 : 2.
The ratio of the total number of non-CS students failing in one of the two courses to the number of CS students failing in one of the two courses was 3 : 1.
30 students failed in ML.
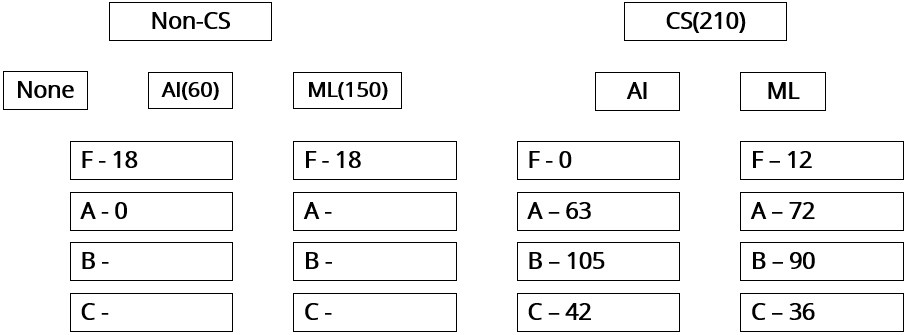
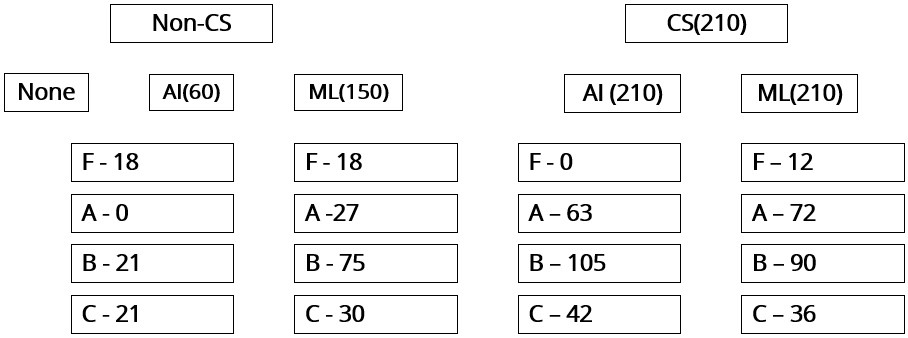
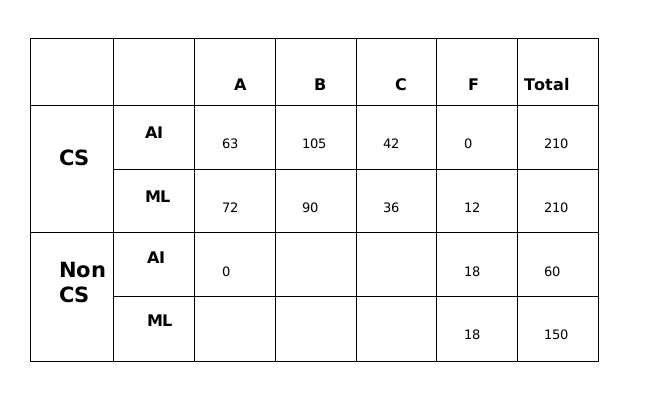
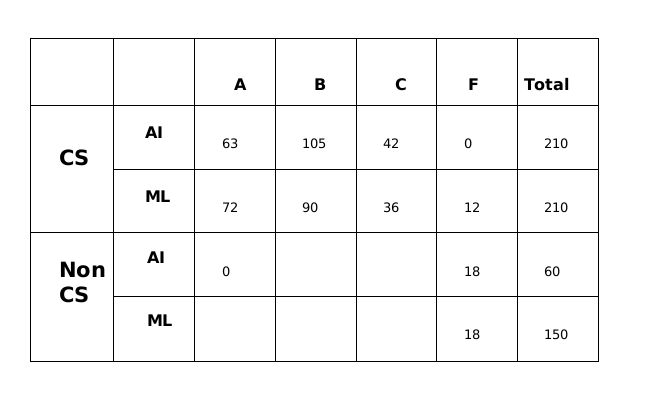
Total number of students in CS = 210. So, non-CS AI = 60; non-CS ML = 150
Now, we can find K.In both the courses, 50% of the students who passed got a B grade. But, while the numbers of students who got A and C grades were the same for AI, they were in the ratio 3 : 2 for ML.
Number of B grades in AI = 252/2 = 126
Number of B grades in ML = 330/2 = 165
Number of C grades in AI = 63.
So, C grades in AI for non-CS = 21.
Total number of candidates who cleared ML = 330.
Of this 165 for B, A + C = 165. Split in the ratio 3 : 2 = 99 : 66Hence, the answer is '270'
Q2: How many CS students failed in ML?
Ans: 12
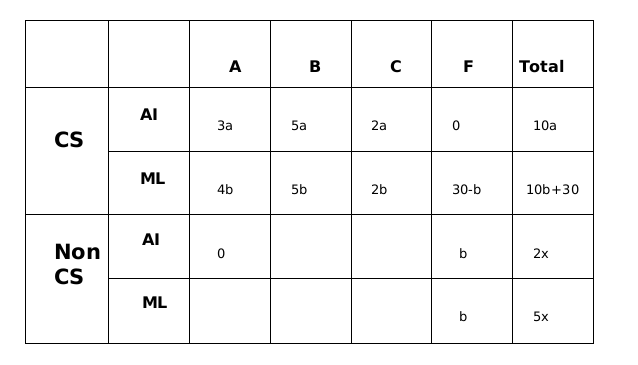
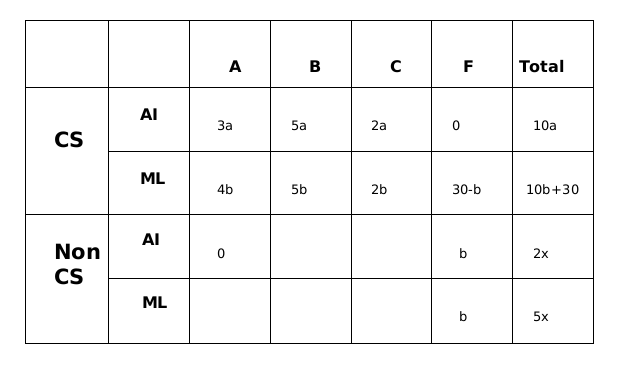
Sol: Let the number of students in non-CS be 7x so no. of students taking AI in non-CS is 2x and no. of students taking ML in non-CS is 5x
All the CS students have taken both the courses, we are given this in the first line of the set.
From statement 5, we can conclude that 0 students from CS failed in AI and 0 students from non-CS got grade A in AI.
From statement 6, let us say that the numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3a, 5a and 2a, while in ML the ratio was 4b, 5b and 2b.
From statement 3 we can say that the number of non- CS students who failed in AI and ML are b in each category.
Now from statement 8, we can say that number of CS students who failed in MI is equal to 30-b.
From statement 7, we can say that,
or, 2b = 90-3b
or, b= 18
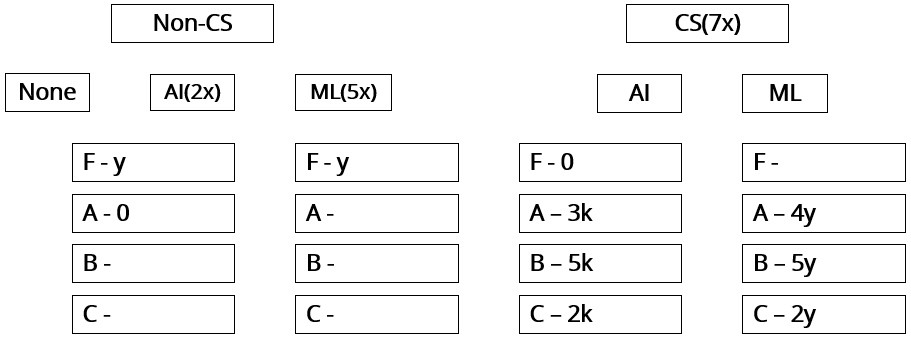
CS students take both the AI and ML courses, therefore 10a= 10b +30
or, a= b+3 = 21
From statement 2, we can say that 10a = 7x
or, x = 30
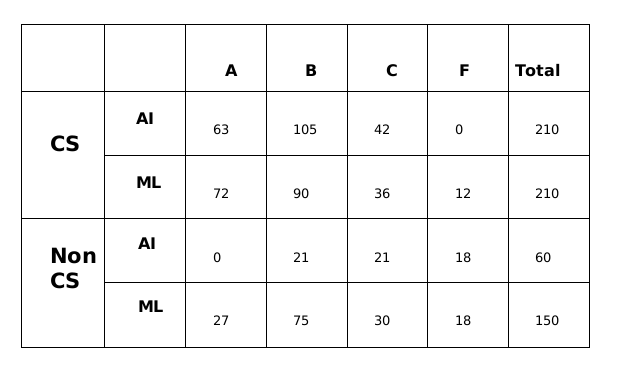
Substituting the values of a, b and x in the above table.A total of 270 students took AI out of which 252 students passed and a total of 360 students took ML out of which 330 students passed.
From statement 4, we can say that out of the 252 students who passed in AI, 126 of them got Grade B and 63 got Grade A and 63 got Grade C.
Similarly, We can say that out of the 330 students who passed in ML, 165 of them got Grade C and 99 got Grade A and 66 got Grade C.
Therefore, the final table which we get is
Q3: How many non-CS students got A grade in ML?
Ans: 27
Sol: Let the number of students in non-CS be 7x so no. of students taking AI in non-CS is 2x and no. of students taking ML in non-CS is 5x
All the CS students have taken both the courses, we are given this in the first line of the set.
From statement 5, we can conclude that 0 students from CS failed in AI and 0 students from non-CS got grade A in AI.
From statement 6, let us say that the numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3a, 5a and 2a, while in ML the ratio was 4b, 5b and 2b.
From statement 3 we can say that the number of non- CS students who failed in AI and ML are b in each category.
Now from statement 8, we can say that number of CS students who failed in MI is equal to 30-b.
From statement 7, we can say that,or, 2b = 90-3b
or, b= 18
CS students take both the AI and ML courses, therefore 10a= 10b +30
or, a= b+3 = 21
From statement 2, we can say that 10a = 7x
or, x = 30
Substituting the values of a, b and x in the above table.
A total of 270 students took AI out of which 252 students passed and a total of 360 students took ML out of which 330 students passed.
From statement 4, we can say that out of the 252 students who passed in AI, 126 of them got Grade B and 63 got Grade A and 63 got Grade C.
Similarly, We can say that out of the 330 students who passed in ML, 165 of them got Grade C and 99 got Grade A and 66 got Grade C.
Therefore, the final table which we get is
Q4: How many students got A grade in AI?
(a) 63
(b) 99
(c) 84
(d) 42
Ans: a
Sol: Let the number of students in non-CS be 7x so no. of students taking AI in non-CS is 2x and no. of students taking ML in non-CS is 5x
All the CS students have taken both the courses, we are given this in the first line of the set.
From statement 5, we can conclude that 0 students from CS failed in AI and 0 students from non-CS got grade A in AI.
From statement 6, let us say that the numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3a, 5a and 2a, while in ML the ratio was 4b, 5b and 2b.
From statement 3 we can say that the number of non- CS students who failed in AI and ML are b in each category.
Now from statement 8, we can say that number of CS students who failed in MI is equal to 30-b.
From statement 7, we can say thator, 2b = 90-3b
or, b= 18
CS students take both the AI and ML courses, therefore 10a= 10b +30
or, a= b+3 = 21
From statement 2, we can say that 10a = 7x
or, x = 30
Substituting the values of a, b and x in the above table.
A total of 270 students took AI out of which 252 students passed and a total of 360 students took ML out of which 330 students passed.
From statement 4, we can say that out of the 252 students who passed in AI, 126 of them got Grade B and 63 got Grade A and 63 got Grade C.
Similarly, We can say that out of the 330 students who passed in ML, 165 of them got Grade C and 99 got Grade A and 66 got Grade C.
Therefore, the final table which we get is
Q5: How many non-CS students got B grade in ML?
(a) 165
(b) 75
(c) 25
(d) 90
Ans: b
Sol: Let the number of students in non-CS be 7x so no. of students taking AI in non-CS is 2x and no. of students taking ML in non-CS is 5x
All the CS students have taken both the courses, we are given this in the first line of the set.
From statement 5, we can conclude that 0 students from CS failed in AI and 0 students from non-CS got grade A in AI.
From statement 6, let us say that the numbers of CS students who got A, B and C grades respectively in AI were in the ratio 3a, 5a and 2a, while in ML the ratio was 4b, 5b and 2b.
From statement 3 we can say that the number of non- CS students who failed in AI and ML are b in each category.
Now from statement 8, we can say that number of CS students who failed in MI is equal to 30-b.
From statement 7, we can say that,or, 2b = 90-3b
or, b= 18
CS students take both the AI and ML courses, therefore 10a= 10b +30
or, a= b+3 = 21
From statement 2, we can say that 10a = 7x
or, x = 30
Substituting the values of a, b and x in the above table.
A total of 270 students took AI out of which 252 students passed and a total of 360 students took ML out of which 330 students passed.
From statement 4, we can say that out of the 252 students who passed in AI, 126 of them got Grade B and 63 got Grade A and 63 got Grade C.
Similarly, We can say that out of the 330 students who passed in ML, 165 of them got Grade C and 99 got Grade A and 66 got Grade C.
Therefore, the final table which we get is
Passage - 4
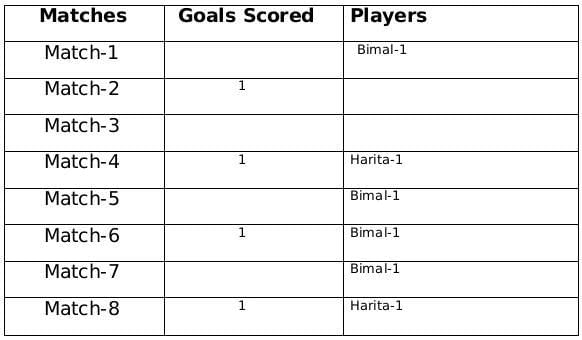
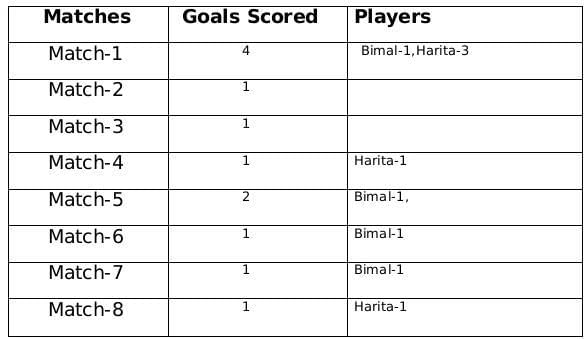
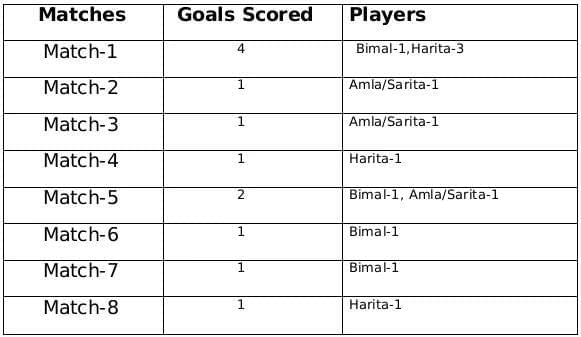
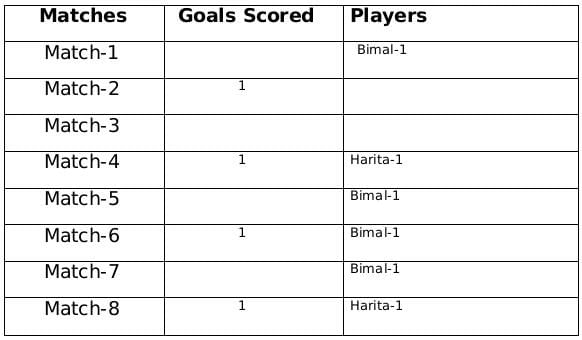
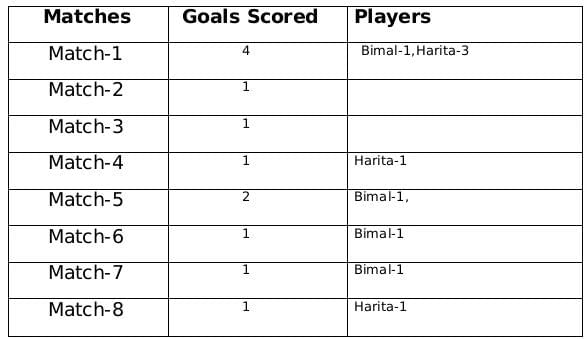
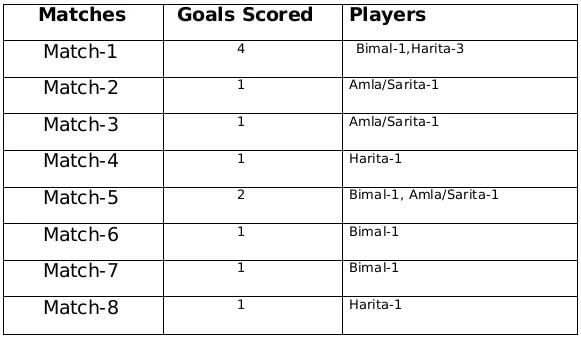
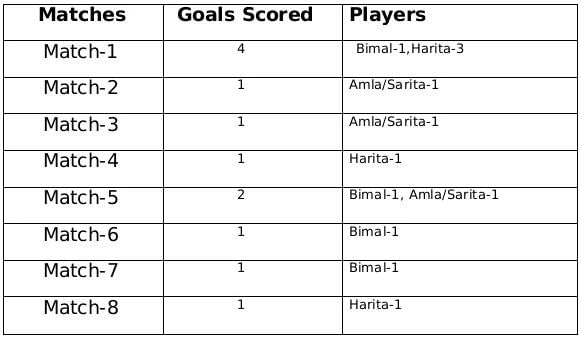
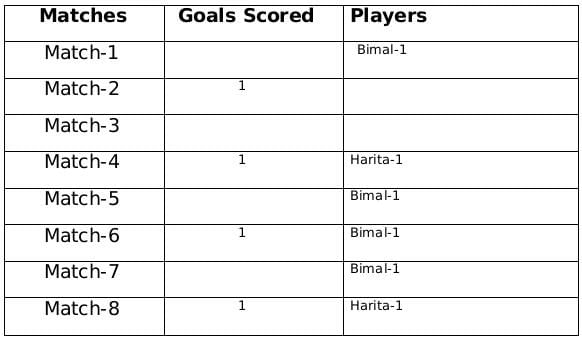
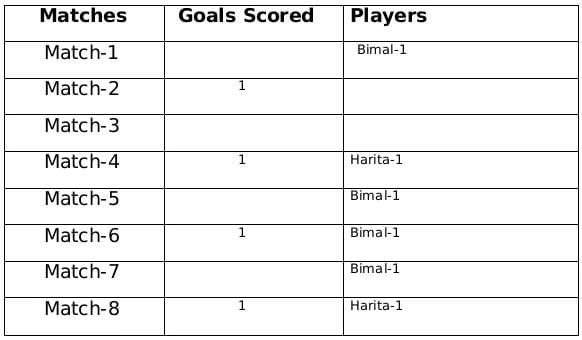
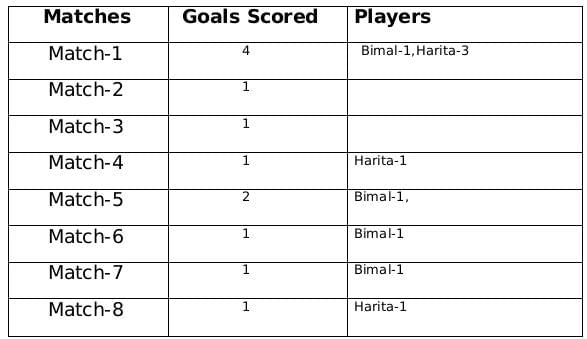
The management of a university hockey team was evaluating performance of four women players - Amla, Bimla, Harita and Sarita for their possible selection in the university team for next year. For this purpose, the management was looking at the number of goals scored by them in the past 8 matches, numbered 1 through 8. The four players together had scored a total of 12 goals in these matches. In the 8 matches, each of them had scored at least one goal. No two players had scored the same total number of goals.
The following facts are known about the goals scored by these four players only. All the questions refer only to the goals scored by these four players.
- Harita scored more goals than Bimla.
- The highest goal scorer scored goals in exactly 3 matches including Match 4 and Match 8.
- Bimla scored a goal in Match 1 and one each in three other consecutive matches.
- An equal number of goals were scored in Match 3 and Match 7, which was different from the number of goals scored in either Match 1 or Match 5.
- The match in which the highest number of goals was scored was unique and it was not Match 5.
- Only one goal was scored in every even numbered match.
Q1: How many goals were scored in Match 7?
(a) Cannot be determined
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 2
Ans: b
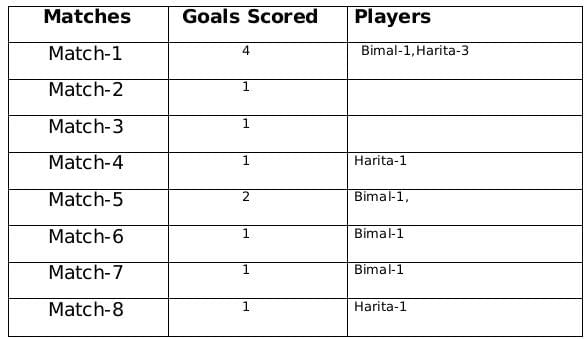
Sol: A total of 12 goals were scored in 8 matches and each player scored atleast one goal and no of goals scored by each one of them is distinct so the possible number of goals scored by the players can be (1,2,3,6) or (1,2,4,5).
From statement 4 we know that Bimal scored 4 goals and since Harita scored more goals than Bimal so we can say that Harita scored 5 goals and the only case possible for total goals scored by each of the players is (1,2,4,5).
Now using statement 1, statement 3 and statement 4 we can say that the three consecutive matches in which Bimal scored will be 5th, 6th and 7th matches as Harita scored in 4th and 8th matches and we get the following table:From statement 5 and 6, we can conclude that the highest number of goals were scored in Match 1.
Let the no. of goals scored in 3rd and 7th match be a each and no. of goals scored in 1st and 5th match be b and c respectively.
Therefore, 2a+b+c= 8
If a=1, then b+c=6 therefore possible solutions for b and c will be 2 and 4 only
If a=2, then b+c=4 therefore possible solution for b and c will be 1 and 3 only but since highest goals scored is in Match 1 so then no. of goals scored in match 1 must be 3 and Harita must have scored 3 goals in match 1 as Harita scored 5 goals in exactly 3 matches. Therefore, we can see this is not possible because then the no. of goals scored in Match 1 becomes 4.
Therefore the only possible solution is a=1, b=4 and c=2
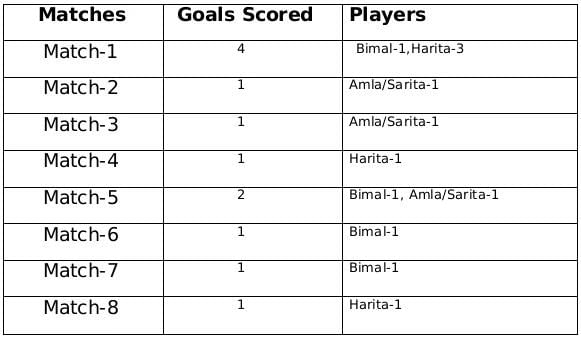
The remaining 3 goals were scored in the match 2, 3 and 5 by Amla and Sarita in some order.
Q2: Which of the following is the correct sequence of goals scored in matches 1, 3, 5 and 7?
(a) 4, 1, 2, 1
(b) 5, 1, 0, 1
(c) 3, 2, 1, 2
(d) 3, 1, 2, 1
Ans: a
Sol: A total of 12 goals were scored in 8 matches and each player scored atleast one goal and no of goals scored by each one of them is distinct so the possible number of goals scored by the players can be (1,2,3,6) or (1,2,4,5).
From statement 4 we know that Bimal scored 4 goals and since Harita scored more goals than Bimal so we can say that Harita scored 5 goals
and the only case possible for total goals scored by each of the players is (1,2,4,5).
Now using statement 1, statement 3 and statement 4 we can say that the three consecutive matches in which Bimal scored will be 5th, 6th and 7th matches as Harita scored in 4th and 8th matches and we get the following table:From statement 5 and 6, we can conclude that the highest number of goals were scored in Match 1.
Let the no. of goals scored in 3rd and 7th match be a each and no. of goals scored in 1st and 5th match be b and c respectively.
Therefore, 2a+b+c= 8
If a=1, then b+c=6 therefore possible solutions for b and c will be 2 and 4 only
If a=2, then b+c=4 therefore possible solution for b and c will be 1 and 3 only but since highest goals scored is in Match 1 so then no. of goals scored in match 1 must be 3 and Harita must have scored 3 goals in match 1 as Harita scored 5 goals in exactly 3 matches. Therefore, we can see this is not possible because then the no. of goals scored in Match 1 becomes 4.
Therefore the only possible solution is a=1, b=4 and c=2
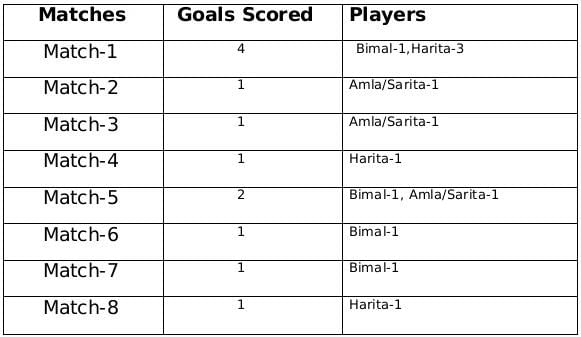
The remaining 3 goals were scored in the match 2, 3 and 5 by Amla and Sarita in some order.
Q3: Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
Statement-1: Amla and Sarita never scored goals in the same match.
Statement-2: Harita and Sarita never scored goals in the same match.
(a) Both the statements
(b) Statement-1 only
(c) None of the statements
(d) Statement-2 only
Ans: a
Sol: A total of 12 goals were scored in 8 matches and each player scored atleast one goal and no of goals scored by each one of them is distinct so the possible number of goals scored by the players can be (1,2,3,6) or (1,2,4,5).From statement 4 we know that Bimal scored 4 goals and since Harita scored more goals than Bimal so we can say that Harita scored 5 goals and the only case possible for total goals scored by each of the players is (1,2,4,5).
Now using statement 1, statement 3 and statement 4 we can say that the three consecutive matches in which Bimal scored will be 5th, 6th and 7th matches as Harita scored in 4th and 8th matches and we get the following table:
From statement 5 and 6, we can conclude that the highest number of goals were scored in Match 1.
Let the no. of goals scored in 3rd and 7th match be a each and no. of goals scored in 1st and 5th match be b and c respectively.
Therefore, 2a+b+c= 8
If a=1, then b+c=6 therefore possible solutions for b and c will be 2 and 4 only
If a=2, then b+c=4 therefore possible solution for b and c will be 1 and 3 only but since highest goals scored is in Match 1 so then no. of goals scored in match 1 must be 3 and Harita must have scored 3 goals in match 1 as Harita scored 5 goals in exactly 3 matches. Therefore, we can see this is not possible because then the no. of goals scored in Match 1 becomes 4.
Therefore the only possible solution is a=1, b=4 and c=2
The remaining 3 goals were scored in the match 2, 3 and 5 by Amla and Sarita in some order.
Q4: Which of the following statement(s) is/are false?
Statement-1: In every match at least one player scored a goal.
Statement-2: No two players scored goals in the same number of matches.
(a) Statement-2 only
(b) Statement-1 only
(c) None of the statements
(d) Both the statements
Ans: c
Sol: A total of 12 goals were scored in 8 matches and each player scored atleast one goal and no of goals scored by each one of them is distinct so the possible number of goals scored by the players can be (1,2,3,6) or (1,2,4,5).
From statement 4 we know that Bimal scored 4 goals and since Harita scored more goals than Bimal so we can say that Harita scored 5 goals and the only case possible for total goals scored by each of the players is (1,2,4,5).
Now using statement 1, statement 3 and statement 4 we can say that the three consecutive matches in which Bimal scored will be 5th, 6th and 7th matches as Harita scored in 4th and 8th matches and we get the following table:From statement 5 and 6, we can conclude that the highest number of goals were scored in Match 1.
Let the no. of goals scored in 3rd and 7th match be a each and no. of goals scored in 1st and 5th match be b and c respectively.
Therefore, 2a+b+c= 8
If a=1, then b+c=6 therefore possible solutions for b and c will be 2 and 4 only
If a=2, then b+c=4 therefore possible solution for b and c will be 1 and 3 only but since highest goals scored is in Match 1 so then no. of goals scored in match 1 must be 3 and Harita must have scored 3 goals in match 1 as Harita scored 5 goals in exactly 3 matches. Therefore, we can see this is not possible because then the no. of goals scored in Match 1 becomes 4.
Therefore the only possible solution is a=1, b=4 and c=2
The remaining 3 goals were scored in the match 2, 3 and 5 by Amla and Sarita in some order.
Q5: If Harita scored goals in one more match as compared to Sarita, which of the following statement(s) is/are necessarily true?
Statement-1: Amla scored goals in consecutive matches.
Statement-2: Sarita scored goals in consecutive matches.
(a) None of the statements
(b) Statement-1 only
(c) Both the statements
(d) Statement-2 only
Ans: a
Sol: A total of 12 goals were scored in 8 matches and each player scored atleast one goal and no of goals scored by each one of them is distinct so the possible number of goals scored by the players can be (1,2,3,6) or (1,2,4,5).
From statement 4 we know that Bimal scored 4 goals and since Harita scored more goals than Bimal so we can say that Harita scored 5 goals and the only case possible for total goals scored by each of the players is (1,2,4,5).
Now using statement 1, statement 3 and statement 4 we can say that the three consecutive matches in which Bimal scored will be 5th, 6th and 7th matches as Harita scored in 4th and 8th matches and we get the following table:From statement 5 and 6, we can conclude that the highest number of goals were scored in Match 1.
Let the no. of goals scored in 3rd and 7th match be a each and no. of goals scored in 1st and 5th match be b and c respectively.
Therefore, 2a+b+c= 8
If a=1, then b+c=6 therefore possible solutions for b and c will be 2 and 4 only
If a=2, then b+c=4 therefore possible solution for b and c will be 1 and 3 only but since highest goals scored is in Match 1 so then no. of goals scored in match 1 must be 3 and Harita must have scored 3 goals in match 1 as Harita scored 5 goals in exactly 3 matches. Therefore, we can see this is not possible because then the no. of goals scored in Match 1 becomes 4.
Therefore the only possible solution is a=1, b=4 and c=2
The remaining 3 goals were scored in the match 2, 3 and 5 by Amla and Sarita in some order.
Passage - 5
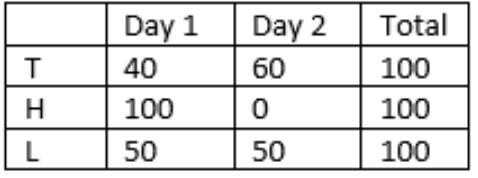
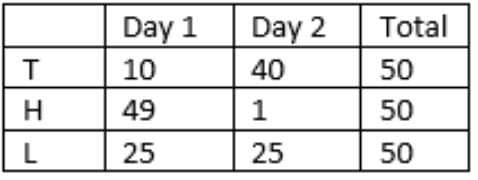
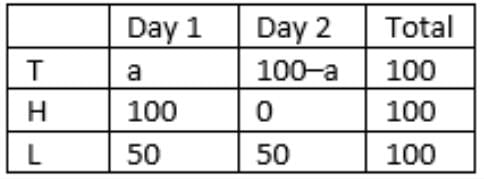
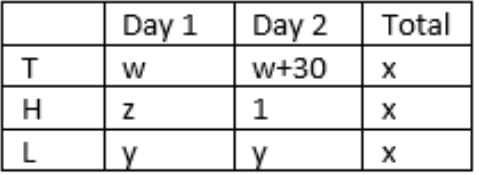
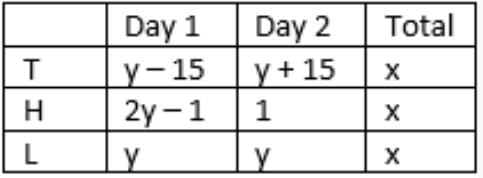
A few salesmen are employed to sell a product called TRICCEK among households in various housing complexes. On each day, a salesman is assigned to visit one housing complex. Once a salesman enters a housing complex, he can meet any number of households in the time available. However, if a household makes a complaint against the salesman, then he must leave the housing complex immediately and cannot meet any other household on that day. A household may buy any number of TRICCEK items or may not buy any item. The salesman needs to record the total number of TRICCEK items sold as well as the number of households met in each day. The success rate of a salesman for a day is defined as the ratio of the number of items sold to the number of households met on that day. Some details about the performances of three salesmen - Tohri, Hokli and Lahur, on two particular days are given
below.
- On both days, Lahur met the same number of households and sold the same number of items.
- Hokli could not sell any item on the second day because the first household he met on that day complained against him.
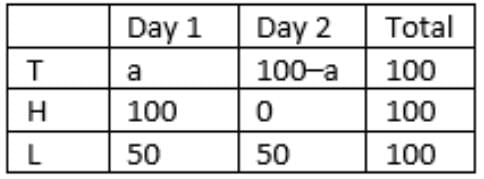
- Tohri met 30 more households on the second day than on the first day. 5. Tohri’s success rate was twice that of Lahur’s on the first day, and it was 75% of Lahur’s on the second day.
- Over the two days, all three of them met the same total number of households, and each of them sold a total of 100 items.
Q1: What was the total number of households met by Tohri, Hokli and Lahur on the first day?
Ans: 84
Sol:
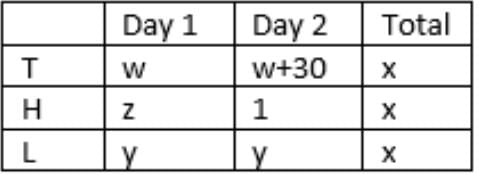
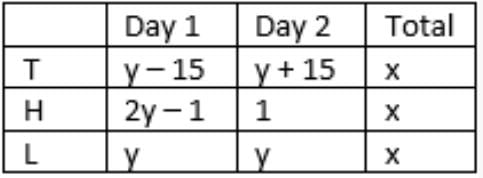
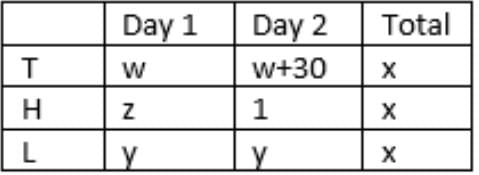
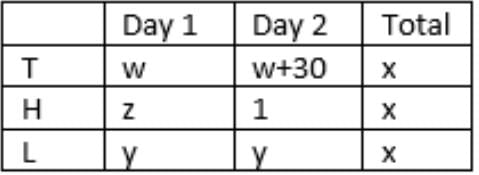
Success rate of a salesman for a day = Number of items sold/Number of households met
Three salesmen – T, H, L
Units sold:
Households met:
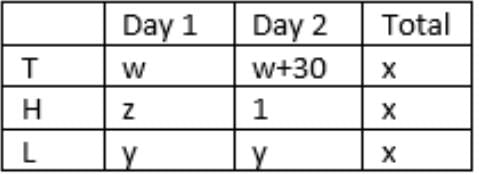
y + y = z + 1
=> z = 2y -1
w + w + 30 = 2y
=> w = y – 15
Households met:
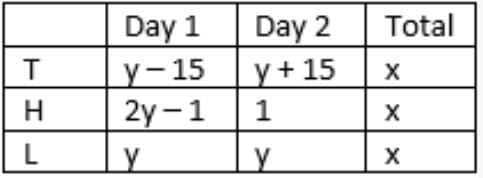
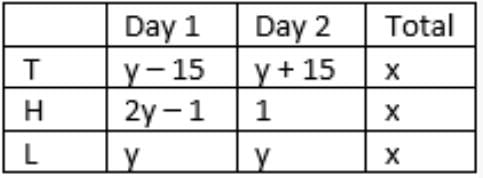
T’s success rate was twice that of L’s on the first day.
=> a/(y – 15) = 2(50/y)
=> ay = 100y – 1500 …….(i)
T’s success rate was 75% of L’s on the second day.
=> (100 – a)/(y + 15) = (3/4)(50/y) = 75/2y
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 2ay
Substitute value of ay from (i)
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 200y + 3000
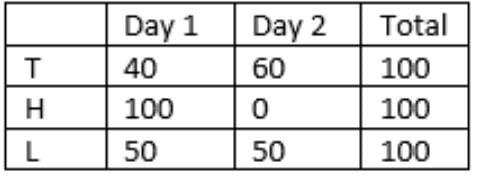
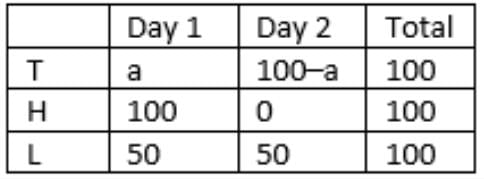
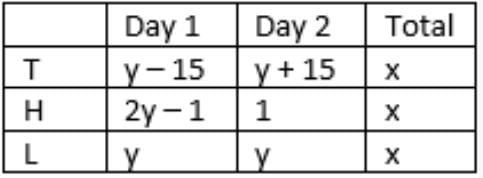
=> y = 25, a = 40
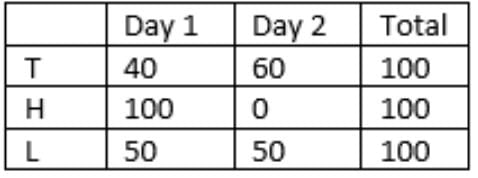
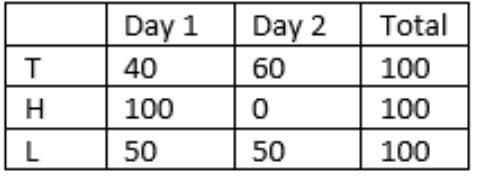
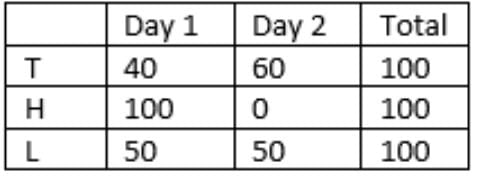
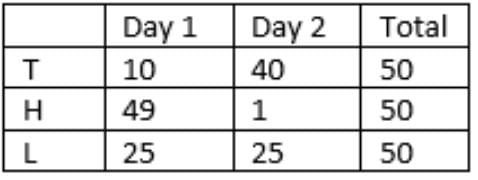
The final tables are:
Units sold:
Households met:
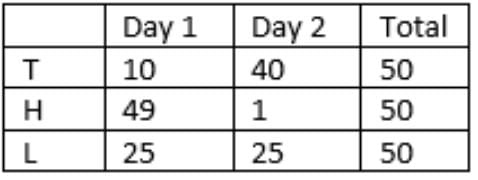
So, 10 + 49 + 25 = 84 households were met on the first day.
Q2: How many TRICCEK items were sold by Tohri on the first day?
Ans: 40
Sol:
Success rate of a salesman for a day = Number of items sold/Number of households met
Three salesmen – T, H, L
Units sold:
Households met:
y + y = z + 1
=> z = 2y -1
w + w + 30 = 2y
=> w = y – 15
Households met:
T’s success rate was twice that of L’s on the first day.
=> a/(y – 15) = 2(50/y)
=> ay = 100y – 1500 …….(i)
T’s success rate was 75% of L’s on the second day.
=> (100 – a)/(y + 15) = (3/4)(50/y) = 75/2y
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 2ay
Substitute value of ay from (i)
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 200y + 3000
=> y = 25, a = 40
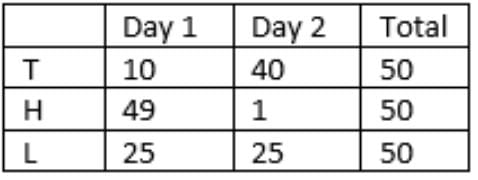
The final tables are:
Units sold:
Households met:
40 TRICCEK items were sold by Tohri on the first day.
Q3: How many households did Lahur meet on the second day?
(a) more than 35
(b) between 30 and 35
(c) 20 or less
(d) between 21 and 29
Ans: d
Sol:
Success rate of a salesman for a day = Number of items sold/Number of households met
Three salesmen – T, H, L
Units sold:
Households met:
y + y = z + 1
=> z = 2y -1
w + w + 30 = 2y
=> w = y – 15
Households met:
T’s success rate was twice that of L’s on the first day.
=> a/(y – 15) = 2(50/y)
=> ay = 100y – 1500 …….(i)
T’s success rate was 75% of L’s on the second day.
=> (100 – a)/(y + 15) = (3/4)(50/y) = 75/2y
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 2ay
Substitute value of ay from (i)
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 200y + 3000
=> y = 25, a = 40
The final tables are:
Units sold:
Households met:
Lahur met 25 households on the second day which is between 21 and 39.
Q4: How many households did Tohri meet on the first day?
(a) between 21 and 40
(b) more than 40
(c) between 11 and 20
(d) 10 or less
Ans: d
Sol:
Success rate of a salesman for a day = Number of items sold/Number of households met
Three salesmen – T, H, L
Units sold:
Households met:
y + y = z + 1
=> z = 2y -1
w + w + 30 = 2y
=> w = y – 15
Households met:
T’s success rate was twice that of L’s on the first day.
=> a/(y – 15) = 2(50/y)
=> ay = 100y – 1500 …….(i)
T’s success rate was 75% of L’s on the second day.
=> (100 – a)/(y + 15) = (3/4)(50/y) = 75/2y
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 2ay
Substitute value of ay from (i)
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 200y + 3000
=> y = 25, a = 40
The final tables are:
Units sold:
Households met:
Tohri met 10 households on the first day, i.e.,
Q5: Which of the following statements is FALSE?
(a) Tohri had a higher success rate on the first day compared to the second day.
(b) Among the three, Lahur had the lowest success rate on the first day.
(c) Among the three, Tohri had the highest success rate on the second day.
(d) Among the three, Tohri had the highest success rate on the first day.
Ans: c
Sol:
Success rate of a salesman for a day = Number of items sold/Number of households met
Three salesmen – T, H, L
Units sold:
Households met:
y + y = z + 1
=> z = 2y -1
w + w + 30 = 2y
=> w = y – 15
Households met:
T’s success rate was twice that of L’s on the first day.
=> a/(y – 15) = 2(50/y)
=> ay = 100y – 1500 …….(i)
T’s success rate was 75% of L’s on the second day.
=> (100 – a)/(y + 15) = (3/4)(50/y) = 75/2y
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 2ay
Substitute value of ay from (i)
=> 75y + 1125 = 200y – 200y + 3000
=> y = 25, a = 40
The final tables are:
Units sold:
Households met:
Tohri’s success rate on 2nd day = 60/40 = 1.5L (50/25 = 2) has a higher success rate than Tohri.
2021
Passage - 1
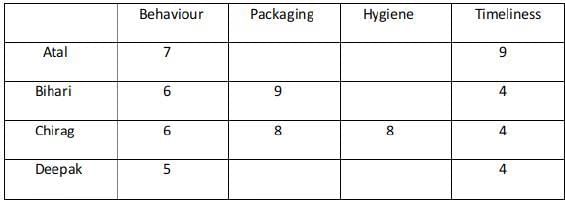
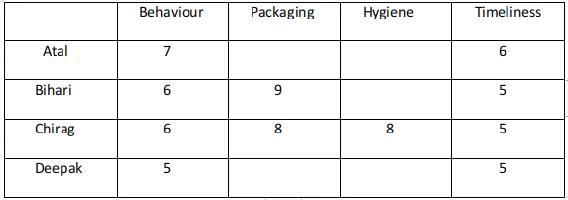
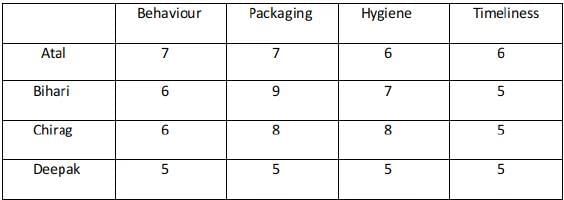
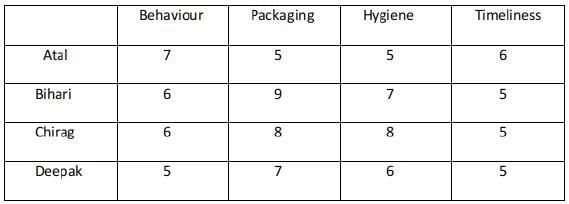
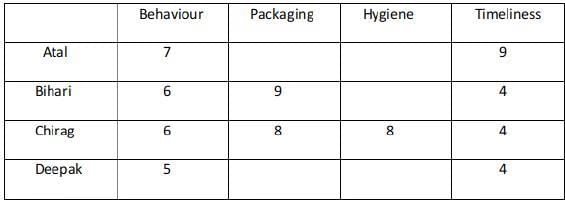
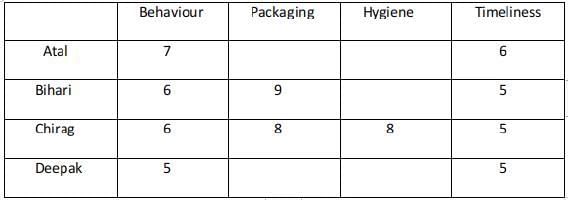
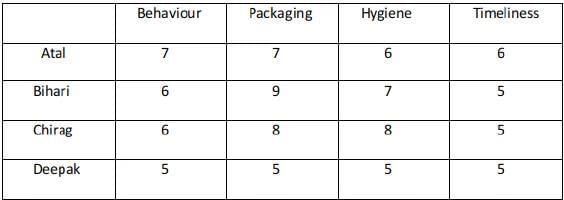
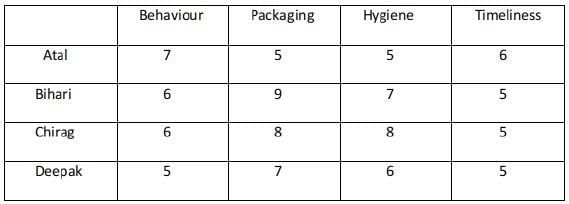
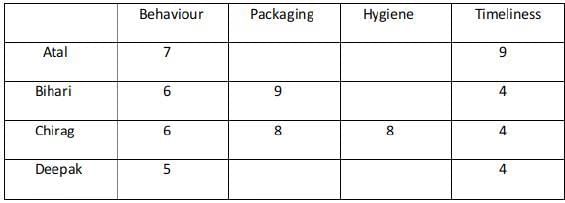
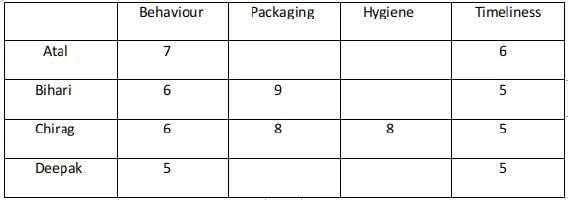
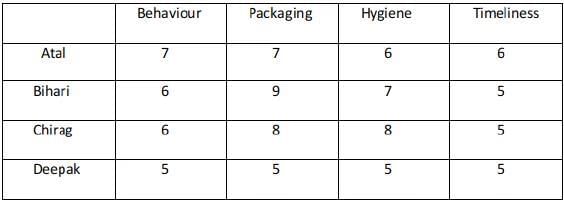
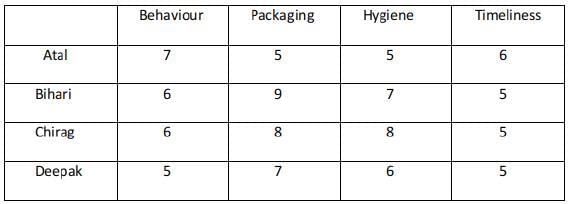
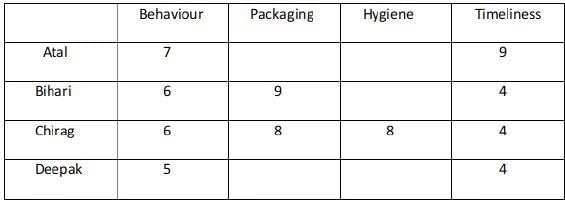
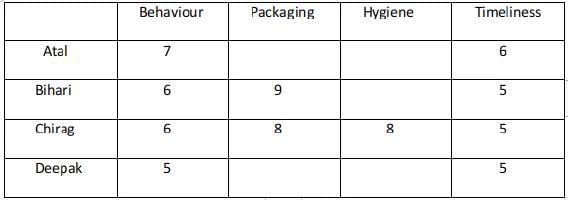
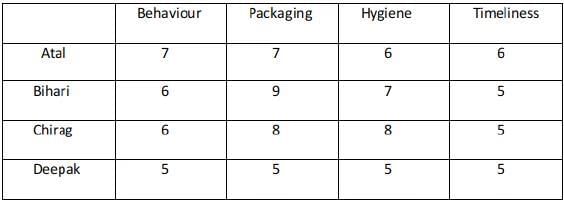
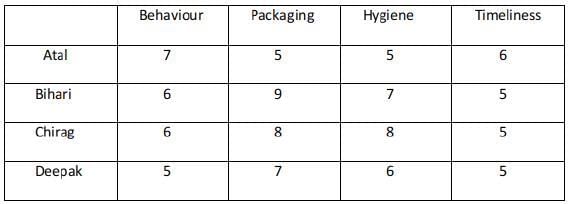
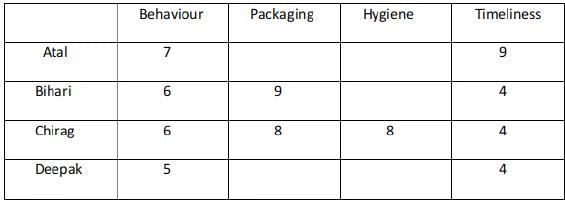
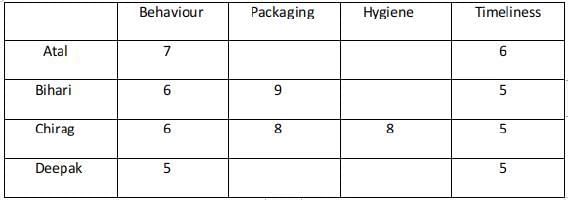
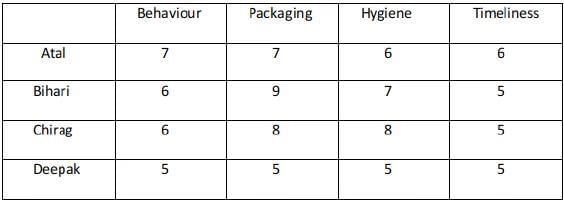
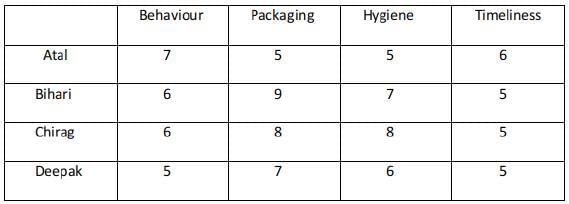
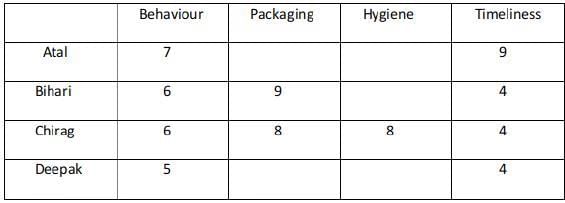
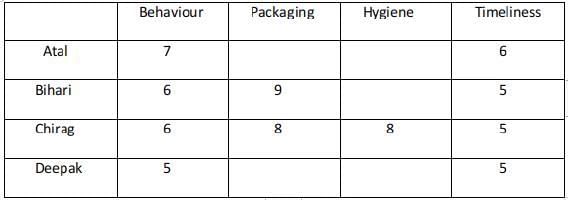
Ravi works in an online food-delivery company. After each delivery, customers rate Ravi on each of four parameters - Behaviour, Packaging, Hygiene, and Timeliness, on a scale from 1 to 9. If the total of the four rating points is 25 or more, then Ravi gets a bonus of ₹20 for that delivery. Additionally, a customer may or may not give Ravi a tip. If the customer gives a tip, it is either ₹30 or ₹50.
One day, Ravi made four deliveries - one to each of Atal, Bihari, Chirag, and Deepak, and received a total of ₹120 in bonus and tips. He did not get both a bonus and a tip from the same customer.
The following additional facts are also known.
- Ravi received distinct rating points in Packaging from the four customers adding up to 29 points. Similarly, Ravi received distinct rating points in Hygiene from the four customers adding up to 26 points.
- Chirag gave the same rating points for Packaging and Hygiene.
- Among the four customers, Bihari gave the highest rating points in Packaging, and Chirag gave the highest rating points in Hygiene.
- Everyone rated Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
- If the customers are ranked based on ratings given by them in individual parameters, then Atal’s rank based on Packaging is the same as that based on Hygiene. This is also true for Deepak.
- In Timeliness, Ravi received a total of 21 points, and three of the customers gave him the same rating points in this parameter. Atal gave higher rating points than Bihari and Chirag in this parameter.
Q1: What was the minimum rating that Ravi received from any customer in any parameter?
Ans: 5
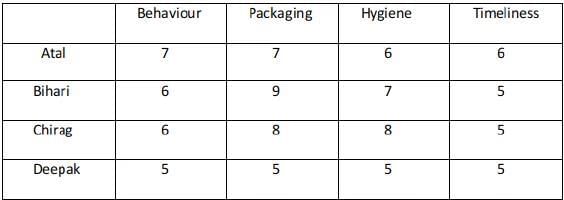
Sol: only B is the possible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
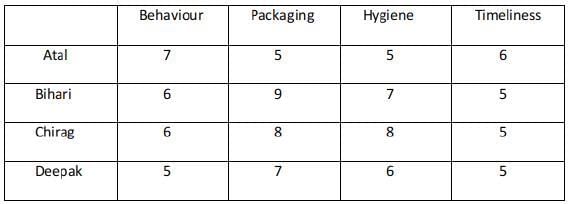
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
The minimum rating awarded is 5.
Q2: The COMPLETE list of customers who gave the maximum total rating points to Ravi is
(a) Atal
(b) Bihari
(c) Bihari and Chirag
(d) Atal and Bihari
Ans: c
Sol: ssible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
Bihari and Chirag has given the highest ratings
Q3: What rating did Atal give on Timeliness?
Ans: 6
Sol: ssible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
Atal has given a rating of 6 in timeliness
Q4: What BEST can be concluded about the tip amount given by Deepak?
(a) Either ₹0 or ₹30 or ₹50
(b) Either ₹30 or ₹50
(c) ₹50
(d) ₹30
Ans: b
Sol: ssible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
Among Atal and Deepak, one of them gives a tip of 30 and the other gives a tip of 50. Hence 30 or 50 any case is possible
Q5: In which parameter did Atal give the maximum rating points to Ravi?
(a) Hygiene
(b) Behaviour
(c) Timeliness
(d) Packaging
Ans: b
Sol: ssible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
Atal has given the maximum rating in Behaviour.
Q6: What rating did Deepak give on Packaging?
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 5
(d) 6
Ans: a
Sol: ssible case with 8 as the maximum score.
In condition 5 it was mentioned that everyone awarded Ravi between 5 and 7 in Behaviour. Unique maximum and minimum ratings in this parameter were given by Atal and Deepak respectively.
Hence Atal must have awarded 7, Deepak 6, Bihari, and Chirag 6 each in Behaviour.
The two possible cases are : Case 1 :Case 2 :
The ratings awarded by Atal and Deepak in Packaging are among 5 and 7.
The ratings awarded by Atal, Bihari, Deepak are among 5,6, and 7.
Atal individual ranking in Packaging and Hygiene are the same. The same is true for Deepak.
Since Atal and Deepak can give the ranking among 3 and 4 in Packaging as Bihari is first and Chirag is second in this parameter.
They can rank 3 or 4 in the Hygiene parameter also. Hence Bihari must rate 7 points in Hygiene.
In both the possibilities Bihari and Chirag award a total of 26 points. Hence he wins 40 because the total ratings are greater than 25 received from Bihari and Chirag.
Since he gets a total of 120 in bonuses and tips. He must have 80 from Atal and Deepak.
This is possible if he gets a tip of 30 ad 50 from them respectively.
In case 1 irrespective of Atal standing at rank 3 or rank 4 in Hygiene and Packaging Atal total rating is greater than 25 which implies Ravi gets a tip from Atal but this is not a possible case because Ravi needs a total of Rs 80 from Atal and Deepak. From Atal if he gets Rs 20 as a bonus he cannot get a total of Rs 120 and hence this case fails.
Hence case 1 fails.
In case 2 there are two possibilities : Atal ranking 3 in both the parameters and Deepak 4 . Atal ranking 4 in both the parameters and Deepak 3 In the case where Atal ranks 3 in Packaging and Hygiene the total score is 26 and is not a feasible case.
Case - 2ACase - 2B :
Case - 2A fails because Atal's total rating is greater than 25 which should not be the case.
Deepak gives a rating of 7 in Packaging.
|
87 videos|166 docs|99 tests
|
FAQs on CAT Previous Year Questions - Quantitative Reasoning - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI)
| 1. What topics are typically covered in the Quantitative Reasoning section of the CAT exam? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively prepare for the Quantitative Reasoning section of the CAT exam? |  |
| 3. Are previous year CAT questions useful for preparing for the Quantitative Reasoning section? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of time management in the Quantitative Reasoning section of the CAT exam? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my speed and accuracy in solving quantitative problems for the CAT exam? |  |