Awareness in Field of IT & Computers- 2 | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Big Data
Big data refers to the study and applications of massive, complex datasets that traditional data-processing software cannot handle. Challenges include data capture, storage, analysis, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, privacy, and sourcing. By 2025, big data integrates with edge computing and AI, enabling real-time analytics for smart cities and governance.
Originally defined by three concepts—volume, variety, velocity—big data now includes veracity (data noise) and value, with India’s Digital Economy Plan 2025 leveraging big data for policy optimization.
Big data can be described by the following characteristics:
- Volume – The quantity of generated and stored data, critical for deriving value and insights, determining its classification as big data.
- Variety – The diverse types of data (text, images, audio, video), enhanced by data fusion to complete missing insights, now including IoT and social media streams.
- Velocity – The speed of data generation and processing, now accelerated by 5G and edge computing for real-time applications in governance and healthcare.
- Veracity – The varying quality of data, impacting analysis accuracy, addressed by AI-driven data cleaning tools in 2025.
Applications
Government: Big data drives policy formation, enhancing cost efficiency, productivity, and innovation. India’s Digital India 2.0 (2025) uses big data for predictive governance, though privacy concerns persist under the DPDP Act, 2023.
International Development: Big data supports ICT4D, improving decision-making in healthcare, employment, and disaster management. By 2025, blockchain-integrated big data ensures transparent aid distribution.
Manufacturing: Predictive manufacturing uses sensory data (acoustics, vibration, pressure) for Prognostics and Health Management (PHM), with 2025 advancements in AI-driven automation.
Healthcare: Big data enables personalized medicine, predictive analytics, and automated patient data reporting. By 2025, India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission integrates big data for universal health coverage.
Education: A 2010 McKinsey study noted a shortage of 1.5 million data professionals. By 2025, Indian institutions like IITs and IIMs offer specialized AI and big data programs, alongside private boot camps like UpGrad.
Media: Big data supports targeted advertising, data capture, and data journalism, with 2025 trends including AI-generated infographics and metaverse-based campaigns.
Insurance: Health insurers use social determinants (e.g., food consumption) for cost predictions, now regulated under the DPDP Act, 2023, sparking debates on pricing ethics.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Big data and IoT are interconnected, mapping device interconnectivity for targeted media and governance. By 2025, India’s Smart Cities Mission leverages IoT for urban planning, with sensory data applications in medical, manufacturing, and transportation contexts, supported by 5G and edge computing.
End-to-end Encryption (E2EE)
E2EE ensures only communicating users can read messages, preventing eavesdropping by telecom or service providers. By 2025, E2EE is standard in apps like WhatsApp and Signal, with quantum-resistant algorithms addressing emerging decryption threats.
Point-to-point Encryption (P2PE)
P2PE, a PCI Security Standards Council standard, instantly converts payment card data into indecipherable code to prevent fraud. By 2025, P2PE integrates with UPI and e-Rupee transactions under India’s Cryptocurrency Act, 2024, enhancing digital payment security.
Deep Web
The deep web, or invisible web, comprises World Wide Web content not indexed by standard search engines, unlike the surface web. Coined by Michael K. Bergman in 2001, it includes webmail, online banking, and paywalled services like video on demand. By 2025, deep web access requires secure authentication, with India’s Cybersecurity Framework 2024 regulating access to prevent misuse.
Dark Web
The dark web exists on darknets, requiring specific software like Tor or I2P for access, forming a small part of the deep web. By 2025, dark web activities are monitored under the Global Cybersecurity Treaty (2024), with India’s CERT-In tracking illicit transactions on networks like Onionland.
 Types of Web
Types of Web
Wannacry
The WannaCry ransomware attack of May 2017 targeted Windows systems, encrypting data and demanding Bitcoin ransoms via the EternalBlue exploit. By 2025, WannaCry’s lessons have shaped India’s Cybersecurity Framework 2024, mandating timely patches and zero-trust architectures.
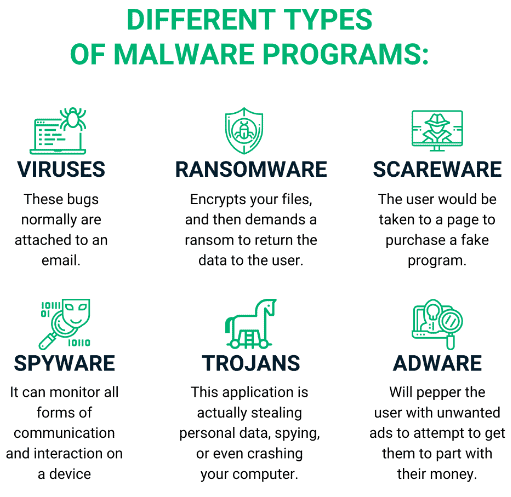 Types of Malware
Types of Malware
Botnet
A botnet is a network of Internet-connected devices running bots for DDoS attacks, data theft, or spam. By 2025, AI-driven botnets pose advanced threats, countered by India’s CERT-In AI Threat Detection System.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attack
A DDoS attack overwhelms servers with traffic from botnets, causing crashes. By 2025, 5G and IoT amplify DDoS risks, mitigated by India’s National Cybersecurity Policy 2024, emphasizing real-time traffic monitoring.
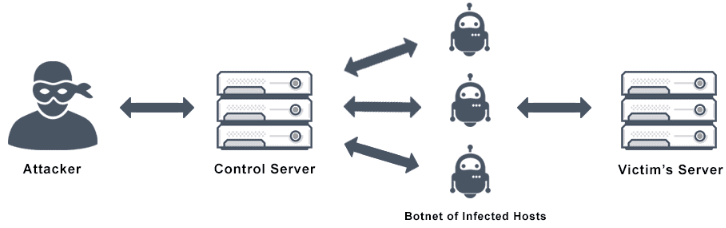 DDoS
DDoS
Reaper Malware
Reaper, a 2017 malware, hacks devices like routers and cameras, hiding its presence. By 2025, advanced malware like Reaper is countered by quantum-resistant firewalls and AI-based intrusion detection systems.
Spectrum Pooling
Spectrum pooling allows multiple users to share radio spectrum, using cognitive radio techniques. By 2025, India’s 6G Vision Document (2024) integrates spectrum pooling for efficient 6G networks.
Cognitive Radio
Cognitive radio dynamically selects wireless channels to avoid interference. By 2025, it supports India’s 5G and 6G rollout, optimizing spectrum for smart cities and rural connectivity.
HTTPS
HTTPS ensures secure communication, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks. By 2025, HTTPS adopts post-quantum cryptography to counter quantum computing threats, aligning with India’s Cybersecurity Framework 2024.

Quantum Computer
Quantum computing uses superposition and entanglement, with qubits enabling simultaneous states. By 2025, India’s National Quantum Mission has developed a 6-qubit prototype, applied in cryptography and drug discovery.
Quantum Supremacy
- Quantum supremacy denotes a quantum computer outperforming classical supercomputers. Google’s Sycamore achieved this in 2019, solving a random number task in 3 minutes versus 10,000 years for IBM’s Summit.
- By 2025, China and the US have advanced quantum supremacy, with India’s National Quantum Mission targeting practical applications in cybersecurity.
Quantum-Enabled Science & Technology (QuEST) Programme
India’s QuEST, under DST, builds quantum infrastructure. Phase 1 (Rs 80 crore) is complete, with Phase 2 (Rs 300 crore) funded by DRDO, ISRO, and DAE. By 2025, QuEST has operationalized quantum communication networks, aligning with National Quantum Mission goals.
Blockchain
Blockchains are immutable digital ledgers, invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 for Bitcoin. By 2025, India’s ONDC and e-Governance platforms use blockchain for transparency in supply chains and land records, regulated under the Cryptocurrency Act, 2024.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin, a decentralized cryptocurrency, uses blockchain to solve double-spending. By 2025, India’s e-Rupee (CBDC), launched under the Cryptocurrency Act, 2024, complements Bitcoin, with regulations addressing volatility and illegal transactions.
Artificial Intelligence
AI enables machines to mimic human abilities like speech and reasoning. By 2025, India’s India AI Mission (2024), with ₹10,000 crore, drives AI supercomputing and startups, led by global firms like Google and Indian players like HCL.
Real-world examples from around us:
- AI-powered autonomous vehicles are deployed in India’s smart cities by 2025.
- Sophia, a humanoid robot, became a Saudi citizen in 2017, inspiring India’s AI robotics initiatives.
- Siri and India’s CoWin AI chatbot handle natural language interactions.
- Autonomous weapons, regulated by India’s AI Ethics Framework 2024, execute military missions.
- Facial recognition aids India’s Aadhaar 2.0 for security and authentication.
- China’s facial recognition, contrasted with India’s privacy-focused systems, detects criminals.
- AI transforms military command, with India’s Defence AI Council (2025) leading innovations.
Applications of AI
AI powers gaming, natural language processing, law enforcement, healthcare, banking, and automotive industries. By 2025, India’s Param Siddhi-AI supercomputer enhances AI applications in climate modeling and governance.
Deep Learning
Deep learning emulates human learning for predictive analytics, using hierarchical algorithms. By 2025, India’s India AI Mission leverages deep learning for healthcare diagnostics and smart agriculture.
Machine Learning
Machine learning enables systems to learn from data autonomously. By 2025, ML drives India’s Smart Cities Mission, optimizing traffic and energy management.
The key difference between AI and ML are:
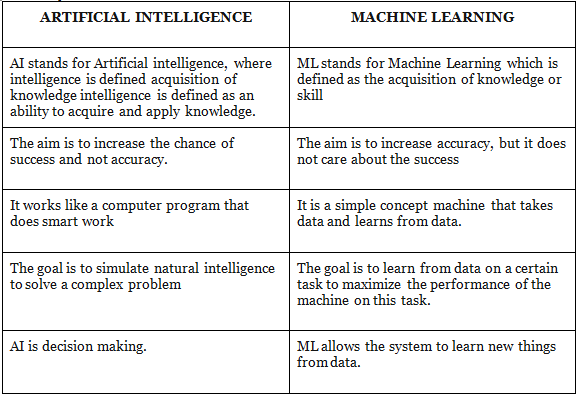
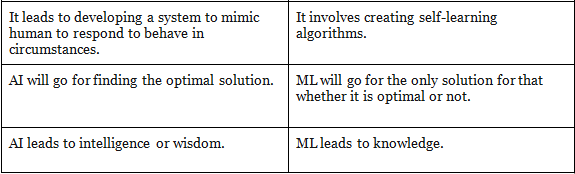
Project Brainwave
Microsoft’s Project Brainwave accelerates real-time AI using FPGAs. By 2025, it supports cloud-based AI for India’s Digital India 2.0, processing live data streams.
Humanoid Robot
Humanoid robots resemble humans for functional or experimental purposes. By 2025, India’s XR Startup Program develops humanoid robots for healthcare and education.
Features of Humanoid Robots –
- Self-maintenance
- Autonomous learning
- Avoiding harm to people, property, and itself
- Safe human interaction
Sophia
Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics, displays 50+ facial expressions. Named UNDP’s Innovation Champion in 2017, it inspires India’s AI robotics by 2025.
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL)
TKDL prevents misappropriation of India’s traditional medicinal knowledge, translating 0.29 million formulations into five languages. By 2025, TKDL integrates blockchain for secure data sharing, enhancing global patent scrutiny.
TKRC
TKRC classifies Indian medicine into 25,000 subgroups, improving patent searches. By 2025, TKRC’s AI-driven classification enhances efficiency at nine international patent offices.
Digiceuticals
Digiceuticals deliver health benefits via software, complementing drugs. By 2025, India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission adopts digiceuticals for mental health and chronic disease management.
CIMON (Crew Interactive Mobile Companion)
- A 3D-printed AI system by Airbus, assisting ISS astronauts.
- By 2025, CIMON’s technology supports India’s Gaganyaan Mission for crew assistance.
Cryptojacking
- Cryptojacking secretly mines cryptocurrency on devices. By 2025, India’s CERT-In uses AI to detect cryptojacking on high-traffic websites.
Haptic Communication
Haptic communication transmits touch sensations, applied in surgery and VR. By 2025, India’s XR Startup Program advances haptic tech for metaverse education.
Digi Shala
Digi Shala, launched under Digi Dhan Abhiyan, educates on digital payments like UPI and e-Rupee. By 2025, it supports Digital India 2.0, promoting financial inclusion in rural areas.
Significance:
- Digi Shala empowers farmers, students, and rural women with digital payment literacy.
- By 2025, it bridges the digital divide, aligning with Digital India 2.0 goals.
Computer Firewall
Firewalls prevent unauthorized network access, implemented in hardware or software. By 2025, AI-driven firewalls with quantum-resistant algorithms protect India’s sovereign cloud infrastructure.
Cyber-Attacks
Cyber-attacks access confidential data, with active (e.g., malware) and passive (e.g., data scraping) types. By 2025, AI-driven attacks like deepfake scams are countered by India’s CERT-In.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
DSC certifies identity via public key infrastructure. By 2025, DSC integrates with Aadhaar 2.0 for secure e-Governance transactions.
Open-source Software (OSS)
OSS provides freely accessible source code. By 2025, India’s MeitY promotes OSS for government applications, enhancing cybersecurity.
Software-defined Radio (SDR)
- SDR implements radio components in software. By 2025, SDR supports India’s 6G networks for efficient communication.
LIDAR-(Light Detection and Ranging)
- LIDAR uses pulsed lasers for ranging, applied in topographic and bathymetric mapping. By 2025, LIDAR supports India’s autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Metaverse and Green IT
The metaverse, a virtual shared space, transforms education and governance. India’s XR Startup Program (2024) fosters metaverse development. Green IT, under the Green IT Policy 2024, promotes energy-efficient data centers, aligning with India’s net-zero goals by 2070.
|
91 videos|501 docs|212 tests
|
FAQs on Awareness in Field of IT & Computers- 2 - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the importance of awareness in the field of IT and computers? |  |
| 2. How can one increase their awareness in the field of IT and computers? |  |
| 3. What are the potential benefits of being aware in the field of IT and computers? |  |
| 4. How does awareness in IT and computers contribute to cybersecurity? |  |
| 5. How can awareness in IT and computers lead to innovation and problem-solving? |  |





















