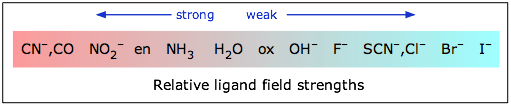|
What are the two types of valences in Werner’s theory of coordination compounds? |
Card: 1 / 40 |
|
Card: 2 / 40 |
|
How did Werner explain the different chloride precipitations in cobalt-ammonia complexes? |
Card: 3 / 40 |
|
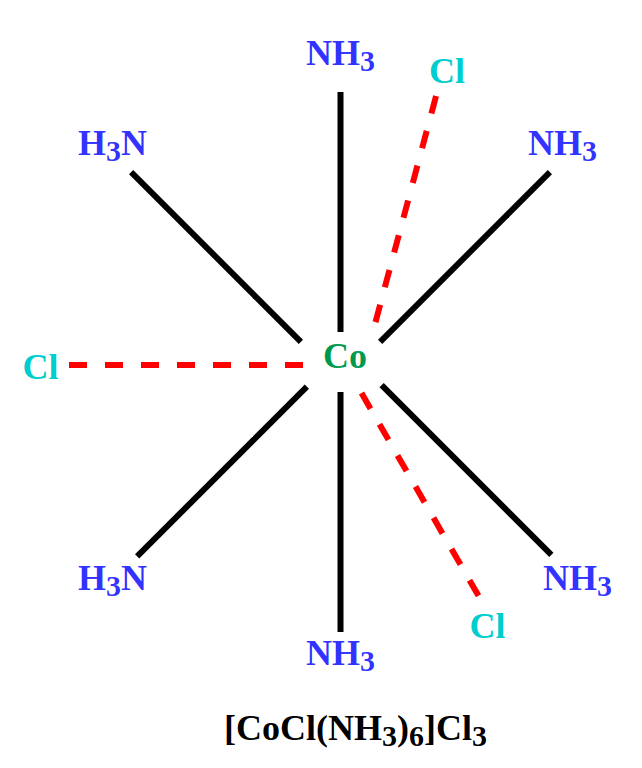
Werner found that in compounds like CoCl3•6NH3, some chloride ions could be precipitated with AgNO3, while others remained in solution. He explained this by proposing secondary valences, which hold ligands and some anions in fixed positions around the metal. These anions do not ionize in solution, leading to different numbers of precipitable chloride ions. |
Card: 4 / 40 |
|
A coordination entity consists of a central metal ion or atom surrounded by ligands in a fixed arrangement. It remains as a single unit in solution. Example: In [Co(NH3)6]3+, cobalt (CO3+) is the central ion, and six ammonia (NH3) molecules act as ligands. |
Card: 6 / 40 |
|
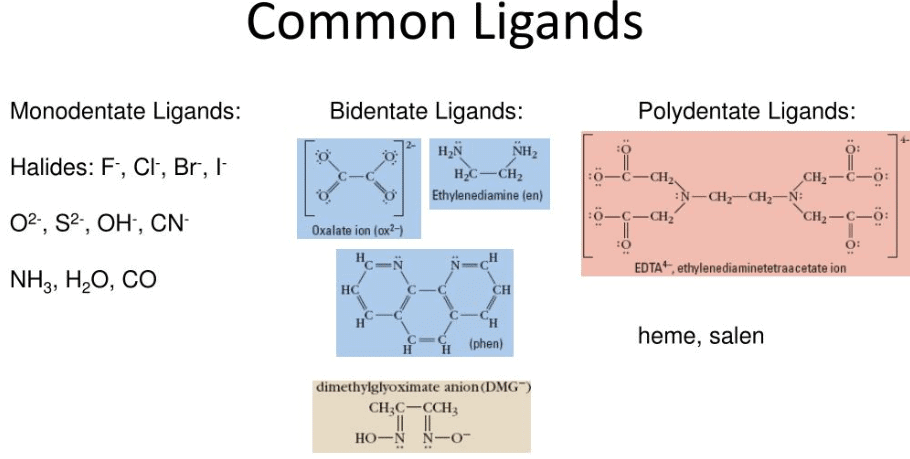
A ligand is an ion or molecule that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. Examples:
|
Card: 8 / 40 |
|
The coordination number is the number of ligand donor atoms directly bonded to the central metal ion. Example: In [Cr(NH3)6]3+, the coordination number of Cr3+ is 6 because six NH3 molecules are attached. |
Card: 10 / 40 |
|
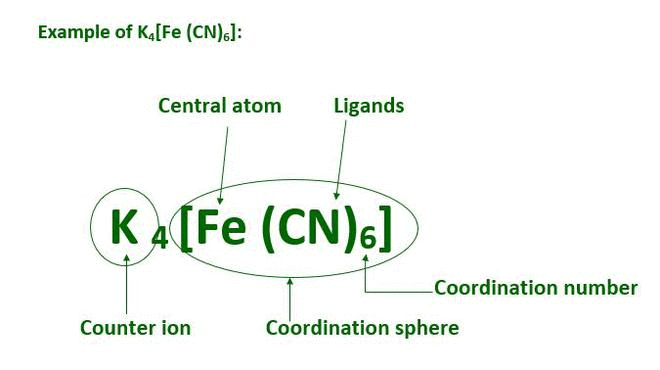
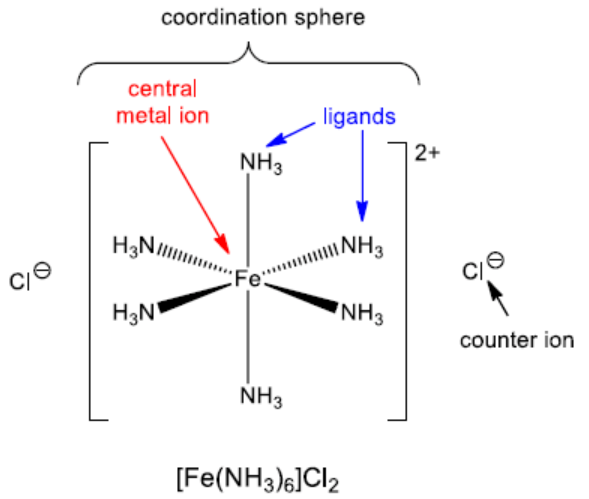
The coordination sphere includes the metal ion and its directly attached ligands, enclosed in square brackets. The ions outside the brackets are counter ions. Example: In K4[Fe(CN)6], the coordination sphere is [Fe(CN)6]4- and the counter ion is K+. |
Card: 12 / 40 |
|
Card: 14 / 40 |
|
Triamminetriaquachromium(III) chloride.
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
|
K3[Al(C2O4)3].
|
Card: 18 / 40 |
|
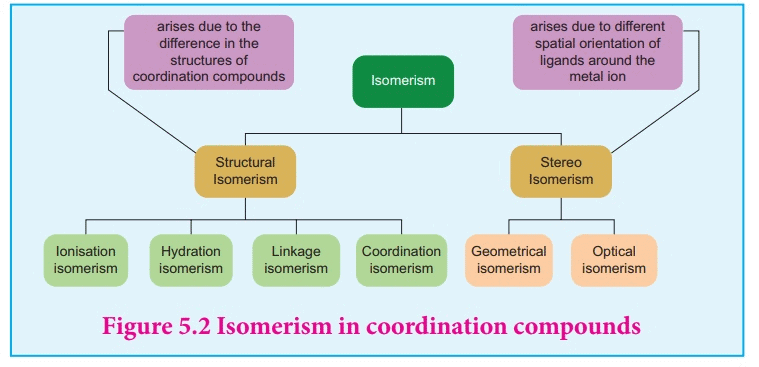
Structural isomerism (differences in connectivity)
Stereoisomerism (same connectivity, different spatial arrangement)
|
Card: 20 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Card: 22 / 40 |
|
Metal hybridizes its orbitals (e.g., d²sp³ or sp³d²) to accommodate ligands.
|
Card: 26 / 40 |
|
Higher energy orbitals (e_g): d(x²-y²), d(z²) |
Card: 28 / 40 |
|
Card: 30 / 40 |
|
Arrange the ligands in increasing crystal field splitting strength (spectrochemical series). |
Card: 33 / 40 |
|
I⁻ < Br⁻ < SCN⁻ < Cl⁻ < F⁻ < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO
|
Card: 34 / 40 |
|
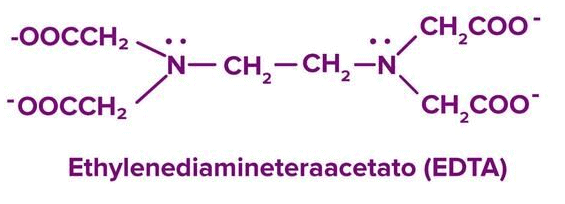
Cisplatin: Cancer treatment. EDTA: Treats lead poisoning by forming stable metal complexes. |
Card: 38 / 40 |