RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 2 - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Mock Test Series - RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 2
The Key Criticism of MARC include
(A) Inflexibility
(B) Complexity
(C) Lack of interoperability
(D) Information management
(A) Inflexibility
(B) Complexity
(C) Lack of interoperability
(D) Information management
Which model is described as a semantic data model and is the basis for object-oriented database management systems (OODBMS)?
Which is/are the part of ISBN?
(A) Suffex element
(B) Check Digit
(C) Publication element
(D) Registration group element
(A) Suffex element
(B) Check Digit
(C) Publication element
(D) Registration group element
In the 6th revised edition of CC, the class number of 'Child Medicine in Ayurveda' is LB, 9C. What is LB in this number?
In Vedic system (1500BC) the division of knowledgeinto categories of Dharm (Normative principles), Arth (social sciences) Kam (Pure sciences and arts) and Moksh (spiritual knowledge) is an example of ____________ principle.
According to Cutter’s “Rules for a Dictionary Catalogue (RDC),” which of the following is not considered a type of corporate body?
In cataloging, which law directs that between two or more possible alterative rules bearing on a particular phenomenon the one leading to over all economy is to be preferred?
Assertion (A): Results from popular web search engines are usually having high recall, but an indexing database can provide high precision.
Reason (R): Indexing databases use controlled vocabulary which is a carefully selected list of words and phrases that are used to tag units of information (document or work) so that they may be more easily retrieved.
The function of a “See also reference” is to ___
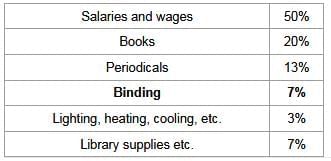
How many percentage of the total money of the budget is to be spent on the binding of the books of the library?
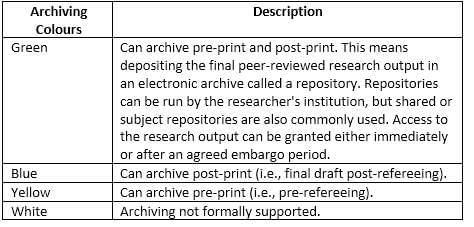
What is the 'green route' in the context of Open Access?
Which of the following is an example of a binary segment system?
Assertion (A) The Classified Catalogue Code (CCC) is an important cataloging method.
Reason (R) It is based on regulatory principles and canons.
Which of the following is true?
(A) According to Bhattacharya, there are eleven steps involved in Chain Procedure:
(B) PRECIS is based on two principles
(C) In PRECIS Role operators consist of a set of alpha-numeric notations.
(D) Uniterm indexing system was devised by Mortimer Taube in 1953
Which of the following is true about the General Principles of the List of Subject Headings?
(A) Subject headings should employ terms in common usage, following prevalent spelling and terminology conventions.
(B) Documents should be indexed under the most precise subject heading that accurately reflects their content.
(C) Subject headings do not need to maintain consistency and reflect current usage.
(D) Uniform headings must be chosen from synonymous terms, avoiding ambiguity and ensuring consistency across documents
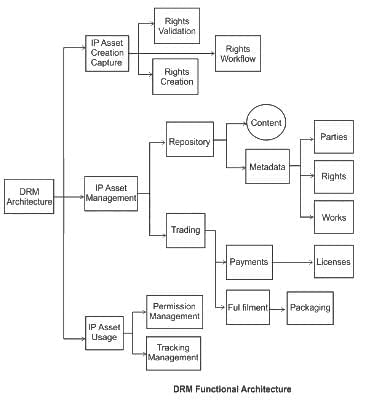
The DRM framework can be divided into three main areas:
(A) Intellectual Property (IP) Asset Creation & Capture
(B) IP Asset Management
(C) IP Asset Usage
(D) IP Rights Management