RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 5 - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Mock Test Series - RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 5
Which of the following statements correctly expresses the need for indexing and abstracting?
1. The number of articles published in journals may amount to millions of items.
2. The volume of primary literature published especially in periodicals is diminishing at a fast speed and rate.
3. The scholars require some help in locating and having access to information from a huge stockpile of information sources.
4. Due to problems of scatter and seepage of information, the scholars are unaware of literature in a particular subject appearing in totally alien sources published in various countries.
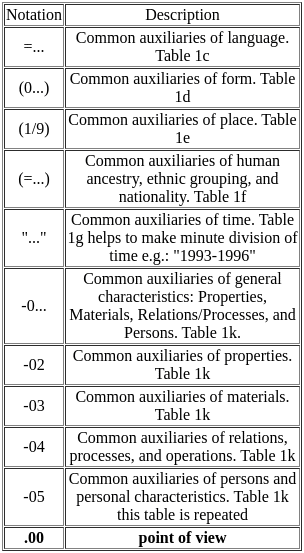
__________ is expressed as "Point of View":
The International Association of Music Libraries, Archives, and Documentation Centres has three official languages
(A) Spanish
(B) English
(C) German
(D) French.
(A) Spanish
(B) English
(C) German
(D) French.
What is the other name of added entries?
Which of the following is incorrect about Integrated Services Digital Network?
(A) ISDN refers to a set of telecommunication standards and techniques that enable the transmission of various forms of communication, such as data, voice, and video, over a public telephone network using digital signals.
(B) BRI encompasses two data-bearing channels ('B' channels) and one signaling channel ('D' channel) used for initiating connections.
(C) B-ISDN relies predominantly on the evolution of fiber optics.
(D) The groundwork for the standard commenced in 1980 at Bell Labs, culminating in its formal standardization in 1988 within the CCITT "Red Book."
Which of the following Internet services are currently using UDC
(A) BUBL
(B) OMNI
(C) GERHARD
(D) SOSIG
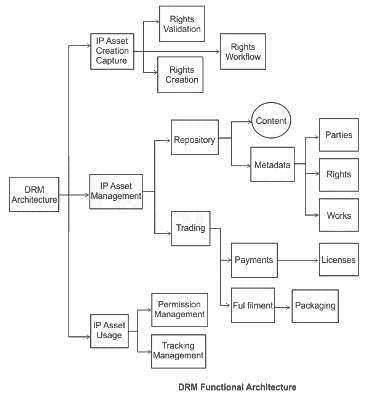
Among the following which one is not the functional architecture of DRM ?
Which of the following are the principles associated with Cutter’s Rules
(A) principle of convenience for the public
(B) principle of systematic association
(C) principle of collocation
(D) principle of probable association
(E) principle of specific and consistent subject entry
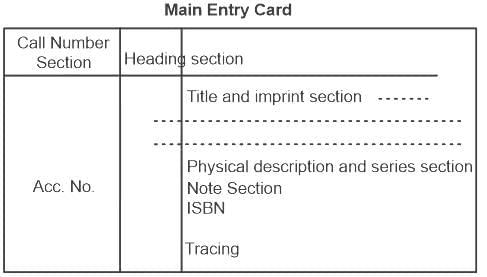
According to AACR 2R, the elements to be included in the physical description area of the main entry are:
i. Pages of a book
ii. Size of a book
iii. Edition statement of a book
iv. Series of a book
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
An empty Digit means a digit
(i) with ordinal value
(ii) without semantic value
(iii) without ordinal value
(iv) with semantic value
Choose the correct answer from the code given below :
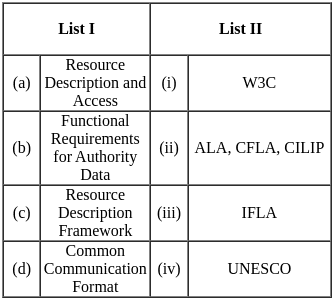
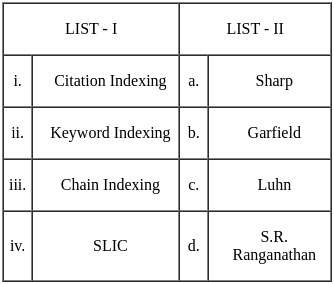
Match the following and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Lemmatization differs from stemming in that it:
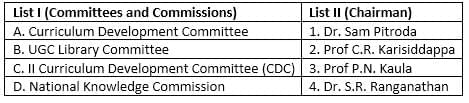
Ranganathan Committee Report on development of university and college libraries was published in 1959 by:
Assertion (A): Users, more or less, have same access points and can broaden up or narrow down their search, both in OPAC and Card Catalogue.
Reason (R): In OPAC, almost every single part of the bibliographic record is accessible through keyword searching which its traditional counterpart cannot.
In the context of these two statements, which one of the following is correct?
Under which license Joomla is distributed?