RSMSSB JE Electrical Mock Test - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB JE Electrical Mock Test Series 2026 - RSMSSB JE Electrical Mock Test - 1
Which Rajput ruler held the highest Mansab under Akbar?
Rajasthan shares the longest border with which state?
'Moti Bharat' is the name of the traditional embroidery of which district?
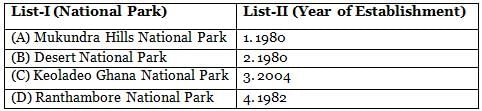
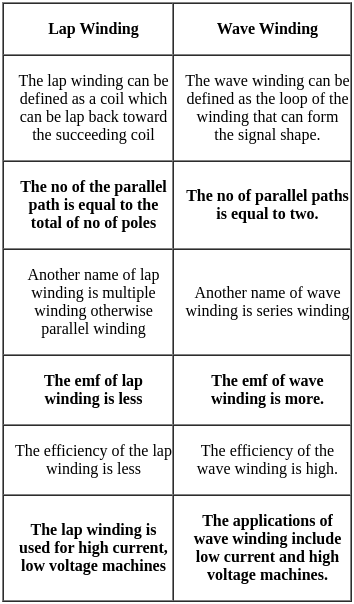
Match List-I with List-II and select the answer from the codes given below:
Which of the following is the best choice for permanent magnets?
Symmetrical components are used in power system for the analysis of
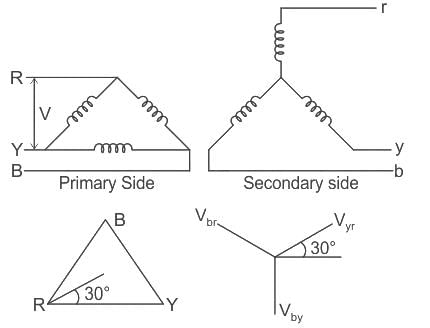
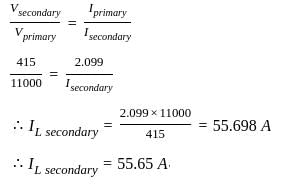
For an 11000/415 V, delta-star transformer the KVA rating is 40 KVA. Find the L.V. side line current.
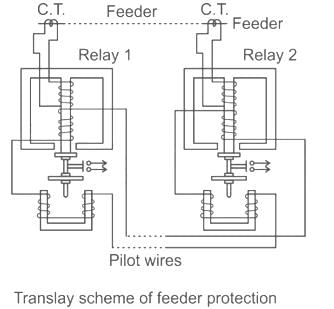
The most commonly used method for the protection of three phase feeder is
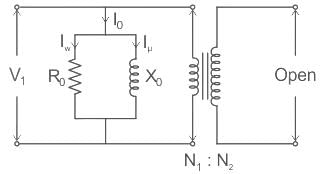
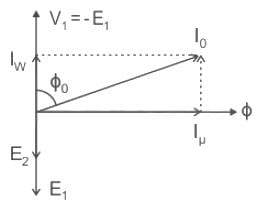
The no load current in transformer lags applied voltage by -
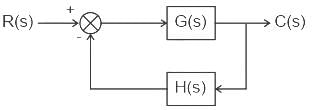
A feedback system is stable if the number of zeros (Z) of a characteristic equation in the right half of the s-plane is -
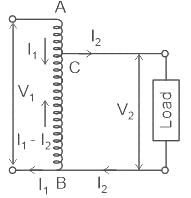
In an autotransformer of voltage ratio, V1/V2 with V1 > V2, the fraction of power transferred inductively is proportional to -
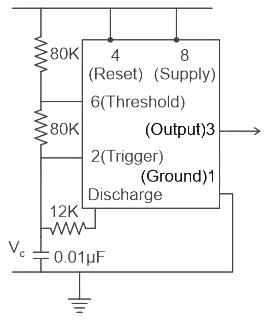
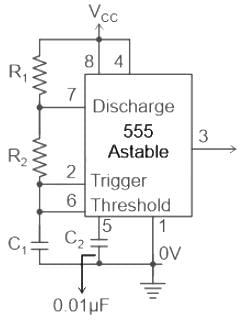
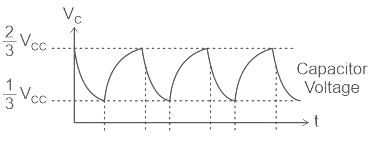
An actable multivibrator circuit using IC 555 timer is shown below. Assume that the circuit is oscillating steadily. The voltage Vc across the capacitor varies between - (Vcc = 9V)
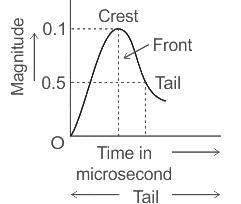
A travelling wave 400/1/50 means crest value of



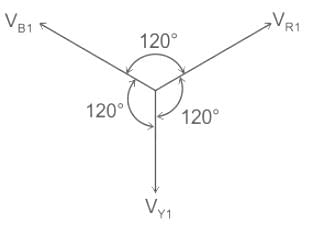
 =
=
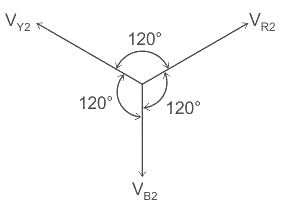
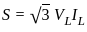
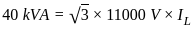
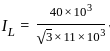
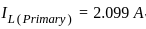
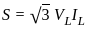
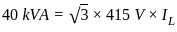
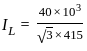
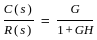
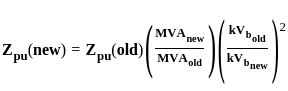
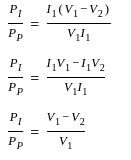
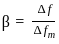
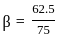
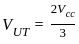
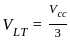
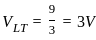
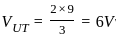
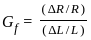
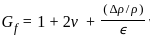
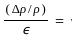
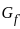 = 4.2
= 4.2