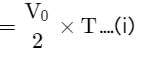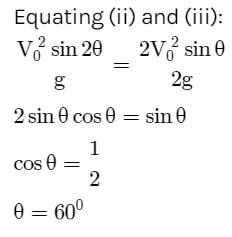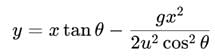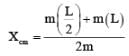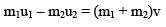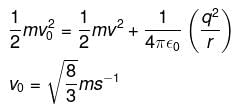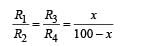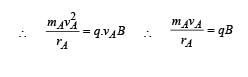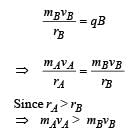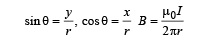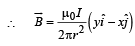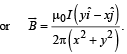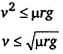DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 2 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test DSSSB PGT Mock Test Series 2025 - DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 2
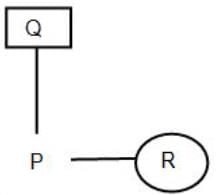
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
If 'A () B' means 'B is the mother of A'
If 'A of B' means 'B is the father of A'
If 'A ÷ B' means 'B is the sister of A'
If 'A × B' means 'B is the brother of A'
If 'A + B' means 'B is the daughter of A'
If 'A - B' means 'B is the son of A'
Q. If 'P of Q + R' is given, then which of the following is true?
The coordinates of a moving particle at any time t are given by 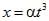 and
and 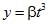 . The speed of the particle at time t is given by:
. The speed of the particle at time t is given by:
[AIEEE 2003]
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed v0 at an angle of projection θ. From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed v0 / 2 to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection?
[AIEEE 2004]
A uniform force of (3 i + j) N acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. Hence the particle is displaced from position (2 i + k) m to position ( 4 i + 3 j - k) m. The work done by the force on the particle is,
Three forces start acting simultaneously on a particle moving with velocity . These forces are represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle ABC (as shown). The particle will now move with velocity
[AIEEE 2003]
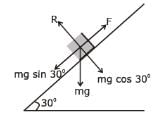
A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0.8. If the frictional force on the block is 10 N, the mass of the block (in kg) is (g = 10 m/s2
[AIEEE 2004]
After the body starts moving, the friction involved with motion is
In an elastic collision in one dimension if a body A collides against the body B of equal mass at rest, then the body A will
In the given figure, what is the work done by the spring force?
Two identical thin uniform rods of length L each are joined to form T shape as shown in the figure. The distance of centre of mass from D is
A body of mass m moving at a constant velocity v hits another body of the same mass moving with a velocity v/2 but in the opposite direction and sticks to it. The common velocity after collision is
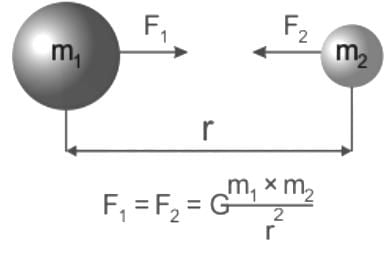
Newton's law of gravitation is called universal law because:
As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximate circular orbit. For the motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would
The angle of contact for the liquid which wets the walls of the vessel is
The potential energy between two atoms in a diatomic molecule varies with x as where a and b are positive constants. Find the equivalent spring constant for
the oscillation of one atom if the other atom is kept
The distance travelled by a particle executing SHM in 10 s, if the time period is 3 s, is
(It is given that the body starts from A√3/3 from equilibrium position, moves is positive direction at t = 0)
The phenomenon of interference is based on the principle of _
What is the number of electric field lines coming out from a 1C charge?
According to the standard convention, the electric potential at a point infinitely far from a charge is taken to be:
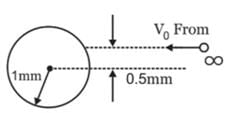
A particle of mass 1 Kg and charge 1/3 μC is projected towards a non conducting fixed spherical shell having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The minimum intial velocity V0 of projection of particle required if the particle just grazes the shell is
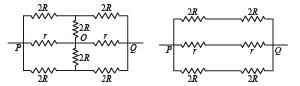
The effective resistance between points P and Q of the electrical circuit shown in the figure is

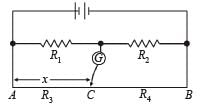
In the shown arrangement of the experiment of the meter bridge if AC corresponding to null deflection of galvanometer is x, what would be its value if the radius of the wire AB is doubled?

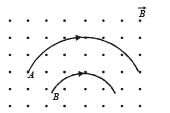
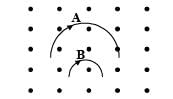
Two particles A and B of masses mA and mB respectively and having the same charge are moving in a plane. A uniform magnetic field exists perpendicular to this plane. The speeds of the particles are vA and vB respectively and the trajectories are as shown in the figure. Then
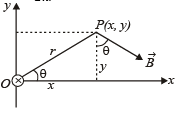
A long straight wire along the Z-axis carries a current I in the negative Z-direction. The magnetic vector field at a point having coordinates (x, y) in the Z = 0 plane is
Which one of the following, when suspended freely, slowly sets itself parallel to the direction of the magnetic field?
In the free oscillations of an LC circuit, the sum of energies stored in the capacitor and the inductor.
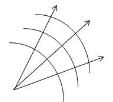
Shape of the wave front of light diverging from a point source is
A car of mass 800 kg moves on a circular track of radius 40 m. If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, then the maximum velocity with which the car can move is