Economics: CUET Mock Test - 5 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 5
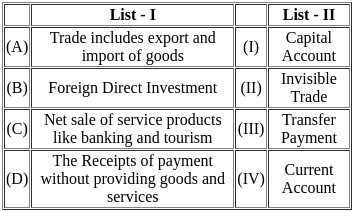
Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

When Cash Reserve Ratio is 20% then with the deposit of Rs. 1000, Money creation will be Rs. 5000, Money multiplier is:
What role does the exchange rate play in an open economy according to the passage?
What limitation is mentioned regarding the labor market in an open economy?
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a factor affecting the exchange rate?
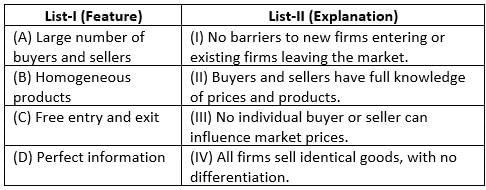
Match List-I with List-II :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
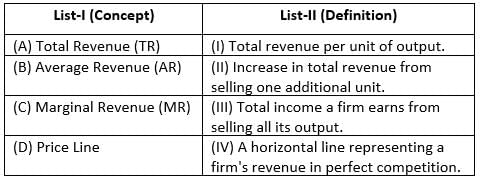
Match List-I with List-II :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List-I with List-II :
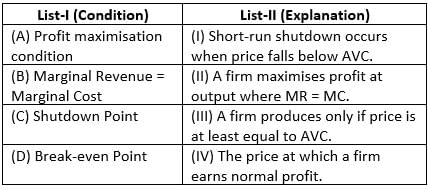
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List-I with List-II :
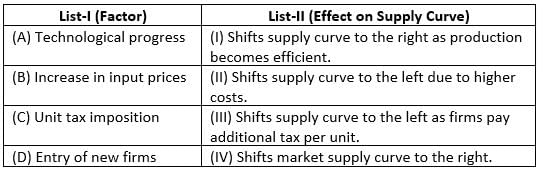
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Consider the following statements:
(A) Every individual in society has unlimited resources compared to their needs.
(B) The concept of scarcity forces individuals to make choices about the goods and services they want.
(C) All individuals face scarcity in terms of resources.
(D) Scarcity does not affect the allocation of resources in an economy.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
What do you mean by credit creation by commercial banks?
What is an example of macroeconomic analysis simplification?
Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?
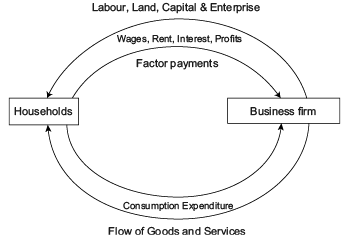
Money Flows from __________ to ____________ as factor payments.
In the circular flow of income described in the passage, what do households provide to firms in the upper loop?
Circular flow of income refers to the flow of activities of production, income generation and expenditure involving different ___________ of the economy.
Which of the following is not the significance of Circular Flow of Income?
Which of these is a Quantitative Method of Credit control?
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will
Why might macroeconomics depart from simplification to examine distinct sectors?
|
39 docs|145 tests
|