History: CUET Mock Test - 6 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - History: CUET Mock Test - 6
Which of the following type of tax was collected during the Delhi Sultanate?
Which of the following was a notable feature of the Harappan cities?
Which one of the following is the correct chronological order of the Afghan rulers to the throne of Delhi?
Mark the year in which the first revenue settlement in Bombay Deccan took place?
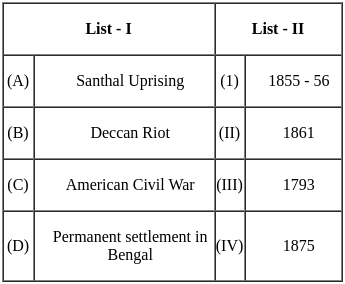
Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What did Bernier criticize about the Mughal system of landownership?
What was Bernier’s observation about Indian artisans?
What did Bernier note about social hierarchy in India?
How did Bernier’s writings influence European views on India?
Which of the following Bhakti saints is known for rejecting caste distinctions?
How did Bhakti saints make religious teachings more accessible?
Which of the following deities were commonly worshipped in the Bhakti tradition?
How did the Bhakti movement contribute to social reform?
Which of the following statements about Harappan economy are correct?
(A) Harappan economy relied solely on agriculture.
(B) Artisans and craftsmen formed an important part of the economy.
(C) Harappans imported precious stones from regions like Gujarat.
(D) There was no evidence of standardized weights and measures.
(E) Trade networks extended to regions like Mesopotamia.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The Dharmashastras and Dharmasutras laid down rules for caste-based duties.
(B) The Kshatriyas were expected to perform rituals and sacrifices.
(C) The Manusmriti was an important legal text composed in Sanskrit.
(D) The caste system was rigid and unchangeable in ancient India.
(E) Endogamy was a common practice in maintaining caste purity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements about marriage rules in ancient India are correct?
(A) The Dharmashastras allowed inter-caste marriages without restrictions.
(B) Gotra was an important factor in marriage selection among Brahmanas.
(C) Polygamy was practiced, especially among the ruling elite.
(D) Women had complete freedom in choosing their marriage partners.
(E) The concept of Kanyadan emphasized the father’s role in giving his daughter in marriage.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements about the Mahabharata are correct?
(A) The Mahabharata was composed in Sanskrit over several centuries.
(B) It describes the conflicts between two groups of cousins, the Pandavas and Kauravas.
(C) The epic does not provide any information about caste and kinship practices.
(D) Women in the Mahabharata, such as Draupadi, had limited agency in decision-making.
(E) The final version of the Mahabharata was compiled by the Gupta period.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements about social hierarchy in ancient India are correct?
(A) The caste system was based entirely on birth.
(B) The concept of purity and pollution played a role in maintaining caste divisions.
(C) Kings were typically chosen from the Kshatriya varna
(D) The Vaishyas were responsible for trade and agriculture.
(E) The Shudras were completely excluded from all economic activities.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
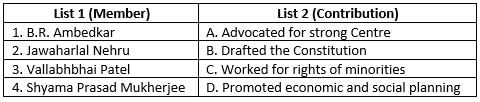
Match the following members of the Constituent Assembly with their contributions
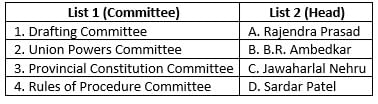
Match the committees with their heads in the Constituent Assembly
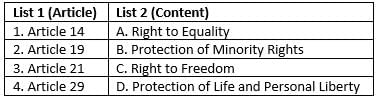
Match the articles of the Indian Constitution with their contents
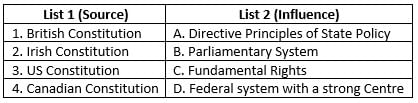
Match the source with their influence on the Indian Constitution
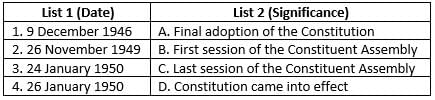
Match the significant dates with their importance in framing the Constitution
|
39 docs|145 tests
|