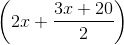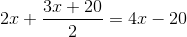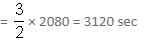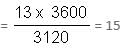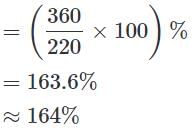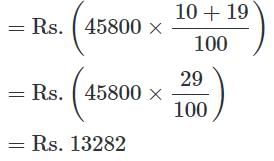SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 4 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test Series 2025 - SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 4
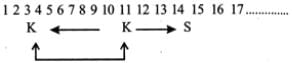
40 persons are sitting in a row. How many persons are sitting between 31st person from left and 25th person from right?
In a row of 40 girls, when Komal was shifted to her left by 4 places her number from the left end of the row become 10. What was the number of Swati from the right end of the row, if Swati was three places to the right of Komal’s original position?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions two statements are given. Which are followed by four conclusions (1), (2), (3) and (4). Choose the conclusions which logically follow from the given statements.
Question -
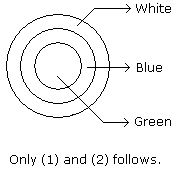
Statements: All green are blue. All blue are white.
Conclusions:
- Some blue are green.
- Some white are green.
- Some green are not white.
- All white are blue.
Pointing towards a girl, Abhisek says, "This girl is the daughter of only a child of my father." What is the relation of Abhisek's wife to that girl?
Directions: This question given below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the following arguments is a ‘strong’ argument and which is a ‘weak’ argument.
Statement:
Should the Government introduce Gross Happiness Index on the lines of that introduced in Bhutan?
Arguments:
I. Yes. It will greatly help India in becoming a prosperous nation.
II. No. Bhutan has not gone anywhere even after introducing GHI over four decades ago.
Directions: This question given below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the following arguments is a ‘strong’ argument and which is a ‘weak’ argument.
Statement:
Should there be restrictions on free media?
Arguments:
I. Yes. Sometimes restrictions are needed to control free media.
II. No. It’s the fourth pillar of our democracy.
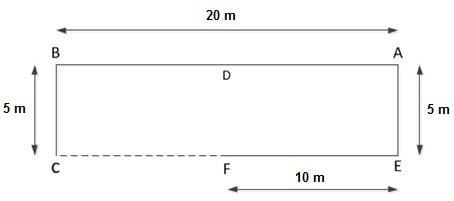
Point A is 20 m to the east of point B. Point B is 5 m to the north of point C. Point D is 10 m to the east of point B. Point E is 5 m to the south of point A. Point F is 10 m to the west of point E.
Which of the following points lie in a straight line?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given question.
In a certain code:
'chest teeth gap limb' is coded as Q&2 C%3 U#4 I?4
'borrow some corn people' is coded as F@3 O#3 X!5 F*5
'eat bank scheme tomato' is coded as P?5 L!3 U^2 F@5
'gossible come person gones' is coded as F#3 T&4 F&7 O*5
What will be the code for 'shaker prospectus trick'?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
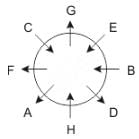
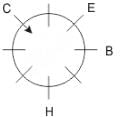
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
Q. Who is immediate neighbor of F?
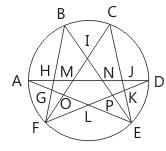
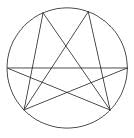
Find the number of triangles in the given figure.
Read the following statements carefully to answer the questions:
I. X is older than L.
II. M and N are of equal age.
III. Z is the youngest.
IV. Y is younger than N.
V. Y is older than X.
Q. Which statement(s) indicate(s) than N is older than Z?
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. Which of the following elements is third to the left of fifth element from right end in step 3?
Directions for questions: Based on the series of numbers given in the question, find the next / missing number in the series.
6, 15, 33, 69, ?, 285
A sum of money is divided among A, B and C in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. C gives Rs. 20 to B and B gives half of what he has now to A. Now, A and C have equal amount. What is the sum of money divided among the three?
A tap drips at an average rate of 2 drops in 3 seconds. It takes 2080 drops of water to completely fill a hemispherical vessel of radius 8.3 cm. How many times can the vessel be filled in this manner in 13 hours?
Directions: Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
Total Number of Employees in different Departments of an Organization and Percentage of Females and Males.
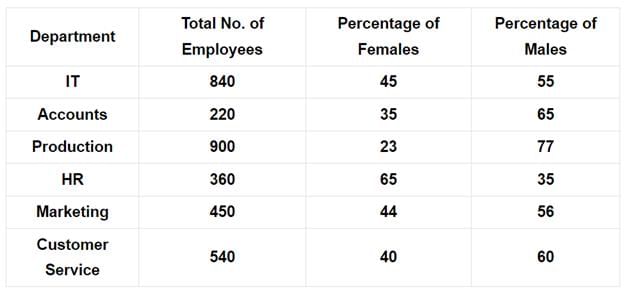
Q. The total number of employees in the HR department forms approximately what per cent of the total number of employees in the Accounts department?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Three online hotel booking website A,B and C listed some hotels on their websites. The all listed 3 star, 4 star and 5 star hotels. One hotel can be listed on exactly one website.
Further it is known that
- Total number of hotels listed on all three website together is 720.
- Total number of 4 star hotels is twice the total number of 3 star hotels on all the three websites taken together. Further, total number of 5 star hotels is thrice the total number of 4 star hotels on all three sites together.
- Out of 200 hotels listed on Websites A, 30% are 3 star hotels.
- Ratio of 5 star hotels on sites A,B and C are 1 : 1 : 2.
- Number of 5 star hotels on B website is 20% more than number of 4 star hotels on the same website.
- Number of 3 star hotels on website B and C are same.
Q. What is the total number of Hotels listed on Website C ?
Directions: Study the following pie-chart carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Degreewise Break-up of Expenditure of a Family in a month
Total Amount Spent In a Month = Rs. 45800.
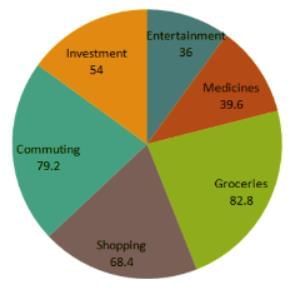
Q. What is the total amount spent by the family on Entertainment and Shopping together?
The manager of the plastic fork factory tried to convince the unruly factory workers they should join forces to optimize production on the belt rather than attemptingto be contrary.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
The government’s move to infuse upfront an additional capital of Rs 70,000 crore into public sector banks (PSBs) is welcome. The promised removal of the Damocles’ sword of punitive investigation of any banking decision hanging over the heads of bankers today will help banks lend the additional liquidity leveraging this capital would enable.
The moves to support non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) — such as enhancing additional liquidity support to housing finance companies to Rs 30,000 crore by National Housing Bank from Rs 20,000 crore and co-origination of loans by PSBs jointly with NBFCs that are reeling under a liquidity crunch — will provide a booster for fresh loans to the MSME sector.
A transparent one-time settlement policy being provided by banks to benefit MSMEs and retail borrowers in settling their overdues is pragmatic. But banks also must acquire the expertise to assess MSME loan viability and invest in data mining.
Making banks link their lending rates to the repo rates will help better transmission of monetary policy. But for this to work without impairing bank financial health, multiple structural rigidities in the system must be removed. Public sector pre-emption of the bulk of household financial savings must end, for the bond market to really take off to provide longer-term funds for infrastructure projects.
Steps such as further development of the credit default swap markets, facilitating increased trading for price discovery, and establishing an organisation to provide credit enhancement for infrastructure and housing projects make eminent sense, as does onshoring the offshore rupee derivative markets.
A coherent policy of managerial reform, including of remuneration, at public sector banks must accompany the measures announced, for them to take effect.
Q. What is the tone of the passage?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
The government’s move to infuse upfront an additional capital of Rs 70,000 crore into public sector banks (PSBs) is welcome. The promised removal of the Damocles’ sword of punitive investigation of any banking decision hanging over the heads of bankers today will help banks lend the additional liquidity leveraging this capital would enable.
The moves to support non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) — such as enhancing additional liquidity support to housing finance companies to Rs 30,000 crore by National Housing Bank from Rs 20,000 crore and co-origination of loans by PSBs jointly with NBFCs that are reeling under a liquidity crunch — will provide a booster for fresh loans to the MSME sector.
A transparent one-time settlement policy being provided by banks to benefit MSMEs and retail borrowers in settling their overdues is pragmatic. But banks also must acquire the expertise to assess MSME loan viability and invest in data mining.
Making banks link their lending rates to the repo rates will help better transmission of monetary policy. But for this to work without impairing bank financial health, multiple structural rigidities in the system must be removed. Public sector pre-emption of the bulk of household financial savings must end, for the bond market to really take off to provide longer-term funds for infrastructure projects.
Steps such as further development of the credit default swap markets, facilitating increased trading for price discovery, and establishing an organisation to provide credit enhancement for infrastructure and housing projects make eminent sense, as does onshoring the offshore rupee derivative markets.
A coherent policy of managerial reform, including of remuneration, at public sector banks must accompany the measures announced, for them to take effect.
Q. With which of the following statements would the author most likely agree?
I. One-time settlement policy that will benefit MSMEs is impractical for banks and is unwise.
II. Banks have not yet developed the required proficiency in judging the sustainability of MSME loans.
III. Banks have made huge investments in data mining.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
The government’s move to infuse upfront an additional capital of Rs 70,000 crore into public sector banks (PSBs) is welcome. The promised removal of the Damocles’ sword of punitive investigation of any banking decision hanging over the heads of bankers today will help banks lend the additional liquidity leveraging this capital would enable.
The moves to support non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) — such as enhancing additional liquidity support to housing finance companies to Rs 30,000 crore by National Housing Bank from Rs 20,000 crore and co-origination of loans by PSBs jointly with NBFCs that are reeling under a liquidity crunch — will provide a booster for fresh loans to the MSME sector.
A transparent one-time settlement policy being provided by banks to benefit MSMEs and retail borrowers in settling their overdues is pragmatic. But banks also must acquire the expertise to assess MSME loan viability and invest in data mining.
Making banks link their lending rates to the repo rates will help better transmission of monetary policy. But for this to work without impairing bank financial health, multiple structural rigidities in the system must be removed. Public sector pre-emption of the bulk of household financial savings must end, for the bond market to really take off to provide longer-term funds for infrastructure projects.
Steps such as further development of the credit default swap markets, facilitating increased trading for price discovery, and establishing an organisation to provide credit enhancement for infrastructure and housing projects make eminent sense, as does onshoring the offshore rupee derivative markets.
A coherent policy of managerial reform, including of remuneration, at public sector banks must accompany the measures announced, for them to take effect.
Q. According to the passage, what will provide a booster for fresh loans to the MSME sector?
I. Loan waivers and collateral free loans.
II. Increasing additional liquidity support of Rs 20,000 cr by 50%.
III. Joint contribution of credit by PSBs and NBFCs.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
The government’s move to infuse upfront an additional capital of Rs 70,000 crore into public sector banks (PSBs) is welcome. The promised removal of the Damocles’ sword of punitive investigation of any banking decision hanging over the heads of bankers today will help banks lend the additional liquidity leveraging this capital would enable.
The moves to support non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) — such as enhancing additional liquidity support to housing finance companies to Rs 30,000 crore by National Housing Bank from Rs 20,000 crore and co-origination of loans by PSBs jointly with NBFCs that are reeling under a liquidity crunch — will provide a booster for fresh loans to the MSME sector.
A transparent one-time settlement policy being provided by banks to benefit MSMEs and retail borrowers in settling their overdues is pragmatic. But banks also must acquire the expertise to assess MSME loan viability and invest in data mining.
Making banks link their lending rates to the repo rates will help better transmission of monetary policy. But for this to work without impairing bank financial health, multiple structural rigidities in the system must be removed. Public sector pre-emption of the bulk of household financial savings must end, for the bond market to really take off to provide longer-term funds for infrastructure projects.
Steps such as further development of the credit default swap markets, facilitating increased trading for price discovery, and establishing an organisation to provide credit enhancement for infrastructure and housing projects make eminent sense, as does onshoring the offshore rupee derivative markets.
A coherent policy of managerial reform, including of remuneration, at public sector banks must accompany the measures announced, for them to take effect.
Q. What is the meaning of the idiom “Damocles’ sword”, as used in the passage?
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1 : The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2 : The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3 : While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. What could be a/some result/s of the function of funding of public institutions being left to the Ministry of Human Resource Development instead of HECI?
I. The government may use its discretion to reward institutions according to its ideological predilections.
II. The Institutions may be forced to comply with even some dubious rules setup by the government.
III. The government can be made accountable for attaining excellence in education.
Directions: Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which can be substituted for the given words/sentence.
A person who pretends to have more knowledge or skill than he really has:
When a bank fails to pay its depositors, the Deposit Insurance Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) provides deposit insurance. What is the maximum amount insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (DICGC)?
When was the Corporate Debt Restructuring implemented by the RBI in India for rearrangement of a distressed company's outstanding commitments?
When was the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India set up?
Which bank has introduced the first floating ATM in India?