UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 1 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC Mock Test Series 2026 - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 1
The Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993 provides for the creation of:
- National Human Rights Commission
- State Human Rights Commission
- Joint State Human Rights Commission
- Human Rights Courts
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Which Article of the Constitution of Indian Republic relates to the Protection of ‘Life and Personal Liberty’ .
Which Indian state is surrounded by Bangladesh to the north, south and west?
Which of the following is/are correct about Right to Property?
- It was made a Constitutional right under Article 300A by the 44th Constitutional Amendment, 1978.
- Right to Property is a Natural Right.
Consider the following statement (s) related to Sustainability.
I. It refers to a process or state that can be maintained indefinitely.
II. Natural resources must use in ways that do not create ecological debts by over-exploiting the carrying and productive capacity of the earth.
III. A minimum necessary condition for sustainability is the maintenance of the total natural capital stock at or above the current level.
Consider the following statements.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) have joined hands to launch a joint lunar polar exploration (LUPEX) mission.
- The mission aims to send a lander and rover to the Moon's north pole around 2024.
- While ISRO will provide the under-development H3 launch vehicle and the rover JAXA would be responsible for the lander.
Which of the above-given statements are correct?
Which of the following statements about the Preamble is NOT correct?
Which country has taken a digital leap by introducing fully digital Schengen visas for the 2024 Olympics?
Which one of the following is not a feature of Indian federalism?
Who among the following opposed Mahatma Gandhi’s association with the Khilafat movement?
The process of using microbes to treat areas of land or sea that have been contaminated by pesticides, oil or solvents is known as:
With reference to the Administration of Sultan Sikandar Lodi, consider the following statements:
- Sultan Sikandar Lodi is praised for introducing sound administrative machinery.
- He instituted auditing to check the accounts of muqtas and walis (governors).
- In order to keep himself informed about the state of the Empire, the Sultan reorganised the intelligence system.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
Peasants’ movement in a few pockets of the United Provinces was characterized by Nai-Dhobi Bandh. In this context, consider the following statements regarding the Nai-Dhobi Bandh.
- It was a form of social boycott witnessed during the Kisan Sabha movement in the United Provinces.
- It was led by Gauri Shankar Mishra.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Zonal Councils:
- They are statutory bodies established by an act of parliament (State reorganization Act of 1956)
- Prime Minister is the common chairman of all the zonal councils.
- For the first time Union Home Minister will be chairing the Zonal Council meet.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
Which one of the following is newer mountain range?
Which of the following is the largest National Park in India?
Choose the correct answer from the codes given below.
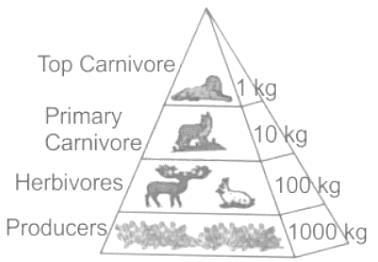
Assertion (A) : The pyramid of grassland ecosystem is upright.
Reason (R) : The producers are maximum in number and tertiary consumers are least in number.
Identify the type of forests based on the features described below.
A. They are commonly found along the eastern margin of the continents, such as South China.
B. Oak, pine, eucalyptus are examples of the trees found here.
Choose the correct option.
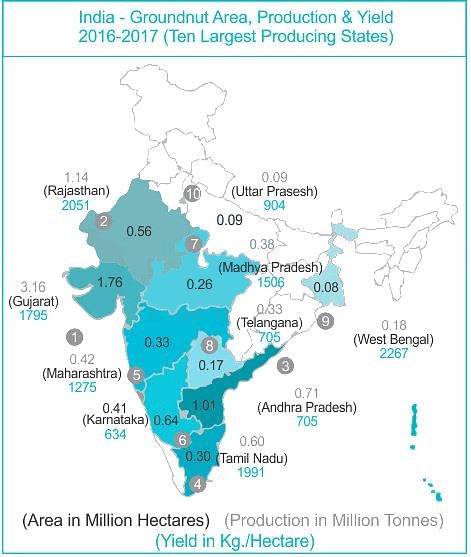
Which of the following are the varieties of groundnut?
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
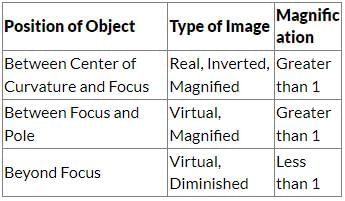
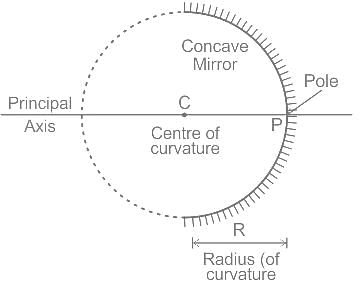
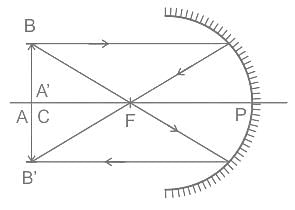
Where should an object be placed in front of a concave mirror such that the image of the object is of the same size as the object?
Which of the following are obtained from Petroleum ?
(A) CNG
(B) LPG
(C) Diesel
(D) Coal Gas
What is the primary aim of the Uttar Pradesh government's initiative to enforce penalties on parents permitting minors to drive?
What is the expected revenue generation of the global semiconductor ecosystem for the fiscal year 2022?
How many airports will be newly inaugurated in Uttar Pradesh according to recent announcements?
What is the target year for Uttar Pradesh to achieve a $1 trillion economy?
|
2 docs|37 tests
|