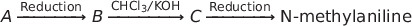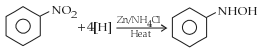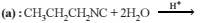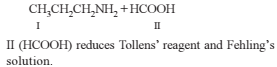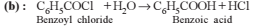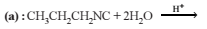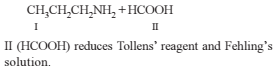Amines - 1 - JEE MCQ
27 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Amines - 1
Arrange the following in order of increasing basicity: aniline, p – nitroaniline, p – toluidine,and p – methoxyaniline
Which of the following represents the correct order of the acidity in the given compounds?
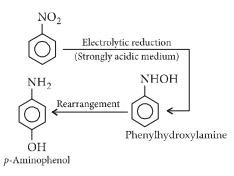
The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces
Which one of the following order is wrong, with respect to the property indicated?
A racemic acid CH3CHClCOOH is allowed to react with (S)-2-methylbutan-1-ol to form ester
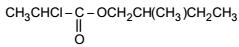
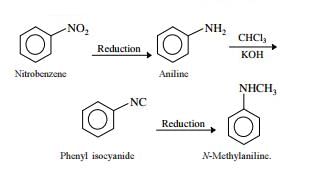
Nitrogen Compoinds
and the reaction mixture is carefully distilled. The correct statement about the mixture distillate is:
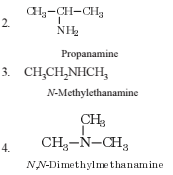
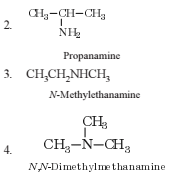
The number of structural isomers possible from the molecular formula C3H9N is
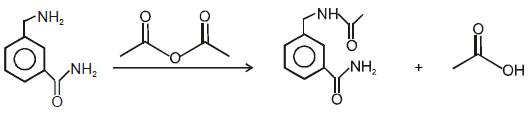
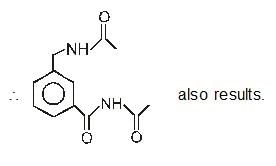
On hydrolysis of a “compound”, two compounds are obtained. One of which on treatment with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid gives a product which does not respond to the iodoform test. The second one reduces Tollens' reagent and Fehling’s solution. The “compound” is
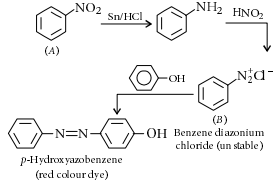
A given nitrogen-containing aromatic compound ‘A’ reacts with Sn/HCl, followed by HNO₂ to give an unstable compound ‘B’. ‘B’, on treatment with phenol, forms a beautiful coloured compound ‘C’ with the molecular formula C₁₂H₁₀N₂O. The structure of compound ‘A’ is
The number of structural ismers possible from the molecular formula C3H9N is
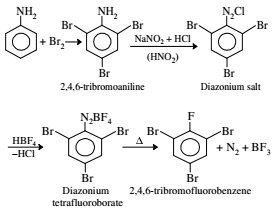
Aniline is reacted with bromine water and the resulting product is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid. The compound so formed is converted into a tetrafluoroborate which is subsequently heated dry. The final product is
|
361 videos|821 docs|301 tests
|