UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 7 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series - UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 7
When was the Panchsheel formally enunciated?
During the non-corporation movement, which person of Haryana returned the Rai Bahadur Samman?
How many gates and towers were mentioned by Megasthenes in Mauryan capital, Pataliputra?
Consider the following statements:
1. Desai-Liaquat Pact proposed an equal number of persons to be nominated by Congress and the Muslim League in the Central Legislature.
2. The Rajagopalachari Formula was accepted by the Muslim League.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
Which of the following is not correctly matched:
Here is a list of wars which were fought in India during the medieval times :
i) Deorai
ii) Dharmat
iii) Samugarh
iv) Samel
Their chronological order is-
Consider the following pairs:
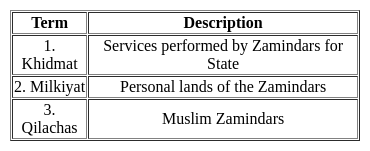
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
With reference to the foreign travelers who visited India during medieval India consider the following pairs:
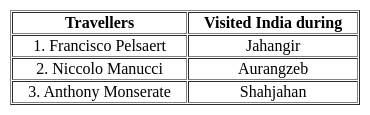
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Which pillar is referred to in the passage?
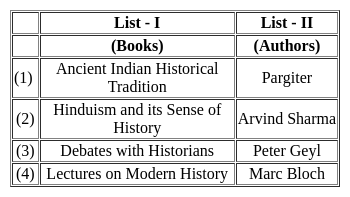
Match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:

Consider the following statements about Raja Ram Mohan Roy and select the incorrect one:
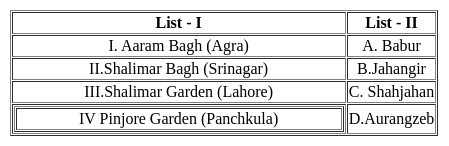
List-I denotes the Mughal Gardens and List-II denotes the rulers under whose reign the Gardens were built. Match the two lists correctly.
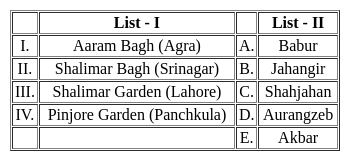
Choose the correct code:
Consider the following statements regarding the Guptas:
- Srigupta was the first Gupta king whose name got mentioned in the Allahabad Pillar inscription.
- The Devichandraguptam mentioned the murder of Ramagupta by Chandragupta II.
- The Bhittari Stone Inscription mentioned the defeat of Hunas by the Skandagupta.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Direction: The following item consists of two statements, statement I and statement II. Examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answer from the code given below.
Statement I:
Market reforms of Alauddin Khilji were focused on internal market restructuring apart from administrative and military necessities.
Statement II:
Allauddin tried to control the price of everything from caps to socks, vegetables, sweetmeats to chapatis etc.
Consider the following statements about the officers Muhtasib appointed by Aurangzeb:
1. They were appointed to see that intoxicants were not consumed in public places.
2. They were also responsible for checking weights and measures.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Who among the following Buddhist Philosophers persuaded the Indo Greek King Meander to Accept Buddhism?
Which of the following statements are correct about the rule of Lord Cornwallis?
- He brought in the separation of revenue administration and civil jurisdiction through the Cornwallis code.
- He introduced the civil services in India.
- The subsidiary alliance system was started under his rule.
Select the correct chronological order using the codes given below :
Who formed the “Indian Parliamentary Committee” along with Dadabhai Naoroji?
Consider the following statements regarding Barabar caves:
- They are the oldest example of rock-cut architecture in India.
- These caves are associated with Buddhism only.
- A famous cave at Barabar caves is Lomas Rishi cave, which is known for a horse shoe fashion decorated facade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Choose the correct pair, with reference to the Jaina Council.
- First Council:- resulted in the compilation of 14 Purvas.
- Second Council:- resulted in final compilation of 12 Angas and 12 Upangas.
Which among the following event led the British government of Lord North to undertake a legislation to meet the situation and provide some form of legal government for the Indian possessions of the East India Company, which resulted in Regulating Act of 1773?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|