NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Biology Class 11 > Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - NEET MCQ
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - NEET MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation for NEET 2025 is part of Biology Class 11 preparation. The Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation below.
Solutions of Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation questions in English are available as part of our Biology Class 11 for NEET & Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation solutions in
Hindi for Biology Class 11 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation | 15 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Biology Class 11 for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 1
Which of the following statements about gaseous exchange in plants is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 1
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 2
Why is oxygen availability not a problem in photosynthesizing cells?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 2
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 3
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 3
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 4
At which step of glycolysis is NADH + H⁺ generated?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 4
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 5
What is the total ATP gain during glycolysis from one molecule of glucose?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 5
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 6
What is the role of lactate dehydrogenase in animal cells during intense exercise?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 6
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 7
Why does fermentation yield less energy compared to aerobic respiration?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 7
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 8
Which enzymes are responsible for alcoholic fermentation in yeast?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 8
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 9
Which of the following is true about glycolysis?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 9
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 10
Why can bulky plants manage gas exchange without specialized organs?
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 10
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 11
Assertion (A): Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of all living organisms.
Reason (R): Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway that does not require oxygen.
Reason (R): Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway that does not require oxygen.
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 11
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 12
Assertion (A): Fermentation releases less than 7% of the energy stored in glucose.
Reason (R): Fermentation involves complete oxidation of glucose.
Reason (R): Fermentation involves complete oxidation of glucose.
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 12
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 13
Match the following glycolytic enzymes with their functions:Options:
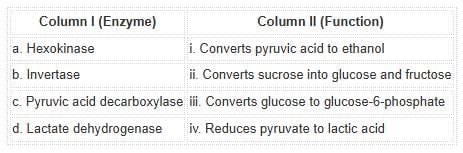
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 13
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 14
Match the pathway with its characteristics
| Column I (Pathway) | Column II (Characteristic) |
|---|---|
| a. Glycolysis | i. Occurs in cytoplasm; partial oxidation of glucose |
| b. Alcoholic fermentation | ii. Produces lactic acid under anaerobic conditions |
| c. Lactic acid fermentation | iii. Produces ethanol and CO2 in anaerobic organisms |
| d. Aerobic respiration | iv. Complete oxidation of glucose in mitochondria |
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 14
Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 15
Match the glycolytic intermediates with the correct carbon number:
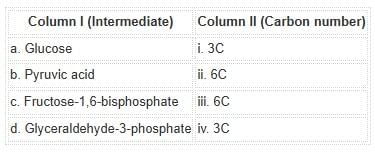
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation - Question 15
|
169 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
Information about Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Introduction to Respiration, Glycolysis & Fermentation, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice














