RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 4 - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Mock Test Series - RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 4
"Canon of Prepotence" is concerned with -
BIBFRAME 2.0 was released in the year
In_________________ any term, not only from the document itself, can be used to describe its contents.
"Current Content" is an example of -
Which of the following is the Characteristics of a Subject
In the context of the Law of Impartiality, what is the recommended approach for a book with joint authors?
What was a key development in 2013 related to the Data Documentation Initiative (DDI)?
(A) First NADDI Conference Held in Lawrence,
(B) Fifth EDDI Conference held in Paris, France.
(C) First DTD prepared at the University of Michigan Library.
(D) Bjorn Henrichsen, NSD, becomes Chair of the DDI Committee
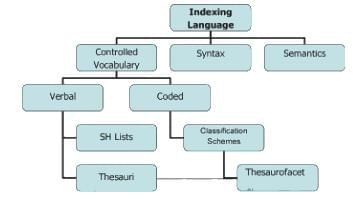
Which of the following statements accurately distinguishes between thesauri and subject headings lists?
American Library Association (ALA) has stated the six functions of Reference Service as a series of library job analysis. These are: Supervisory function, Instructional function, Informatory function, Guidance function, Bibliographic function and ________.
In AACR-2R if there is no space for transcribing any other section of the main entry except tracing, the phrase _____________ is recorded on the righthand side of the main entry card and the remaining sections are recorded on a new card/continued card.
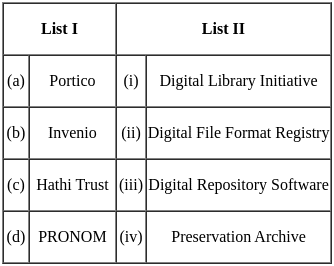
"Lots of Copies Keep Stuff Safe (LOCKSS), a Digital Preservation Project," was developed by
Assertion (A): A Thesauri are hierarchical in structure and hence referred as Taxonomies.
Reason (R): Thesaurus and taxonomy are not the same things.
Arrange the following according to their increasing year of origin -
(I) Shodhganga
(II) e - Shodhsindhu
(III) N - List
(IV) Shodh - Chakra
Arrange the following according to their year of occurrence:
(a) International Study Conference on Classification, Dorking.
(b) International Study Conference on Classification Research, Bombay.
(c) International Study Conference on Classification Research, Elsinore.
(d) Royal Society Scientific Information Conference, London.
Match the following Standard Sub Divisions (Table - 1) of DDC (19th edition) with their
notation.
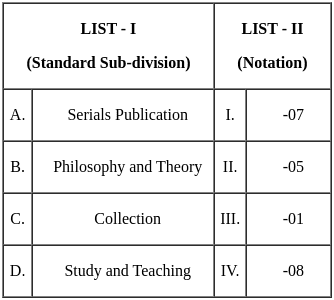
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Assertion(A): The decimal notation used in DDC refers to the principle of dividing each class into ten sub-divisions and each of these sub-divisions into another ten sub-divisions and so on
Reason(R): One of the objections to classified catalog and systematic arrangement had been the problem of knowing just where to look for a book. Dewey solved this problem 'in the shape of the relative index.
____________ in indexing languages refers to the rules or grammar governing the arrangement of terms within subject headings or classification notations.
Which of the following statements are correct regarding Project SAILS?
a) Its goal is to develop a standardized test of information literacy skills
b) Began in 2001 at Kent State University
c) Test is free of cost and can be availed by anyone across the globe