RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 3 - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Mock Test Series - RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 3
The evaluation program of an information system involves several distinct steps. Arrange the following steps in correct order.
(A) Design Evaluation Program
(B) Modify the System
(C) Execute the Program
(D) Define Scope
(E) Analyze and Interpret Results
(A) Design Evaluation Program
(B) Modify the System
(C) Execute the Program
(D) Define Scope
(E) Analyze and Interpret Results
Which data model uses tree structures to represent relationships among records?
Lancaster [1979] considers that an Information Retrieval System (IRS) comprises the following components:
(A) the document selection sub-system
(B) the indexing sub-system
(C) the vocabulary sub-system
(D) the searching sub-system
(A) the document selection sub-system
(B) the indexing sub-system
(C) the vocabulary sub-system
(D) the searching sub-system
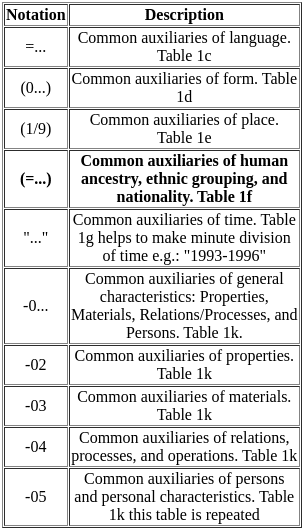
Digit of International Standard Book Number (ISBN) divided into
The Newark system was adopted by the Newark Public Library, ______, and soon became popular,
_____________ defines author as, “the person or corporate body chiefly responsible for the creation of the intellectual or artistic content of a work e.g. the writer of a book, the compiler of a bibliography, the composer of a musical work, the artist who paints a picture, the photographer who takes a photograph.
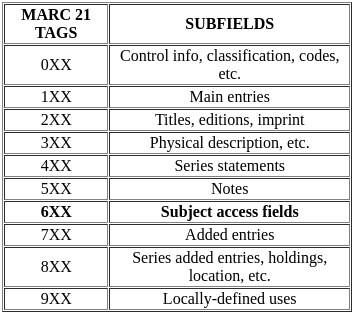
Which of the following is true about MARC
(A) developed by Henriette Avram at the Library of Congress
(B) It was used for the automation of processes to print cards or catalogs (book catalogs, microfiche catalogs, etc.).
(C) MARC 21 is a result of the harmonization of U.S. and French MARC formats.
(D) MARC 21 Tag 7xx is for Added entries.
In Town Planning we can arrange Village Planning, Town Planning, City Planning, and Metropolitan Planning. is guided by which principle
Assertion (A): The entry element in Leading Section has the potency to decide the position of an entry among the various entries in a catalogue.
Reason (R): The potency of entries, sorted letter by letter or digit by digit goes on increasing rightwards and upwards.
In the context of these two statements, which one of the following is correct?
Which of the following International standards are related to library building and planning?
(a) ISO11799 ∶ 2015
(b) ISO5678 ∶ 1993
(c) ISO/TR 11219 ∶ 2012
(d) ISO16000-7 ∶ 2007
In a Personal Computer, the Network Interface Card (NIC) is connected with the internet switch through ___________ connector.
ISO 2709 Consists of
(A) Record label
(B) Check digit
(C) Data fields
(D) Record separator
Research in Progress database developed by INFLIBNET is known as:
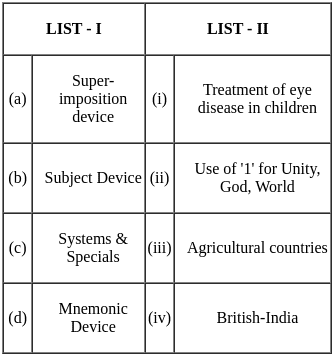
Match the canons with their respective purpose.
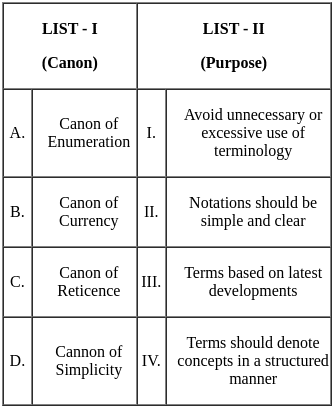
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements is true?
(A) The ESTC is a catalog that compiles short titles of publications released from 1473 to 1800.
(B) ISAN-IA (ISAN International Agency) is a nonprofit organization located in Geneva, established in 2005 by AGICOA, CISAC, and FIAPF to manage the ISAN standard.
(C) ISRC codes consistently consist of 12 characters in a specific format.
(D) The ISTC, or International Standard Text Code, serves as a distinctive identifier for text-based works. This ISO standard was formulated by TC 46/SC 9 and officially released in March 2009.
Match the following databases with their metadata service provider.
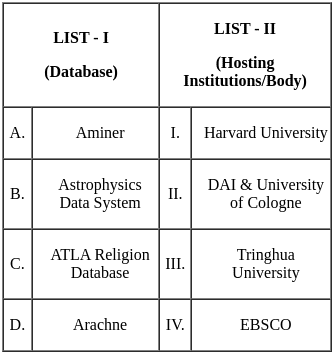
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: