RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 1 - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Mock Test Series - RSMSSB Librarian Grade-III Paper 2 Mock Test- 1
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
1. In library classification, the first division is by disciplines.
2. Basic subjects are postulated by the classification system.
3. Number of compound subjects tends to be finite.
4. Complex subjects are mostly interdisciplinary in nature.
5. While classifying a document, we do not determine its subject, but the specific subject for co-extensive classification.
1. In library classification, the first division is by disciplines.
2. Basic subjects are postulated by the classification system.
3. Number of compound subjects tends to be finite.
4. Complex subjects are mostly interdisciplinary in nature.
5. While classifying a document, we do not determine its subject, but the specific subject for co-extensive classification.
Which of the following are the basic components involved in the IR process
(A) Selection
(B) Indexing
(C) Query Formulation
(D) 3 Matching the query
(A) Selection
(B) Indexing
(C) Query Formulation
(D) 3 Matching the query
Who suggested 'Seven Lamps of Conduct' as a must for Library professionals?
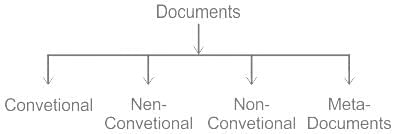
Which of the following is a neo conventional source of information?
Who defines knowledge as an organized set of statements of fact or ideas, presenting reasoned judgments or experimental results transmitted to others through communication mediums in systematic form.
Which of the following are the Characteristics of segments
(A) A segment is born simultaneously with the birth of a subject.
(B) A segment does not possess a constant shape or size. Both may undergo change with the passage of time.
(C) There are four categories of segments such as objects, action, space and time.
(D) A segment is capable of splitting into only two subdivisions
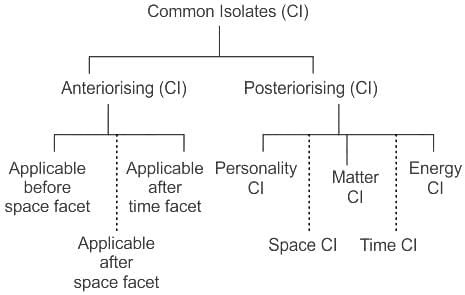
In Colon Classification 6th edition, the letter 'd' is an Anteriorising Common Isolate represents which of the following?
A MARC record involves which of the following three elements?
1. The record structure
2. The data designation
3. The content designation
4. The data content of the record
Which of the following is not true about the directory in the record structure of MARC 21 ?
What is an idea, which is a component of a compound subject, known as ?
The relationship between two or more isolates within one and the same schedule of facet isolates is called _____ phase relation.
Which classification scheme was first library classification based on some definite and objectively expressed principles.
International Conference on Cataloguing Principles at Paris was held in _______.
PLANNER 2024 is being organized by INFLIBNET Centre in collaboration with ___________
Which of the following are special auxiliaries of UDC?
A. Zero auxiliaries
B. Hyphen auxiliaries
C. Apostrophe auxiliaries
D. Literary warrant auxiliaries
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Identify the key attributes of ephemeral literature from the following.
A. Any transitory or printed matter
B. Not intended to be retained or preserved
C. Holding high archival value
D. Shorter lasting value
E. Materials with cultural importance
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are serious issues of the Internet?
A. Obesity and depression
B. Age-inappropriate content
C. Social isolation
D. Abundant information resources
E. Global audience
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following databases according to their year of launch/inception in ascending order.
A. Hathi Trust
B. DOAJ
C. ScienceOpen
D. SSRN
E. NDLTD
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: