RPSC Senior Grade II (Social Studies) Mock Test - 1 - REET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RPSC Senior Teacher Grade II Mock Test Series 2026 - RPSC Senior Grade II (Social Studies) Mock Test - 1
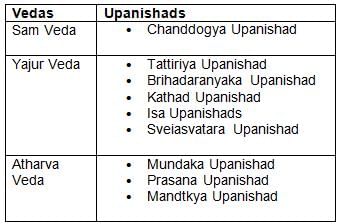
Which of the following is an Upanishad of Rigveda?
The call for ‘renunciation of (all) voluntary associations with the (British) Government’ was given during
"The ancient coastal city belongs to the Indus Valley Civilisation period which had dominant rice production. It is recognized for unique town planning than other Indus Valley Sites. It was the oldest dock and busiest trade centre.”
Skewness in a distribution is measured by which of the following methods?
Consider the following statements regarding India's trade performance in the first nine months of FY25:
1. India's total exports (merchandise and services) grew by 6% YoY, reaching USD 602.6 billion, with non-petroleum, non-gems and jewellery exports growing by 9.1%.
2. India's total imports during this period stood at USD 682.2 billion, registering a 5.2% YoY growth, driven by steady domestic demand.
Which of the following is correct?
Match List I with List II
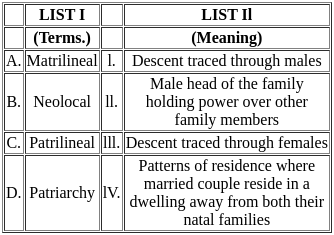
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which administrative reform in India aims to improve the efficiency and transparency of government services by providing citizens with a unique identification number?
For a field trip to be successful, it needs to be organized carefully at three stages viz;
Choose the correct order.