Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test
electromagnetic induction i.e currents can be induced in coils (Select the best)
Predict the polarity of the capacitor in the situation described by fig.

A circular coil of radius 8.0 cm and 20 turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of 50 rad s-1 in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 3×10-2 T. If the coil resistance is 10Ω, maximum emf induced in the coil,maximum value of current in the coil and average power loss due to Joule heating are
An ac generator consists of 8 turns of wire, each of area A=0.0900m2 , and the total resistance of the wire is 12.0Ω. The loop rotates in a 0.500-T magnetic field at a constant frequency of 60.0 Hz. Maximum induced emf is
Heat is supplied to the gas, but its internal energy does not increase. What is the process involved?
Find the final temperature of one mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature to t K.The gas does 9 R joules of work adiabatically. The ratio of specific heats of this gas at constant pressure and at constant volume is 4/3.
Arrange the following alcohols, hydrocarbon and ether in order of their increasing boiling points Pentan – 1 – ol, n – butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane.
The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethyl benzene by KMnO4 is
The reagents to bring about the change from but – 2 – ene to ethanal
Propanamide on treatment with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide gives:
We can obtain ethylamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide used in this reaction is:
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines. The catalyst that is preferred is:
What is the expected outcome of a cross between a homozygous dominant tall pea plant (TT) and a homozygous recessive dwarf pea plant (tt)?
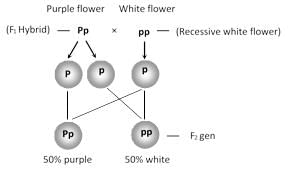
Heterozygous purple flower is crossed with recessive white flower. The progeny has the ratio:
Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is called
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called?
A DNA segment which serves as a kind of “ON-OFF switch” for transcription is a/an






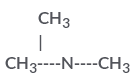 is a tertiary amine having IUPAC name as:
is a tertiary amine having IUPAC name as: