MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 4 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MPTET Varg 2 (MPESB Middle School) Mock Test Series 2026 - MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 4
Direction: Study the given line graph carefully and answer the given questions accordingly.
Given line graph shows the sales of mobile phones in a showroom on different days of a week.
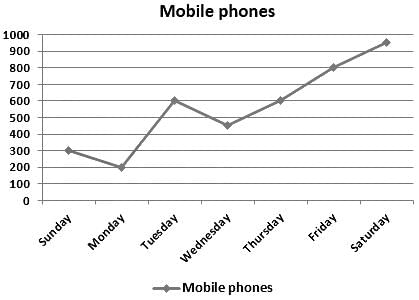
Find the ratio of the number of mobiles sold on Wednesday and Saturday together to the number of mobiles sold on Sunday, Tuesday and Friday together?

The average of 16 numbers is 10, If the average of first 7 numbers is 9 and the average of last 7 numbers is 72/7, then find the summation of 8th and 9th number.
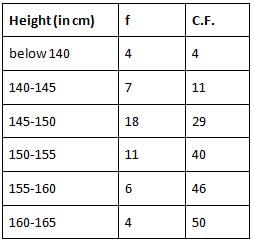
If the survey data (in cm) of height of 50 girls of class X in a school are as follows:
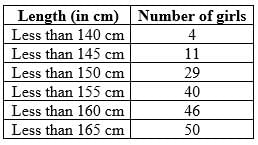
Find the median of their height
Direction: Study the given line graph carefully and answer the given questions accordingly.
Given line graph shows the sales of mobile phones in a showroom on different days of a week.
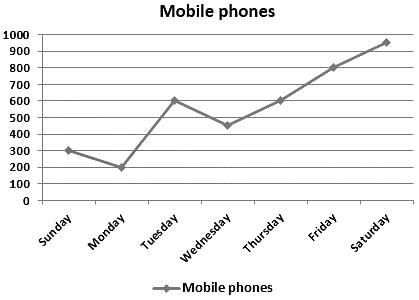
What is the total number of mobile phones sold on all the given days?
Direction: Study the given line graph carefully and answer the given questions accordingly.
Given line graph shows the sales of mobile phones in a showroom on different days of a week.
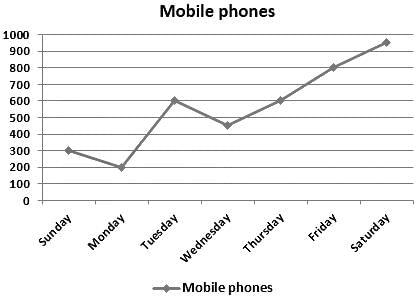
Number of mobile phones sold on Wednesday is how much percent of the number of mobile phone sold on Tuesday?
A Sum becomes ₹ 8,800 in 4 years at simple interest at the yearly interest rate of 25% p.a. What is the sum (in rupees)?
A 6 cm cube is cut into 2 cm cubes. The total surface area of the small cubes (in cm2) is
The radius of a hemisphere is 6.3 cm. What will be its volume?
What annual payment will discharge a debt of Rs. 8480 in 8 yrs at 8% per annum?
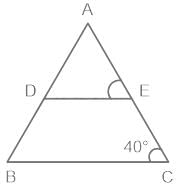
In ΔABC, DE || BC in such a way that A-D-B and A-E-C are equal. If ∠ACB = 40°, then ∠DAE + ∠ADE = ____.
An old man does 1000 J of work in 50 s and a young boy does 2000 J of work in 80 s. The ratio of the power delivered by the old man to that by the young boy is
Which of the following objectives is most suitable for teaching grade 3 children the concept of 3-D and 2-D Shapes?
Neeraja studies from 7:00 PM to 8:15 PM then the time allotted for her studies is (in minutes)
|
1 docs|15 tests
|
|
1 docs|15 tests
|



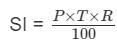
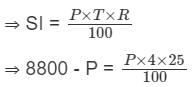
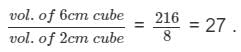
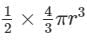
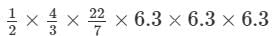
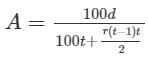
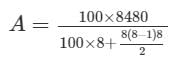
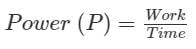
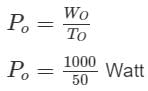
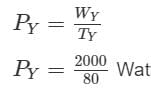
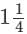 hours
hours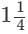 × 60 = 5/4 × 60 = 75 min
× 60 = 5/4 × 60 = 75 min










