Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Geography) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Kerala SET Mock Test Series 2025 - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Geography)
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Assertion (A): The hilly topography of Jammu and Kashmir is most favorable for development of ground water resources.
Reason (R) : Groundwater level is falling rapidly all over the country.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Which of the following statements about inversion of temperature is/are correct?
1. Temperature increases with increasing altitude.
2. A long winter night with clear skies is an ideal situation.
3. It is a short term phenomenon and is common all over the globe except at the poles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
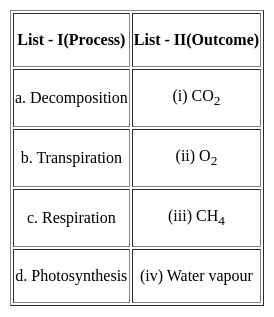
Match the List - I with List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below:
Assertion(A)- Exogenous processes are responsible for gradation.
Reason(R)- Weathering and erosion is often described as the essential phase in the denudation process of landscapes.
Choose the correct option:
After which period the political geography came into limelight?
Consider the following statements
- Active remote sensing uses the sun as a source of electromagnetic energy.
- Passive remote sensing is significantly affected by adverse weather conditions.
- Active remote sensing can collect data at day and night hence having more working timeframe.
- Active remote sensing requires less amount of energy to generate adequate electromagnetic radiation for illumination.
Choose the incorrect statements.
The use of microorganism metabolism to remove pollutants such as oil spills in the water bodies is known as :
Consider the following statements-
1. These winds blow from the subtropical high-pressure belts towards the sub-polar low-pressure belts.
2. They are stronger in the southern hemisphere.
3. These winds are best developed between 40° and 65°S latitudes.
Statements given-above are about which planetary wind?
Which among the following is / are common features of the drainage pattern of Ganges river system?
- Parallel Courses of rivers
- Tributaries meeting their master streams at acute angles
- Most rivers are of perennial nature
- Lower reaches of rivers with steep gradient suitable for hydropower generation
Choose the correct option from the codes given below:
Geographers would most likely use the term shatter belt—an area of recurrent political division and fragmentation—to describe which of the following regions of Europe?