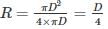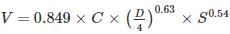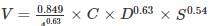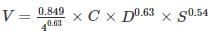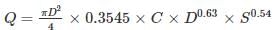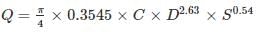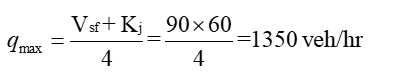GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 6 (Architecture) - GATE Architecture and Planning MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Architecture and Planning 2026 Mock Test Series - GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 6 (Architecture)
If in a particular language, DESIM is represented as CDRHL, how is the word TIGER encoded?
Complete the sentence: In an effort to discreetly communicate his message to the team, the coach’s remarks pertained only _____ to a prior match.
In spite of a series of underwhelming performances, the likelihood of K. L. Rahul being chosen for the team is _______.
The distance from Delhi to Agra measures 233 km. A vehicle P departed from Delhi towards Agra, while another vehicle Q commenced its journey from Agra to Delhi on the same road one hour after vehicle P. The two vehicles met each other 75 minutes after vehicle Q began its trip. Both vehicles maintained a consistent speed throughout their journeys. The speed of vehicle P was 10 km/hr greater than that of vehicle Q.
What distance had vehicle Q covered when the two vehicles met?
The profit distributions of two firms, P and Q, are illustrated in the figure. Assuming both companies have invested a consistent and equal amount each year, what is the ratio of the total revenue generated by company P to that of company Q from 2013 to 2018?

The echo of sound is more noticeable when the surface is
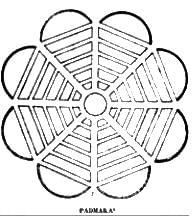
The Vedic city layout that resembles the petals of a lotus spreading outward from a central point is known as
According to NBC 2016, the required minimum width for driveways and the necessary turning radius for the movement of fire tenders are:
The polar polyhedron corresponding to a cube is:
The height measurement of a livable room is taken from:
The component of work that is excluded from the plinth area estimate is
Which of the following factors is/are linked to the occurrence of gentrification in a community?
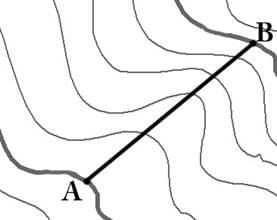
On the contour map, the distance between points 'A' and 'B' is 600 m. Given that the slope of the line is 1 in 10, what is the contour interval (in m)?
Based on the maximum gradient of ramp allowed according to the standards set in the Handbook on Barrier Free and Accessibility, CPWD, 2014; the height achieved by a ramp with a horizontal length (run) of 6 meters, expressed in cm, will be ________
Nations can meet their Kyoto obligations by
Pair the items in Group I with their corresponding purpose/function listed in Group II.

Pair the elements in Group-I with their relevant counterparts in Group-II.
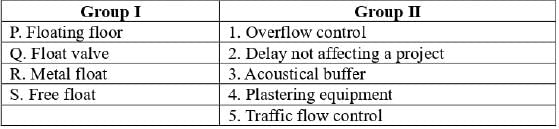
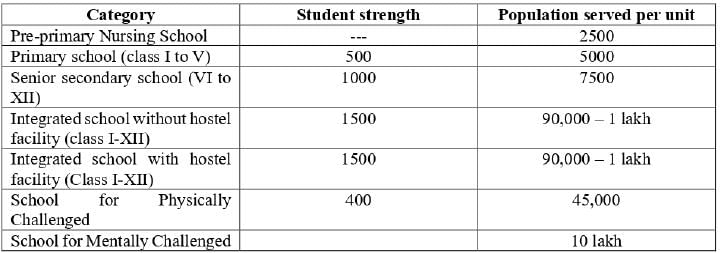
According to the URDPFI Guidelines 2015, align the types of educational facilities in Group-I with their respective minimum population requirements to be served per facility in Group-II.
Which of the following locations were included in the RAMSAR list in 2022?
Consider a circular cross-section with an internal diameter of ‘D’ (in m) positioned at a slope of ‘S’ – the following Hazen-Williams Formula (applicable when the specified cross-section involves piped flow) should be applied:
V = X1 × C × DX2 × SX3 and Q = X4 × C × DX5 × SX6
In this context, V represents the flow velocity (in m/s); C denotes the Hazen Williams coefficient (unitless); and Q indicates the discharge rate (in cum/s). Identify the accurate statements from the options provided below.
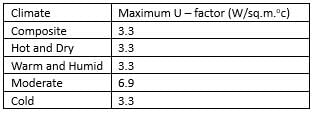
As per the recommendations of ECBC, what is the maximum U-value for glazing in a hot and dry climate? (Provide your answer up to one decimal place)
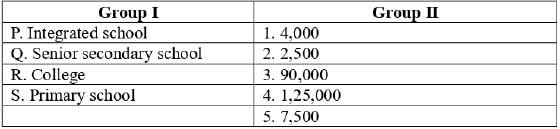
A real estate developer is undertaking the creation of a township through a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model. The total land area designated for this project is 2.672 hectares, with an allowable Floor Area Ratio (FAR) of 2.25, out of which 20% is allocated for the Middle-Income Group (MIG) category. The total area for each MIG unit, including shared spaces and amenities, measures 72 m2. Assuming that the super built-up area is equivalent to the FAR, what is the maximum number of MIG apartments that can be built (in whole numbers)?
A town needs a total volume of 70,000 m3 of compacted solid waste to fill an area of low elevation.
The municipality comprises 10,000 households.
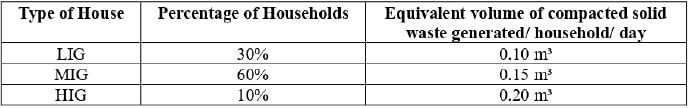
Number of days to fill the low-lying land = ?
It was observed that on a particular stretch of road, the free speed was recorded at 90 km/h and the jam density measured 60 veh/km. What is the maximum flow, in veh/h, that can be anticipated on this road? Please provide your answer as a whole number.
A room measuring 10m × 25m × 4m needs to achieve 3 air changes every hour. Given an air speed of 2 m/s, what is the required duct cross-sectional area (in m²)?
The design of the Mahatma Gandhi Labour Institute, located in Ahmedabad, is attributed to which architect?
Which of the following describes a ventilation system that features a large shaft extending significantly above the roof of a building?
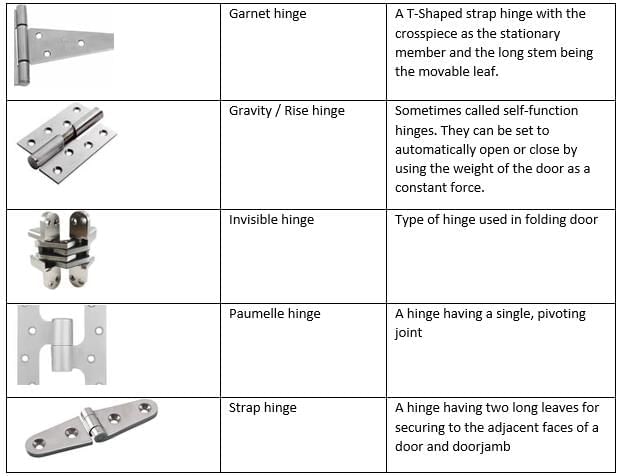
Pair the types of fixtures and fastenings needed for doors in Group I with their corresponding characteristics listed in Group II.
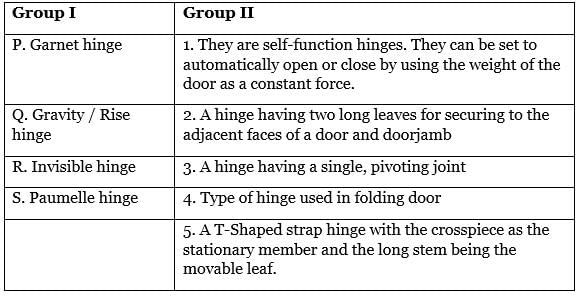
Pair the construction machinery in Group I with their corresponding functions in Group II.

A room measuring 3m x 3m x 3m has walls with an absorption coefficient of 0.2, a ceiling with an absorption coefficient of 0.5, and a floor with an absorption coefficient of 0.1. What is the reverberation time in the room in ____ seconds?