Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 2
Assertion : The acidity of Mg(OH)2 is two.
Reason : The acidity of a base is equal to the number of hydroxyl ions.
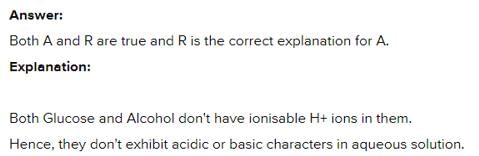
Assertion : The aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not show acidic character. Reason : Aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not give H+ ions.
Assertion : When zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen is given off.
Reason : Hydrogen chloride molecules contain hydrochloric acid and hydrogen atoms.
Assertion : During electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen is produced at anode and chlorine gas is produced at cathode.
Reason : Ions get attracted to oppositely charged electrodes.
Assertion : pH = 7 signifies pure water.
Reason : At this pH, [H+] = [OH-]= 10-7.
Assertion : Weak acids have low electrical conductivity.
Reason : Strong acids and weak acids have equal concentration of hydrogen ions in their solutions.
Assertion : If the pH inside the mouth decreases below5.5, the decay of tooth enamel begins.
Reason : The bacteria present in the mouth degrades the sugar and left over food particles and produce acids that remain in the mouth after eating.
Assertion (A): The pH scale is used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidic or basic nature.
Reason (R): The "p" in pH stands for 'potenz' in German, which means power, and the scale ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): When common salt having impurities (like magnesium chloride) is kept open, it absorbs moisture from the air.
Reason (R): Magnesium chloride absorbs moisture.
|
80 videos|661 docs|80 tests
|