APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (History) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test APSET Mock Test Series 2026 - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (History)
Consider the following statement about Hellenistic art :
1. The Sakas introduced features of Hellenistic art in the North-West frontiers of India.
2. The Hellenistic influence appears in the Pillars of Ashoka.
3. Gandhara art is the best example of Hellenistic influence.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The ‘Dastaks’, the misuse of which was a source of constant friction between the nawab and the East Indian Company, were actually:
Consider the following events in the history of India:
1. Rise of Pratiharas under King Bhoja.
2. Establishment of Pallava power under Narshimhavarman I.
3. Establishment of Rashtrakutas power by Dantidurga.
4. Rise of Pala dynasty under Dharmapala.
What is the correct chronological order of the above events, starting from the earliest time?
Who was the first Muslim to invade India in 712 AD?
“Go Back to Vedas“. Who among the following gave this motto?
Who played a pivotal role in the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- V.P. Menon
- The Maharaja of Kashmir
- The Nizam of Hyderabad
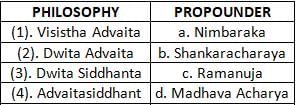
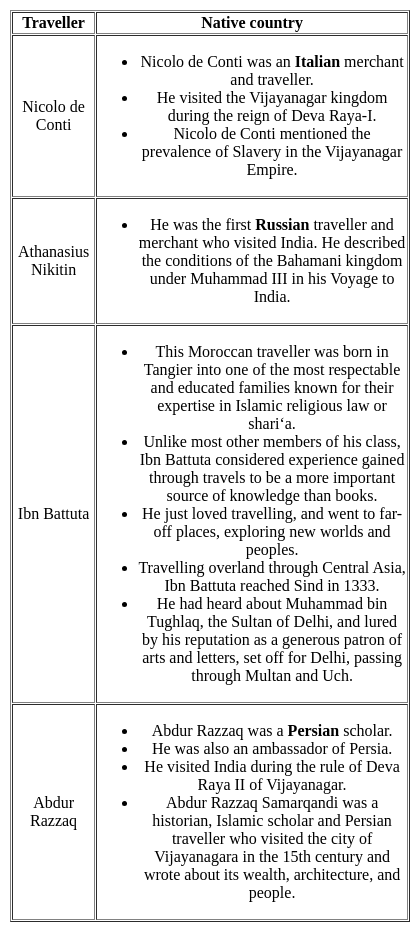
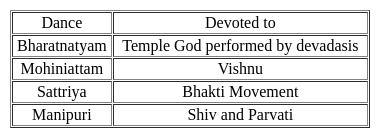
Which of the following pair is not correctly matched?
Read the statements (A) and (R) and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A) - During Aurangzeb’s reign, there was a decrease in the number of Mansabdars.
Reason (R) - Their was an increase in the number of jagirs in his reign.
On which among the following dates, execution of Bhagat Singh took place ?
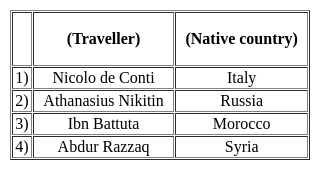
Consider the following pairs:
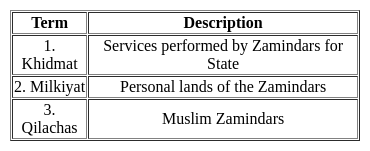
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Which of the following is a similarity between Jainism and Buddhism?
In which year English was made the medium of instruction in India ?
Consider the following:
1. Sutanati
2. Kalikata
3. Govindpur
For how many of the above villages East India Company acquired the Zamindari In 1698?
Which European power's intervention significantly altered the Maratha Confederacy's dominance in India, leading to the eventual decline of Maratha power in the subcontinent through a series of conflicts known collectively as the Maratha Wars?
Which of the following ancient Tamil Kingdoms came to be known from Sangam Literature?
With respect to the paintings in South India, consider the following statements.
I. Tanjore school of painting was developed by Chola rulers, dominated by the pictures of child Krishna.
II. The distinct school of Mysore painting evolved from the paintings of Vijayanagar times during the reign of the Vijayanagar Kings.
Choose the incorrect statements.
According to Historical Materialism, the primary driver of social change is
Which of the following is the oldest Smriti?
During British Era, the Duke Memorandum became the basis of which among the following?
|
60 tests
|