All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Engineering Mechanics >
All Questions
All questions of Friction for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Calculate the frictional force developed between the body and the surface.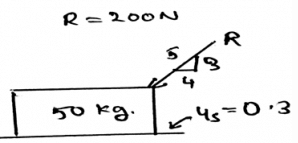
- a)160N
- b)16N
- c)10N
- d)180N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the frictional force developed between the body and the surface.
a)
160N
b)
16N
c)
10N
d)
180N

|
Trilochan Thakur answered |
Friction force =F*cos¥ and cos¥=4/5 after putting F=200 the value is 160N
The frictional force always acts ____________ to the surface of the application of the friction.- a)Tangential
- b)Perpendicular
- c)Parallel
- d)Normal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The frictional force always acts ____________ to the surface of the application of the friction.
a)
Tangential
b)
Perpendicular
c)
Parallel
d)
Normal
|
|
Nishanth Basu answered |
The friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. This friction is applied tangentially to the surfaces in contact. Thus the main thing is that the forces on both of the surfaces act tangential to each other.
Who gave the concept of Dry friction?- a)C.A. Coulomb
- b)GA. Coulomb
- c)C.P Coulomb
- d)Albert Einstein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who gave the concept of Dry friction?
a)
C.A. Coulomb
b)
GA. Coulomb
c)
C.P Coulomb
d)
Albert Einstein
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The dry friction is also termed as the Coulomb friction as it was given by C.A. Coulomb. And they are tangential to each other. As we know the friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces.
The frictional force is directly proportional to the surface of the solid.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The frictional force is directly proportional to the surface of the solid.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Sai Reddy answered |
The frictional force is directly proportional to the vertical forces that is being applied normal to the surface of the body. The force of friction is not dependent on the type of the surface. Thus the only thing the frictional force does depend is the normal force.
The frictional force is directly proportional to the ____________- a)Applied load
- b)Type of surface used
- c)The normal force
- d)The horizontal load
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The frictional force is directly proportional to the ____________
a)
Applied load
b)
Type of surface used
c)
The normal force
d)
The horizontal load
|
|
Meera Bose answered |
The frictional force is directly proportional to the vertical force that is being applied normal to the surface of the body. The force of friction is not dependent on the type of the surface. Thus the only thing the frictional force does depend is the normal force.
The collar bearings are generally used in __________- a)Belts
- b)Columns
- c)Beams
- d)Machines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The collar bearings are generally used in __________
a)
Belts
b)
Columns
c)
Beams
d)
Machines

|
Nayanika Joshi answered |
The collar bearings are being used in the machines. They are used as to support the loadings. This means that the more the collar bearings the more is the stable the structure. Thus the use of collar bearings.
The normal force exerted by the surface of the wedge is normal to the surface of the ________- a)Base of the wedge
- b)Base of the body residing over it
- c)Base of the body just neighbour to the wedge
- d)Earth’s surface
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The normal force exerted by the surface of the wedge is normal to the surface of the ________
a)
Base of the wedge
b)
Base of the body residing over it
c)
Base of the body just neighbour to the wedge
d)
Earth’s surface

|
Sparsh Unni answered |
Understanding the Normal Force on a Wedge
The normal force is a critical concept in mechanics, particularly when dealing with inclined surfaces such as wedges. In this scenario, the normal force is essential for understanding how objects interact with these inclined planes.
Definition of Normal Force
- The normal force is the force exerted by a surface that supports the weight of an object resting on it.
- It acts perpendicular (normal) to the contact surface between two objects.
Normal Force on the Wedge
- When an object rests on a wedge, the normal force exerted by the wedge is directed perpendicular to the inclined surface of the wedge.
- This force counteracts the component of the gravitational force acting perpendicular to the surface of the wedge.
Why Option B is Correct
- The normal force acts perpendicular to the base of the body residing over the wedge (option B).
- This is because the body (often a block or another object) makes contact with the surface of the wedge, and the normal force arises from this contact.
Comparison with Other Options
- Option A (Base of the wedge): The normal force pertains to the object resting on the wedge, not the wedge itself.
- Option C (Base of the body just neighbor to the wedge): This might imply a different contact surface, which isn't relevant to the normal force acting on the wedge.
- Option D (Earth's surface): The normal force acts at the interface of the wedge and the resting object, not at the Earth's surface.
In conclusion, understanding the direction and application of the normal force is vital in analyzing forces in mechanical systems, especially in scenarios involving wedges.
The normal force is a critical concept in mechanics, particularly when dealing with inclined surfaces such as wedges. In this scenario, the normal force is essential for understanding how objects interact with these inclined planes.
Definition of Normal Force
- The normal force is the force exerted by a surface that supports the weight of an object resting on it.
- It acts perpendicular (normal) to the contact surface between two objects.
Normal Force on the Wedge
- When an object rests on a wedge, the normal force exerted by the wedge is directed perpendicular to the inclined surface of the wedge.
- This force counteracts the component of the gravitational force acting perpendicular to the surface of the wedge.
Why Option B is Correct
- The normal force acts perpendicular to the base of the body residing over the wedge (option B).
- This is because the body (often a block or another object) makes contact with the surface of the wedge, and the normal force arises from this contact.
Comparison with Other Options
- Option A (Base of the wedge): The normal force pertains to the object resting on the wedge, not the wedge itself.
- Option C (Base of the body just neighbor to the wedge): This might imply a different contact surface, which isn't relevant to the normal force acting on the wedge.
- Option D (Earth's surface): The normal force acts at the interface of the wedge and the resting object, not at the Earth's surface.
In conclusion, understanding the direction and application of the normal force is vital in analyzing forces in mechanical systems, especially in scenarios involving wedges.
In the equation Wa/r generally used in the rolling frictional calculations, what does each stands for?- a)P is the force, W is weight of the body, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction all in normal powers
- b)P is the force in nano Newton, W is weight of the body, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction
- c)P is the force, W is weight of the body in kg, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction
- d)P is the force, W is weight of the body, r radius cm and a coefficient of rolling friction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the equation Wa/r generally used in the rolling frictional calculations, what does each stands for?
a)
P is the force, W is weight of the body, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction all in normal powers
b)
P is the force in nano Newton, W is weight of the body, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction
c)
P is the force, W is weight of the body in kg, r radius and a coefficient of rolling friction
d)
P is the force, W is weight of the body, r radius cm and a coefficient of rolling friction
|
|
Mehul Yadav answered |
The rolling of the cylinder is termed as perfect rolling only when the cylinder is rolling at a constant velocity. Also the rolling should be along the rigid surface. The normal forces are acting perpendicular to the surface of the rolling. And for rolling equation Wa/r is generally used.
Which of the following statement for the three force system applied in the screws is true?- a)The moment need not to be seen for the equilibrium, they are always in equilibrium
- b)The forces are not always in the equilibrium
- c)The forces are always in equilibrium
- d)The moments are always in equilibrium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement for the three force system applied in the screws is true?
a)
The moment need not to be seen for the equilibrium, they are always in equilibrium
b)
The forces are not always in the equilibrium
c)
The forces are always in equilibrium
d)
The moments are always in equilibrium
|
|
Nandini Basak answered |
The forces in the three force system are not always in the equilibrium. The equilibrium is established when the forces cancels out each other. Also when the net moment is zero. Then only the equilibrium is established in the three force system.
For determination of the equilibrium state in the free body diagram the basic way of getting the direction of the moment caused by the force is:- a)The use of left hand rule with thumb giving the direction of moment
- b)The use of right hand rule with thumb giving the direction of moment
- c)The use of right hand rule with forefinger giving the direction of moment
- d)The use of left hand rule with forefinger giving the direction of moment
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For determination of the equilibrium state in the free body diagram the basic way of getting the direction of the moment caused by the force is:
a)
The use of left hand rule with thumb giving the direction of moment
b)
The use of right hand rule with thumb giving the direction of moment
c)
The use of right hand rule with forefinger giving the direction of moment
d)
The use of left hand rule with forefinger giving the direction of moment
|
|
Gopal Choudhury answered |
The basic way of doing so is to use right hand rule and not the left hand rule. The direction of the moment axis is given by the thumb. The direction of the force is given by the fingers. As we place the fingers on the force and curl towards the rotational direction of the body about the axis.
The block used to explain the theory of friction is kept over non-deformable surface.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The block used to explain the theory of friction is kept over non-deformable surface.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Anjali Shah answered |
The block used to explain the theory of friction is a used in a deformable surface. As we know that the theory of friction says that when there is no lubricating fluid present between the surfaces in contact, the dry friction occurs. Thus to show the same experiments are done over a non-rigid/deformable surface.
In rolling there is the involvement of the vector math. So for rolling which of the following is correct? (For A representing the vector representation of the axis of rotation, r the radius vector and F the force vector)- a)A.(rxF)
- b)Ax(rxF)
- c)A.(r.F)
- d)Fx(r.F)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In rolling there is the involvement of the vector math. So for rolling which of the following is correct? (For A representing the vector representation of the axis of rotation, r the radius vector and F the force vector)
a)
A.(rxF)
b)
Ax(rxF)
c)
A.(r.F)
d)
Fx(r.F)
|
|
Raj Kumar answered |
The correct form of the equation is given by A.(rxF). Where A represents the vector representation of the axis of rotation, r the radius vector and F the force vector. This is usually done for determining the moment of the force about the axis. That is if body is being rotated by the force about an axis.
As the free body diagram of the problem statement involves the use of forces. So in them the ___________ forces do not cause the rotation.- a)Non-concurrent
- b)Concurrent
- c)Parallel
- d)Non-Parallel
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As the free body diagram of the problem statement involves the use of forces. So in them the ___________ forces do not cause the rotation.
a)
Non-concurrent
b)
Concurrent
c)
Parallel
d)
Non-Parallel
|
|
Sai Reddy answered |
The concurrent forces are the one are somewhere touching the axis of rotation. If any of the force is touching that axis, that force is not considered, or is insufficient to cause a rotation. If a force is concurrent then the perpendicular distance of the force from the line of axis is zero, thus no rotation. As we know rotation is caused by moment.
The horizontal distance used in the inverse trigonometry function is called as _____________- a)Lead
- b)Un-lead
- c)Major
- d)Cut-off
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The horizontal distance used in the inverse trigonometry function is called as _____________
a)
Lead
b)
Un-lead
c)
Major
d)
Cut-off
|
|
Nandini Basak answered |
The angle of the threading in the screw is determined by inverse tangent trigonometric function. This is the generalised form of the function which is being used so as to get the value of the angle. In wedges the same function is used so as to find the angle of wedge. And thus the horizontal distance is called as lead.
When does the two wedge system is termed as self-locking system?- a)If friction forces hold the block in plane
- b)If friction forces doesn’t hold the block in plane
- c)If friction forces hold the block in phase
- d)If friction forces doesn’t hold the block in phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When does the two wedge system is termed as self-locking system?
a)
If friction forces hold the block in plane
b)
If friction forces doesn’t hold the block in plane
c)
If friction forces hold the block in phase
d)
If friction forces doesn’t hold the block in phase
|
|
Arnav Menon answered |
If friction forces hold the block in plane the two wedge system is termed as self-locking system. This is generally the concept used to lift up the boxes and then it is also used as to make the very heavy works easy. Thus the wedges are very useful in the industries, and it has a wide application.
The frictional force developed always acts ____________ to the surface of the application of the friction.- a)Tangential
- b)Perpendicular
- c)Parallel
- d)Normal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The frictional force developed always acts ____________ to the surface of the application of the friction.
a)
Tangential
b)
Perpendicular
c)
Parallel
d)
Normal
|
|
Ayush Chawla answered |
The friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. This friction is applied tangentially to the surfaces in contact. Thus the main thing is that the forces on both of the surfaces act tangential to each other.
The difference between the two and the three force members is:- a)The former is collinear and the latter is parallel
- b)The former is parallel and the latter is perpendicular
- c)The former is perpendicular and the latter is collinear
- d)The former is acting on two points in the body while the latter is on three points
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between the two and the three force members is:
a)
The former is collinear and the latter is parallel
b)
The former is parallel and the latter is perpendicular
c)
The former is perpendicular and the latter is collinear
d)
The former is acting on two points in the body while the latter is on three points
|
|
Anjali Shah answered |
The definition of the two force member only defines that the forces are being acted on the two points on the body. So does is the definition of the three forces members. The points of action of the three forces are three.
The coefficient of static friction does depend upon the surface on which the body is being slide.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The coefficient of static friction does depend upon the surface on which the body is being slide.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Anshul Basu answered |
The constant in the equation F = µN is known as the coefficient of static friction. This is the proportionality constant and is generally used to express the equation of the frictional force. The value of this constant is generally from 0 to infinite, depending on the surface.
The moment is the cross product of which two vectors in the calculations of the pivots and disks?- a)Force and Radius vectors
- b)Radius and Force vectors
- c)Force and Radius scalars
- d)Radius and Force scalars
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The moment is the cross product of which two vectors in the calculations of the pivots and disks?
a)
Force and Radius vectors
b)
Radius and Force vectors
c)
Force and Radius scalars
d)
Radius and Force scalars
|
|
Sai Reddy answered |
The cross product needs to take in the proper sequence. If not taken then the answer is just the opposite of the true answer. That’s why, the answer is not the Force and Radius vectors, but the Radius and Force vectors. Because the moment has its direction, as many of the cross products have, and thus precaution needs to be taken.
If we apply oil on door hinges, the friction will- a)increase
- b)disappear altogether
- c)decrease
- d)will remain unchanged
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If we apply oil on door hinges, the friction will
a)
increase
b)
disappear altogether
c)
decrease
d)
will remain unchanged
|
|
Athul Kumar answered |
Explanation:
When we apply oil on door hinges, the friction between the moving parts will decrease. This is due to the lubricating properties of the oil. Let's understand this in more detail:
Friction:
Friction is the force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact. It can be classified into two types: static friction and kinetic friction. Static friction acts when there is no relative motion between the surfaces, while kinetic friction acts when there is relative motion.
Effect of oil on friction:
When oil is applied to door hinges, it forms a thin layer between the surfaces that come in contact. This layer acts as a lubricant, reducing the friction between the surfaces. Here's how it happens:
1. Lubrication:
The oil fills the small gaps and irregularities on the surface of the door hinge, creating a smooth and slippery layer. This smooth layer separates the surfaces and prevents direct contact between them.
2. Reduced adhesion:
When two surfaces come in contact, there is a certain level of adhesion between them. This adhesion can increase the friction between the surfaces. When oil is applied, it reduces the adhesion between the surfaces, resulting in lower friction.
3. Viscosity:
The viscosity of the oil also plays a role in reducing friction. The oil's viscosity determines its resistance to flow. When the oil is applied to the door hinge, its viscosity allows it to spread evenly and fill the gaps. This reduces the resistance between the moving parts, resulting in lower friction.
Overall:
By reducing the friction, oil allows the door hinge to move more easily. It prevents wear and tear on the hinge and reduces the effort required to open or close the door. However, it is important to note that excessive oiling can attract dirt and dust, which can lead to increased friction over time. Therefore, it is recommended to apply a moderate amount of oil for optimal lubrication.
When we apply oil on door hinges, the friction between the moving parts will decrease. This is due to the lubricating properties of the oil. Let's understand this in more detail:
Friction:
Friction is the force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact. It can be classified into two types: static friction and kinetic friction. Static friction acts when there is no relative motion between the surfaces, while kinetic friction acts when there is relative motion.
Effect of oil on friction:
When oil is applied to door hinges, it forms a thin layer between the surfaces that come in contact. This layer acts as a lubricant, reducing the friction between the surfaces. Here's how it happens:
1. Lubrication:
The oil fills the small gaps and irregularities on the surface of the door hinge, creating a smooth and slippery layer. This smooth layer separates the surfaces and prevents direct contact between them.
2. Reduced adhesion:
When two surfaces come in contact, there is a certain level of adhesion between them. This adhesion can increase the friction between the surfaces. When oil is applied, it reduces the adhesion between the surfaces, resulting in lower friction.
3. Viscosity:
The viscosity of the oil also plays a role in reducing friction. The oil's viscosity determines its resistance to flow. When the oil is applied to the door hinge, its viscosity allows it to spread evenly and fill the gaps. This reduces the resistance between the moving parts, resulting in lower friction.
Overall:
By reducing the friction, oil allows the door hinge to move more easily. It prevents wear and tear on the hinge and reduces the effort required to open or close the door. However, it is important to note that excessive oiling can attract dirt and dust, which can lead to increased friction over time. Therefore, it is recommended to apply a moderate amount of oil for optimal lubrication.
The basic type of motion of a body is translation motion only.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic type of motion of a body is translation motion only.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Saptarshi Nair answered |
Explanation:
Translation motion is not the only type of motion a body can exhibit. There are several types of motion that a body can undergo. Let's explore the different types of motion:
1. Translation Motion:
Translation motion involves the movement of an object from one point to another without any rotation. This is the simplest form of motion where all points on the body move in parallel paths, maintaining the same orientation relative to each other.
2. Rotational Motion:
Rotational motion involves the movement of an object around an axis. In this type of motion, different points on the body move in circles around the axis of rotation. Examples of rotational motion include the spinning of a top or the rotation of a wheel.
3. Oscillatory Motion:
Oscillatory motion involves the back and forth movement of an object around a central point or equilibrium position. This type of motion is characterized by periodic changes in position. Examples of oscillatory motion include the swinging of a pendulum or the vibrations of a guitar string.
4. Circular Motion:
Circular motion involves the movement of an object along a circular path. In this type of motion, the object moves in a circular trajectory around a fixed point. Examples of circular motion include the motion of planets around the sun or the motion of a car around a roundabout.
Therefore, it is incorrect to say that the basic type of motion of a body is translation motion only. Bodies can exhibit various types of motion, including translation, rotation, oscillation, and circular motion.
Rotation is termed as rolling when _______- a)Constant velocity of rolling
- b)Variable velocity of rolling
- c)Constant speed of rolling
- d)Variable speed of rolling
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rotation is termed as rolling when _______
a)
Constant velocity of rolling
b)
Variable velocity of rolling
c)
Constant speed of rolling
d)
Variable speed of rolling
|
|
Anshu Patel answered |
The rolling of the cylinder is termed as perfect rolling only when the cylinder is rolling at a constant velocity. Also the rolling should be along the rigid surface. The normal forces are acting perpendicular to the surface of the rolling.
For the rolling of the body right handed coordinate system means (consider the mentioned axis to be positive)?- a)Thumb is z-axis, fingers curled from x-axis to y-axis
- b)Thumb is x-axis, fingers curled from z-axis to y-axis
- c)Thumb is y-axis, fingers curled from x-axis to z-axis
- d)Thumb is z-axis, fingers curled from y-axis to x-axis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the rolling of the body right handed coordinate system means (consider the mentioned axis to be positive)?
a)
Thumb is z-axis, fingers curled from x-axis to y-axis
b)
Thumb is x-axis, fingers curled from z-axis to y-axis
c)
Thumb is y-axis, fingers curled from x-axis to z-axis
d)
Thumb is z-axis, fingers curled from y-axis to x-axis
|
|
Nandita Chakraborty answered |
As right handed coordinate system means that you are curling your fingers from positive x-axis towards y-axis and the thumb which is projected is pointed to the positive z-axis. Thus visualizing the same and knowing the basic members of axis will not create much problem. The right handed coordinate system is universal throughout.
What does the moment of the force measure in the rolling of the body?- a)The tendency of rotation of the body along any axis
- b)The moment of inertia of the body about any axis
- c)The couple moment produce by the single force acting on the body
- d)The total work done on the body by the force
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the moment of the force measure in the rolling of the body?
a)
The tendency of rotation of the body along any axis
b)
The moment of inertia of the body about any axis
c)
The couple moment produce by the single force acting on the body
d)
The total work done on the body by the force
|
|
Anuj Chauhan answered |
The moment of the force measures the tendency of the rotation of the body along any axis, whether it be the centroid axis of the body, or any of the outside axis. The couple moment is produced by two forces, not by a single force. The total work done is the dot product of force and distance not the cross.
There are main two types of forces which are being stated in the free body diagram, they are generally the resultant forces which are being acted over the body. Which are they?- a)Normal and Frictional
- b)Normal and Vertical
- c)Vertical and Frictional
- d)Normal and Fractional
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There are main two types of forces which are being stated in the free body diagram, they are generally the resultant forces which are being acted over the body. Which are they?
a)
Normal and Frictional
b)
Normal and Vertical
c)
Vertical and Frictional
d)
Normal and Fractional

|
Sagnik Sen answered |
Normal and Frictional Forces in Free Body Diagram
The two main types of forces in a free body diagram are the normal force and the frictional force. Let's break down these forces:
Normal Force:
- The normal force is the force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it.
- It acts perpendicular to the surface and prevents objects from falling through it.
- In a free body diagram, the normal force is represented by a vector pointing away from the surface.
Frictional Force:
- The frictional force is the force that opposes the motion of an object when in contact with a surface.
- It acts parallel to the surface and its magnitude depends on the coefficient of friction between the surfaces.
- In a free body diagram, the frictional force is represented by a vector opposite to the direction of motion.
Therefore, in a free body diagram, the normal force and the frictional force are typically shown as the two main forces acting on an object. These forces play a crucial role in analyzing the equilibrium and motion of the object in mechanical engineering applications.
For equilibrium the normal forces acts in which direction in the free body diagrams if they are constructed for the friction part calculations?- a)Vertically Upward
- b)Vertically Downward
- c)Horizontally Right
- d)Horizontally Left
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For equilibrium the normal forces acts in which direction in the free body diagrams if they are constructed for the friction part calculations?
a)
Vertically Upward
b)
Vertically Downward
c)
Horizontally Right
d)
Horizontally Left
|
|
Aditya Chavan answered |
As the loads are being acting in the downward direction. Thus to make the forces balance, the normal forces act in the vertically upward direction. As we know that when there is no lubricating fluid present between the surfaces in contact, the dry friction occurs. This friction magnitude is taken out from these normal forces.
The moment is the cross product of which two vectors in the calculations of the journal bearings?- a)Force and Radius vectors
- b)Radius and Force vectors
- c)Force and Radius scalars
- d)Radius and Force scalars
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The moment is the cross product of which two vectors in the calculations of the journal bearings?
a)
Force and Radius vectors
b)
Radius and Force vectors
c)
Force and Radius scalars
d)
Radius and Force scalars

|
Garima Basak answered |
Explanation:
Journal Bearings:
Journal bearings are mechanical elements used to support rotating shafts. They are designed to provide support and reduce friction in rotating machinery.
Cross Product of Vectors:
In the context of journal bearings, the cross product of two vectors is calculated to determine the moment acting on the bearing. The cross product of two vectors results in a vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by the original vectors.
Force and Radius Vectors:
- In the calculations of journal bearings, the force vector represents the force applied on the bearing due to the load on the shaft.
- The radius vector represents the distance from the center of the bearing to the point where the force is applied.
- When these two vectors are used in a cross product operation, the resulting vector represents the moment acting on the bearing.
Therefore, in the calculations of journal bearings, the moment is the cross product of the Force and Radius vectors. This relationship helps engineers analyze and design journal bearings to ensure optimal performance and durability in various applications.
Journal Bearings:
Journal bearings are mechanical elements used to support rotating shafts. They are designed to provide support and reduce friction in rotating machinery.
Cross Product of Vectors:
In the context of journal bearings, the cross product of two vectors is calculated to determine the moment acting on the bearing. The cross product of two vectors results in a vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by the original vectors.
Force and Radius Vectors:
- In the calculations of journal bearings, the force vector represents the force applied on the bearing due to the load on the shaft.
- The radius vector represents the distance from the center of the bearing to the point where the force is applied.
- When these two vectors are used in a cross product operation, the resulting vector represents the moment acting on the bearing.
Therefore, in the calculations of journal bearings, the moment is the cross product of the Force and Radius vectors. This relationship helps engineers analyze and design journal bearings to ensure optimal performance and durability in various applications.
In the explanation of the theory of friction, the block used have an assumption. That is the upper portion of the block is considered to be rigid.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the explanation of the theory of friction, the block used have an assumption. That is the upper portion of the block is considered to be rigid.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Rajat Basu answered |
The block used to explain the theory of friction is placed on a deformable surface. As we know that the theory of friction says that when there is no lubricating fluid present between the surfaces in contact, the dry friction occurs. Thus to show the same, experiments are done over a non-rigid/deformable surface which is having a rigid shape.
We slip while walking on a path having pond scum or green algae because: - a)The inertia of motion
- b)The friction is zero
- c)The friction between the feet and the path is increased.
- d)The friction between the feet and the path is reduced.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
We slip while walking on a path having pond scum or green algae because:
a)
The inertia of motion
b)
The friction is zero
c)
The friction between the feet and the path is increased.
d)
The friction between the feet and the path is reduced.
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Important Points
- Friction is a force between two surfaces that are sliding, or trying to slide, across each other.
- For example, when you try to push or pull luggage along the floor, friction makes this difficult.
- Friction always works in the opposite of the direction in which the object is moving or trying to move.
- There are four types of friction:
- Static Friction: Static friction acts on objects when they are resting on a surface.
- For example, hiking in the woods, there is static friction between shoes and the trail each time put down the foot.
- Without this static friction, feet would slip out and making it difficult to walk.
- Sliding Friction: Sliding friction is friction that acts on objects when they are sliding over a surface.
- Sliding friction is weaker than static friction.
- Rolling Friction: Rolling friction is friction that acts on objects when they are rolling over a surface.
- Rolling friction is much weaker than sliding friction or static friction.
- For example, ground transportation use wheels, including bicycles, cars, 4-wheelers, roller skates, scooters, skateboards, Ball bearings.
- Fluid Friction: Fluid friction is friction that acts on objects that are moving through a fluid.
- A fluid is a substance that can flow and take the shape of its container. Fluids include liquids and gases.
- Static Friction: Static friction acts on objects when they are resting on a surface.
Dry friction is also called _____________- a)Column Friction
- b)Coulomb Friction
- c)Dry column friction
- d)Surface friction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dry friction is also called _____________
a)
Column Friction
b)
Coulomb Friction
c)
Dry column friction
d)
Surface friction

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
The dry friction is acted upon the surfaces. And they are tangential to each other. As we know the friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. The dry friction is also termed as the Coulomb friction as it was given by C.A. Coulomb.
The ___________ forces do not cause the rotation/rolling of the body if the rotation is considered in about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body.- a)Non-concurrent
- b)Concurrent
- c)Parallel
- d)Non-Parallel
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ___________ forces do not cause the rotation/rolling of the body if the rotation is considered in about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body.
a)
Non-concurrent
b)
Concurrent
c)
Parallel
d)
Non-Parallel

|
Poulomi Khanna answered |
Concurrent and Non-concurrent Forces:
Concurrent forces refer to forces whose lines of action intersect at a common point. In other words, all the forces act through a single point. On the other hand, non-concurrent forces are forces that do not intersect at a common point. They have different lines of action.
Rotation and Rolling:
Rotation refers to the movement of a body about a fixed axis. When a body rotates, different points on the body move in circular paths around the axis of rotation. Rolling, on the other hand, is a combination of rotational and translational motion. In rolling, a body moves forward while also rotating about its axis.
Forces causing Rotation and Rolling:
When a body is subjected to forces, these forces can cause both rotation and rolling. The forces that cause rotation are called torque or moment of forces. Torque is the product of force and the perpendicular distance between the point of rotation and the line of action of the force.
Concurrent Forces causing Rotation:
If the forces acting on a body are concurrent, meaning they intersect at a common point, they can cause rotation about any axis passing through that point. The sum of the torques produced by these concurrent forces about any axis passing through the common point is zero. Therefore, concurrent forces can cause rotation of the body.
Non-concurrent Forces causing Rotation:
On the other hand, if the forces acting on a body are non-concurrent, they cannot cause rotation of the body about any arbitrary axis passing through the point of intersection. The sum of the torques produced by these non-concurrent forces about any arbitrary axis is not zero. Therefore, non-concurrent forces do not cause rotation of the body.
Rotation about the Axis of the Body or Centroid Axis:
The question specifically mentions that the rotation is considered about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body. Since the forces are non-concurrent, they cannot cause rotation about these axes. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Concurrent forces do not cause the rotation/rolling of the body if the rotation is considered about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body.
Concurrent forces refer to forces whose lines of action intersect at a common point. In other words, all the forces act through a single point. On the other hand, non-concurrent forces are forces that do not intersect at a common point. They have different lines of action.
Rotation and Rolling:
Rotation refers to the movement of a body about a fixed axis. When a body rotates, different points on the body move in circular paths around the axis of rotation. Rolling, on the other hand, is a combination of rotational and translational motion. In rolling, a body moves forward while also rotating about its axis.
Forces causing Rotation and Rolling:
When a body is subjected to forces, these forces can cause both rotation and rolling. The forces that cause rotation are called torque or moment of forces. Torque is the product of force and the perpendicular distance between the point of rotation and the line of action of the force.
Concurrent Forces causing Rotation:
If the forces acting on a body are concurrent, meaning they intersect at a common point, they can cause rotation about any axis passing through that point. The sum of the torques produced by these concurrent forces about any axis passing through the common point is zero. Therefore, concurrent forces can cause rotation of the body.
Non-concurrent Forces causing Rotation:
On the other hand, if the forces acting on a body are non-concurrent, they cannot cause rotation of the body about any arbitrary axis passing through the point of intersection. The sum of the torques produced by these non-concurrent forces about any arbitrary axis is not zero. Therefore, non-concurrent forces do not cause rotation of the body.
Rotation about the Axis of the Body or Centroid Axis:
The question specifically mentions that the rotation is considered about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body. Since the forces are non-concurrent, they cannot cause rotation about these axes. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Concurrent forces do not cause the rotation/rolling of the body if the rotation is considered about the axis of the body or the centroid axis of the body.
Which of the following is correct for a screw being rotated?- a)The couple moment depends on the axis of rotation
- b)The couple moment depends directly on the radius vector of forces
- c)The couple moment depends only on the distance vector between the forces
- d)The couple moment’s direction is given by the left hand rule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct for a screw being rotated?
a)
The couple moment depends on the axis of rotation
b)
The couple moment depends directly on the radius vector of forces
c)
The couple moment depends only on the distance vector between the forces
d)
The couple moment’s direction is given by the left hand rule

|
Sahana Choudhary answered |
Depends on both the radius vector of forces and the distance vector between the forces
For equilibrium the normal forces acts in which direction in the free body diagrams?- a)Vertically Upward
- b)Vertically Downward
- c)Horizontally Right
- d)Horizontally Left
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For equilibrium the normal forces acts in which direction in the free body diagrams?
a)
Vertically Upward
b)
Vertically Downward
c)
Horizontally Right
d)
Horizontally Left

|
Isha Bajaj answered |
The normal force is a contact force that acts perpendicular to the surface of an object. It arises due to the interaction between two surfaces in contact with each other. In the context of free body diagrams, the normal force represents the force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it.
Explanation:
The normal force is always directed perpendicular to the surface of contact. It acts in a direction that is away from the surface, pushing against the object to prevent it from sinking into or passing through the surface. In the case of equilibrium, the normal force and the weight of the object are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in a net force of zero.
- The normal force is always directed vertically upward in the free body diagrams.
- It acts in the opposite direction to the force of gravity.
- It counteracts the weight of the object to keep it in equilibrium.
- The normal force is exerted by the surface, and it is transmitted through the object to maintain stability.
- If the object is on a horizontal surface, the normal force acts vertically upward, perpendicular to the surface.
- The normal force can also act at an angle if the object is on an inclined plane, but it still acts perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact.
- In a vertical free body diagram, the normal force acts upward while the weight force acts downward.
- When the object is in equilibrium, the normal force is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the weight force, resulting in a net force of zero.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the normal force in a free body diagram always acts vertically upward. It is a contact force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object. The normal force is crucial in maintaining equilibrium and preventing objects from sinking into or passing through surfaces.
Explanation:
The normal force is always directed perpendicular to the surface of contact. It acts in a direction that is away from the surface, pushing against the object to prevent it from sinking into or passing through the surface. In the case of equilibrium, the normal force and the weight of the object are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in a net force of zero.
- The normal force is always directed vertically upward in the free body diagrams.
- It acts in the opposite direction to the force of gravity.
- It counteracts the weight of the object to keep it in equilibrium.
- The normal force is exerted by the surface, and it is transmitted through the object to maintain stability.
- If the object is on a horizontal surface, the normal force acts vertically upward, perpendicular to the surface.
- The normal force can also act at an angle if the object is on an inclined plane, but it still acts perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact.
- In a vertical free body diagram, the normal force acts upward while the weight force acts downward.
- When the object is in equilibrium, the normal force is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the weight force, resulting in a net force of zero.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the normal force in a free body diagram always acts vertically upward. It is a contact force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object. The normal force is crucial in maintaining equilibrium and preventing objects from sinking into or passing through surfaces.
A phenomena is there in these collar bearings and pivots, which is very helpful in the supporting of the machines, and that is _____________- a)Column Friction
- b)Coulomb Friction
- c)Dry column friction
- d)Surface friction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A phenomena is there in these collar bearings and pivots, which is very helpful in the supporting of the machines, and that is _____________
a)
Column Friction
b)
Coulomb Friction
c)
Dry column friction
d)
Surface friction
|
|
Prateek Mukherjee answered |
The dry friction is acted upon the surfaces. And they are tangential to each other. As we know the friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. This Coulomb friction is also known as dry friction.
In the simplification of the forces applied in the wedges net force acts at the ___________ of the loading body.
a) Centroid
b) The centre axis
c) The corner
d) The baseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the simplification of the forces applied in the wedges net force acts at the ___________ of the loading body.
a) Centroid
b) The centre axis
c) The corner
d) The base
a) Centroid
b) The centre axis
c) The corner
d) The base

|
Devanshi Iyer answered |
In the simplification of the loading system the net force acts at the centroid of the loading body. That is if the loading system is in the form of the triangle then the at the distance 2 by 3 of the base the net force of the loading will act. And the load will be half the area of the loading.
In the equation A.(rxF) the r is heading from ______________ and ending at _____________- a)Axis of rolling, Force vector
- b)Axis of rolling, Force vector’s point of action on the body
- c)Force vector, Axis of rolling
- d)Force vector’s point of action on the body, Axis of rolling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the equation A.(rxF) the r is heading from ______________ and ending at _____________
a)
Axis of rolling, Force vector
b)
Axis of rolling, Force vector’s point of action on the body
c)
Force vector, Axis of rolling
d)
Force vector’s point of action on the body, Axis of rolling
|
|
Raj Kumar answered |
It is the radius vector. The radius vector is always from the axis of rolling to the point of action of the force on the body. Which means that the radius vector is not on any point on the force vector. Rather it ending at the point on the force vector, where it is being in contact of the body.
The angle of the threading in the screw is determined by which of the following trigonometric function?- a)Tangent Inverse
- b)Sine
- c)Cosine
- d)Secant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of the threading in the screw is determined by which of the following trigonometric function?
a)
Tangent Inverse
b)
Sine
c)
Cosine
d)
Secant
|
|
Jhanvi Datta answered |
The angle of the threading in the screw is determined by inverse tangent trigonometric function. This is the generalised form of the function which is being used so as to get the value of the angle. In wedges the same function is used so as to find the angle of wedge.
What is not the condition for the equilibrium in free body diagram for calculation of the normal forces?- a)∑Fx=0
- b)∑Fy=0
- c)∑Fz=0
- d)∑F≠0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is not the condition for the equilibrium in free body diagram for calculation of the normal forces?
a)
∑Fx=0
b)
∑Fy=0
c)
∑Fz=0
d)
∑F≠0
|
|
Kirti Bose answered |
For the equilibrium in the three dimensional system of axis we have all the conditions true as, ∑Fx=0, ∑Fy=0 and ∑Fz=0. Also we have the summation of the forces equal to zero. Which is not a non-zero value.
The value of coefficient of friction is taken at that moment when the block is at the verge of moving.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of coefficient of friction is taken at that moment when the block is at the verge of moving.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Devansh Sengupta answered |
The constant in the equation F = µN is known as the coefficient of static friction. This is the proportionality constant and is generally used to express the equation of the frictional force. And this coefficient is calculated by the help of experiments and is generally observed when the block is at the verge of moving.
The phenomena of horizontal pull and push explains what?- a)Theory of friction
- b)Theory of relativity
- c)Theory of action
- d)Theory of forces
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomena of horizontal pull and push explains what?
a)
Theory of friction
b)
Theory of relativity
c)
Theory of action
d)
Theory of forces

|
Garima Basak answered |
Horizontal Pull and Push
Horizontal pull and push refer to the forces acting on an object in the horizontal direction. These forces are essential to understand the theory of friction in mechanical engineering.
Theory of Friction
Friction is the resistance to motion when two objects are in contact with each other. When an object is pulled or pushed horizontally, the force required to move it is affected by the friction between the two surfaces. The horizontal pull and push forces play a crucial role in determining the amount of friction present.
Explanation
- When an object is pulled horizontally, the force applied must overcome the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on.
- Similarly, when an object is pushed horizontally, the force applied must also overcome the friction to move the object.
- The theory of friction helps to understand how these horizontal pull and push forces interact with the surfaces in contact and affect the motion of the object.
Significance
Understanding horizontal pull and push forces is vital in various mechanical engineering applications. It helps in designing systems that minimize frictional losses and optimize the efficiency of machines and mechanisms.
In conclusion, the phenomena of horizontal pull and push are essential in explaining the theory of friction in mechanical engineering. By considering these forces, engineers can better understand and control the interactions between objects in contact and improve the performance of mechanical systems.
Horizontal pull and push refer to the forces acting on an object in the horizontal direction. These forces are essential to understand the theory of friction in mechanical engineering.
Theory of Friction
Friction is the resistance to motion when two objects are in contact with each other. When an object is pulled or pushed horizontally, the force required to move it is affected by the friction between the two surfaces. The horizontal pull and push forces play a crucial role in determining the amount of friction present.
Explanation
- When an object is pulled horizontally, the force applied must overcome the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on.
- Similarly, when an object is pushed horizontally, the force applied must also overcome the friction to move the object.
- The theory of friction helps to understand how these horizontal pull and push forces interact with the surfaces in contact and affect the motion of the object.
Significance
Understanding horizontal pull and push forces is vital in various mechanical engineering applications. It helps in designing systems that minimize frictional losses and optimize the efficiency of machines and mechanisms.
In conclusion, the phenomena of horizontal pull and push are essential in explaining the theory of friction in mechanical engineering. By considering these forces, engineers can better understand and control the interactions between objects in contact and improve the performance of mechanical systems.
The three force system can also be in the equilibrium if:- a)All the forces are parallel to each other heading towards the same direction
- b)The force components cancel each other
- c)The forces are very small in magnitude
- d)The forces are very huge in magnitude
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The three force system can also be in the equilibrium if:
a)
All the forces are parallel to each other heading towards the same direction
b)
The force components cancel each other
c)
The forces are very small in magnitude
d)
The forces are very huge in magnitude
|
|
Isha Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
Force Components Cancel Each Other:
- When the force components of a three-force system cancel each other out, the system is said to be in equilibrium.
- This means that the net force acting on the system is zero, resulting in no acceleration.
Balanced Force System:
- In a balanced force system, the forces are arranged in such a way that their magnitudes and directions offset each other.
- This balance ensures that the system remains stationary or moves at a constant velocity.
Newton's First Law:
- This condition of equilibrium aligns with Newton's First Law of Motion, which states that an object will remain at rest or move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
- In the case of a three-force system, the cancellation of force components leads to a state of equilibrium.
Practical Applications:
- Understanding how force components cancel each other out is crucial in various engineering applications.
- Engineers use this concept to design structures, machines, and systems that remain stable and balanced under different loading conditions.
By ensuring that the force components of a three-force system cancel each other out, engineers can achieve equilibrium and stability in their designs. This principle plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of various mechanical systems.
For a vector F, Fcosβ is equal to zero. What does this refer?- a)X-axis component is zero
- b)Y-axis component is zero
- c)Z-axis component is zero
- d)β = 180˚
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a vector F, Fcosβ is equal to zero. What does this refer?
a)
X-axis component is zero
b)
Y-axis component is zero
c)
Z-axis component is zero
d)
β = 180˚

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
As we know the α, β and γ are the angles made by the x, y and z-axis respectively. Thus y-axis component is zero, or β = 90˚. And thus if the angle is giving component to be zero this means the vector in that particular axis is perpendicular to that axis.
Why are square threaded screws are used in the machines?- a)Large forces act along the axis of the screws
- b)Small forces act along the axis of the screws
- c)Large forces act perpendicular the axis of the screws
- d)Small forces act perpendicular the axis of the screws
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are square threaded screws are used in the machines?
a)
Large forces act along the axis of the screws
b)
Small forces act along the axis of the screws
c)
Large forces act perpendicular the axis of the screws
d)
Small forces act perpendicular the axis of the screws
|
|
Anjali Shah answered |
The square threaded screws are used in the machines. As these screws are generally used as the fasteners. The main thing about these screws is that the friction helps the holding of the structures. Also screws help make the structure join fast and efficiently. And in these screws forces act along the axis of screws.
The kinetic friction is applied when the body is __________- a)Moving
- b)Stopped
- c)Just stopped
- d)Just started to move
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The kinetic friction is applied when the body is __________
a)
Moving
b)
Stopped
c)
Just stopped
d)
Just started to move
|
|
Gayatri Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
Kinetic Friction:
When a body is in motion, the force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact is known as kinetic friction. This type of friction occurs when the body is moving.
Static Friction:
Static friction, on the other hand, is the force that prevents the body from moving when it is at rest. This force must be overcome in order to set the body in motion.
Justification:
In the given question, the kinetic friction is applied when the body is moving. This is because kinetic friction comes into play once the body is already in motion and is trying to resist the motion by opposing the relative movement between the surfaces in contact.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Moving. Kinetic friction is not applied when the body is stopped, just stopped, or just started to move, as these scenarios involve static friction or no friction being present.
Kinetic Friction:
When a body is in motion, the force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact is known as kinetic friction. This type of friction occurs when the body is moving.
Static Friction:
Static friction, on the other hand, is the force that prevents the body from moving when it is at rest. This force must be overcome in order to set the body in motion.
Justification:
In the given question, the kinetic friction is applied when the body is moving. This is because kinetic friction comes into play once the body is already in motion and is trying to resist the motion by opposing the relative movement between the surfaces in contact.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Moving. Kinetic friction is not applied when the body is stopped, just stopped, or just started to move, as these scenarios involve static friction or no friction being present.
What is B in the equation T2 = T1eµB ?- a)Angle of the belt to surface contact in radians
- b)Angle of the belt to surface contact in degrees
- c)Angle of the belt in radians
- d)Angle of the belt in degrees
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is B in the equation T2 = T1eµB ?
a)
Angle of the belt to surface contact in radians
b)
Angle of the belt to surface contact in degrees
c)
Angle of the belt in radians
d)
Angle of the belt in degrees
|
|
Atharva Majumdar answered |
For solving of the unknown tension in the belts, T2 = T1eµB equation is used. In this the R.H.S tension is the maximum tension of the two tensions. While the other one is the smaller one. And the µ is coefficient of friction between the belt and the surface. And the B is the angle of belt to the surface in radians.
The pivots are generally used in __________- a)Belts
- b)Columns
- c)Beams
- d)Machines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pivots are generally used in __________
a)
Belts
b)
Columns
c)
Beams
d)
Machines
|
|
Prateek Mukherjee answered |
Pivots in Machines
Pivots are mechanical components that are used extensively in various types of machines. They play a crucial role in enabling movement, rotation, and oscillation in machines. Pivots are designed to provide support, stability, and smooth motion to different machine components.
Function of Pivots in Machines
Pivots are primarily used to facilitate movement and rotation in machines. They allow different parts of a machine to move in a controlled manner, enabling the desired functionality. The main functions of pivots in machines include:
1. Rotational Motion: Pivots enable rotational motion by providing a central point of rotation. They allow the connected components to rotate around the pivot point, facilitating various operations in machines.
2. Support and Stability: Pivots provide support and stability to machine components by acting as a fixed point or axis. They help in maintaining the alignment and balance of the moving parts, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
3. Articulation: Pivots allow the articulation of different machine components, enabling them to move in different directions. This flexibility is essential for machines that require multi-axis movement or adjustable parts.
4. Reducing Friction: Pivots are often equipped with bearings or bushings to reduce friction and wear. This helps in minimizing energy losses and prolonging the lifespan of the machine.
Applications of Pivots in Machines
Pivots find numerous applications in a wide range of machines across various industries. Some common examples include:
1. Industrial Machinery: Pivots are used in industrial machinery such as conveyor systems, assembly lines, robots, and machine tools. They enable precise movement and positioning of the machine components.
2. Automotive Industry: Pivots are essential in vehicles for various functions such as suspension systems, steering mechanisms, and engine components. They provide smooth and controlled movement, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
3. Printing and Packaging: Pivots are used in printing presses, packaging machines, and paper handling equipment. They allow the movement of printing plates, cutting tools, and paper feed mechanisms.
4. Medical Devices: Pivots are utilized in medical devices like surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and prosthetic limbs. They enable precise and controlled movement, enhancing the functionality of these devices.
In conclusion, pivots are widely used in machines to facilitate movement, rotation, and oscillation. They provide support, stability, and enable the articulation of different machine components. Pivots find applications in various industries, including industrial machinery, automotive, printing and packaging, and medical devices.
Pivots are mechanical components that are used extensively in various types of machines. They play a crucial role in enabling movement, rotation, and oscillation in machines. Pivots are designed to provide support, stability, and smooth motion to different machine components.
Function of Pivots in Machines
Pivots are primarily used to facilitate movement and rotation in machines. They allow different parts of a machine to move in a controlled manner, enabling the desired functionality. The main functions of pivots in machines include:
1. Rotational Motion: Pivots enable rotational motion by providing a central point of rotation. They allow the connected components to rotate around the pivot point, facilitating various operations in machines.
2. Support and Stability: Pivots provide support and stability to machine components by acting as a fixed point or axis. They help in maintaining the alignment and balance of the moving parts, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
3. Articulation: Pivots allow the articulation of different machine components, enabling them to move in different directions. This flexibility is essential for machines that require multi-axis movement or adjustable parts.
4. Reducing Friction: Pivots are often equipped with bearings or bushings to reduce friction and wear. This helps in minimizing energy losses and prolonging the lifespan of the machine.
Applications of Pivots in Machines
Pivots find numerous applications in a wide range of machines across various industries. Some common examples include:
1. Industrial Machinery: Pivots are used in industrial machinery such as conveyor systems, assembly lines, robots, and machine tools. They enable precise movement and positioning of the machine components.
2. Automotive Industry: Pivots are essential in vehicles for various functions such as suspension systems, steering mechanisms, and engine components. They provide smooth and controlled movement, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
3. Printing and Packaging: Pivots are used in printing presses, packaging machines, and paper handling equipment. They allow the movement of printing plates, cutting tools, and paper feed mechanisms.
4. Medical Devices: Pivots are utilized in medical devices like surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and prosthetic limbs. They enable precise and controlled movement, enhancing the functionality of these devices.
In conclusion, pivots are widely used in machines to facilitate movement, rotation, and oscillation. They provide support, stability, and enable the articulation of different machine components. Pivots find applications in various industries, including industrial machinery, automotive, printing and packaging, and medical devices.
The angle of the inclination of wedge over which the block is sliding and is experiencing the kinetic friction is determined by which of the following trigonometric function?- a)Tangent Inverse
- b)Cosine
- c)Sine
- d)Secant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of the inclination of wedge over which the block is sliding and is experiencing the kinetic friction is determined by which of the following trigonometric function?
a)
Tangent Inverse
b)
Cosine
c)
Sine
d)
Secant
|
|
Sanskriti Basu answered |
The angle of the wedge over which the block is being slided is generally taken out by the help of the tangent inverse trigonometric function. Whether it may be the static or the kinetic friction, the ratio is the frictional force to the normal force. And this ratio is kept inside the inverse function.
We first make equilibrium equations of the body by considering all the three dimensional forces acting on the section chosen and then the free body diagram is made and solved.- a)The first part of the statement is false and other part is true
- b)The first part of the statement is false and other part is false too
- c)The first part of the statement is true and other part is false
- d)The first part of the statement is true and other part is true too
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
We first make equilibrium equations of the body by considering all the three dimensional forces acting on the section chosen and then the free body diagram is made and solved.
a)
The first part of the statement is false and other part is true
b)
The first part of the statement is false and other part is false too
c)
The first part of the statement is true and other part is false
d)
The first part of the statement is true and other part is true too
|
|
Aniket Saini answered |
Equilibrium equations and free body diagram are two important steps in solving mechanics problems. Let's break down the given statement:
Equilibrium equations:
When we talk about equilibrium equations, we are referring to the equations that describe the state of balance or equilibrium of an object. These equations are based on Newton's laws of motion and they help us determine the forces acting on an object and their direction. We can make equilibrium equations by considering all the three-dimensional forces acting on the section chosen.
Free body diagram:
A free body diagram is a visual representation of the forces acting on an object. It is a simplified diagram that shows the object as a dot and all the forces acting on it as arrows. The direction of the arrows indicates the direction of the force, and the length of the arrows indicates the magnitude of the force. Free body diagrams are used to analyze and solve mechanics problems.
Now, let's analyze the given statement:
a) The first part of the statement is false and the other part is true.
This is incorrect because equilibrium equations are indeed an important step in solving mechanics problems.
b) The first part of the statement is false and the other part is false too.
This is also incorrect because the second part of the statement is true.
c) The first part of the statement is true and the other part is false.
This is incorrect because both parts of the statement are true.
d) The first part of the statement is true and the other part is true too.
This is the correct answer because both equilibrium equations and free body diagrams are essential steps in solving mechanics problems.
In summary, the correct answer is option D because both equilibrium equations and free body diagrams are important steps in solving mechanics problems.
Equilibrium equations:
When we talk about equilibrium equations, we are referring to the equations that describe the state of balance or equilibrium of an object. These equations are based on Newton's laws of motion and they help us determine the forces acting on an object and their direction. We can make equilibrium equations by considering all the three-dimensional forces acting on the section chosen.
Free body diagram:
A free body diagram is a visual representation of the forces acting on an object. It is a simplified diagram that shows the object as a dot and all the forces acting on it as arrows. The direction of the arrows indicates the direction of the force, and the length of the arrows indicates the magnitude of the force. Free body diagrams are used to analyze and solve mechanics problems.
Now, let's analyze the given statement:
a) The first part of the statement is false and the other part is true.
This is incorrect because equilibrium equations are indeed an important step in solving mechanics problems.
b) The first part of the statement is false and the other part is false too.
This is also incorrect because the second part of the statement is true.
c) The first part of the statement is true and the other part is false.
This is incorrect because both parts of the statement are true.
d) The first part of the statement is true and the other part is true too.
This is the correct answer because both equilibrium equations and free body diagrams are essential steps in solving mechanics problems.
In summary, the correct answer is option D because both equilibrium equations and free body diagrams are important steps in solving mechanics problems.
Chapter doubts & questions for Friction - Engineering Mechanics 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Friction - Engineering Mechanics in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Engineering Mechanics
23 videos|61 docs|53 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










