All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Transportation Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Highway Materials & Testing for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
The aggregate impact test was conducted on a sample and the following readings were taken:
Weight of sample taken () = 350 g
Weight of sample passing 2.36 mm sieve () = 92 g
What will be the aggregate impact value for the sample?
- a)27%
- b)26 g
- c)26.29 g
- d)26.29%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The aggregate impact test was conducted on a sample and the following readings were taken:
Weight of sample taken () = 350 g
Weight of sample passing 2.36 mm sieve () = 92 g
What will be the aggregate impact value for the sample?
Weight of sample taken () = 350 g
Weight of sample passing 2.36 mm sieve () = 92 g
What will be the aggregate impact value for the sample?
a)
27%
b)
26 g
c)
26.29 g
d)
26.29%

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
The aggregate impact value is obtained as the ratio of the weight of sample passing 2.36 mm sieve to the weight of the sample taken for the test. For the readings in the question, the aggregate impact value can be found out as
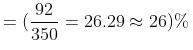
and is expressed as a whole number in percentage.
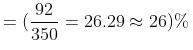
and is expressed as a whole number in percentage.
Tar is a by-product of __________- a)Wood
- b)Petroleum
- c)coal
- d)1,2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Tar is a by-product of __________
a)
Wood
b)
Petroleum
c)
coal
d)
1,2 and 3
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
It is a natural substance, oozing out of the ground in places like the La Brea tar pits. Usually it is made by heating coal inside a chemical apparatus. Most tar is produced from coal as a byproduct of coke production, but it can also be produced from petroleum, peat or wood.
Bitumen is a by-product of __________- a)Wood
- b)Petroleum
- c)Kerosene
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bitumen is a by-product of __________
a)
Wood
b)
Petroleum
c)
Kerosene
d)
Coal
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Bitumen is obtained by burning the petroleum at high temperatures, it is mostly used in the construction of flexible pavements.
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.- a)5 to 10
- b)10 to 100
- c)0 to 11
- d)0 to 15
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.
a)
5 to 10
b)
10 to 100
c)
0 to 11
d)
0 to 15
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Angularity:
It is the absence of roundness. An aggregate particle, which is more rounded, is less angular and vice versa.
Angularity number:
It is the absence of roundness. An aggregate particle, which is more rounded, is less angular and vice versa.
Angularity number:
- Angularity number of an aggregate is the amount (to the higher whole number) by which the percentage of voids in it after compacting in a prescribed manner exceeds 33.
- Where “33” is the percentage of the volume of voids in a perfectly rounded aggregate. And, “67” is the percentage of the volume of solids in a perfectly rounded aggregate when compacted in a specified manner.
- The value of angularity number generally lies between 0 & 11.
Determination of angularity number:
(a) From the solids
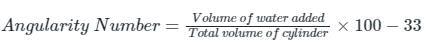
(b) From the voids
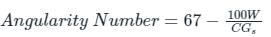
Where C = weight of the cylinder, W = weight of aggregate in the cylinder, Gs = specific gravity of aggregate
(a) From the solids
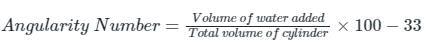
(b) From the voids
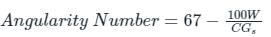
Where C = weight of the cylinder, W = weight of aggregate in the cylinder, Gs = specific gravity of aggregate
The layer which is constructed above embankment is called __________- a)Sub grade
- b)Fill
- c)Base
- d)Sub base
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The layer which is constructed above embankment is called __________
a)
Sub grade
b)
Fill
c)
Base
d)
Sub base
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The embankment is the lowest layer and it is below the sub grade, base is above sub base, sub base is above the sub grade.
Which of the below tar type – application pairs matched correctly?- a)RT-1 – renewal coat
- b)RT-2 – standard surface painting
- c)RT-3 – cold weather surface painting
- d)RT-4 – grouting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the below tar type – application pairs matched correctly?
a)
RT-1 – renewal coat
b)
RT-2 – standard surface painting
c)
RT-3 – cold weather surface painting
d)
RT-4 – grouting
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Tar can be of five types based on its viscosity. They are RT-1, RT-2, RT-3, RT-4 and RT-5. RT-1 has the least viscosity and is used for surface painting in extremely cold weather, RT-2 is used for standard surface painting in Indian climate, RT-3 is used for renewal coats, RT-4 is used for premixing tar macadam in the base course and RT-5 is used for grouting.
Which of the following test is used for the bitumen?- a)Slump test
- b)Abrasion test
- c)Penetration test
- d)Fineness test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following test is used for the bitumen?
a)
Slump test
b)
Abrasion test
c)
Penetration test
d)
Fineness test
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
- The penetration test is carried out to know the hardness or softness of bitumen used in road construction by measuring the distance in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard needle will penetrate vertically into a sample of bitumen under the stipulated condition of temperature, time, and loading.
- The slump test is conducted to test the workability of concrete.
- The fineness test is checked to test the proper grinding of the cement which significantly influences the rate of hydration.
- It is carried out to test the hardness property of aggregates and to decide whether they are suitable for different pavement construction works.
Various tests conducted on bitumen for testing its various properties are as follows:
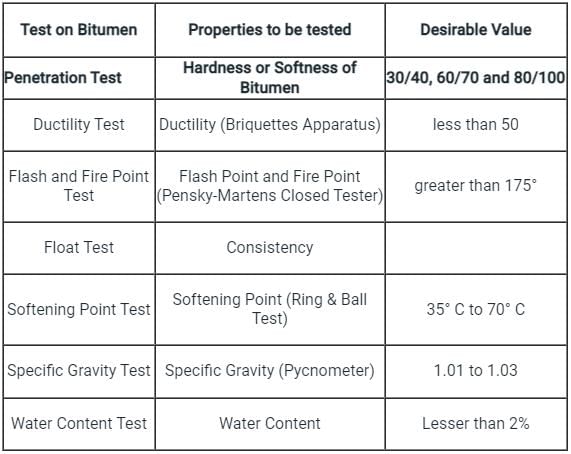
Marshal test is used for designing the bituminous concrete for pavement construction, Beckenham Beam Method is used to determine the deflection of the pavement slab.
Bitumen is classified on the basis of either its penetration value or its viscosity.
Classification based on the penetration value of bitumen:
The penetration test is carried out to know the hardness or softness of bitumen used in road construction by measuring the distance in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard needle will penetrate vertically into a sample of bitumen under the stipulated condition of temperature, time and loading.
A bitumen specified as of grade 80/100 means that the range of penetration value of the sample is between 80 to 100 (i.e. actual penetration would range between 8 mm to 10 mm).
∴ Hardest grade of bitumen among the following is 30/40, as penetration would be as less as 3 to 4 mm only.
Note: It can be stated that for a hot climate, lower penetration grades of bitumen are preferred, and for cold climates, higher penetration grades of bitumen are preferred.

Marshal test is used for designing the bituminous concrete for pavement construction, Beckenham Beam Method is used to determine the deflection of the pavement slab.
Bitumen is classified on the basis of either its penetration value or its viscosity.
Classification based on the penetration value of bitumen:
The penetration test is carried out to know the hardness or softness of bitumen used in road construction by measuring the distance in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard needle will penetrate vertically into a sample of bitumen under the stipulated condition of temperature, time and loading.
A bitumen specified as of grade 80/100 means that the range of penetration value of the sample is between 80 to 100 (i.e. actual penetration would range between 8 mm to 10 mm).
∴ Hardest grade of bitumen among the following is 30/40, as penetration would be as less as 3 to 4 mm only.
Note: It can be stated that for a hot climate, lower penetration grades of bitumen are preferred, and for cold climates, higher penetration grades of bitumen are preferred.
There are six types of tests to conduct the adhesion test on aggregates.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There are six types of tests to conduct the adhesion test on aggregates.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
The tests to determine the stripping value can be classified into six types. They are static immersion test, dynamic immersion test, chemical immersion test, immersion mechanical test, immersion trafficking test and coating test.
The layer which is constructed above embankment is called __________- a)Sub grade
- b)Fill
- c)Base
- d)Sub base
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The layer which is constructed above embankment is called __________
a)
Sub grade
b)
Fill
c)
Base
d)
Sub base
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The embankment is the lowest layer and it is below the sub grade, base is above sub base, sub base is above the sub grade.
The polished stone value of an aggregate is reported as the ______ of the two values of ______- a)Mean, abrasion number
- b)Mean, skid number
- c)Sum, skid number
- d)Sum, abrasion number
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The polished stone value of an aggregate is reported as the ______ of the two values of ______
a)
Mean, abrasion number
b)
Mean, skid number
c)
Sum, skid number
d)
Sum, abrasion number
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
There are two stages conducted for this test. The sample is polished in the first stage and subjected to pendulum type friction tester in the second stage. The result obtained is the skid number and the mean of two values of the same is taken as the polished stone value.
In a length gauge used for determination of elongation index, what is the length of gauge size for sieve sets 25 mm and 20 mm?- a)25.65
- b)40.5
- c)81
- d)32.4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a length gauge used for determination of elongation index, what is the length of gauge size for sieve sets 25 mm and 20 mm?
a)
25.65
b)
40.5
c)
81
d)
32.4

|
Sreemoyee Chauhan answered |
Length Gauge and Elongation Index:
A length gauge is used in civil engineering to determine the elongation index of aggregates. The elongation index is a measure of the elongated and flat particles in the aggregate sample. It is expressed as a percentage of the total weight of the sample.
Gauge Size for Sieve Sets 25 mm and 20 mm:
To determine the gauge size for sieve sets with sizes 25 mm and 20 mm, we need to calculate the combined length of the two sieves.
Calculating the Combined Length:
The combined length is the sum of the lengths of both sieve sizes. We can calculate it by adding the diameter of each sieve to the length of the sieve.
Given:
Sieve size 25 mm: Diameter = 25 mm
Sieve size 20 mm: Diameter = 20 mm
To calculate the length of the sieve, we need to use the following formula:
Length of sieve = (Diameter of sieve - Thickness of wire) / 2
Since we don't have the thickness of the wire, we assume it to be negligible.
Calculating the Length of Sieve Size 25 mm:
Length of sieve size 25 mm = (25 - 0) / 2
= 12.5 mm
Calculating the Length of Sieve Size 20 mm:
Length of sieve size 20 mm = (20 - 0) / 2
= 10 mm
Calculating the Combined Length:
Combined length = Length of sieve size 25 mm + Length of sieve size 20 mm
= 12.5 mm + 10 mm
= 22.5 mm
Conclusion:
Therefore, the length of the gauge size for sieve sets 25 mm and 20 mm is 22.5 mm. None of the given options (a, b, c, d) match the correct answer.
A length gauge is used in civil engineering to determine the elongation index of aggregates. The elongation index is a measure of the elongated and flat particles in the aggregate sample. It is expressed as a percentage of the total weight of the sample.
Gauge Size for Sieve Sets 25 mm and 20 mm:
To determine the gauge size for sieve sets with sizes 25 mm and 20 mm, we need to calculate the combined length of the two sieves.
Calculating the Combined Length:
The combined length is the sum of the lengths of both sieve sizes. We can calculate it by adding the diameter of each sieve to the length of the sieve.
Given:
Sieve size 25 mm: Diameter = 25 mm
Sieve size 20 mm: Diameter = 20 mm
To calculate the length of the sieve, we need to use the following formula:
Length of sieve = (Diameter of sieve - Thickness of wire) / 2
Since we don't have the thickness of the wire, we assume it to be negligible.
Calculating the Length of Sieve Size 25 mm:
Length of sieve size 25 mm = (25 - 0) / 2
= 12.5 mm
Calculating the Length of Sieve Size 20 mm:
Length of sieve size 20 mm = (20 - 0) / 2
= 10 mm
Calculating the Combined Length:
Combined length = Length of sieve size 25 mm + Length of sieve size 20 mm
= 12.5 mm + 10 mm
= 22.5 mm
Conclusion:
Therefore, the length of the gauge size for sieve sets 25 mm and 20 mm is 22.5 mm. None of the given options (a, b, c, d) match the correct answer.
In the initial stage of construction which type of pavement is cheap?- a)Flexible
- b)Rigid
- c)Composite
- d)WBM
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the initial stage of construction which type of pavement is cheap?
a)
Flexible
b)
Rigid
c)
Composite
d)
WBM
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Flexible pavements are easy to construct and have cheaper cost than C. C pavements and also they are easily accessible to the users.
Ductility of bitumen is measured in terms of ______- a)Time
- b)Distance
- c)Temperature
- d)Colour
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ductility of bitumen is measured in terms of ______
a)
Time
b)
Distance
c)
Temperature
d)
Colour

|
Nishanth Banerjee answered |
Ductility of Bitumen
Ductility is a crucial property of bitumen, especially in civil engineering applications, as it reflects the material's ability to deform under tensile stress without breaking.
Measurement of Ductility
The ductility of bitumen is primarily measured in terms of:
Significance of Ductility
Other Factors
While distance is the primary measurement for ductility, other parameters can influence the performance of bitumen:
In conclusion, ductility is a vital property for evaluating bitumen's performance in construction, with distance as the key measurement metric to determine its ability to endure stress without failure.
Ductility is a crucial property of bitumen, especially in civil engineering applications, as it reflects the material's ability to deform under tensile stress without breaking.
Measurement of Ductility
The ductility of bitumen is primarily measured in terms of:
- Distance: Ductility is quantified by the distance that a standard sample of bitumen can be stretched before it breaks. Typically, this is measured using a ductility testing apparatus, where a sample is pulled apart at a specified rate.
Significance of Ductility
- Performance in Pavements: High ductility indicates that the bitumen can accommodate the deformations caused by temperature changes and traffic loads, making it suitable for road construction.
- Resistance to Cracking: Ductile bitumen can resist cracking, especially in colder climates where thermal stresses can lead to pavement failure.
Other Factors
While distance is the primary measurement for ductility, other parameters can influence the performance of bitumen:
- Temperature: The ductility of bitumen can vary with temperature, requiring analysis at different thermal conditions.
- Bitumen Grade: Different grades of bitumen will exhibit varied ductility, impacting their use in specific applications.
In conclusion, ductility is a vital property for evaluating bitumen's performance in construction, with distance as the key measurement metric to determine its ability to endure stress without failure.
The following particulars are obtained after conducting the test for angularity number:
Volume of cylinder = 3000 g
Specific gravity = 2.68
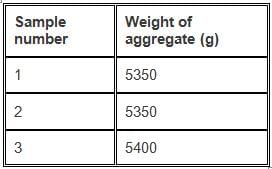 What is the angularity number for the above sample?
What is the angularity number for the above sample?- a)0
- b)0.5
- c)0.4
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The following particulars are obtained after conducting the test for angularity number:
Volume of cylinder = 3000 g
Specific gravity = 2.68

Volume of cylinder = 3000 g
Specific gravity = 2.68

What is the angularity number for the above sample?
a)
0
b)
0.5
c)
0.4
d)
1
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Angularity number is obtained using the formula,
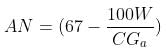
Where W represents the mean weight of aggregate (g),
C represents the volume of the cylinder (g) and,
Ga represents the specific gravity
From the readings, mean value,
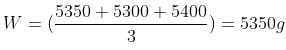
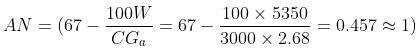
The angularity number is represented as a whole number and is rounded off to nearest one.
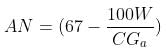
Where W represents the mean weight of aggregate (g),
C represents the volume of the cylinder (g) and,
Ga represents the specific gravity
From the readings, mean value,
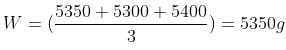
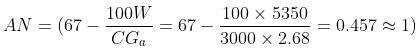
The angularity number is represented as a whole number and is rounded off to nearest one.
The materials not included in highway construction are __________- a)Stone
- b)Dust
- c)Soil
- d)Petrol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The materials not included in highway construction are __________
a)
Stone
b)
Dust
c)
Soil
d)
Petrol
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Petrol is not used directly in highway construction, but by-product like bitumen is used. Stone, dust and soil may be used in subgrade and base.
In the Pensky Marten test for Bitumen, a momentary flash was seen at a temperature of 200° Celsius and the bitumen burned for at least 5 seconds at a temperature of 240° Celsius. The flash and fire point of bitumen is _________ and _________, respectively. - a)200° Celsius, 240° Celsius
- b)200° Celsius, 200° Celsius
- c)240° Celsius, 240° Celsius
- d)240° Celsius, 200° Celsius
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the Pensky Marten test for Bitumen, a momentary flash was seen at a temperature of 200° Celsius and the bitumen burned for at least 5 seconds at a temperature of 240° Celsius. The flash and fire point of bitumen is _________ and _________, respectively.
a)
200° Celsius, 240° Celsius
b)
200° Celsius, 200° Celsius
c)
240° Celsius, 240° Celsius
d)
240° Celsius, 200° Celsius
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Flashpoint:
- It is the lowest temperature at which the application of a test flame causes the vapors of the binder to catch an instant fire in the form of a flash under specified test conditions.
- Two types of test apparatus may be used for conducting flash point tests on bitumen, namely the Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester and Open Cup Tester.
- Here, In the bitumen test, momentary flash was seen at a temperature of 200° Celsius. So, the flash point is 200° Celsius.
- If the bituminous binder is further heated to a temperature higher than the flash point, the binder material itself catches fire and continues to burn, the lowest temperature causing this condition is called the fire point.
Fire Point:
- It is the lowest temperature at which the application of test flame causes the binder material to ignite and burn at least for five seconds under specified test conditions.
- Here, bitumen burned for at least 5 seconds at a temperature of 240° Celsius. So, the fire point is 240° Celsius.
Important Points
- The fire point is always higher than the flash point of a material.
- Pensky-Martens open cup tester is used to determine the flash & fire point of the bituminous binders.
What type of pavement can aggregate with an aggregate impact value of 26% not be used in?- a)Cement concrete base course
- b)Bitumen bound macadam base course
- c)Bituminous concrete surface course
- d)Water bound macadam base course
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of pavement can aggregate with an aggregate impact value of 26% not be used in?
a)
Cement concrete base course
b)
Bitumen bound macadam base course
c)
Bituminous concrete surface course
d)
Water bound macadam base course
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
For the bituminous concrete surface course, the impact value should not exceed 24%, so the sample in the question cannot be used. For cement concrete base course, it must not exceed 45%, bitumen bound macadam base course 35% and for water bound macadam base course 40%.
For places where there is a passage of flood water then the highway has to be built on __________- a)Embankment
- b)Subway
- c)Overpass
- d)Underpass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For places where there is a passage of flood water then the highway has to be built on __________
a)
Embankment
b)
Subway
c)
Overpass
d)
Underpass

|
Arnab Saini answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
In areas prone to flooding, it is crucial to design and construct highways in a way that allows for the passage of floodwater without causing damage to the road or hindering the flow of water. One of the most effective methods for achieving this is by building the highway on an embankment.
Embankment:
An embankment is an elevated mound of earth or rock that is constructed to raise the level of a road or railway track above the surrounding ground. It is typically built using compacted soil or other suitable materials to provide a stable foundation for the highway.
Advantages of an embankment:
- Elevation: By constructing the highway on an embankment, it is raised above the flood level, ensuring that floodwater can pass beneath it without causing any obstruction.
- Stability: The embankment provides a stable base for the highway, preventing it from being washed away or damaged during floods.
- Drainage: Embankments are designed with proper slope and drainage systems to ensure that water does not accumulate on the road surface, reducing the risk of hydroplaning.
- Accessibility: Unlike other options such as subways or underpasses, an embankment allows for continuous access to the highway during normal conditions, minimizing disruptions to traffic flow.
- Cost-effectiveness: Building an embankment is generally more cost-effective compared to constructing subways or underpasses, as it requires less excavation and construction materials.
Disadvantages of other options:
- Subway: A subway involves constructing a tunnel beneath the flood-prone area. However, building and maintaining a subway can be expensive and may require complex engineering solutions to ensure water does not enter the tunnel during floods.
- Overpass: An overpass involves constructing a bridge over the flood-prone area. While this option allows for the passage of floodwater, it may require a significant investment in terms of construction materials and engineering design.
- Underpass: An underpass involves constructing a tunnel beneath the flood-prone area, similar to a subway. It suffers from the same disadvantages as a subway, including higher costs and potential issues with water infiltration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an embankment is the most suitable option for building a highway in areas prone to flooding. It provides the necessary elevation, stability, and accessibility while being cost-effective. Other options such as subways, overpasses, or underpasses may have their advantages, but an embankment offers the best combination of functionality and practicality in such situations.
Introduction:
In areas prone to flooding, it is crucial to design and construct highways in a way that allows for the passage of floodwater without causing damage to the road or hindering the flow of water. One of the most effective methods for achieving this is by building the highway on an embankment.
Embankment:
An embankment is an elevated mound of earth or rock that is constructed to raise the level of a road or railway track above the surrounding ground. It is typically built using compacted soil or other suitable materials to provide a stable foundation for the highway.
Advantages of an embankment:
- Elevation: By constructing the highway on an embankment, it is raised above the flood level, ensuring that floodwater can pass beneath it without causing any obstruction.
- Stability: The embankment provides a stable base for the highway, preventing it from being washed away or damaged during floods.
- Drainage: Embankments are designed with proper slope and drainage systems to ensure that water does not accumulate on the road surface, reducing the risk of hydroplaning.
- Accessibility: Unlike other options such as subways or underpasses, an embankment allows for continuous access to the highway during normal conditions, minimizing disruptions to traffic flow.
- Cost-effectiveness: Building an embankment is generally more cost-effective compared to constructing subways or underpasses, as it requires less excavation and construction materials.
Disadvantages of other options:
- Subway: A subway involves constructing a tunnel beneath the flood-prone area. However, building and maintaining a subway can be expensive and may require complex engineering solutions to ensure water does not enter the tunnel during floods.
- Overpass: An overpass involves constructing a bridge over the flood-prone area. While this option allows for the passage of floodwater, it may require a significant investment in terms of construction materials and engineering design.
- Underpass: An underpass involves constructing a tunnel beneath the flood-prone area, similar to a subway. It suffers from the same disadvantages as a subway, including higher costs and potential issues with water infiltration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an embankment is the most suitable option for building a highway in areas prone to flooding. It provides the necessary elevation, stability, and accessibility while being cost-effective. Other options such as subways, overpasses, or underpasses may have their advantages, but an embankment offers the best combination of functionality and practicality in such situations.
After the abrasion test, the sample is passed through which sieve?- a)2.36 mm
- b)1.45 mm
- c)1.7 mm
- d)2.5 mm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
After the abrasion test, the sample is passed through which sieve?
a)
2.36 mm
b)
1.45 mm
c)
1.7 mm
d)
2.5 mm
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
The sample after removing from the abrasion machine is passed through 1.7 mm sieve and the weight is noted down. 2.36 mm is used in the impact and crushing test on aggregates.
The highest CBR number is required for __________- a)Pavement
- b)Sub grade
- c)Sub base
- d)Base
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The highest CBR number is required for __________
a)
Pavement
b)
Sub grade
c)
Sub base
d)
Base
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
CBR number decreases with an increase in height, the soil requires the highest CBR and the pavement requires the lowest CBR.
What is the weight of the charge used in the Los Angeles abrasion test?- a)416.67 mg
- b)450.55 mg
- c)450.55 g
- d)416.67 g
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the weight of the charge used in the Los Angeles abrasion test?
a)
416.67 mg
b)
450.55 mg
c)
450.55 g
d)
416.67 g
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
As per IS 2386 part 4, the steel balls are used as the charge for the test. They are of 48 mm diameter and each ball weighs around 416.67 g. Depending on the grading used for the test, the number of balls used changes.
Which one of the following causes raveling in bituminous pavement?- a)Use of soft bitumen
- b)Use of open graded aggregates
- c)Excessive bitumen content
- d)Low bitumen content
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following causes raveling in bituminous pavement?
a)
Use of soft bitumen
b)
Use of open graded aggregates
c)
Excessive bitumen content
d)
Low bitumen content
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Revelling: It is characterized by progressive disintegration of the surface due to the failure of the binder to hold the material together.
The following are the causes of raveling:
The following are the causes of raveling:
- Insufficient binder in the mix.
- Inadequate compaction during construction.
- Construction during wet weather leads to the stripping of binder from aggregate.
- Construction during cold weather results in fracture, crushing, and opening of new faces.
- over-heating of mix or the binder.
- Improper coating of aggregates by binder
The highest CBR number is required for __________- a)Pavement
- b)Sub grade
- c)Sub base
- d)Base
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The highest CBR number is required for __________
a)
Pavement
b)
Sub grade
c)
Sub base
d)
Base
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
CBR number decreases with an increase in height, the soil requires the highest CBR and the pavement requires the lowest CBR.
The indirect method of determining viscosity is not applicable to which of the below?- a)Tar
- b)Cut-back bitumen
- c)Modified bitumen
- d)Bitumen emulsion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The indirect method of determining viscosity is not applicable to which of the below?
a)
Tar
b)
Cut-back bitumen
c)
Modified bitumen
d)
Bitumen emulsion

|
Tanishq Nair answered |
Indirect Method of Determining Viscosity
The indirect method of determining viscosity involves measuring certain properties or characteristics of a substance and using them to determine its viscosity. This method is commonly used for substances such as tar, cut-back bitumen, bitumen emulsion, and modified bitumen. However, it is not applicable to modified bitumen.
Explanation
1. Tar
Tar is a viscous, black, and sticky substance that is obtained by the destructive distillation of organic materials such as wood, coal, or petroleum. The viscosity of tar can be determined indirectly by measuring its flow properties, such as its ability to spread or flow on a surface. This can be done using various tests such as the ring and ball test or the flow cup test.
2. Cut-back Bitumen
Cut-back bitumen is a type of bitumen that has been diluted or "cut back" with a volatile solvent, such as kerosene or gasoline, to reduce its viscosity and improve its workability. The viscosity of cut-back bitumen can be determined indirectly by measuring its penetration or softening point using standardized tests such as the penetration test or the softening point test.
3. Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is a mixture of bitumen (asphalt) and water, stabilized with an emulsifying agent to form a homogeneous liquid. The viscosity of bitumen emulsion can be determined indirectly by measuring its viscosity using a viscometer, such as a rotational or capillary viscometer. The viscosity of bitumen emulsion is an important parameter that affects its ability to coat and bind aggregates in road construction.
4. Modified Bitumen
Modified bitumen is a type of bitumen that has been modified or improved by the addition of certain polymers or additives to enhance its performance characteristics, such as elasticity, durability, or resistance to aging and deformation. The viscosity of modified bitumen cannot be accurately determined using the indirect method because the presence of polymers or additives can significantly alter its flow properties. Instead, the viscosity of modified bitumen is usually determined using specific tests or methods designed for modified bitumen, such as the rotational viscometer test or the dynamic shear rheometer test.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the indirect method of determining viscosity is applicable to substances such as tar, cut-back bitumen, and bitumen emulsion. However, it is not applicable to modified bitumen due to the presence of polymers or additives that can alter its flow properties. To accurately determine the viscosity of modified bitumen, specific tests or methods designed for modified bitumen should be used.
The indirect method of determining viscosity involves measuring certain properties or characteristics of a substance and using them to determine its viscosity. This method is commonly used for substances such as tar, cut-back bitumen, bitumen emulsion, and modified bitumen. However, it is not applicable to modified bitumen.
Explanation
1. Tar
Tar is a viscous, black, and sticky substance that is obtained by the destructive distillation of organic materials such as wood, coal, or petroleum. The viscosity of tar can be determined indirectly by measuring its flow properties, such as its ability to spread or flow on a surface. This can be done using various tests such as the ring and ball test or the flow cup test.
2. Cut-back Bitumen
Cut-back bitumen is a type of bitumen that has been diluted or "cut back" with a volatile solvent, such as kerosene or gasoline, to reduce its viscosity and improve its workability. The viscosity of cut-back bitumen can be determined indirectly by measuring its penetration or softening point using standardized tests such as the penetration test or the softening point test.
3. Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is a mixture of bitumen (asphalt) and water, stabilized with an emulsifying agent to form a homogeneous liquid. The viscosity of bitumen emulsion can be determined indirectly by measuring its viscosity using a viscometer, such as a rotational or capillary viscometer. The viscosity of bitumen emulsion is an important parameter that affects its ability to coat and bind aggregates in road construction.
4. Modified Bitumen
Modified bitumen is a type of bitumen that has been modified or improved by the addition of certain polymers or additives to enhance its performance characteristics, such as elasticity, durability, or resistance to aging and deformation. The viscosity of modified bitumen cannot be accurately determined using the indirect method because the presence of polymers or additives can significantly alter its flow properties. Instead, the viscosity of modified bitumen is usually determined using specific tests or methods designed for modified bitumen, such as the rotational viscometer test or the dynamic shear rheometer test.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the indirect method of determining viscosity is applicable to substances such as tar, cut-back bitumen, and bitumen emulsion. However, it is not applicable to modified bitumen due to the presence of polymers or additives that can alter its flow properties. To accurately determine the viscosity of modified bitumen, specific tests or methods designed for modified bitumen should be used.
Bitumen is a by-product of __________- a)Wood
- b)Petroleum
- c)Kerosene
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bitumen is a by-product of __________
a)
Wood
b)
Petroleum
c)
Kerosene
d)
Coal
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Bitumen is obtained by burning the petroleum at high temperatures, it is mostly used in the construction of flexible pavements.
Softening test was performed on a bitumen sample and it was found out to be 62°. Which grade does it belong to?- a)VG 10
- b)VG 20
- c)VG 30
- d)VG 40
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Softening test was performed on a bitumen sample and it was found out to be 62°. Which grade does it belong to?
a)
VG 10
b)
VG 20
c)
VG 30
d)
VG 40

|
Nilesh Kapoor answered |
The softening test was performed on a bitumen sample, and the result obtained was a softening point of 62.
Which IS code is referred to for conducting the float test for bitumen?- a)IS 1209
- b)IS 1211
- c)IS 1210
- d)IS 1212
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which IS code is referred to for conducting the float test for bitumen?
a)
IS 1209
b)
IS 1211
c)
IS 1210
d)
IS 1212

|
Aditi Chakraborty answered |
Float Test for Bitumen
The float test is a critical procedure in the evaluation of bitumen, primarily used to assess its consistency and viscous properties. The relevant Indian Standard (IS) code for conducting this test is IS 1210.
Purpose of the Float Test
- The float test measures the time taken for a specific weight to sink through a column of bitumen.
- It provides insights into the temperature susceptibility and the flow characteristics of the material.
IS 1210 Specification
- IS 1210 specifically outlines the method for determining the consistency of bituminous materials using the float test.
- It details the apparatus, procedure, and interpretation of results to ensure uniformity and reliability in testing.
Importance in Civil Engineering
- Understanding the properties of bitumen is essential in construction and road paving.
- The results from the float test help engineers select the appropriate grade of bitumen for specific environmental and load conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, IS 1210 is the designated standard for conducting the float test for bitumen. This standard ensures that the testing process is standardized, yielding reliable results that are crucial for the effective application of bituminous materials in civil engineering projects.
The float test is a critical procedure in the evaluation of bitumen, primarily used to assess its consistency and viscous properties. The relevant Indian Standard (IS) code for conducting this test is IS 1210.
Purpose of the Float Test
- The float test measures the time taken for a specific weight to sink through a column of bitumen.
- It provides insights into the temperature susceptibility and the flow characteristics of the material.
IS 1210 Specification
- IS 1210 specifically outlines the method for determining the consistency of bituminous materials using the float test.
- It details the apparatus, procedure, and interpretation of results to ensure uniformity and reliability in testing.
Importance in Civil Engineering
- Understanding the properties of bitumen is essential in construction and road paving.
- The results from the float test help engineers select the appropriate grade of bitumen for specific environmental and load conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, IS 1210 is the designated standard for conducting the float test for bitumen. This standard ensures that the testing process is standardized, yielding reliable results that are crucial for the effective application of bituminous materials in civil engineering projects.
In a standard California bearing ratio test (sample height is 125 mm), the difference between the initial and final dial gauge readings is found to be 0.125 mm. What is the expansion ratio of this soil?- a)10
- b)100
- c)0.1
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard California bearing ratio test (sample height is 125 mm), the difference between the initial and final dial gauge readings is found to be 0.125 mm. What is the expansion ratio of this soil?
a)
10
b)
100
c)
0.1
d)
1

|
Rashi Shah answered |
Standard California Bearing Ratio Test
The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test is a penetration test used to evaluate the strength of subgrade soil. It is commonly used in geotechnical engineering to assess the quality and load-bearing capacity of soil for road and pavement construction.
Expansion Ratio
The expansion ratio is a measure of the increase in volume or height of the soil specimen during the CBR test. It is calculated by dividing the difference between the initial and final dial gauge readings by the initial dial gauge reading, and then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
Given Information
- Sample height (H) = 125 mm
- Difference between initial and final dial gauge readings (∆h) = 0.125 mm
Calculation
The expansion ratio (ER) can be calculated using the formula:
ER = (∆h / H) * 100
Substituting the given values:
ER = (0.125 / 125) * 100
ER = 0.001 * 100
ER = 0.1
Therefore, the expansion ratio of the soil sample is 0.1 or 10%.
Interpretation
The expansion ratio of 0.1 indicates that the soil specimen expanded by 10% of its initial height during the CBR test. This expansion is typically caused by the compaction of the soil under the applied load.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option C) 0.1. The expansion ratio of the soil, calculated using the formula (∆h / H) * 100, is 0.1 or 10%.
The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test is a penetration test used to evaluate the strength of subgrade soil. It is commonly used in geotechnical engineering to assess the quality and load-bearing capacity of soil for road and pavement construction.
Expansion Ratio
The expansion ratio is a measure of the increase in volume or height of the soil specimen during the CBR test. It is calculated by dividing the difference between the initial and final dial gauge readings by the initial dial gauge reading, and then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
Given Information
- Sample height (H) = 125 mm
- Difference between initial and final dial gauge readings (∆h) = 0.125 mm
Calculation
The expansion ratio (ER) can be calculated using the formula:
ER = (∆h / H) * 100
Substituting the given values:
ER = (0.125 / 125) * 100
ER = 0.001 * 100
ER = 0.1
Therefore, the expansion ratio of the soil sample is 0.1 or 10%.
Interpretation
The expansion ratio of 0.1 indicates that the soil specimen expanded by 10% of its initial height during the CBR test. This expansion is typically caused by the compaction of the soil under the applied load.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option C) 0.1. The expansion ratio of the soil, calculated using the formula (∆h / H) * 100, is 0.1 or 10%.
What is the most common waste material used in construction?- a)Fly ash
- b)Slag
- c)Pozzolona
- d)Rice husk
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the most common waste material used in construction?
a)
Fly ash
b)
Slag
c)
Pozzolona
d)
Rice husk
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Fly ash is an industrial waste obtained from the thermal plants, it has been mandatory to use the fly ash in bricks.
Rapid curing cutback is produced by blending bitumen with- a)kerosene
- b)benzene
- c)petrol
- d)diesel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rapid curing cutback is produced by blending bitumen with
a)
kerosene
b)
benzene
c)
petrol
d)
diesel
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Cutback bitumen:
(i) Cutback bitumen is bitumen with less viscosity which, is achieved by the addition of volatile diluent. Hence, to increase the fluidity of the bitumen binder at low temperature the binder is blended with a volatile solvent.
(ii) The viscosity of the cutback bitumen and the rate at which hardness on the road depends on the characteristics and quantity of both bitumen and volatile oil used as diluent.
(iii) Cutback bitumen is available in three types:
(i) Cutback bitumen is bitumen with less viscosity which, is achieved by the addition of volatile diluent. Hence, to increase the fluidity of the bitumen binder at low temperature the binder is blended with a volatile solvent.
(ii) The viscosity of the cutback bitumen and the rate at which hardness on the road depends on the characteristics and quantity of both bitumen and volatile oil used as diluent.
(iii) Cutback bitumen is available in three types:
- Rapid curing (RC) → In this bitumen is fluxed with Naptha/gasoline, petroleum
- Medium curing (MC) → In this bitumen is fluxed with Kerosene or high diesel oil
- Slow Curing (SC) → In this bitumen is fluxed with High boiling point gas oil
Additional Information
(i) MC and SC cutback are used for priming and viscosity increases as the grade increases like RC-0, RC-1, RC-2.
(ii) RT-1 is lowest viscosity used for surface painting but RT-4 may be used for premix in macadam.
(iii) RT-5 is used for grouting which has highest viscosity.
(iv) MC-2 will be thicker than MC-1 but RC-5 and SC-5 will have same viscosity.
(i) MC and SC cutback are used for priming and viscosity increases as the grade increases like RC-0, RC-1, RC-2.
(ii) RT-1 is lowest viscosity used for surface painting but RT-4 may be used for premix in macadam.
(iii) RT-5 is used for grouting which has highest viscosity.
(iv) MC-2 will be thicker than MC-1 but RC-5 and SC-5 will have same viscosity.
For places where there is a passage of flood water then the highway has to be built on __________- a)Embankment
- b)Subway
- c)Overpass
- d)Underpass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For places where there is a passage of flood water then the highway has to be built on __________
a)
Embankment
b)
Subway
c)
Overpass
d)
Underpass

|
Raksha Nair answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
When planning the construction of a highway, it is important to consider the potential risks and challenges posed by natural disasters such as flooding. In areas where there is a passage of flood water, the highway should be built on an embankment. This choice is made to ensure the safety and functionality of the road during flood events. Let's explore the reasons behind this decision.
Reasons for building the highway on an embankment:
1. Flood protection: An embankment acts as a barrier between the highway and floodwaters, protecting the road from damage caused by inundation. It prevents floodwater from directly reaching the road, reducing the risk of erosion, subsidence, and structural damage.
2. Elevation: By constructing the highway on an embankment, its elevation is raised above the floodplain level. This elevation helps to keep the road surface above the water level during flood events, ensuring that it remains passable and functional.
3. Drainage: Embankments are designed to include proper drainage systems, such as culverts or ditches, which allow water to flow away from the road efficiently. These drainage measures help to prevent waterlogging or ponding on the highway, maintaining its usability even during heavy rainfall or flooding.
4. Stability: Embankments are engineered to provide stability and strength to the highway. They are constructed using suitable materials, compacted in layers to withstand the weight of the road and the forces exerted by floodwaters. This ensures that the highway remains intact and safe for vehicles to travel on, even in challenging flood conditions.
5. Cost-effectiveness: Building a highway on an embankment is often a more cost-effective solution compared to other alternatives such as constructing subways, overpasses, or underpasses. Embankments require less complex construction methods and materials, resulting in lower construction costs and reduced maintenance expenses.
Conclusion:
Constructing a highway on an embankment in areas prone to flooding is the most suitable option due to its flood protection capabilities, elevation advantages, efficient drainage systems, stability, and cost-effectiveness. By considering these factors, a properly designed and constructed embankment can ensure the safety, functionality, and longevity of the highway in flood-prone regions.
Introduction:
When planning the construction of a highway, it is important to consider the potential risks and challenges posed by natural disasters such as flooding. In areas where there is a passage of flood water, the highway should be built on an embankment. This choice is made to ensure the safety and functionality of the road during flood events. Let's explore the reasons behind this decision.
Reasons for building the highway on an embankment:
1. Flood protection: An embankment acts as a barrier between the highway and floodwaters, protecting the road from damage caused by inundation. It prevents floodwater from directly reaching the road, reducing the risk of erosion, subsidence, and structural damage.
2. Elevation: By constructing the highway on an embankment, its elevation is raised above the floodplain level. This elevation helps to keep the road surface above the water level during flood events, ensuring that it remains passable and functional.
3. Drainage: Embankments are designed to include proper drainage systems, such as culverts or ditches, which allow water to flow away from the road efficiently. These drainage measures help to prevent waterlogging or ponding on the highway, maintaining its usability even during heavy rainfall or flooding.
4. Stability: Embankments are engineered to provide stability and strength to the highway. They are constructed using suitable materials, compacted in layers to withstand the weight of the road and the forces exerted by floodwaters. This ensures that the highway remains intact and safe for vehicles to travel on, even in challenging flood conditions.
5. Cost-effectiveness: Building a highway on an embankment is often a more cost-effective solution compared to other alternatives such as constructing subways, overpasses, or underpasses. Embankments require less complex construction methods and materials, resulting in lower construction costs and reduced maintenance expenses.
Conclusion:
Constructing a highway on an embankment in areas prone to flooding is the most suitable option due to its flood protection capabilities, elevation advantages, efficient drainage systems, stability, and cost-effectiveness. By considering these factors, a properly designed and constructed embankment can ensure the safety, functionality, and longevity of the highway in flood-prone regions.
The result for soundness test is expressed in terms of ______- a)Percentage density gain
- b)Percentage density loss
- c)Percentage weight loss
- d)Percentage weight gain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The result for soundness test is expressed in terms of ______
a)
Percentage density gain
b)
Percentage density loss
c)
Percentage weight loss
d)
Percentage weight gain
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
To conduct the soundness test, the aggregates are subjected to solutions of sodium sulphate or magnesium sulphate as per IS 2386. After cycles of immersion and drying, the loss in weight of aggregate is noted down in percentage and that gives the soundness result.
Name the test conducted on bitumen using the Pensky-Martens closed cup apparatus?- a)Specific gravity test
- b)Softening point test
- c)Viscosity test
- d)Flash and Fire point test
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the test conducted on bitumen using the Pensky-Martens closed cup apparatus?
a)
Specific gravity test
b)
Softening point test
c)
Viscosity test
d)
Flash and Fire point test
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Various tests conducted on bitumen for testing its various properties are as follows:
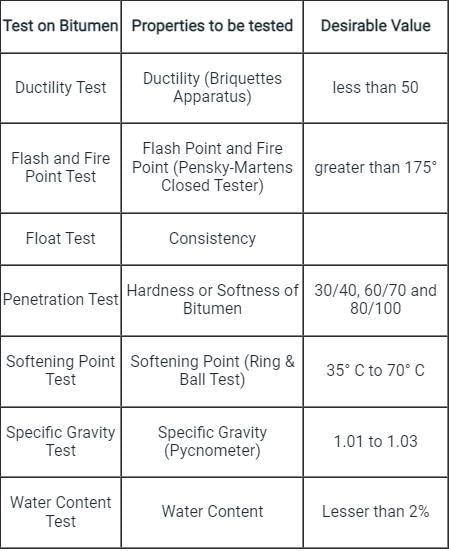
Marshal test is used for designing the bituminous concrete for pavement construction, Beckenham Beam Method is used to determine the deflection of the pavement slab.

Marshal test is used for designing the bituminous concrete for pavement construction, Beckenham Beam Method is used to determine the deflection of the pavement slab.
_____ mould is used for conducting the ductility test.- a)Block
- b)Briquette
- c)Urethane
- d)Latex
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ mould is used for conducting the ductility test.
a)
Block
b)
Briquette
c)
Urethane
d)
Latex
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Briquette mould is metallic and can be split into two halves. Bitumen is filled in the mould after it is fixed properly. Block mould is made of silicone and can be used for casting items. Urethane mould and latex mould can be used for casting concrete or plastic.
Bitumen is obtained from- a)Natural organic base
- b)Synthetic
- c)Petroleum
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bitumen is obtained from
a)
Natural organic base
b)
Synthetic
c)
Petroleum
d)
Coal
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Bitumen
- Bituminous materials consist of bitumen which is a black or dark-colored solid or viscous cementitious substance consisting chiefly of high molecular weight hydrocarbons derived from the distillation of petroleum or natural asphalt. It has adhesive properties and is soluble in carbon disulfide.
- Tars are residues from the destructive distillation of organic substances such as coal, wood, or petroleum and are temperature sensitive than bitumen.
- Bitumen is soluble in petroleum oils where, unlike tar.
Which of the below test – procedure pairs are matched correctly?- a)Impact test – 2 layers tamped 25 times each
- b)Angularity number – 3 layers tamped 100 times each
- c)Bulk density – 2 layers tamped 25 times each
- d)Crushing value – 3 layers tamped 50 times each
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the below test – procedure pairs are matched correctly?
a)
Impact test – 2 layers tamped 25 times each
b)
Angularity number – 3 layers tamped 100 times each
c)
Bulk density – 2 layers tamped 25 times each
d)
Crushing value – 3 layers tamped 50 times each
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
As per IS 2386 part 3, in the impact test, the sample is filled in three layers and given 25 tamping each. As per IS 2386 part 1, the sample is filled in three layers and tamped 100 times each for the angularity number. As per IS 2386 part 3, in the bulk density test, the sample is filled in three layers and given 25 tamping each. As per IS 2386 part4, the sample for crushing test is filled in three layers and tamped 25 times each.
The materials not included in highway construction are __________- a)Stone
- b)Dust
- c)Soil
- d)Petrol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The materials not included in highway construction are __________
a)
Stone
b)
Dust
c)
Soil
d)
Petrol
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Petrol is not used directly in highway construction, but by-product like bitumen is used. Stone, dust and soil may be used in subgrade and base.
What is used as a charge in the Dorry abrasion test?- a)Sand
- b)Steel balls
- c)Steel shavings
- d)Crushed gravel
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is used as a charge in the Dorry abrasion test?
a)
Sand
b)
Steel balls
c)
Steel shavings
d)
Crushed gravel
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Dorry abrasion test was used way back and is not used these days. The charge used for the test was sand. It was let into the machine to cause abrasive action. Crushed gravel cannot be used as it is the same material and it would cause attrition, not abrasion.
For how long is the needle allowed to penetrate in the penetration test?- a)5 seconds
- b)5 minutes
- c)10 seconds
- d)10 minutes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For how long is the needle allowed to penetrate in the penetration test?
a)
5 seconds
b)
5 minutes
c)
10 seconds
d)
10 minutes
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The guidelines for the penetration test have been laid down in IS 1203. As per the same, the time allotted to the needle for penetration into the sample is 5 seconds. There are machines that automatically stop the penetration at the end of 5 seconds.
The combined index is obtained by ______ the flakiness and elongation index.- a)Subtracting
- b)Adding
- c)Taking average
- d)Multiplying
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The combined index is obtained by ______ the flakiness and elongation index.
a)
Subtracting
b)
Adding
c)
Taking average
d)
Multiplying
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Combined index is obtained as the sum of both flakiness and elongation index. The sample is first subjected to flakiness test, then the non-flaky particles are subjected to the elongation test. Their indices are found out and added together.
Chapter doubts & questions for Highway Materials & Testing - Transportation Engineering 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Highway Materials & Testing - Transportation Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Transportation Engineering
27 videos|118 docs|58 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









