All Exams >
Class 12 >
Chemistry Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Solid State (Old NCERT) for Class 12 Exam
Among the following solids, which one shows the strongest bonding?
- a)Metallic solids
- b)Ionic solids
- c)Covalent solids
- d)Molecular solids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following solids, which one shows the strongest bonding?
a)
Metallic solids
b)
Ionic solids
c)
Covalent solids
d)
Molecular solids
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
1. Covalent (or network) solids are extended-lattice compounds, in which each atom is covalently bonded to its nearest neighbors. Because there are no delocalized electrons, covalent solids do not conduct electricity.
2. The rearranging or breaking of covalent bonds requires large amounts of energy; therefore, covalent solids have high melting points.
3. Covalent bonds are extremely strong, so covalent solids are very hard. Generally, covalent solids are insoluble due to the difficulty of solvating very large molecules.
4. Diamond is the hardest material known, while cubic boron nitride (BN) is the second-hardest. Silicon carbide (SiC) is very structurally complex and has at least 70 crystalline forms.
Which state of matter is incompressible?
- a)Both B and C
- b)Liquid
- c)Solid
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which state of matter is incompressible?
a)
Both B and C
b)
Liquid
c)
Solid
d)
None of these
|
|
Shanaya Choudhary answered |
Solids form closed packed structure with negligible intermolecular space. So, they do not change their shape in presence of external pressure. Liquids have very less intermolecular spaces so even they are resistant to external pressure and does not change their shape hence are incompressible.
Note: Due to less intermolecular force of attraction, they acquire the shape of the container in which they are kept. The volume of the liquid doesn't change with pressure. Thus making them practically incompressible.
What are the basic particles of ice crystals?
- a)Atoms
- b)Anions
- c)Cations
- d)Molecules
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the basic particles of ice crystals?
a)
Atoms
b)
Anions
c)
Cations
d)
Molecules
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
-
Basic particle forming ice crystals are water molecules. It is a molecular crystal.
-
Water molecules are arranged in a cage-like structure orderly array resulting in a crystalline structure.
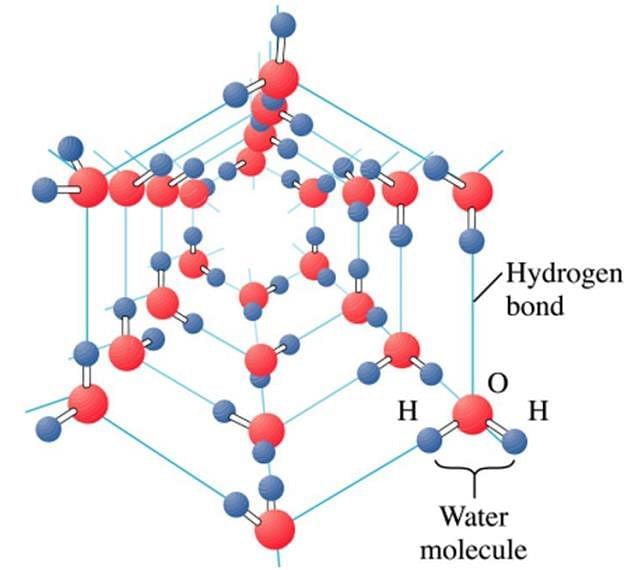
- Crystalline compounds are made up of particles or molecules that are organized in a specific order, such as ice particles or water molecules, resulting in an ordered structure known as a crystalline compound.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 3 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
In which of the following primitive cells axial distances or edge lengths (a, b, c)are different?
- a)Orthorhombic
- b)Tetragonal
- c)Monoclinic
- d)Triclinic
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 3 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
In which of the following primitive cells axial distances or edge lengths (a, b, c)are different?
This section contains 3 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
In which of the following primitive cells axial distances or edge lengths (a, b, c)are different?
a)
Orthorhombic
b)
Tetragonal
c)
Monoclinic
d)
Triclinic
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Correct Answer :- a,c,d
Explanation : orthorhombic : a ≠ b ≠ c, γ = 90
monoclinic : a ≠ b ≠ c, γ = 90, b ≠ 90
triclinic : a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ
Which of the following is a covalent crystal?
- a)Ice
- b)Rock salt
- c)Quartz
- d)Dry ice
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a covalent crystal?
a)
Ice
b)
Rock salt
c)
Quartz
d)
Dry ice

|
Aarya Dasgupta answered |
- Quartz (SiO2), or silicon dioxide also known as silica has a giant covalent structure. In SiO2, each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms.
- Each oxygen atom is covalently bonded to two silicon atoms and has an extended covalent structure similar to diamond.
- The overall ratio is two oxygen atoms to each silicon atom, giving the formula SiO2,
- Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:What are the basic constituent particles forming diamond crystals?
- A:
Molecules
- B:
Cations
- C:
Anions
- D:
Atoms
The answer is d.
What are the basic constituent particles forming diamond crystals?
Molecules
Cations
Anions
Atoms
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In diamond, carbon atoms are joined together by strong covalent bonds tetrahedrally.
In which of the following solids, ions of opposite charges are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction?
- a)Metallic solids
- b)Ionic solids
- c)Non metallic solids
- d)Covalent solids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following solids, ions of opposite charges are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction?
a)
Metallic solids
b)
Ionic solids
c)
Non metallic solids
d)
Covalent solids
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- Ionic solids or compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom.
- Hence there is always the formation of anion and cation due to opposite charges electrostatic force of attraction formed between them which holds them together.
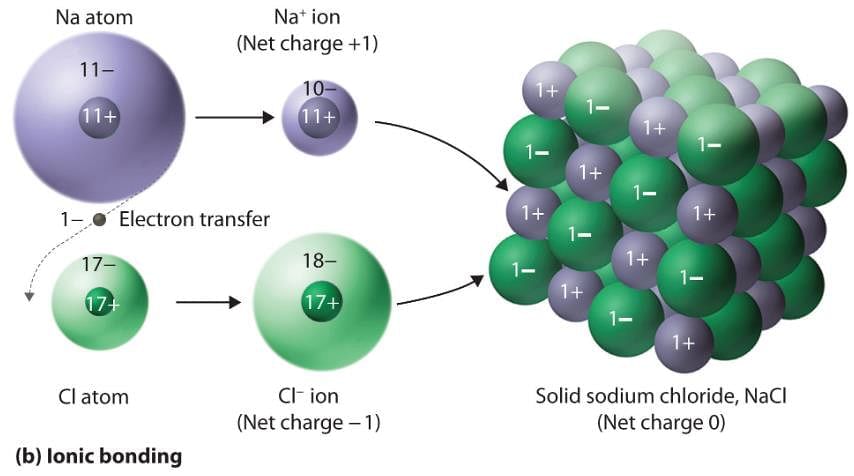
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Which of the following crystalline solids have highest melting point?
- a)Diamond
- b)Zinc
- c)Sulphur
- d)Ice
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following crystalline solids have highest melting point?
a)
Diamond
b)
Zinc
c)
Sulphur
d)
Ice
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
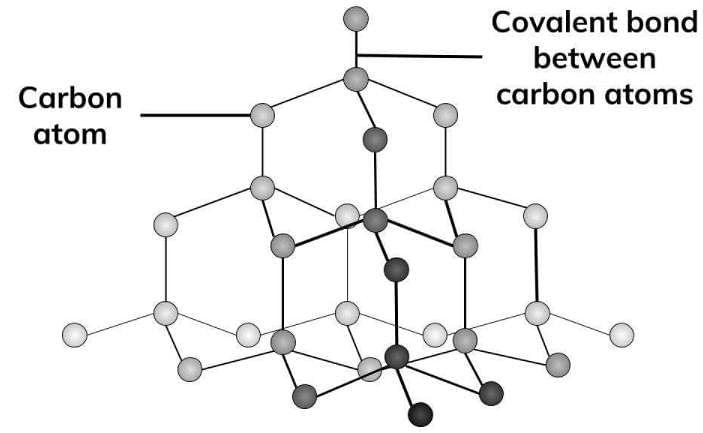
Diamond has a very high melting point (almost 4000°C) due to very strong carbon-carbon covalent bonds having to be broken throughout the structure before melting occurs.
Explanation:
- Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a diamond.
- A lot of energy is needed to separate the atoms.
- This is because covalent bonds are strong.
- This is the reason why diamond has a high melting point.
Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
- a)Quartz Glass(SiO2)
- b)Chrome Alum
- c)Silicon Carbide(SiC)
- d) Graphite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
a)
Quartz Glass(SiO2)
b)
Chrome Alum
c)
Silicon Carbide(SiC)
d)
Graphite
|
|
Abhijeet Sharma answered |
Amorphous Solid: Definition
An amorphous solid is a solid material that lacks a definite long-range ordered structure, meaning the molecules or atoms are arranged randomly. They are also known as non-crystalline solids.
Examples of Amorphous Solids
a) Quartz Glass (SiO2): Quartz glass is an amorphous solid that is formed by the rapid cooling of molten quartz. It has a random arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms, which prevents the formation of a regular crystal lattice.
b) Chrome Alum: Chrome alum is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
c) Silicon Carbide (SiC): Silicon carbide is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
d) Graphite: Graphite is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
Conclusion
Among the given options, only quartz glass (SiO2) is an example of an amorphous solid, while the other options are crystalline solids with well-defined structures.
An amorphous solid is a solid material that lacks a definite long-range ordered structure, meaning the molecules or atoms are arranged randomly. They are also known as non-crystalline solids.
Examples of Amorphous Solids
a) Quartz Glass (SiO2): Quartz glass is an amorphous solid that is formed by the rapid cooling of molten quartz. It has a random arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms, which prevents the formation of a regular crystal lattice.
b) Chrome Alum: Chrome alum is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
c) Silicon Carbide (SiC): Silicon carbide is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
d) Graphite: Graphite is a crystalline solid that has a well-defined structure. Therefore, it is not an example of an amorphous solid.
Conclusion
Among the given options, only quartz glass (SiO2) is an example of an amorphous solid, while the other options are crystalline solids with well-defined structures.
Which of the following properties is generally exhibited by amorphous solids?- a)Anisotropy
- b)Glass-transition
- c)Equal strength of all bonds
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following properties is generally exhibited by amorphous solids?
a)
Anisotropy
b)
Glass-transition
c)
Equal strength of all bonds
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Shraddha Dey answered |
Due to random organization of particles, amorphous solids have same physical properties along all directions, or are isotropic. Random organization of particles also results in unequal bond strengths. Upon cooling, amorphous solids turn into brittle glass-like state from a flexible rubber-like state. This is called glass-transition.
The crystalline solids are:- a)Enantiotropic
- b)Atropic
- c)Isotropic
- d)anisotropic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The crystalline solids are:
a)
Enantiotropic
b)
Atropic
c)
Isotropic
d)
anisotropic
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Some crystalline solids are anisotropic because despite showing periodicity they are not exactly the same in all directions. It all depends on the symmetry of the unit cell of the crystal. If its size in the x, y and z direction is the same, it would be isotropic and anisotropic otherwise.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Dry ice is an example of:- A:ionic solid
- B:covalent solid
- C:metallic solid
- D:molecular solid
The answer is d.
Dry ice is an example of:
A:
ionic solid
B:
covalent solid
C:
metallic solid
D:
molecular solid

|
Shivam Upadhyay answered |
It is molecular solid because it is made up of molecules of carbon dioxide and the force of attraction between co2 ,co2 is dispersion force
If an element crystallizes as a simple cube, what is the volume of an element provided its density is 1.5 g/cm3 and atomic mass of the element is 63?- a)69.7 x 10 -23 cm3
- b)6.97 x 10 -23 cm3
- c)63 x 10 -23 cm3
- d)5.97 x 10 -23 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an element crystallizes as a simple cube, what is the volume of an element provided its density is 1.5 g/cm3 and atomic mass of the element is 63?
a)
69.7 x 10 -23 cm3
b)
6.97 x 10 -23 cm3
c)
63 x 10 -23 cm3
d)
5.97 x 10 -23 cm3
|
|
Sankar Banerjee answered |
Given:
Density of the element = 1.5 g/cm³
Atomic mass of the element = 63
To find:
Volume of the element if it crystallizes as a simple cube
Solution:
1. Calculation of the edge length of the cube:
In a simple cube, the atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with one atom at each corner of the cube.
The edge length of the cube can be calculated using the formula:
a = (4/3 πr³)^(1/3)
where,
a = edge length of the cube
r = radius of the atom = (atomic mass/molar mass)^(1/3)
Here,
molar mass of the element = atomic mass
r = (63/6.022 x 10²³)^(1/3) = 1.27 x 10^-8 cm
Therefore,
a = (4/3 π(1.27 x 10^-8)³)^(1/3) = 3.57 x 10^-8 cm
2. Calculation of the volume of the cube:
The volume of the cube can be calculated using the formula:
V = a³
where,
V = volume of the cube
a = edge length of the cube
Substituting the value of a, we get:
V = (3.57 x 10^-8)³ = 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³
3. Comparison with the given options:
The calculated volume of the element is 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³, which matches with option (B).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B) 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³.
Density of the element = 1.5 g/cm³
Atomic mass of the element = 63
To find:
Volume of the element if it crystallizes as a simple cube
Solution:
1. Calculation of the edge length of the cube:
In a simple cube, the atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with one atom at each corner of the cube.
The edge length of the cube can be calculated using the formula:
a = (4/3 πr³)^(1/3)
where,
a = edge length of the cube
r = radius of the atom = (atomic mass/molar mass)^(1/3)
Here,
molar mass of the element = atomic mass
r = (63/6.022 x 10²³)^(1/3) = 1.27 x 10^-8 cm
Therefore,
a = (4/3 π(1.27 x 10^-8)³)^(1/3) = 3.57 x 10^-8 cm
2. Calculation of the volume of the cube:
The volume of the cube can be calculated using the formula:
V = a³
where,
V = volume of the cube
a = edge length of the cube
Substituting the value of a, we get:
V = (3.57 x 10^-8)³ = 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³
3. Comparison with the given options:
The calculated volume of the element is 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³, which matches with option (B).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B) 6.97 x 10^-23 cm³.
The vacant space in b.c.c. unit cell is-- a)32%
- b)10%
- c)23%
- d)46%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The vacant space in b.c.c. unit cell is-
a)
32%
b)
10%
c)
23%
d)
46%
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
B.C.C. has the packing efficieny is 68%
so the vacant space in BCCk is 32%
so the vacant space in BCCk is 32%
How many types of primitive unit cells are there?
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
How many types of primitive unit cells are there?
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Primitive unit cells are
(i) Cubic
(ii) Tetragonal
(iii) Orthorhombic
(iv) Hexagonal
(v) Rhombohedral
(vi) Monoclinic
(vii) Triclinic
Which of the following solid is isotropic?- a)Ionic
- b)Amorphous
- c)Metallic
- d)Molecular
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solid is isotropic?
a)
Ionic
b)
Amorphous
c)
Metallic
d)
Molecular

|
Naincy Tripathi answered |
Option B is correct as the values of certain physical properties like Refractive Index DOES NOT CHANGES with change in direction of observation . Therefore amorphous solids are isotropic
Why ice is a crystalline compound?- a)Because water molecules are arranged in cage like ordered structure.
- b)Because water is condensed to form solid.
- c)Because ice melts to form water.
- d)Because water molecules are arranged in random way.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why ice is a crystalline compound?
a)
Because water molecules are arranged in cage like ordered structure.
b)
Because water is condensed to form solid.
c)
Because ice melts to form water.
d)
Because water molecules are arranged in random way.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Crystalline compounds are those in which particles/molecules are arranged in proper order as in ice particles/water molecules are arranged in a cage-like ordered manner so this ordered structure is called a crystalline compound.

Why some of the physical properties of solids show different values when measured along different directions in the same crystals?- a)Because solid crystals are anisotropic.
- b)Because solid crystals have short bond distances.
- c)Because solid crystals are isotropic.
- d)Because solid crystals are rigid.
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why some of the physical properties of solids show different values when measured along different directions in the same crystals?
a)
Because solid crystals are anisotropic.
b)
Because solid crystals have short bond distances.
c)
Because solid crystals are isotropic.
d)
Because solid crystals are rigid.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature, that is, some of their physical properties like electrical resistance or refractive index show different values when measured along different directions in the same crystals. This arises from different arrangements of particles in different directions.
Which of the following properties is NOT exhibited by metallic solids?
- a)Low Boiling Point
- b)Ductility
- c)Electrical Conductivity
- d)Malleability
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following properties is NOT exhibited by metallic solids?
a)
Low Boiling Point
b)
Ductility
c)
Electrical Conductivity
d)
Malleability
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
Low boiling point is the property which is not exhibited by metallic solids. the reason is metallic solid's atoms r bonded with strong molecular force of attraction coz of which the bond between the atoms doesn't breaks easily. Very high temp. is req. to break the bond between the atoms. though the boiling point varies from element to element. so, as a result, metallic solids have a strong molecular force of attraction, they do not have a low boiling point.
Why do metallic solids conducts electricity?- a)Due to closely packed positive ions.
- b)Due to loosely bounded particles.
- c)Due to free or delocalised electrons.
- d)Due to close packing of negative charge.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why do metallic solids conducts electricity?
a)
Due to closely packed positive ions.
b)
Due to loosely bounded particles.
c)
Due to free or delocalised electrons.
d)
Due to close packing of negative charge.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In a metal, the valence electrons are loosely held. They leave their “own” metal atoms, forming a "sea" of electrons surrounding the metal cations in the solid.
Thus, metals are good conductors of electricity.
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is [CBSE AIPMT 2012]- a)2
- b)4
- c)1
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
a)
2
b)
4
c)
1
d)
3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The total number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close packed structure is 4. Besides the body centre, there is one octahedral void at the centre of each of the 12 edges. It is surrounded by six atoms, four belonging to the same unit cell (2 on the corners and 2 on face centres) and two belonging to two adjacent unit cells. Since each edge of the cube is shared between four adjacent unit cells, so is the octahedral void located on it. Only 1/4th of each void belongs to a particular unit cell. Thus, in cubic close packed structure, octahedral void at the body-centre of the cube is 1.
12 octahedral voids located at each edge and shared between four unit cells=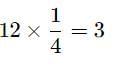
Total number of octahedral voids =4
We know that in ccp structure, each unit cell has 4 atoms. Thus, the number of octahedral voids is equal to 4/4=1.
12 octahedral voids located at each edge and shared between four unit cells=
Total number of octahedral voids =4
We know that in ccp structure, each unit cell has 4 atoms. Thus, the number of octahedral voids is equal to 4/4=1.
An element with bcc geometry has atomic mass 50 and edge length 290 pm. The density of unit cell will be- a)8.16 g/cm3
- b)6.81 g/cm3
- c)68.1 g/cm3
- d)1.86 g/cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An element with bcc geometry has atomic mass 50 and edge length 290 pm. The density of unit cell will be
a)
8.16 g/cm3
b)
6.81 g/cm3
c)
68.1 g/cm3
d)
1.86 g/cm3
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Length of the edge , a = 290 pm =290 x 10^-10 cm
Volume of unit cell = ( 290 x 10^-10 cm )^3 = 24.39 x 10^-24 cm^3
Since it is bcc arrangement,
Number of atoms in the unit cell, Z = 2
Atomic mass of the element = 50
Mass of the atom = atomic mass/ Avogadro number = M/No = 50/6.02 x 10^23
Mass of the unit cell = Z x M/No = 2 x 50/6.02 x 10^23 = 100/6.23 x 10^23
Therefore , density = mass of unit cell / volume of unit cell
= 100/6.023 x 10^23 x 24.39 x 10^-24 = 6.81 g cm^-3
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Why ancient glass becomes milky?
- A:
On ageing refractive index changes.
- B:
On ageing cracks develop.
- C:
On ageing amorphous nature increases.
- D:
On ageing crystallization occurs.
The answer is d.
Why ancient glass becomes milky?
On ageing refractive index changes.
On ageing cracks develop.
On ageing amorphous nature increases.
On ageing crystallization occurs.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Amorphous solids become crystalline on ageing e.g. ancient glass appears milky due to crystallization.
Which of the following is NOT a molecular solid?
- a)Solid SO2
- b)Solid CO2
- c)HCl
- d)Diamond
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a molecular solid?
a)
Solid SO2
b)
Solid CO2
c)
HCl
d)
Diamond
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A diamond is not considered a molecule because each carbon atom is covalently bonded with four other carbon atoms. This is what makes a diamond a network solid.
Additional Information:
- A network solid or covalent network solid (also called atomic crystalline solids) is a chemical compound (or element) in which the atoms are bonded by covalent bonds in a continuous network extending throughout the material.
- Examples of network solids include diamond with a continuous network of carbon atoms and silicon dioxide or quartz with a continuous three-dimensional network of SiO2 units.
Hydrogen bonding occurs in which type of crystalline solids?
- a)Molecular solids
- b)Ionic solids
- c)Network solids
- d)Metallic solids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding occurs in which type of crystalline solids?
a)
Molecular solids
b)
Ionic solids
c)
Network solids
d)
Metallic solids
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Molecular solids consist of atoms or molecules held to each other by dipole-dipole interactions, London dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, or any combination of these.
Additional Information: Hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of Hydrogen bonds, which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arise due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom which lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
Packing efficiency of body centred cubic unit cell is:- a)60%
- b)68%
- c)88%
- d)78%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Packing efficiency of body centred cubic unit cell is:
a)
60%
b)
68%
c)
88%
d)
78%
|
|
Shraddha Choudhury answered |
Packing efficiency of body centred cubic unit cell
Body centred cubic (BCC) unit cell is one of the three types of cubic unit cells. In this type of unit cell, the lattice points are located at the corners and in the centre of the cube. The coordination number of each lattice point is 8.
Packing efficiency is the ratio of the volume occupied by the atoms in a unit cell to the volume of the unit cell. It gives an idea of how closely the atoms are packed in the unit cell.
To calculate the packing efficiency of a BCC unit cell, we need to consider the following:
- Each corner atom contributes 1/8th of its volume to the unit cell.
- Each centre atom contributes its entire volume to the unit cell.
So, the total volume of atoms in a BCC unit cell can be calculated as:
Volume of atoms = (Number of corner atoms x Volume of each corner atom)/8 + (Number of centre atoms x Volume of each centre atom)
Volume of atoms = (8 x (4/3)πr³)/8 + (1 x (4/3)πr³)
Volume of atoms = (4/3)πr³ + (4/3)πr³
Volume of atoms = (8/3)πr³
The volume of the unit cell can be calculated as:
Volume of unit cell = a³
where a is the edge length of the cube.
Now, the packing efficiency can be calculated as:
Packing efficiency = (Volume of atoms/Volume of unit cell) x 100%
Packing efficiency = [(8/3)πr³/a³] x 100%
Packing efficiency = (8π/3√3)(r/a)³ x 100%
For a BCC unit cell, the ratio of r/a is √3/2. So, the packing efficiency can be calculated as:
Packing efficiency = (8π/3√3)(√3/2)³ x 100%
Packing efficiency = 68%
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, 68%.
Body centred cubic (BCC) unit cell is one of the three types of cubic unit cells. In this type of unit cell, the lattice points are located at the corners and in the centre of the cube. The coordination number of each lattice point is 8.
Packing efficiency is the ratio of the volume occupied by the atoms in a unit cell to the volume of the unit cell. It gives an idea of how closely the atoms are packed in the unit cell.
To calculate the packing efficiency of a BCC unit cell, we need to consider the following:
- Each corner atom contributes 1/8th of its volume to the unit cell.
- Each centre atom contributes its entire volume to the unit cell.
So, the total volume of atoms in a BCC unit cell can be calculated as:
Volume of atoms = (Number of corner atoms x Volume of each corner atom)/8 + (Number of centre atoms x Volume of each centre atom)
Volume of atoms = (8 x (4/3)πr³)/8 + (1 x (4/3)πr³)
Volume of atoms = (4/3)πr³ + (4/3)πr³
Volume of atoms = (8/3)πr³
The volume of the unit cell can be calculated as:
Volume of unit cell = a³
where a is the edge length of the cube.
Now, the packing efficiency can be calculated as:
Packing efficiency = (Volume of atoms/Volume of unit cell) x 100%
Packing efficiency = [(8/3)πr³/a³] x 100%
Packing efficiency = (8π/3√3)(r/a)³ x 100%
For a BCC unit cell, the ratio of r/a is √3/2. So, the packing efficiency can be calculated as:
Packing efficiency = (8π/3√3)(√3/2)³ x 100%
Packing efficiency = 68%
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, 68%.
Amorphous solids are also known as:
- a)Isotropic and super cooled liquids.
- b)Isoenthalpic and superheated liquids.
- c)Anisotropic and super cooled liquids.
- d)Isotropic and superheated solids.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amorphous solids are also known as:
a)
Isotropic and super cooled liquids.
b)
Isoenthalpic and superheated liquids.
c)
Anisotropic and super cooled liquids.
d)
Isotropic and superheated solids.
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
- Amorphous solids are isotropic in nature.
- The structure of amorphous solids is similar to that of liquids.
- Hence, these are also called pseudo solids or supercooled liquids.
- Isotropy of amorphous solids is due to the same irregular arrangement of constituent particles along with all the directions.
- Cotton candy is a classic example of amorphous solids.
Ionization enthalpy is lowest in- a)Hydrogen bond
- b)Covalent bond
- c)Metallic bond
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ionization enthalpy is lowest in
a)
Hydrogen bond
b)
Covalent bond
c)
Metallic bond
d)
All of these
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Metals have low ionization energy because of there tendency to lose electrons.
A second order Bragg’s diffraction of X-rays from a set of parallel planes separated by 1.155 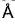 occurs at an angle 60° using wavelength of x
occurs at an angle 60° using wavelength of x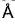 . What is the value of x?
. What is the value of x?
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
A second order Bragg’s diffraction of X-rays from a set of parallel planes separated by 1.155 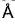 occurs at an angle 60° using wavelength of x
occurs at an angle 60° using wavelength of x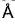 . What is the value of x?
. What is the value of x?
|
|
Om Desai answered |
(1) By Bragg's equation,
n = 2 (second order diffraction)
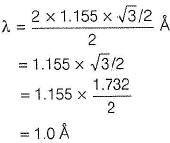
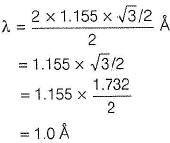
Potassium chloride is:- a)Molecular solid
- b)Ionic solid
- c)Metallic solid
- d)Covalent solid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Potassium chloride is:
a)
Molecular solid
b)
Ionic solid
c)
Metallic solid
d)
Covalent solid
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Potassium chloride is Ionic. The periodic table is split into three sections. Metals, metalloids, and non-metals. From what I understand, metalloids are neutral, so if a metal or a non-metal is mixed with a metalloid or mixed with a different element from the same section, it will be covalent, but if a metal is mixed with a non-metal, it is ionic.
Which of the following is a non-conductor in solid state but good conductor in molten state?
- a)Silicon dioxide
- b)Sodium
- c)Diamond
- d)Potassium chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non-conductor in solid state but good conductor in molten state?
a)
Silicon dioxide
b)
Sodium
c)
Diamond
d)
Potassium chloride
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
- In order to conduct electricity, a substance must have charge particles, such as electrons and ions, that are free to move freely through it.
- In the solid-state, ionic compounds such as sodium chloride and potassium chloride have their ions fixed in position and therefore these ions cannot move so solid ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity.
- However, in the molten state, ions in ionic compounds are free to flow and therefore molten sodium chloride and potassium chloride can conduct electricity.
In a face centred cubic arrangement of A & B atoms whose A atoms are at the corner of the unit cell & B atoms at the face centres. One of the A atom is missing from one corner in unit cell. The simplest formula of compound is-- a)A7B3
- b)AB3
- c)A7B24
- d)A7/8 B3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a face centred cubic arrangement of A & B atoms whose A atoms are at the corner of the unit cell & B atoms at the face centres. One of the A atom is missing from one corner in unit cell. The simplest formula of compound is-
a)
A7B3
b)
AB3
c)
A7B24
d)
A7/8 B3
|
|
Roshni Desai answered |
Explanation:
Given:
- Face-centred cubic arrangement of A and B atoms
- A atoms at corner of unit cell
- B atoms at face centres
- One A atom missing from one corner
To find:
- Simplest formula of compound
Solution:
Step 1: Determine the number of A atoms in one unit cell
- A atoms are at the corner of the unit cell
- Each corner atom is shared between 8 unit cells
- Therefore, each corner atom contributes 1/8th of its atom to the unit cell
- There are 8 corner atoms in a unit cell
- Therefore, the total contribution of A atoms in one unit cell is 8 x 1/8 = 1 A atom
Step 2: Determine the number of B atoms in one unit cell
- B atoms are at the face centres
- Each face-centred atom is shared between 2 unit cells
- Therefore, each face-centred atom contributes 1/2 of its atom to the unit cell
- There are 6 face-centred atoms in a unit cell
- Therefore, the total contribution of B atoms in one unit cell is 6 x 1/2 = 3 B atoms
Step 3: Determine the simplest formula of the compound
- The ratio of A to B atoms in the compound is 1:3
- The formula of the compound is A1B3
- However, one A atom is missing from one corner in the unit cell
- Therefore, the formula of the compound becomes A7B24
Answer: The simplest formula of the compound is A7B24.
Given:
- Face-centred cubic arrangement of A and B atoms
- A atoms at corner of unit cell
- B atoms at face centres
- One A atom missing from one corner
To find:
- Simplest formula of compound
Solution:
Step 1: Determine the number of A atoms in one unit cell
- A atoms are at the corner of the unit cell
- Each corner atom is shared between 8 unit cells
- Therefore, each corner atom contributes 1/8th of its atom to the unit cell
- There are 8 corner atoms in a unit cell
- Therefore, the total contribution of A atoms in one unit cell is 8 x 1/8 = 1 A atom
Step 2: Determine the number of B atoms in one unit cell
- B atoms are at the face centres
- Each face-centred atom is shared between 2 unit cells
- Therefore, each face-centred atom contributes 1/2 of its atom to the unit cell
- There are 6 face-centred atoms in a unit cell
- Therefore, the total contribution of B atoms in one unit cell is 6 x 1/2 = 3 B atoms
Step 3: Determine the simplest formula of the compound
- The ratio of A to B atoms in the compound is 1:3
- The formula of the compound is A1B3
- However, one A atom is missing from one corner in the unit cell
- Therefore, the formula of the compound becomes A7B24
Answer: The simplest formula of the compound is A7B24.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
- A:
2
- B:
4
- C:
1
- D:
3
The answer is c.
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
2
4
1
3

|
Rutuja Pawar answered |
No. of octahedral voids=2 × no. of atoms.As cubic closed pack is nothing but FCCno. of octahedral voids=2 × 4=8But here in the que it is asked no. of octahedral voids per atom...So the ans is (C)1Hope u understood😄😄😄
Group 14 element is converted to p – type semiconductor by dopping it with- a)B
- b)P
- c)Mg
- d)Ar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Group 14 element is converted to p – type semiconductor by dopping it with
a)
B
b)
P
c)
Mg
d)
Ar
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Doping of group 14 elements with group 13 forms p type semiconductor.
Which type of solids are held by weak dispersion forces?- a)Non polar molecular solids
- b)Covalent solids
- c)Metallic solids
- d)Polar molecular solids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of solids are held by weak dispersion forces?
a)
Non polar molecular solids
b)
Covalent solids
c)
Metallic solids
d)
Polar molecular solids
|
|
Siddharth Tiwari answered |
Non-polar molecular solids are held by weak dispersion forces.
Explanation:
Non-polar molecular solids are composed of molecules that have no permanent dipole moment. Hence, the intermolecular forces holding these molecules together are London dispersion forces or Van der Waals forces. London dispersion forces are the weakest intermolecular force, and they occur between all types of molecules, whether they are polar or non-polar.
In contrast, polar molecular solids are held together by dipole-dipole forces, which are stronger than London dispersion forces. Covalent solids are held together by covalent bonds, which are also stronger than London dispersion forces. Metallic solids are held together by metallic bonds, which are even stronger than covalent bonds.
Therefore, the correct option is A) Non-polar molecular solids.
Explanation:
Non-polar molecular solids are composed of molecules that have no permanent dipole moment. Hence, the intermolecular forces holding these molecules together are London dispersion forces or Van der Waals forces. London dispersion forces are the weakest intermolecular force, and they occur between all types of molecules, whether they are polar or non-polar.
In contrast, polar molecular solids are held together by dipole-dipole forces, which are stronger than London dispersion forces. Covalent solids are held together by covalent bonds, which are also stronger than London dispersion forces. Metallic solids are held together by metallic bonds, which are even stronger than covalent bonds.
Therefore, the correct option is A) Non-polar molecular solids.
In the frmula to calculate the density of a unit cell 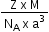 what is z ?
what is z ?- a)Volume of unit cell.
- b)Number of atoms in a unit cell.
- c)Mass of atoms in a unit cell.
- d)Molar mass of unit cell.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the frmula to calculate the density of a unit cell 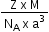 what is z ?
what is z ?
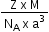 what is z ?
what is z ?a)
Volume of unit cell.
b)
Number of atoms in a unit cell.
c)
Mass of atoms in a unit cell.
d)
Molar mass of unit cell.
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Mass of unit cell = number of atoms in unit cell × mass of each atom = z × m
Where, z = number of atoms in unit cell,
m = Mass of each atom
Mass of an atom can be given with the help of Avogadro number and molar mass as: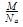
Where, M = molar mass
NA = Avogadro’s number
Volume of unit cell, V = a3
⇒ Density of unit cell =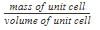
⇒ Density of unit cell =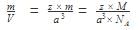
Mass of unit cell = number of atoms in unit cell × mass of each atom = z × m
Where, z = number of atoms in unit cell,
m = Mass of each atom
Mass of an atom can be given with the help of Avogadro number and molar mass as:
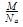
Where, M = molar mass
NA = Avogadro’s number
Volume of unit cell, V = a3
⇒ Density of unit cell =
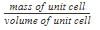
⇒ Density of unit cell =
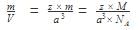
The mass of a unit cell of NaCL corresponds to- a)1 Na+,6 Cl-
- b)4 Na+,4 Cl-
- c)1 Na+,1 Cl-
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of a unit cell of NaCL corresponds to
a)
1 Na+,6 Cl-
b)
4 Na+,4 Cl-
c)
1 Na+,1 Cl-
d)
none of these
|
|
Shalini Choudhary answered |
(d) Every unit cell of NaCI (fee) has f our Na+ and four Cl- ions at alternate position
The following diagram shows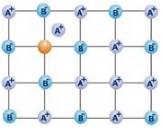
- a)Frenkel defect
- b)Interstitial
- c)F – centers
- d)Schottky defect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The following diagram shows
a)
Frenkel defect
b)
Interstitial
c)
F – centers
d)
Schottky defect
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
A Frenkel defect or dislocation defect is a type of point defect in crystalline solids named after its discoverer Yakov Frenkel. The defect forms when an atom or smaller ion (usually cation) leaves its place in the lattice, creating a vacancy, and becomes an interstitial by lodging in a nearby location.
What is the formula of a magnetic oxide of cobalt used in recording tapes that crystallises with cobalt atoms occupying one-eighth of the tetrahedral holes and one-half of the octahedral holes in a closest packed array of oxide ions?- a)CoO
- b)Co2O3
- c)CoO2
- d)Co3O4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the formula of a magnetic oxide of cobalt used in recording tapes that crystallises with cobalt atoms occupying one-eighth of the tetrahedral holes and one-half of the octahedral holes in a closest packed array of oxide ions?
a)
CoO
b)
Co2O3
c)
CoO2
d)
Co3O4
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
(c)
Tetrahedral holes = 8, Octahedral holes = 4 Cobalt atoms = 8/8 =1
Oxide ions = 4/2 =2
Thus, formula is CoO2
Which is/are amorphous solids-- a)Rubber
- b)Plastics
- c)Glass
- d)All
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is/are amorphous solids-
a)
Rubber
b)
Plastics
c)
Glass
d)
All
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Rubber, P lastics and glass, all are amorphous solids so
What are the basic particles of ice crystals?- a)atoms
- b)anions
- c)cations
- d)molecules
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the basic particles of ice crystals?
a)
atoms
b)
anions
c)
cations
d)
molecules
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Ice is a hydrogen bonded molecular solid.
- It is a crystalline substance in which the constituent particles are molecules.
- These molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds.
How many types of voids are generated if the spheres of second layer are placed in the depressions of a 2D hcp?- a)12
- b)6
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many types of voids are generated if the spheres of second layer are placed in the depressions of a 2D hcp?
a)
12
b)
6
c)
2
d)
4
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Two types of voids are generated if the spheres of second layer are placed in the depressions of a 2D hcp – octahedral and tetrahedral void.
Which of the following solids are also called as super cooled liquids?- a)Metallic solids
- b)Crystalline solids
- c)Covalent solids
- d)Amorphous solids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solids are also called as super cooled liquids?
a)
Metallic solids
b)
Crystalline solids
c)
Covalent solids
d)
Amorphous solids
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The amorphous solids are called as super cooled liquid which allows molecules in the material to continue to move but in very very less large time and as it does not form a crystalline structure , or we can say they have a tendency to flow like liquids that's why they are called as pseudo solids or supercooled liquids.
A solid has a structure in which W-atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, OF-atoms at the centre of edges and Na atom at the centre of the cube. The formula for the compound is- a) Na2WO3
- b) Na2WO2
- c) NaWO2
- d) NaWO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solid has a structure in which W-atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, OF-atoms at the centre of edges and Na atom at the centre of the cube. The formula for the compound is
a)
Na2WO3
b)
Na2WO2
c)
NaWO
2
d)
NaWO3
|
|
Mihir Joshi answered |
Given information:
- W-atoms are present at the corners of a cubic lattice
- OF-atoms are present at the centre of edges
- Na atom is present at the centre of the cube
To find:
The formula of the compound
Solution:
1. Determine the number of Na atoms in the unit cell:
- Na atom is present at the centre of the cube
- Therefore, only 1 Na atom is present in the unit cell
2. Determine the number of W atoms in the unit cell:
- W atoms are present at the corners of the cubic lattice
- Each corner is shared by 8 unit cells, so each W atom will contribute 1/8th to the unit cell
- Therefore, the total number of W atoms in the unit cell = 8 x 1/8 = 1
3. Determine the number of O atoms in the unit cell:
- O atoms are present at the centre of edges
- Each edge is shared by 4 unit cells, so each O atom will contribute 1/4th to the unit cell
- There are 12 edges in a cubic lattice, so the total number of O atoms in the unit cell = 12 x 1/4 = 3
4. Determine the ratio of Na, W, and O atoms:
- From the above calculations, we have 1 Na atom, 1 W atom, and 3 O atoms in the unit cell
- To get the simplest ratio, we need to divide by the smallest number (which is 1 in this case)
- Therefore, the ratio of Na:W:O = 1:1:3
5. Write the formula of the compound:
- The formula of the compound is given by the ratio of the atoms present in the unit cell
- From step 4, we have the ratio of Na:W:O = 1:1:3
- Therefore, the formula of the compound is NaWO3
Hence, the correct answer is option D (NaWO3).
- W-atoms are present at the corners of a cubic lattice
- OF-atoms are present at the centre of edges
- Na atom is present at the centre of the cube
To find:
The formula of the compound
Solution:
1. Determine the number of Na atoms in the unit cell:
- Na atom is present at the centre of the cube
- Therefore, only 1 Na atom is present in the unit cell
2. Determine the number of W atoms in the unit cell:
- W atoms are present at the corners of the cubic lattice
- Each corner is shared by 8 unit cells, so each W atom will contribute 1/8th to the unit cell
- Therefore, the total number of W atoms in the unit cell = 8 x 1/8 = 1
3. Determine the number of O atoms in the unit cell:
- O atoms are present at the centre of edges
- Each edge is shared by 4 unit cells, so each O atom will contribute 1/4th to the unit cell
- There are 12 edges in a cubic lattice, so the total number of O atoms in the unit cell = 12 x 1/4 = 3
4. Determine the ratio of Na, W, and O atoms:
- From the above calculations, we have 1 Na atom, 1 W atom, and 3 O atoms in the unit cell
- To get the simplest ratio, we need to divide by the smallest number (which is 1 in this case)
- Therefore, the ratio of Na:W:O = 1:1:3
5. Write the formula of the compound:
- The formula of the compound is given by the ratio of the atoms present in the unit cell
- From step 4, we have the ratio of Na:W:O = 1:1:3
- Therefore, the formula of the compound is NaWO3
Hence, the correct answer is option D (NaWO3).
. Packing efficiency in a unit cell is never 100% because constituent particles are assumed to be:- a)Spheres
- b)Cuboid
- c)Cubes
- d)Conical
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. Packing efficiency in a unit cell is never 100% because constituent particles are assumed to be:
a)
Spheres
b)
Cuboid
c)
Cubes
d)
Conical
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The constituent particles i.e. atoms, molecules and ions are assumed to be spheres.
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is
- a)2
- b)4
- c)1
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is
a)
2
b)
4
c)
1
d)
3
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
There will be one octahedral void per atom
No. of atom per unit cell = 4
Total octahedral voids = 2 = 4
Octahedral void per atom = 4/4 = 1
The number of atoms in primitive cubic unit cell, body-centred cubic unit cell and face-centred cubic unit cell are A , B and C respectively. Select the correct values.- a)A B C1 2 3
- b)A B C1 2 4
- c)A B C1 1 3
- d)A B C2 3 4
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of atoms in primitive cubic unit cell, body-centred cubic unit cell and face-centred cubic unit cell are A , B and C respectively. Select the correct values.
a)
A B C
1 2 3
b)
A B C
1 2 4
c)
A B C
1 1 3
d)
A B C
2 3 4

|
Debraj Kundu answered |
Primitive no. of cell means rank of cell its in ncert how to find check it
Chapter doubts & questions for Solid State (Old NCERT) - Chemistry Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Solid State (Old NCERT) - Chemistry Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry Class 12
147 videos|405 docs|163 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











