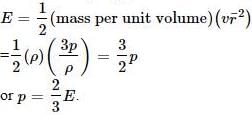All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Physics 2 >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 2: Thermodynamics for Grade 9 Exam
Value of gas constant, R for one mole of a gas is independent of the- a)Atomicity of the gas
- b)Mass of gas
- c)Distance between two molecules of gas at 273 K
- d)Volume of gas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Value of gas constant, R for one mole of a gas is independent of the
a)
Atomicity of the gas
b)
Mass of gas
c)
Distance between two molecules of gas at 273 K
d)
Volume of gas

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
We know that PV=nRT also PM=dRT
So in the equation The value of R depends on P , V , n , T , d , M
except atomicity
so the ans is A
So in the equation The value of R depends on P , V , n , T , d , M
except atomicity
so the ans is A
The kinetic energy of one mole of an ideal gas is E=3/2 RT. Then Cρ will be- a)0.5 R
- b)1.5 R
- c)2.5 R
- d)2.2 R
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The kinetic energy of one mole of an ideal gas is E=3/2 RT. Then Cρ will be
a)
0.5 R
b)
1.5 R
c)
2.5 R
d)
2.2 R
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know that,
Cp=cv+R
E=3Rt/2
also,
E=Cv
cp=R+3RT/2
=5/2 RT
=2.5R
Cp=cv+R
E=3Rt/2
also,
E=Cv
cp=R+3RT/2
=5/2 RT
=2.5R
A region of the earth’s atmosphere contains n molecules (treated as ideal gas molecules) per unit volume. The temperature of air in the region is T. If k represents Boltzmann’s constant and R represents universal gas constant, the pressure of air in the region is- a)RT/n
- b)nRkT
- c)nkT
- d)nT/k
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A region of the earth’s atmosphere contains n molecules (treated as ideal gas molecules) per unit volume. The temperature of air in the region is T. If k represents Boltzmann’s constant and R represents universal gas constant, the pressure of air in the region is
a)
RT/n
b)
nRkT
c)
nkT
d)
nT/k
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
PV = nRT
Where n = number of moles = m/NA
So, P = (m/V)(R/NA)T
Also, we know that R/NA = k
So, P = nkT
Where n = number of moles = m/NA
So, P = (m/V)(R/NA)T
Also, we know that R/NA = k
So, P = nkT
In the case of real gases, the equation of state, PV = RT (where P, V and T are respectively the pressure, volume and absolute temperature), is strictly satisfied only if corrections are applied to the measured pressure P and the measured volume V. The corrections for P and V arise respectively due to- a)kinetic energy of molecules and collision of molecules
- b)size of molecules and expansion of the container
- c)expansion of the container and intermolecular attraction
- d)intermolecular attraction and the size of molecules
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the case of real gases, the equation of state, PV = RT (where P, V and T are respectively the pressure, volume and absolute temperature), is strictly satisfied only if corrections are applied to the measured pressure P and the measured volume V. The corrections for P and V arise respectively due to
a)
kinetic energy of molecules and collision of molecules
b)
size of molecules and expansion of the container
c)
expansion of the container and intermolecular attraction
d)
intermolecular attraction and the size of molecules

|
Ashish Mishra answered |
D is correct
Oxygen and nitrogen in two enclosures have the same mass, volume and pressure. The ratio of the temperature of oxygen to that of nitrogen is:- a)8/7
- b)49/64
- c)1
- d)7/8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen and nitrogen in two enclosures have the same mass, volume and pressure. The ratio of the temperature of oxygen to that of nitrogen is:
a)
8/7
b)
49/64
c)
1
d)
7/8
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
For same mass the ratio of moles of oxygen to that of nitrogen is 14:16 = 7:8
And we know that PV = nRT
Hence as V and P are also same, ratio of temperature of oxygen to that of nitrogen is inverse of the ratio of moles that is 8:7
And we know that PV = nRT
Hence as V and P are also same, ratio of temperature of oxygen to that of nitrogen is inverse of the ratio of moles that is 8:7
Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is initially in the state A shown in the adjoining pressure-temperature graph. It is taken to state B without changing its pressure. If R is the universal gas constant, the work done by the gas in this process is
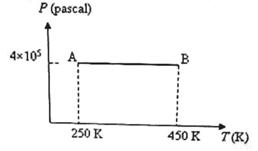
- a)600 R
- b)400 R
- c)300 R
- d)200 R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is initially in the state A shown in the adjoining pressure-temperature graph. It is taken to state B without changing its pressure. If R is the universal gas constant, the work done by the gas in this process is


a)
600 R
b)
400 R
c)
300 R
d)
200 R

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The work done by the gas in taking it from state A to state B = PΔV where ΔW is the increase in volume at constant pressure P.
We have PV = μRT where p is the number of moles in the sample of the gas and R is the universal gas constant.
Therefore we have PΔV = μR ΔT = 3 xR(450 - 250) = 600R
Which one of the following quantities can be zero on an average for the molecules of an ideal gas in equilibrium?- a)Speed
- b)Momentum
- c)Kinetic Energy
- d)Density
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following quantities can be zero on an average for the molecules of an ideal gas in equilibrium?
a)
Speed
b)
Momentum
c)
Kinetic Energy
d)
Density
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
In case of ideal gases the average velocity is always zero. Hence the average momentum is zero.
Whereas average speed is non- zero so the kinetic energy is also non-zero, as these two are scalar quantities.
Whereas average speed is non- zero so the kinetic energy is also non-zero, as these two are scalar quantities.
Four moles of an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant volume from 20° C to 30° C. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure (Cp) is 30.3 Jmol-1K-1 and the universal gas constant (R) is 8.3 Jmol-1K-1. The increase in internal energy of the gas is- a)332 J
- b)80.3 J
- c)303 J
- d)880 J
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Four moles of an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant volume from 20° C to 30° C. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure (Cp) is 30.3 Jmol-1K-1 and the universal gas constant (R) is 8.3 Jmol-1K-1. The increase in internal energy of the gas is
a)
332 J
b)
80.3 J
c)
303 J
d)
880 J
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The value of Cp is 30.3
and as Cp-Cv = R(8.3)
hence Cv = 30.3-8.3
Cv is 22
change in internal energy = no of moles × Cv × change in temperature
hence
change in internal energy = 22 × 4 × 10
= 880j
Hence Option D is correct.
and as Cp-Cv = R(8.3)
hence Cv = 30.3-8.3
Cv is 22
change in internal energy = no of moles × Cv × change in temperature
hence
change in internal energy = 22 × 4 × 10
= 880j
Hence Option D is correct.
According to kinetic theory of gases, 0K is that temperature at which for an ideal gas- a)pressure is not zero
- b)internal energy is zero
- c)nearly all molecular motion becomes very rapid
- d)volume is not zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to kinetic theory of gases, 0K is that temperature at which for an ideal gas
a)
pressure is not zero
b)
internal energy is zero
c)
nearly all molecular motion becomes very rapid
d)
volume is not zero

|
Sara Saldi answered |
Because at temperature 0K nearly all molecular motion happen to stop. insisting the internal energy to be simple.
I hope it helped
I hope it helped
At absolute zero temperature may be defined as that temperature at which- a)Volume is maximum
- b)Root mean square velocity of the gas molecule reduces to zero
- c)Temperature is 273 K
- d)Mass of molecules of gas is zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At absolute zero temperature may be defined as that temperature at which
a)
Volume is maximum
b)
Root mean square velocity of the gas molecule reduces to zero
c)
Temperature is 273 K
d)
Mass of molecules of gas is zero
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At 0K temperature we know that there is no molecular motion, that is the KE of the particles gets 0. Thus we can say the combined KE of a gaseous system is zero, but as there combined mass cant be zero thus the combined of the square of velocities of the particles is zero, which means that the root mean square velocity of the gas is zero.
When the temperature goes up, the pressure inside a rigid container will _____.- a)remain unchanged
- b)go down
- c)cause particles to cool
- d)go up
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When the temperature goes up, the pressure inside a rigid container will _____.
a)
remain unchanged
b)
go down
c)
cause particles to cool
d)
go up
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The pressure law states that for a constant volume of gas in a sealed container the temperature of the gas is directly proportional to its pressure. This can be easily understood by visualising the particles of gas in the container moving with a greater energy when the temperature is increased.
The average kinetic energy of a molecule in an ideal gas is- a)proportional to the pressure
- b)depends on the nature of the ideal gas
- c)proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
- d)proportional to the volume
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The average kinetic energy of a molecule in an ideal gas is
a)
proportional to the pressure
b)
depends on the nature of the ideal gas
c)
proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
d)
proportional to the volume
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
SHOW THAT THE AVERAGE TRANSLATIONAL KINETIC ENERGY OF THE MOLECULES OF A GAS IS DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE. kinetic energy of the molecules of a gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature.
In a mixture of ideal gases at a fixed temperature the heavier molecule has the lower average speed. This is easiest to conclude from the equation- a)
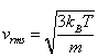
- b)
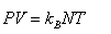
- c)
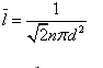
- d)
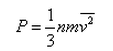
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a mixture of ideal gases at a fixed temperature the heavier molecule has the lower average speed. This is easiest to conclude from the equation
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In option A, v is inversely proportional to mass. Hence, the condition of the question is seen accurately in that option.
The perfect gas equation is PV = nRT where n is the- a)mass of molecules
- b)number of moles
- c)number of molecules
- d)number of atoms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The perfect gas equation is PV = nRT where n is the
a)
mass of molecules
b)
number of moles
c)
number of molecules
d)
number of atoms
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
In SI units, P is measured in pascals, V is measured in cubic metres, n is measured in moles, and T in kelvins (the Kelvin scale is a shifted Celsius scale, where 0.00 K = −273.15 degreeC, the lowest possible temperature). R has the value 8.314 J/(K. mol) ≈ 2 cal/(K. mol), or 0.08206 L.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 2: Thermodynamics - AP Physics 2 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 2: Thermodynamics - AP Physics 2 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Physics 2
65 videos|83 docs|37 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup