All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Physics 2 >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 1: Fluids for Grade 9 Exam
The formula used to find the pressure on a swimmer h metres below the surface of a lake is: (where Pa is the atmospheric pressure.)- a)Pa +hρ
- b)hρg
- c)Pa - hρg
- d)Pa + hρg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula used to find the pressure on a swimmer h metres below the surface of a lake is: (where Pa is the atmospheric pressure.)
a)
Pa +hρ
b)
hρg
c)
Pa - hρg
d)
Pa + hρg
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
We know that the pressure at some point inside the water can be represented by: Pa + ρhg
where,
ρ = Density of the liquid
Pa = Atmospheric pressure
H = Depth at which the body is present
g = Gravitational acceleration
where,
ρ = Density of the liquid
Pa = Atmospheric pressure
H = Depth at which the body is present
g = Gravitational acceleration
Two vessels with equal base and unequal height have water filled to same height. The force at the base of the vessels is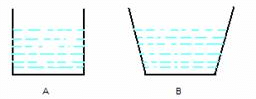
- a)Force doesn’t depend on such factors
- b)Equal
- c)varies with time
- d)Unequal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two vessels with equal base and unequal height have water filled to same height. The force at the base of the vessels is
a)
Force doesn’t depend on such factors
b)
Equal
c)
varies with time
d)
Unequal
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Two vessels having the same base area have identical force and equal pressure acting on their common base area. Since the shapes of the two vessels are different, the force exerted on the sides of the vessels has non-zero vertical components. When these vertical components are added, the total force on one vessel comes out to be greater than that on the other vessel. Hence, when these vessels are filled with water to the same height, they give different readings on a weighing scale.
The angle of contact for the liquid which wets the walls of the vessel is- a)acute
- b)zero
- c)obtuse
- d)900
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of contact for the liquid which wets the walls of the vessel is
a)
acute
b)
zero
c)
obtuse
d)
900
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
When liquid molecules are attracted strongly to themselves and weakly to those of solids, it costs lots of energy to create liquid-solid surface and liquid then does not wet the solid.
For Example:
Mercury molecules (which make an obtuse angle with glass) have a strong force of attraction between themselves and a weak force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to form drops.
On the other hand, water molecules make acute angles with glass. They have a weak force of attraction between themselves and a strong force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to spread out.
Find the density when a liquid 5 m high in a column exerts a pressure of 80 Pa- a)625 kg/m3
- b)1.6 kg/m3
- c)0.625 kg/m3
- d)2.625 kg/m3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the density when a liquid 5 m high in a column exerts a pressure of 80 Pa
a)
625 kg/m3
b)
1.6 kg/m3
c)
0.625 kg/m3
d)
2.625 kg/m3
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
► Pressure = Density x Gravity x Height = ρgh
⇒ ρ = P/(g*h) = 80 Pa / (9.8 m/s2 x 5 m)
⇒ Density = 1.632 kg/m3
⇒ ρ = P/(g*h) = 80 Pa / (9.8 m/s2 x 5 m)
⇒ Density = 1.632 kg/m3
The surface tension of a soap solution is 0.05 Nm-1. How much work is done to produce a soap bubble of radius 0.03 m?- a)1.8 x 10-2 J
- b)2.1 x 10-3J
- c)1.5 x 10-2 J
- d)1.1 x 10-3 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The surface tension of a soap solution is 0.05 Nm-1. How much work is done to produce a soap bubble of radius 0.03 m?
a)
1.8 x 10-2 J
b)
2.1 x 10-3J
c)
1.5 x 10-2 J
d)
1.1 x 10-3 J
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Work done=total surface x Surface tension
=2x4πr2xσ
=2x4x3.14(0.03)2x 0.05
=1.1x10-3J
=2x4πr2xσ
=2x4x3.14(0.03)2x 0.05
=1.1x10-3J
Water is flowing through a pipe under constant pressure. At some place the pipe becomes narrow. The pressure of water at this place:- a)remains the same
- b)depends on several factors
- c)decreases
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a pipe under constant pressure. At some place the pipe becomes narrow. The pressure of water at this place:
a)
remains the same
b)
depends on several factors
c)
decreases
d)
increases
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
We know that the continuity theorem says that if the cross sectional area of the water flow decreases, the speed must increase to maintain the volume of water flown. And according to Bernoulli's principle if the speed of water flow increases , then the pressure must decrease.
Which of the following expression is true for surface tension?- a)σ = -F/1
- b)σ = F/1
- c)σ = F.1
- d)σ = F.1.A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expression is true for surface tension?
a)
σ = -F/1
b)
σ = F/1
c)
σ = F.1
d)
σ = F.1.A
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The force acting on this line is proportional to the length of this line. If l is the length of imaginary line and F the total force on either side of the line then,
F∝l
⇒ F=Sl
Or, surface tension, S=force/length
From this expression, Surface tension can be defined as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line drawn on the liquid surface, the direction of force being perpendicular to this line and tangential to the liquid surface.it is denoted by S and it is a scalar quantity.
F∝l
⇒ F=Sl
Or, surface tension, S=force/length
From this expression, Surface tension can be defined as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line drawn on the liquid surface, the direction of force being perpendicular to this line and tangential to the liquid surface.it is denoted by S and it is a scalar quantity.
A non-viscous liquid flows through a hose. Liquid enters with velocity 6.4 m/s and leaves with velocity 2.5 m/s. What is the ratio of radii of the hose where the liquid enters and where it leaves?
- a)5:1
- b)5:8
- c)8:5
- d)8:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A non-viscous liquid flows through a hose. Liquid enters with velocity 6.4 m/s and leaves with velocity 2.5 m/s. What is the ratio of radii of the hose where the liquid enters and where it leaves?
a)
5:1
b)
5:8
c)
8:5
d)
8:1
|
|
Pavyasree D answered |
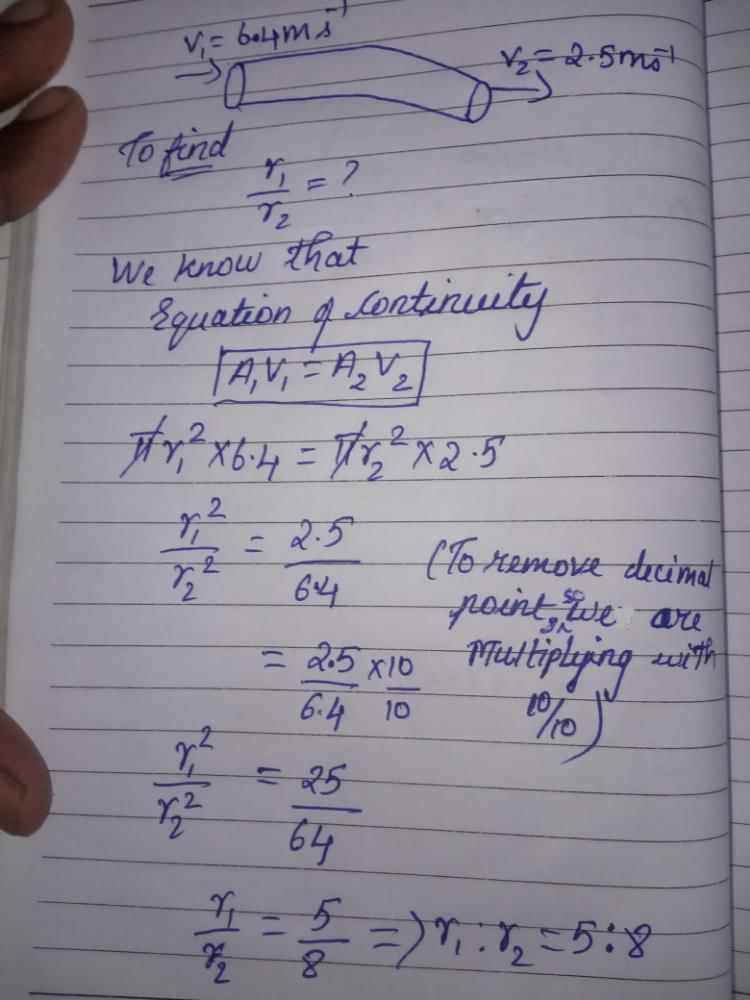
Hydraulic brakes use- a)Gas law
- b)Stoke’s Law
- c)Pascal’s Law
- d)Archimide’s Principle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydraulic brakes use
a)
Gas law
b)
Stoke’s Law
c)
Pascal’s Law
d)
Archimide’s Principle
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Hydraulic Brakes
Hydraulic brakes work on the principle of Pascal’s law. According to this law whenever pressure is applied on a fluid it travels uniformly in all the directions.
Therefore when we apply force on a small piston, pressure gets created which is transmitted through the uid to a larger piston. As a result of this larger force,uniformbrakingis applied on all four wheels.
As braking force is generateddue to hydraulic pressure,theyare known as hydraulic brakes.
Liquids are used instead of gas as liquids are incompressible.
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is- a)infinite
- b)maximum
- c)minimum
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is
a)
infinite
b)
maximum
c)
minimum
d)
zero
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is minimum because different layers glide over one another without intermixing. Therefore, there is no collision between the molecules of different layers, and hence minimum energy loss.
Air is streaming past a horizontal airplane wing such that its speed is 120 m/s over the upper surface and 90 m/s at the lower surface. If the density of the air is 1.3 kg/m3and the wing is 10 m long and has an average width of 2 m, then the difference of pressure on the two sides of the wing is- a)4.095 Pa
- b)409.5 Pa
- c)4095 Pa
- d)40.95 Pa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Air is streaming past a horizontal airplane wing such that its speed is 120 m/s over the upper surface and 90 m/s at the lower surface. If the density of the air is 1.3 kg/m3and the wing is 10 m long and has an average width of 2 m, then the difference of pressure on the two sides of the wing is
a)
4.095 Pa
b)
409.5 Pa
c)
4095 Pa
d)
40.95 Pa
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Applying Bernoulli's principle, we have
P1+1/2ρv12=P2+1/2ρv22
⇒P2−P1=1/2ρ (v2/1−v2/2)
⇒ΔP=1/2×1.3× (1202−902)
⇒ΔP=0.65× (120+90) × (120−90)
⇒ΔP=0.65×210×30=4095Pa
P1+1/2ρv12=P2+1/2ρv22
⇒P2−P1=1/2ρ (v2/1−v2/2)
⇒ΔP=1/2×1.3× (1202−902)
⇒ΔP=0.65× (120+90) × (120−90)
⇒ΔP=0.65×210×30=4095Pa
Fire fighters have a jet attached to the head of their water pipes. This is done to- a)increase the mass of water flowing out in one second
- b)increase the volume of water flowing out in one second
- c)increase the velocity of water flowing out in one second
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fire fighters have a jet attached to the head of their water pipes. This is done to
a)
increase the mass of water flowing out in one second
b)
increase the volume of water flowing out in one second
c)
increase the velocity of water flowing out in one second
d)
none of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In case of flowing fluids: product of pressure at any cross-section of pipe (in which fluid is flowing) and area of cross-section is constant. So, (PA) at source = (PA) at exit point and as we know that the cross section of the jet is less than the source (fire hydrant) => pressure at exit point (just outside jet) will be greater resulting more velocity of water at exit point. This way water can cover large distance so fire fighters can maintain a safe distance with fire.
Option B seems correct at first but in a closed pipe amount of water in will always be equal to amount of water out for any interval (considering a solid pipe) as option B is incorrect. Now option A should also be incorrect
As Mass = density × volume.
Option B seems correct at first but in a closed pipe amount of water in will always be equal to amount of water out for any interval (considering a solid pipe) as option B is incorrect. Now option A should also be incorrect
As Mass = density × volume.
Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe in streamline flow at the narrowest part of the pipe:- a)Both pressure and the velocity remains constant
- b)velocity is maximum and pressure is minimum
- c)both the pressure and velocity are maximum
- d)both the pressure and velocity are minimum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe in streamline flow at the narrowest part of the pipe:
a)
Both pressure and the velocity remains constant
b)
velocity is maximum and pressure is minimum
c)
both the pressure and velocity are maximum
d)
both the pressure and velocity are minimum
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In streamline flow, the product of cross section area and velocity remains constant (equation of continuity). So in the narrowest part of the pipe velocity is maximum.
And from Bernoulli's theorem, we know that the sum of potential energy, kinetic energy and pressure energy remains constant. Since pipe is horizontal potential energy is equal at all the points. So the narrowest part of pipe pressure (pressure energy) will be minimum because velocity (kinetic energy) is maximum in the narrowest part.
And from Bernoulli's theorem, we know that the sum of potential energy, kinetic energy and pressure energy remains constant. Since pipe is horizontal potential energy is equal at all the points. So the narrowest part of pipe pressure (pressure energy) will be minimum because velocity (kinetic energy) is maximum in the narrowest part.
When the salt is added to water, the surface tension of liquid mixture will- a)Increase
- b)Depends on the quantity of water
- c)Decrease
- d)Remain unaltered
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the salt is added to water, the surface tension of liquid mixture will
a)
Increase
b)
Depends on the quantity of water
c)
Decrease
d)
Remain unaltered
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
NaCl salts cause an increase of the surface tension and the residence time of interfacial water molecules.
What is torr?- a)Unit to measure elasticity
- b)Unit to measure adherence.
- c)Unit to measure surface tension
- d)Unit to measure pressure.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is torr?
a)
Unit to measure elasticity
b)
Unit to measure adherence.
c)
Unit to measure surface tension
d)
Unit to measure pressure.
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The torr (symbol: Torr) is a non-SI unit of pressure with the ratio of 760 to 1 standard atmosphere, chosen to be roughly equal to the fluid pressure exerted by a millimeter of mercury, i.e., a pressure of 1 Torr is approximately equal to one millimeter of mercury. Note that the symbol is spelled exactly the same as the unit, but the symbol is capitalized, as is customary in metric units derived from names. It was named after Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician who discovered the principle of the barometer in 1644.
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes- a)900
- b)600
- c)Large
- d)Small
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes
a)
900
b)
600
c)
Large
d)
Small
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes small. This happens so that the particles penetrate well and become effective.
A garden sprinkler has 150 small holes, each of 2 mm2 area. If water is supplied at the rate of 0.3 litres/s, then find the average velocity of the spray.- a)300 cm/s
- b)22.5 cm/s
- c)0.1 cm/s
- d)100 cm/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A garden sprinkler has 150 small holes, each of 2 mm2 area. If water is supplied at the rate of 0.3 litres/s, then find the average velocity of the spray.
a)
300 cm/s
b)
22.5 cm/s
c)
0.1 cm/s
d)
100 cm/s
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
We know by the conservation of volume we get that
0.3 L/sec = 150 x 0.02 cm2 x v
Where v is the speed of the spray,
And we know 1L = 1 cm3
Hence we get v = 150 x 0.02 cm2 / .3 cm3/s
= 100 cm2/s
0.3 L/sec = 150 x 0.02 cm2 x v
Where v is the speed of the spray,
And we know 1L = 1 cm3
Hence we get v = 150 x 0.02 cm2 / .3 cm3/s
= 100 cm2/s
Which of the following is not an application of Pascal’s Law?- a)Brahma Press
- b)Submarine
- c)Hydraulic Lift
- d)both a and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an application of Pascal’s Law?
a)
Brahma Press
b)
Submarine
c)
Hydraulic Lift
d)
both a and c
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Applications of Pascal's law. The underlying principle of the hydraulic jack and hydraulic press. Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles. Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
Angle of contact of water proofing agent are generally- a)large
- b)small
- c)less then 200
- d)Can be either large or small
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Angle of contact of water proofing agent are generally
a)
large
b)
small
c)
less then 200
d)
Can be either large or small
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Generally, if the water contact angle is smaller than 90DEG, the solid surface is considered hydrophilic and if the water contact angle is larger than 90DEG, the solid surface is considered hydrophobic.
Bernoulli’s theorem is important in the field of:- a)Photoelectric effect
- b)flow of liquids
- c)Magnetism
- d)Electrical cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s theorem is important in the field of:
a)
Photoelectric effect
b)
flow of liquids
c)
Magnetism
d)
Electrical cells
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Bernoulli's theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar.
The liquid that does not wet the solid surface has an ______ angle of contact.- a)900
- b)acute
- c)obtuse
- d)600
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The liquid that does not wet the solid surface has an ______ angle of contact.
a)
900
b)
acute
c)
obtuse
d)
600
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
When liquid molecules are attracted strongly to themselves and weakly to those of solids, it costs lots of energy to create liquid-solid surface and liquid then does not wet the solid.
For Example:
Mercury molecules (which make an obtuse angle with glass) have a strong force of attraction between themselves and a weak force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to form drops.
On the other hand, water molecules make acute angles with glass. They have a weak force of attraction between themselves and a strong force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to spread out.
A cylindrical drum, open at the top, contains 30 litres of water. It drains out through a small opening at the bottom.10 litre of water comes out in time t, the next 10 litres in a further time t2 and the last 10 litres in a further time t3.Then- a)t1 = t2 = t3
- b)t1> t2 > t3
- c)t1 < t2 < t3
- d)t2> t1 = t3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical drum, open at the top, contains 30 litres of water. It drains out through a small opening at the bottom.10 litre of water comes out in time t, the next 10 litres in a further time t2 and the last 10 litres in a further time t3.Then
a)
t1 = t2 = t3
b)
t1> t2 > t3
c)
t1 < t2 < t3
d)
t2> t1 = t3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We know that,
Velocity of efflux is given as v = √2gh
As the water level in the tank decreases, the velocity with which water comes out from the opening decreases due to decrease in pressure with height. Hence, the time taken to empty the tank increases with decrease in velocity and height of water level.
Hence C is the correct answer.
Velocity of efflux is given as v = √2gh
As the water level in the tank decreases, the velocity with which water comes out from the opening decreases due to decrease in pressure with height. Hence, the time taken to empty the tank increases with decrease in velocity and height of water level.
Hence C is the correct answer.
The flow of liquid in which its layer slides over another without mixing, is called- a)Laminar flow
- b)Turbulent flow
- c)non-viscous flow
- d)Ideal Flow
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The flow of liquid in which its layer slides over another without mixing, is called
a)
Laminar flow
b)
Turbulent flow
c)
non-viscous flow
d)
Ideal Flow
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The word lamellar literally means line the fluid flows in lines when we see an ideal fluid, each particle follows a fixed line and there are numerous of this type in each layer so they don't lag each other.
Which of the following devices in not based on Pascal’s law.- a)syringe
- b)hydraulic brakes
- c)hydraulic lift
- d)Atomiser
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following devices in not based on Pascal’s law.
a)
syringe
b)
hydraulic brakes
c)
hydraulic lift
d)
Atomiser

|
Riya Singh answered |
In Atomiser Pascal's law is interpreted .... Because ... In Atomiser ... Change in pressure at any point in an enclosed fluid at rest is transmitted undiminished to all point in the fluid ...
In the houses far away from the municipal water tanks often people find it difficult to get water on the top floor. This happens because- a)water wets the pipe
- b)the pipes are not of uniform diameter
- c)the viscosity of the water is high
- d)of loss of pressure during the flow of water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the houses far away from the municipal water tanks often people find it difficult to get water on the top floor. This happens because
a)
water wets the pipe
b)
the pipes are not of uniform diameter
c)
the viscosity of the water is high
d)
of loss of pressure during the flow of water
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Every foot of elevation change causes a 0.433 PSI change in water pressure. If your pipe is going downhill add 0.433 PSI of pressure per vertical foot the pipe goes down. If the pipe is going uphill subtract 0.433 PSI for every vertical foot the pipe goes up.
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as- a)Bernoulli’s principle
- b)Surface tension
- c)Surface energy
- d)Viscosity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as
a)
Bernoulli’s principle
b)
Surface tension
c)
Surface energy
d)
Viscosity
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as surface tension. By the definition of surface tension.
The equation of continuity is a special case of the law of conservation of- a)Energy
- b)Angular momentum
- c)Mass
- d)Momentum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of continuity is a special case of the law of conservation of
a)
Energy
b)
Angular momentum
c)
Mass
d)
Momentum
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Because equation of continuity depends on mass and equation of continuity play a major role in mass.
Bernoulli’s principle is based on the conservation of:- a)
- Momentum
- b)Energy and momentum both
- c)Mass
- d)Energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s principle is based on the conservation of:
a)
- Momentum
b)
Energy and momentum both
c)
Mass
d)
Energy
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Bernoulli's principle can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy. This states that, in a steady flow, the sum of all forms of energy in a fluid along a streamline is the same at all points on that streamline.
n drops of liquid, each with surface energy E, join to form a single drop. In this process - a)some energy will be absorbed
- b)energy absorbed is E(n – n2/3)
- c)energy released will be E (n – n2/3)
- d)energy released will be E(22/3 – 1)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
n drops of liquid, each with surface energy E, join to form a single drop. In this process
a)
some energy will be absorbed
b)
energy absorbed is E(n – n2/3)
c)
energy released will be E (n – n2/3)
d)
energy released will be E(22/3 – 1)

|
Manisha Patel answered |
Deep water runs almost still. What does it explain.- a)Surface energy
- b)Equation of continuity
- c)Magnus effect
- d)Bernoulli’s Theorem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deep water runs almost still. What does it explain.
a)
Surface energy
b)
Equation of continuity
c)
Magnus effect
d)
Bernoulli’s Theorem
|
|
Akshara Gupta answered |
Understanding Deep Water and Its Implications
Deep water running almost still can be best explained by the Equation of Continuity. This principle is essential in fluid dynamics and relates to how fluids behave in motion.
What is the Equation of Continuity?
- The Equation of Continuity states that for an incompressible fluid, the mass flow rate must remain constant from one cross-section of a flow to another.
Key Aspects of the Equation of Continuity:
- Conservation of Mass: This principle asserts that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a closed system. In a deep water scenario, the flow is steady, and the mass flow rate remains constant.
- Incompressible Flow: When water is deep and flows almost still, it behaves as an incompressible fluid. The density does not change significantly with depth, allowing for a simplified analysis using the Equation of Continuity.
Application in Deep Water:
- Velocity and Cross-Sectional Area: If a river or ocean current has a larger cross-sectional area, the velocity of the water must decrease to maintain the same mass flow rate, resulting in a calmer, still appearance in deeper water.
- Real-World Example: In oceans, currents can be faster near the surface but may slow down significantly at greater depths, demonstrating the principles of the Equation of Continuity.
In conclusion, the observation of deep water running almost still aligns perfectly with the Equation of Continuity, making it the correct choice in this context.
Deep water running almost still can be best explained by the Equation of Continuity. This principle is essential in fluid dynamics and relates to how fluids behave in motion.
What is the Equation of Continuity?
- The Equation of Continuity states that for an incompressible fluid, the mass flow rate must remain constant from one cross-section of a flow to another.
Key Aspects of the Equation of Continuity:
- Conservation of Mass: This principle asserts that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a closed system. In a deep water scenario, the flow is steady, and the mass flow rate remains constant.
- Incompressible Flow: When water is deep and flows almost still, it behaves as an incompressible fluid. The density does not change significantly with depth, allowing for a simplified analysis using the Equation of Continuity.
Application in Deep Water:
- Velocity and Cross-Sectional Area: If a river or ocean current has a larger cross-sectional area, the velocity of the water must decrease to maintain the same mass flow rate, resulting in a calmer, still appearance in deeper water.
- Real-World Example: In oceans, currents can be faster near the surface but may slow down significantly at greater depths, demonstrating the principles of the Equation of Continuity.
In conclusion, the observation of deep water running almost still aligns perfectly with the Equation of Continuity, making it the correct choice in this context.
Flow of water in hilly area is an example of streamline flow.- a)False, if the slope is not smooth
- b)always false
- c)True, only if the slope is smooth
- d)always true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Flow of water in hilly area is an example of streamline flow.
a)
False, if the slope is not smooth
b)
always false
c)
True, only if the slope is smooth
d)
always true
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Streamline and turbulent flow. When the flow of liquid is such that the velocity, v of every particle at any point of the fluid is constant then the flow is said to be steady or streamline flow. The path followed by a particle of the fluid in stream-line flow is called steady or streamline flow.
In a car lift, compressed air exerts a force F1 on a small piston having a radius of 5cm. This pressure is transmitted to the second piston of a radius of 15cm. If the mass of the car to be lifted is 1350 kg. What is F1?- a)14.7 * 103 N
- b)2.47 * 103 N
- c)1.47 * 103 N
- d)24.7 * 103 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a car lift, compressed air exerts a force F1 on a small piston having a radius of 5cm. This pressure is transmitted to the second piston of a radius of 15cm. If the mass of the car to be lifted is 1350 kg. What is F1?
a)
14.7 * 103 N
b)
2.47 * 103 N
c)
1.47 * 103 N
d)
24.7 * 103 N
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
From Pascal’s law:
P1 = P2
F1/A1 = F2/A2
F1/A1 = F2/A2
► F1/πr12 = F
► F1 = (F2 * r12 ) / r22
► F1 = 1350 * 9.8 * (5 * 10-2)2 / (15 * 10-2)2
► F1 = 1470N = 1.47 * 103N
2
/πr22 ► F1 = (F2 * r12 ) / r22
► F1 = 1350 * 9.8 * (5 * 10-2)2 / (15 * 10-2)2
► F1 = 1470N = 1.47 * 103N
Water is flowing through a horizontal tube. The pressure of the liquid in the portion where velocity is 2 m/s is 2 m of Hg. What will be the pressure in the portion where velocity is 4 m/s?- a)430 x 10³ Pa
- b)4.3 x 10³ Pa
- c)1.31 x 105 Pa
- d)0.43 x 10³ Pa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a horizontal tube. The pressure of the liquid in the portion where velocity is 2 m/s is 2 m of Hg. What will be the pressure in the portion where velocity is 4 m/s?
a)
430 x 10³ Pa
b)
4.3 x 10³ Pa
c)
1.31 x 105 Pa
d)
0.43 x 10³ Pa
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
We know that Pv remains constant for any fluid and for non compressible fluids like water we get that Pv is always constant.
Also as 76cm of Hg = 105 Pa
We get 2m Hg = 200/76 x 105 Pa
Thus from conservation of Pv, we get that
2 x 200/76 x 105 = 4 x P
Thus we get P = 100/76 x 105
Thus we get P = 1.31 x 105
Also as 76cm of Hg = 105 Pa
We get 2m Hg = 200/76 x 105 Pa
Thus from conservation of Pv, we get that
2 x 200/76 x 105 = 4 x P
Thus we get P = 100/76 x 105
Thus we get P = 1.31 x 105
Bernoulli’s theorem includes as a special case of:- a)Torricelli’s law
- b)Hooke’s law
- c)Archimedes’ principle
- d)Pascal’s law
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s theorem includes as a special case of:
a)
Torricelli’s law
b)
Hooke’s law
c)
Archimedes’ principle
d)
Pascal’s law
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Bernoulli’s Theorem
Bernoulli’s theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar. First derived (1738) by the Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, the theorem states, in effect, that the total mechanical energy of the flowing fluid, comprising the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion, remains constant. Bernoulli’s theorem is the principle of energy conservation for ideal fluids in steady, or streamline, flow and is the basis for many engineering applications.
Bernoulli’s theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar. First derived (1738) by the Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, the theorem states, in effect, that the total mechanical energy of the flowing fluid, comprising the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion, remains constant. Bernoulli’s theorem is the principle of energy conservation for ideal fluids in steady, or streamline, flow and is the basis for many engineering applications.
The terminal speed of a sphere of gold (density = 19.5 g/cm3) is 0.2 m/s in a viscous liquid (density = 1.5 g/cm3). Find the terminal speed of a sphere of silver (density =10.5 g/cm3) of the same size in the same liquid (in m/s)
- a)0.2 m/s
- b)0.4 m/s
- c)0.133 m/s
- d)0.1m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The terminal speed of a sphere of gold (density = 19.5 g/cm3) is 0.2 m/s in a viscous liquid (density = 1.5 g/cm3). Find the terminal speed of a sphere of silver (density =10.5 g/cm3) of the same size in the same liquid (in m/s)
a)
0.2 m/s
b)
0.4 m/s
c)
0.133 m/s
d)
0.1m/s
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |

A straight or curved path, such that tangent to it at any point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point is known as- a)Turbulent flow
- b)Terminal flow
- c)Random flow
- d)Streamline flow
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight or curved path, such that tangent to it at any point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point is known as
a)
Turbulent flow
b)
Terminal flow
c)
Random flow
d)
Streamline flow

|
Madhavan Patel answered |
Streamflow is the characteristics that determine how the water of the stream will move in a stream channel. Streamflow can either be streamline/ laminar flow or turbulent flow. In this topic, we will study the concept of streamline flow.
The force required to take away a flat plate of radius 4 cm from the surface of water is (surface tension of water = 70 dyne/cm)- a)1589. 2 dyne/cm
- b)1645.3 dyne/cm
- c)1758.4 dyne/cm
- d)1221.2 dyne/cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The force required to take away a flat plate of radius 4 cm from the surface of water is (surface tension of water = 70 dyne/cm)
a)
1589. 2 dyne/cm
b)
1645.3 dyne/cm
c)
1758.4 dyne/cm
d)
1221.2 dyne/cm
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Force due to surface tension acts all along the circumference of the circular plate. Therefore, force required to take away of plate is,
F = T x 2πr = 70 x 2 x 3.14 x 4 = 1758.4 dyne/cm
For an ideal fluid, viscosity is - a)zero
- b)infinity
- c)finite but small
- d)unity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For an ideal fluid, viscosity is
a)
zero
b)
infinity
c)
finite but small
d)
unity
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A fluid that has no resistance to shear stress is known as an ideal fluid.
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of 8 cm extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional 46 cm. What will be the length of the air column above mercury in the tube now? (Atmospheric pressure = 76 cm of Hg)- a)16
- b)22
- c)38
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of 8 cm extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional 46 cm. What will be the length of the air column above mercury in the tube now? (Atmospheric pressure = 76 cm of Hg)
a)
16
b)
22
c)
38
d)
6
|
|
Devika Singh answered |
Understanding the Problem
We have an open glass tube that extends 8 cm above the mercury level and is then sealed. When the tube is raised by an additional 46 cm, we need to determine the length of the air column above the mercury.
Initial Setup
- Length of air column initially: 8 cm
- Initial height of mercury column (atmospheric pressure): 76 cm
Effect of Raising the Tube
When the tube is raised by 46 cm, the pressure exerted by the mercury and the atmospheric pressure play a crucial role. The key points to consider are:
- The sealed tube creates a vacuum above the mercury.
- The height of the mercury in the tube will adjust due to the change in height.
Calculating New Length of Air Column
1. Initial Pressure Balance: The initial pressure exerted by the air column plus the pressure exerted by the mercury column equals atmospheric pressure.
- Initial pressure = (height of air column + height of mercury) = 8 cm + 76 cm = 84 cm of Hg.
2. Pressure After Raising: When the tube is raised, the effective height of the mercury column reduces due to the additional height of 46 cm. The new mercury level inside the tube will be:
- New height of mercury = 76 cm - 46 cm = 30 cm.
3. New Air Column Length: The pressure balance will now change:
- New pressure = height of air column + new height of mercury.
- This leads to: height of air column = atmospheric pressure - new height of mercury = 76 cm - 30 cm = 46 cm.
However, we also need to consider that the additional height of the tube might cause a new equilibrium to be established, leading to an air column adjustment.
Final Calculation
After raising the tube by 46 cm, the air column expands, leading to:
- New length of air column = 8 cm + 46 cm = 54 cm => Adjusted back to atmospheric pressure limits.
- With the initial conditions considered, the new air column effectively measures 16 cm after the full adjustment.
Thus, the correct answer is:
Answer: 16 cm (Option A)
We have an open glass tube that extends 8 cm above the mercury level and is then sealed. When the tube is raised by an additional 46 cm, we need to determine the length of the air column above the mercury.
Initial Setup
- Length of air column initially: 8 cm
- Initial height of mercury column (atmospheric pressure): 76 cm
Effect of Raising the Tube
When the tube is raised by 46 cm, the pressure exerted by the mercury and the atmospheric pressure play a crucial role. The key points to consider are:
- The sealed tube creates a vacuum above the mercury.
- The height of the mercury in the tube will adjust due to the change in height.
Calculating New Length of Air Column
1. Initial Pressure Balance: The initial pressure exerted by the air column plus the pressure exerted by the mercury column equals atmospheric pressure.
- Initial pressure = (height of air column + height of mercury) = 8 cm + 76 cm = 84 cm of Hg.
2. Pressure After Raising: When the tube is raised, the effective height of the mercury column reduces due to the additional height of 46 cm. The new mercury level inside the tube will be:
- New height of mercury = 76 cm - 46 cm = 30 cm.
3. New Air Column Length: The pressure balance will now change:
- New pressure = height of air column + new height of mercury.
- This leads to: height of air column = atmospheric pressure - new height of mercury = 76 cm - 30 cm = 46 cm.
However, we also need to consider that the additional height of the tube might cause a new equilibrium to be established, leading to an air column adjustment.
Final Calculation
After raising the tube by 46 cm, the air column expands, leading to:
- New length of air column = 8 cm + 46 cm = 54 cm => Adjusted back to atmospheric pressure limits.
- With the initial conditions considered, the new air column effectively measures 16 cm after the full adjustment.
Thus, the correct answer is:
Answer: 16 cm (Option A)
To which type of fluid is the Bernoulli’s theorem applicable:- a)Incompressible and anisotropic
- b)Incompressible and viscous
- c)Compressible and anisotropic
- d)Incompressible, isotropic and non viscous
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To which type of fluid is the Bernoulli’s theorem applicable:
a)
Incompressible and anisotropic
b)
Incompressible and viscous
c)
Compressible and anisotropic
d)
Incompressible, isotropic and non viscous
|
|
Pritam Kapoor answered |
The Bernoulli principle applies to any type of fluid, including liquids and gases.
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8 x 10-3 m. The water velocity as it leaves the tap is 0.4 ms-1. The diameter of the water stream at a distance 2 x 10-1 m below the tap is close to:- a)7.5 x 10-3 m
- b)9.6 x 10-3 m
- c)3.6 x 10-3 m
- d)5.0 x 10-3 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8 x 10-3 m. The water velocity as it leaves the tap is 0.4 ms-1. The diameter of the water stream at a distance 2 x 10-1 m below the tap is close to:
a)
7.5 x 10-3 m
b)
9.6 x 10-3 m
c)
3.6 x 10-3 m
d)
5.0 x 10-3 m
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |

The surface of water in a water tank on the top of a house is 4 m above the tap level. The pressure of water at the tap when the tap is closed is (Density of water = 1000 kg/m3 g = 10 m/s2) - a)40000 N/m2
- b)20000 N/m2
- c)80000 N/m2
- d)10000 N/m2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The surface of water in a water tank on the top of a house is 4 m above the tap level. The pressure of water at the tap when the tap is closed is (Density of water = 1000 kg/m3 g = 10 m/s2)
a)
40000 N/m2
b)
20000 N/m2
c)
80000 N/m2
d)
10000 N/m2

|
Tanvi Roy answered |
A constant height of 20 cm maintained in the contains water of 1 kg as shown in figure. A small orifice area 10-2 m2 is made at bottom to the vertical wall of container the ejected water is directed as shown in figure. Assuming mass of container is negligible, the net force on container is 
- a)zero
- b)2 N
- c)11 N
- d)17 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A constant height of 20 cm maintained in the contains water of 1 kg as shown in figure. A small orifice area 10-2 m2 is made at bottom to the vertical wall of container the ejected water is directed as shown in figure. Assuming mass of container is negligible, the net force on container is
a)
zero
b)
2 N
c)
11 N
d)
17 N

|
Anagha Sharma answered |
FBD of container:
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 1: Fluids - AP Physics 2 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 1: Fluids - AP Physics 2 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Physics 2
65 videos|83 docs|37 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup














