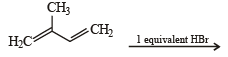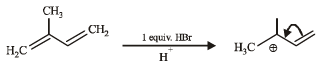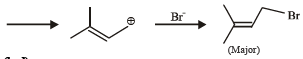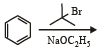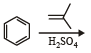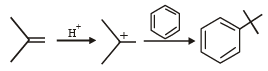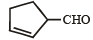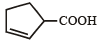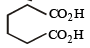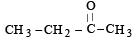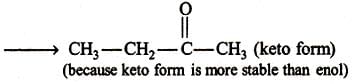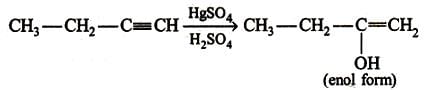All Exams >
JEE >
35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Hydrocarbons for JEE Exam
One mole of a symmetrical alkene on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having a molecular mass of 44 u. The alkene is[2010]- a)propene
- b)1-butene
- c)2-butene
- d)ethene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of a symmetrical alkene on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having a molecular mass of 44 u. The alkene is[2010]
a)
propene
b)
1-butene
c)
2-butene
d)
ethene

|
Defence Exams answered |
The given molecular formula suggests that the aldehyde formed will be acetaldehyde hence the alkene will be
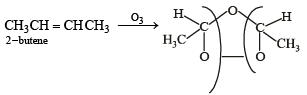
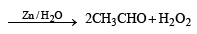
Which of the following compounds does not dissolve in conc. H2SO4 even on warming? (1983 - 1 Mark)- a)ethylene
- b)benzene
- c)hexane
- d)aniline
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds does not dissolve in conc. H2SO4 even on warming? (1983 - 1 Mark)
a)
ethylene
b)
benzene
c)
hexane
d)
aniline
|
|
Advait Singh answered |
CH2 = CH2 + H2SO4 → CH3CH2OSO3H
C6H6 + H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
C6H14 + H2SO4 → No reaction
C6H6 + H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
C6H14 + H2SO4 → No reaction
Only hexane does not dissolve in conc. H2SO4 even on warming.
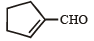
Which compound would give 5 - keto - 2 - methylhexanal upon ozonolysis ? [JEE M 2015]- a)
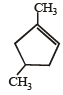
- b)
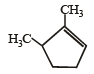
- c)
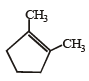
- d)
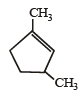
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which compound would give 5 - keto - 2 - methylhexanal upon ozonolysis ? [JEE M 2015]
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
When 1, 3-dimethylcyclopentene is heated with ozone and then with zinc and acetic acid, oxidative cleavage leads to keto - aldehyde.
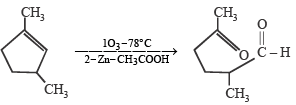
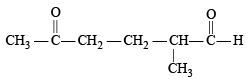
5- keto – 2 – methylhexanal
Identify the product, P in the following reaction : CH3 - CH = CH2 + NOCl —→ P (2006 - 3M, –1)- a)
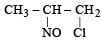
- b)
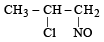
- c)
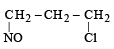
- d)
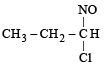
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the product, P in the following reaction : CH3 - CH = CH2 + NOCl —→ P (2006 - 3M, –1)
a)
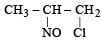
b)
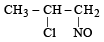
c)
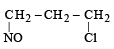
d)
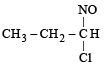
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Nitrosyl chloride adds on olefins accor ding to Markovnikof’s rule, where NO+ constitutes the positive part of the addendum.
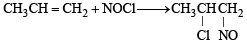
On monochlorination of 2-methylbutane, the total number of chiral compounds formed is (2004S)- a)2
- b)4
- c)6
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On monochlorination of 2-methylbutane, the total number of chiral compounds formed is (2004S)
a)
2
b)
4
c)
6
d)
8
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
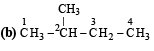
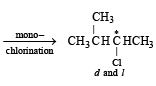
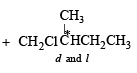
(i) Chlorination at C-2 and C-4 produces no chiral compounds
(ii) Chlorination at C-3 produces a chiral carbon marked with star (d and l form).
(iii) Chlorination at C-1 also produces a chiral carbon marked with star (d and l form).
(ii) Chlorination at C-3 produces a chiral carbon marked with star (d and l form).
(iii) Chlorination at C-1 also produces a chiral carbon marked with star (d and l form).
Butene-1 may be converted to butane by reaction with- a)Sn – HCl
- b)Zn – Hg [2003]
- c)Pd/H2
- d)Zn – HCl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Butene-1 may be converted to butane by reaction with
a)
Sn – HCl
b)
Zn – Hg [2003]
c)
Pd/H2
d)
Zn – HCl

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Alkenes combine with hydrogen under pressure and in presence of a catalyst (Ni, Pt or Pd) and form alkanes.
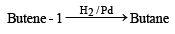
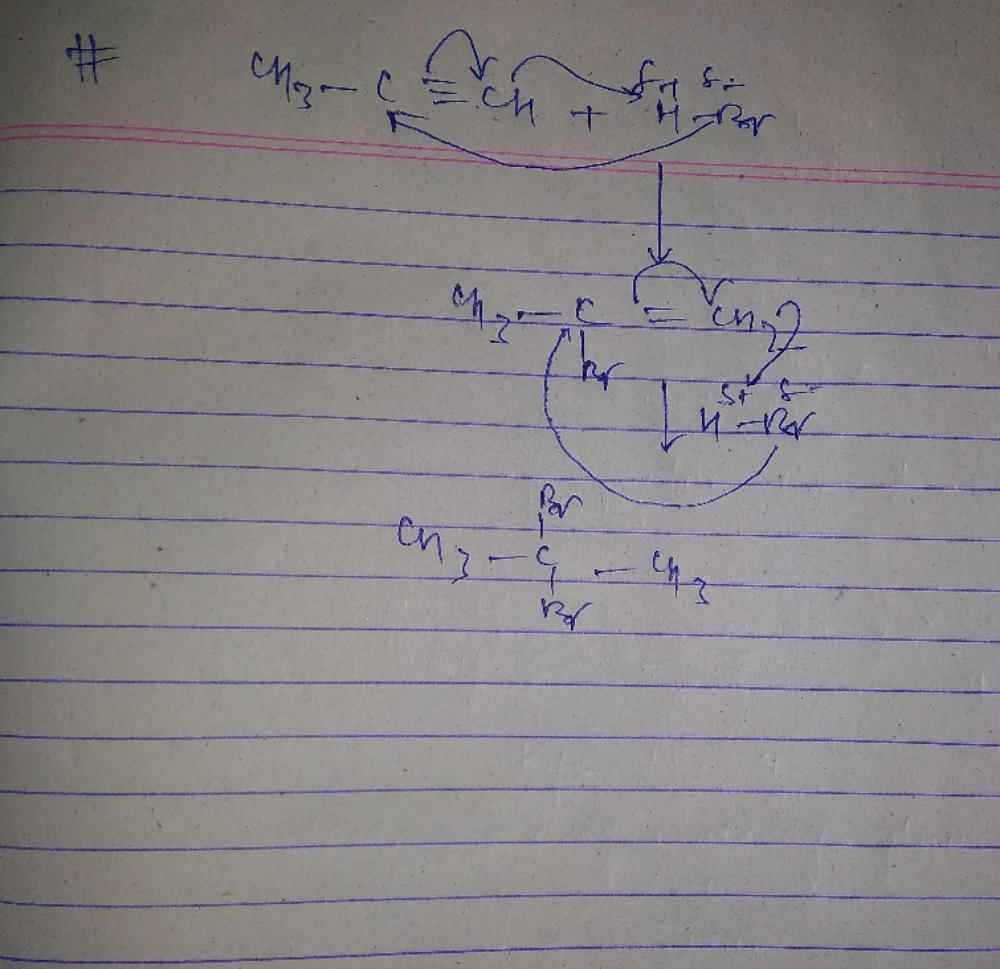
The synthesis of 3-octyne is achieved by adding a bromoalkane into a mixture of sodium amide and an alkyne.The bromoalkane and alkyne respectively are (2010)- a)BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH2CH2C ≡ CH
- b)BrCH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2C ≡ CH
- c)BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3C ≡ CH
- d)BrCH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2C ≡ CH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The synthesis of 3-octyne is achieved by adding a bromoalkane into a mixture of sodium amide and an alkyne.The bromoalkane and alkyne respectively are (2010)
a)
BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH2CH2C ≡ CH
b)
BrCH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2C ≡ CH
c)
BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3C ≡ CH
d)
BrCH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2C ≡ CH
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Only (d) can form 3-Octyne
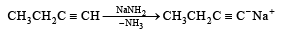
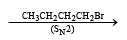
CH3CH2C ≡ CCH2CH2CH2CH3+ NaBr
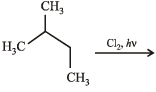 N(isomeric products) ; C5H11Cl
N(isomeric products) ; C5H11Cl (isomeric products) Identify N and M (2006 - 5M,)Identify N and M (2006 - 5M, –1)
(isomeric products) Identify N and M (2006 - 5M,)Identify N and M (2006 - 5M, –1)- a)6, 4
- b)6, 6
- c)4, 4
- d)3, 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
 N(isomeric products) ; C5H11Cl
N(isomeric products) ; C5H11Cl (isomeric products) Identify N and M (2006 - 5M,)
(isomeric products) Identify N and M (2006 - 5M,)Identify N and M (2006 - 5M, –1)
a)
6, 4
b)
6, 6
c)
4, 4
d)
3, 3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
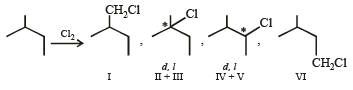
So, the value of N will be 1 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 6.
Since enantiomers have nearly same physical properties, II and III as well as IV and V can’t be separated, hence the number of isomers (M) will be 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4.
Since enantiomers have nearly same physical properties, II and III as well as IV and V can’t be separated, hence the number of isomers (M) will be 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4.
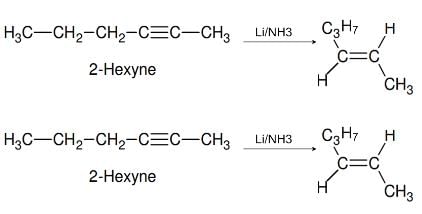
2-Hexyne gives trans-2-Hexene on treatment with :- a)Pt/H2
- b)Li / NH3 [2012]
- c)Pd/BaSO4
- d)Li AlH4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
2-Hexyne gives trans-2-Hexene on treatment with :
a)
Pt/H2
b)
Li / NH3 [2012]
c)
Pd/BaSO4
d)
Li AlH4
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
It's B, which is the process of Birch Reduction where trans form of Alkene is formed. cis form is formed on reaction with H2+ Lindlar's catalyst.
The bond energy (in kcal mol–1) of a C–C single bond is approximately (2010)- a)1
- b)10
- c)100
- d)1000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond energy (in kcal mol–1) of a C–C single bond is approximately (2010)
a)
1
b)
10
c)
100
d)
1000
|
|
Neer Shreyansh answered |
•The bond energy (in kcal/mol) of C-C single bond is approximately 100Kcal/mol.________________________________
•Explanation:___________________________
•Bond Energy is an important concept while dealing with the Chemical Compound.__________________________
•Bond Energy is also known by the name 'bond Enthalpy'._______________________
•It is used to describe the strength of the bond in a chemical compound.________
•Bond Energy can be defined as the energy needed to dissociate a bond in a chemical compound.______________________________
•These values are determined through experiments on various chemical compounds._____________________________________
•It can take '100 kcal of energy' to break' 1 mol of C–H bonds'._____________________
That's all
Isomers of hexane, based on their branching, can be divided into three distinct classes as shown in the figure. (JEE Adv. 2014)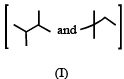
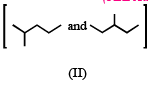
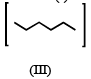 The correct order of their boiling point is
The correct order of their boiling point is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)II > III > I
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Isomers of hexane, based on their branching, can be divided into three distinct classes as shown in the figure. (JEE Adv. 2014)

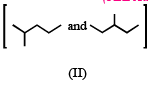

The correct order of their boiling point is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
II > III > I
d)
III > I > II
|
|
Anand Kumar answered |
Note:-(1)boiling point is directly proportional to surface area
Note:-(2) branching increases then surface area decreases
So, option Bis correct.
Note:-(2) branching increases then surface area decreases
So, option Bis correct.
Toluene, when treated with Br2/Fe, gives p-bromotoluene as the major product because CH3 group (1999 - 3 Marks)- a)is para directing
- b)is meta directing
- c)activates the ring by hyperconjugation
- d)deactivates the ring
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Toluene, when treated with Br2/Fe, gives p-bromotoluene as the major product because CH3 group (1999 - 3 Marks)
a)
is para directing
b)
is meta directing
c)
activates the ring by hyperconjugation
d)
deactivates the ring

|
Avantika Saha answered |
Hyperconjugation in toluene activates the benzene ring for electrophilic substitution.
Which types of isomerism is shown by 2, 3-dichlorobutane? [2005]- a)Structural
- b)Geometric
- c)Optical
- d)Diastereo
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which types of isomerism is shown by 2, 3-dichlorobutane? [2005]
a)
Structural
b)
Geometric
c)
Optical
d)
Diastereo
|
|
Jyoti Patel answered |
Explanation:
2,3-dichlorobutane has the chemical formula C4H8Cl2. It contains a chain of four carbon atoms with two chlorine atoms attached to the second and third carbon atoms. This compound exhibits different types of isomerism.
Structural Isomerism:
Structural isomerism refers to the isomers that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule. In the case of 2,3-dichlorobutane, it does not exhibit structural isomerism because there is only one way to arrange the carbon atoms and chlorine atoms in the molecule.
Geometric Isomerism:
Geometric isomerism occurs when two or more isomers have the same connectivity of atoms but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms due to restricted rotation around a double bond or a ring. Since 2,3-dichlorobutane does not contain any double bonds or rings, it does not exhibit geometric isomerism.
Optical Isomerism:
Optical isomerism, also known as enantiomerism, occurs when a compound is chiral and has non-superimposable mirror images. Chirality arises when a carbon atom is bonded to four different groups. In 2,3-dichlorobutane, there is no carbon atom with four different groups, so it does not exhibit optical isomerism.
Diastereomerism:
Diastereomerism occurs when two or more isomers have the same connectivity of atoms but differ in their spatial arrangement, and they are not mirror images of each other. In the case of 2,3-dichlorobutane, it does not exhibit diastereomerism because there is no other isomer with the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement.
Therefore, the correct type of isomerism exhibited by 2,3-dichlorobutane is Optical Isomerism (Enantiomerism).
2,3-dichlorobutane has the chemical formula C4H8Cl2. It contains a chain of four carbon atoms with two chlorine atoms attached to the second and third carbon atoms. This compound exhibits different types of isomerism.
Structural Isomerism:
Structural isomerism refers to the isomers that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule. In the case of 2,3-dichlorobutane, it does not exhibit structural isomerism because there is only one way to arrange the carbon atoms and chlorine atoms in the molecule.
Geometric Isomerism:
Geometric isomerism occurs when two or more isomers have the same connectivity of atoms but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms due to restricted rotation around a double bond or a ring. Since 2,3-dichlorobutane does not contain any double bonds or rings, it does not exhibit geometric isomerism.
Optical Isomerism:
Optical isomerism, also known as enantiomerism, occurs when a compound is chiral and has non-superimposable mirror images. Chirality arises when a carbon atom is bonded to four different groups. In 2,3-dichlorobutane, there is no carbon atom with four different groups, so it does not exhibit optical isomerism.
Diastereomerism:
Diastereomerism occurs when two or more isomers have the same connectivity of atoms but differ in their spatial arrangement, and they are not mirror images of each other. In the case of 2,3-dichlorobutane, it does not exhibit diastereomerism because there is no other isomer with the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement.
Therefore, the correct type of isomerism exhibited by 2,3-dichlorobutane is Optical Isomerism (Enantiomerism).
Which of the following will have least hindered rotation about carbon-carbon bond? (1987 - 1 Mark)- a)Ethane
- b)Ethylene
- c)Acetylen e
- d)Hexachloroethane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have least hindered rotation about carbon-carbon bond? (1987 - 1 Mark)
a)
Ethane
b)
Ethylene
c)
Acetylen e
d)
Hexachloroethane
|
|
Ruchi Tiwari answered |
Ethylene has restricted rotation [due to C = C], acetylene no rotation [due to C ≡ C], hexachloroethane has more rotation than ethylene but less than ethane because of greater size of the substituent (chlorine) than in ethane (substituent is hydrogen).
Acidic hydrogen is present in : (1985 - 1 Mark)- a)ethyne
- b)ethene
- c)benzene
- d)ethane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acidic hydrogen is present in : (1985 - 1 Mark)
a)
ethyne
b)
ethene
c)
benzene
d)
ethane
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Acidic hydrogen is present in alkynes, attached to the triply bonded C-atoms. They can be easily removed by means of a strong base.
The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in- a)the molecular plane (2002S)
- b)a plane parallel to the molecular plane
- c)a plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which bisects the carbon - carbon σ -bond at right angle
- d)a plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which contains the carbon - carbon σ -bond.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in
a)
the molecular plane (2002S)
b)
a plane parallel to the molecular plane
c)
a plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which bisects the carbon - carbon σ -bond at right angle
d)
a plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which contains the carbon - carbon σ -bond.
|
|
Saranya Choudhary answered |
TIPS/Formulae : The π bond is formed by the sideways overlapping of two p-orbitals of the two carbon atoms.
The molecular plane does not have any π electron density as the p-orbitals are perpendicular to the plane containing the ethene molecule. The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in the molecular plane.
The molecular plane does not have any π electron density as the p-orbitals are perpendicular to the plane containing the ethene molecule. The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in the molecular plane.
Identify the reagent from the following list which can easily distinguish between 1-butyne and 2-butyne (2002S)- a)bromine, CCl4
- b)H2, Lindlar catalyst
- c)dilute H2SO4, HgSO4
- d)ammonical Cu2Cl2 solution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the reagent from the following list which can easily distinguish between 1-butyne and 2-butyne (2002S)
a)
bromine, CCl4
b)
H2, Lindlar catalyst
c)
dilute H2SO4, HgSO4
d)
ammonical Cu2Cl2 solution
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
TIPS/Formulae : In 1-butyne terminal hydrogen is acidic where as in 2-butyne there is no terminal hydrogen. Thus 2-butyne will not react with ammonical Cu2Cl2. While 1-butyne, being terminal alkyne, will give red ppt. with ammonical cuprous chloride
Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives formaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of : [2011]- a)two ethylenic double bonds
- b)a vinyl group
- c)an isopropyl group
- d)an acetylenic triple bond
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives formaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of : [2011]
a)
two ethylenic double bonds
b)
a vinyl group
c)
an isopropyl group
d)
an acetylenic triple bond

|
Ritika Kulkarni answered |
The correct answer is:
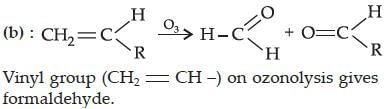
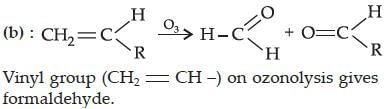
At 300 K and 1 atm, 15 mL of a gaseous hydrocarbon requires 375 mL air containing 20% O2 by volume for complete combustion. After combustion the gases occupy 330 mL.Assuming that the water formed is in liquid form and the volumes were measured at the same temperature and pressure, the formula of the hydrocarbon is: [JEE M 2016]- a)C4H8
- b)C4H10
- c)C3H6
- d)C3H8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At 300 K and 1 atm, 15 mL of a gaseous hydrocarbon requires 375 mL air containing 20% O2 by volume for complete combustion. After combustion the gases occupy 330 mL.Assuming that the water formed is in liquid form and the volumes were measured at the same temperature and pressure, the formula of the hydrocarbon is: [JEE M 2016]
a)
C4H8
b)
C4H10
c)
C3H6
d)
C3H8
|
|
Shruti Patel answered |
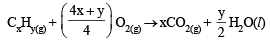
Volume of O2 used = 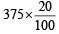 = 75 ml
= 75 ml
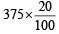 = 75 ml
= 75 ml∴ From the reaction of combustion
1 ml CxHy requires =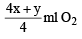
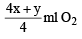
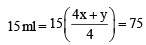
So, 4x + y = 20
x = 3
y = 8
x = 3
y = 8
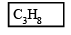
The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethyl benzene by KMnO4 is [2007]- a)benzyl alcohol
- b)benzophenone
- c)acetophenone
- d)benzoic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethyl benzene by KMnO4 is [2007]
a)
benzyl alcohol
b)
benzophenone
c)
acetophenone
d)
benzoic acid.
|
|
Vaibhav Datta answered |
When alkyl benzene are oxidised with alkaline KMnO4, (strong oxidising agent) the entire alkyl group is oxidised to –COOH group regardless of length of side chain.
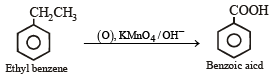
Of the five isomeric hexanes, the isomer which can give two monochlorinated compounds is [2005]- a)2-methylpentane
- b)2, 2-dimethylbutane
- c)2, 3-dimethylbutane
- d)n-hexane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the five isomeric hexanes, the isomer which can give two monochlorinated compounds is [2005]
a)
2-methylpentane
b)
2, 2-dimethylbutane
c)
2, 3-dimethylbutane
d)
n-hexane
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
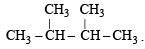 Since it contains only two types of H-atoms hence it will give only two mono chlorinated compounds viz.
Since it contains only two types of H-atoms hence it will give only two mono chlorinated compounds viz. 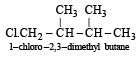 and
and 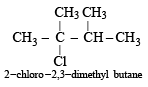
Among P, Q, R and S, the aromatic compound(s) is/are (JEE Advanced 2013-I)
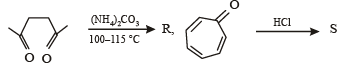
- a)P
- b)R
- c)Q
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among P, Q, R and S, the aromatic compound(s) is/are (JEE Advanced 2013-I)
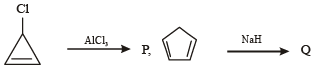
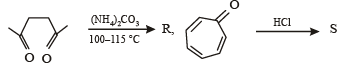
a)
P
b)
R
c)
Q
d)
S
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
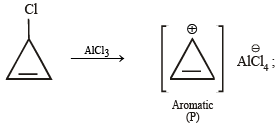
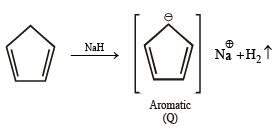
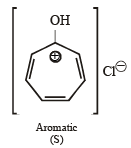
Note : P has 2 p electrons, while Q, R & S have 6 p electrons each. Hence all the 4 are aromatic.
In the presence of peroxide, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do not give anti-Markovnikov addition to alkenes because(2001S)- a)both are highly ionic
- b)one is oxidizing and the other is reducing
- c)one of the steps is endothermic in both the cases
- d)all the steps are exothermic in both the cases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the presence of peroxide, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do not give anti-Markovnikov addition to alkenes because(2001S)
a)
both are highly ionic
b)
one is oxidizing and the other is reducing
c)
one of the steps is endothermic in both the cases
d)
all the steps are exothermic in both the cases
|
|
Harshitha Shah answered |
TIPS/Formulae : Peroxide effect is effective only in case of HBr and not in case of HCl and HI.
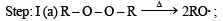
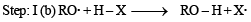
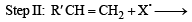
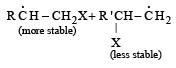
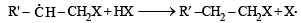
For HCl, Step-I (b) is endothermic while step-II is exothermic but for HI, Step-I(b) is exothermic while Step-II is endothermic.
On mixing a certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, it forms only one monochloroalkane.This alkane could be [2003]- a)pentane
- b)isopen tane
- c)neopentane
- d)pr opane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On mixing a certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, it forms only one monochloroalkane.This alkane could be [2003]
a)
pentane
b)
isopen tane
c)
neopentane
d)
pr opane
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
As monochlorination is taking place, only one product will be formed as neopentane has a symmetrical structure with all the H having degree as 1.
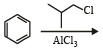
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives predominantly [2007]- a)m-chlorobenzene
- b)benzoyl chloride
- c)benzyl chloride
- d)o- and p-chlorotoluene.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives predominantly [2007]
a)
m-chlorobenzene
b)
benzoyl chloride
c)
benzyl chloride
d)
o- and p-chlorotoluene.
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
The CH3 group in toluene shows both +I and Hyperconjugation effects which activate the Benzene ring. Thus -ve charge density increases (at the o- and p- positions). Now, the above reaction includes halogenation of Benzene which is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. FeCl3 acts as a Lewis acid and takes Cl from Cl2 forming FeCl4- and Cl+. The latter being an electrophile attacks the ring at the o- and p- positions to form the respective products.
Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes except ethene leads to the formation of- a)mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
- b)mixture of primary and secondary alcohols
- c)secondary or tertiary alcohol
- d)primary alcohol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes except ethene leads to the formation of
a)
mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
b)
mixture of primary and secondary alcohols
c)
secondary or tertiary alcohol
d)
primary alcohol
|
|
Naveen Goyal answered |
Water adds directly to the more reactive alkene in presence of a strongly acidic catalyst forming alcohols.
Addition occurs according to Markonikov’s rule.
Addition occurs according to Markonikov’s rule.
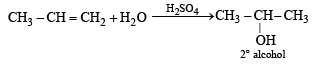
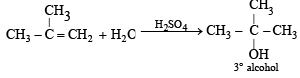
NOTE : Addition follows Markownikoff’s rule.
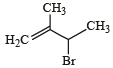
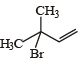
Anti-Markovnikoff addition of HBr is not observed in : (1985 - 1 Mark)- a)propene
- b)1-butene
- c)but-2-ene
- d)pent-2-ene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti-Markovnikoff addition of HBr is not observed in : (1985 - 1 Mark)
a)
propene
b)
1-butene
c)
but-2-ene
d)
pent-2-ene
|
|
Nandita Sharma answered |
TIPS/Formulae : Anti-Markovnikoff’s addition of HBr is observed only with unsymmetrical alkenes, a, b, and d.
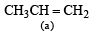
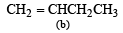
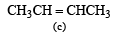
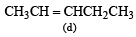
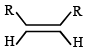
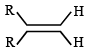
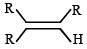
Which one of the following will react fastest with H2 under catalytic hydrogenation condition ? (2000S)- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
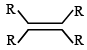
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following will react fastest with H2 under catalytic hydrogenation condition ? (2000S)
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Palak Datta answered |
TIPS/Formulae : The relative rates of hydrogenation decreases with increase of steric hinderance.
R2C = CH2 > RCH = CHR > R2C = CHR > R2C = CR2
Among the four olefins, (a) and (b) are less stable (Saytzeff rule). Further in (a), the bulky alkyl groups are on same side (cis-isomer), hence it is less stable.
R2C = CH2 > RCH = CHR > R2C = CHR > R2C = CR2
Among the four olefins, (a) and (b) are less stable (Saytzeff rule). Further in (a), the bulky alkyl groups are on same side (cis-isomer), hence it is less stable.
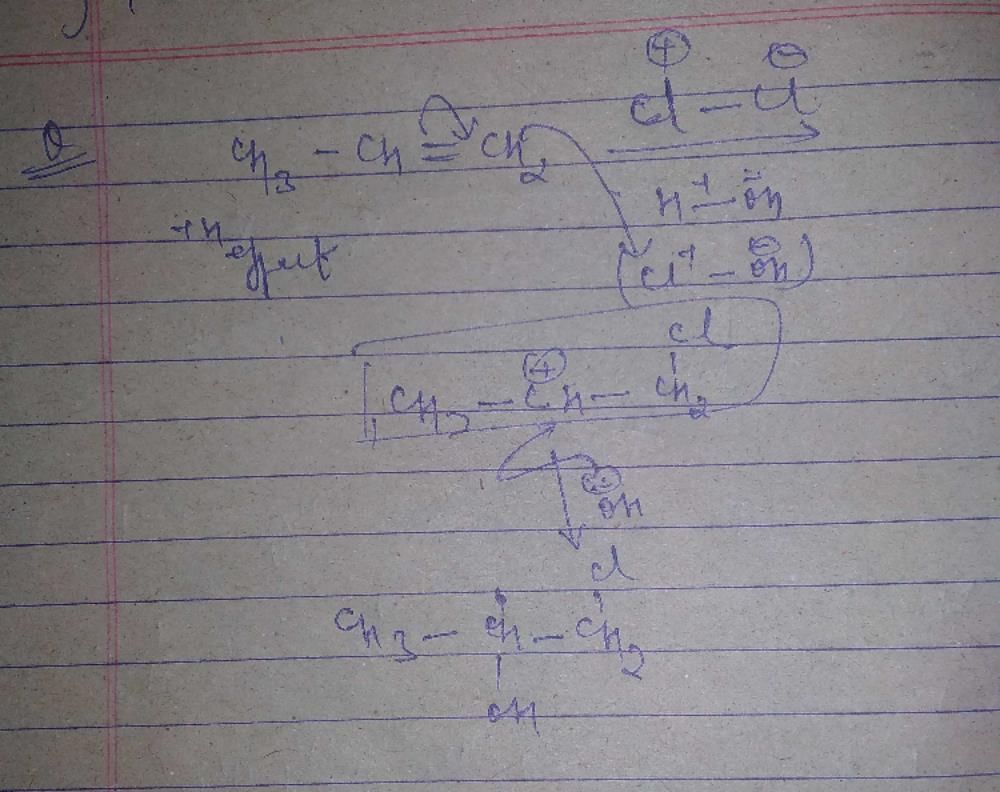
The reaction of propene with HOCl proceeds via the addition of(2001S)- a)H+ in the first step
- b)Cl+ in the first step
- c)OH– in the first step
- d)Cl+ and OH– in a single step
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of propene with HOCl proceeds via the addition of(2001S)
a)
H+ in the first step
b)
Cl+ in the first step
c)
OH– in the first step
d)
Cl+ and OH– in a single step

|
Rohit Yadav answered |
Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions.HOCl on self ionisation produces Cl^+ which attacks first.
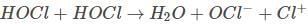
∴ The option is (b) Cl^+ in the first step.
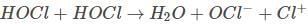
∴ The option is (b) Cl^+ in the first step.
Compound(s) that on hydrogenation produce(s) optically inactive compound(s) is (are) (JEE Adv. 2015)- a)

- b)
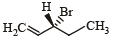
- c)
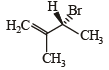
- d)
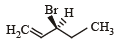
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Compound(s) that on hydrogenation produce(s) optically inactive compound(s) is (are) (JEE Adv. 2015)
a)

b)
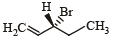
c)

d)
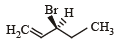
|
|
Prakash answered |
Break the double bond and add Hydrogen both side and then check 4 different group
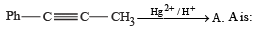 (2003S)
(2003S)- a)
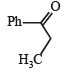
- b)
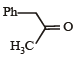
- c)
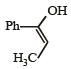
- d)
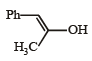
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
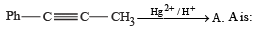 (2003S)
(2003S)a)

b)
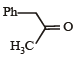
c)

d)
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
Carbocation will be formed in the Phenyl position (1st C outside ring). That will be resonance stabilized. The water will attack there, forming an -enol. This will tautomerise to form the corresponding ketone. That will be A.
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide ? [2012]- a)Tertiary butyl chloride
- b)Neopentane
- c)Isohexane
- d)Neohexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide ? [2012]
a)
Tertiary butyl chloride
b)
Neopentane
c)
Isohexane
d)
Neohexane
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
As in neopentane, the degree of all the H atoms is same and the molecule is symmetric
The hottest region of Bunsen flame shown in the figure below is : [JEE M 2016]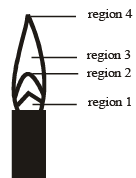
- a)region 3
- b)region 4
- c)region 1
- d)region 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The hottest region of Bunsen flame shown in the figure below is : [JEE M 2016]

a)
region 3
b)
region 4
c)
region 1
d)
region 2
|
|
Akash Paila answered |
Region 2 is blue region so it is the most hottest region in the candle
it is jee main previously asked bit from chemistry
2-Methylbutane on reacting with bromine in the presence of sunlight gives mainly [2005]- a)1-bromo-3-methylbutane
- b)2-bromo-3-methylbutane
- c)2-bromo-2-methylbutane
- d)1-bromo-2-methylbutane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
2-Methylbutane on reacting with bromine in the presence of sunlight gives mainly [2005]
a)
1-bromo-3-methylbutane
b)
2-bromo-3-methylbutane
c)
2-bromo-2-methylbutane
d)
1-bromo-2-methylbutane

|
Mihir Patel answered |
(C) : The reactivity order of abstraction of H atoms towards bromination of alkane is 3 degree H > 2 degree H > 1 degree H.
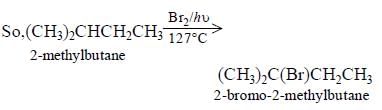
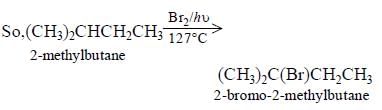
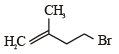
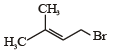
Consider the following reaction (2002S)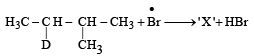 Identify the structure of the major product 'X'
Identify the structure of the major product 'X'- a)
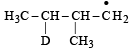
- b)
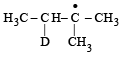
- c)
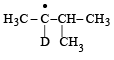
- d)
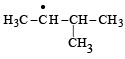
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction (2002S)
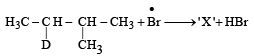
Identify the structure of the major product 'X'
a)
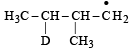
b)
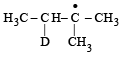
c)
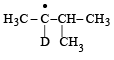
d)
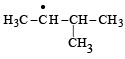
|
|
Akshay Chauhan answered |
Br• is less reactive and more selective and so the most stable free radical (3°) will be the major product.
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by (2000S)- a)conc. H2SO4
- b)Br2 in CCl4
- c)dil. KMnO4
- d)AgNO3 in ammonia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by (2000S)
a)
conc. H2SO4
b)
Br2 in CCl4
c)
dil. KMnO4
d)
AgNO3 in ammonia
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
AgNO3 gives ppt with alkynes due to presence of acidic H. Alkenes do not show this test.
Chapter doubts & questions for Hydrocarbons - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Hydrocarbons - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily