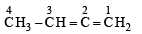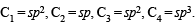All Exams >
JEE >
35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Organic Chemistry — Some Basic Principles & Technique for JEE Exam
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds;CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2COOH- a)1 > 2 > 3
- b)3 > 1 > 2
- c)1 > 3 > 2
- d)3 > 2 > 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds;
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2COOH
a)
1 > 2 > 3
b)
3 > 1 > 2
c)
1 > 3 > 2
d)
3 > 2 > 1

|
Ishita Reddy answered |
In car boxylic acids, molecules ar e more str ongly associated followed by alcohols.
The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether is - a)n-propyl methyl ether
- b)butan-1-ol
- c)2-methylpropan-2-ol
- d)butan on e
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether is
a)
n-propyl methyl ether
b)
butan-1-ol
c)
2-methylpropan-2-ol
d)
butan on e
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The first three are isomers of diethyl ether, C2H5OC2H5 (C4H10O).
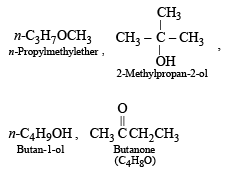
Among the following, the molecule with the highest dipole moment is:- a)CH3Cl
- b)CH2Cl2
- c)CHCl3
- d)CCl4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the molecule with the highest dipole moment is:
a)
CH3Cl
b)
CH2Cl2
c)
CHCl3
d)
CCl4
|
|
Nandita Chopra answered |
NOTE : Dipole moment is a vector quantity.
Methane molecule being symmetrical, has zero dipole moment. Replacement of one of the H– atoms by Cl atom increases the dipole moment. The increase in dipole moment is rather more than what can be expected because of the fact that the bond dipole moment of C – H bond and that of C – Cl bond reinforce one another.
Replacement of another H atom by Cl increases the bond angle due to lone pair – lone pair repulsion between two Cl–atoms thereby reducing the dipole moment of the molecule. Increase in angle is again caused by the the introduction of the third Cl–atom.
When the fourth Cl–atom is introduced, the molecule (CCl4) again becomes symmetrical and dipole moment reduces to zero. So, CH3Cl will have the maximum dipole moment.
Methane molecule being symmetrical, has zero dipole moment. Replacement of one of the H– atoms by Cl atom increases the dipole moment. The increase in dipole moment is rather more than what can be expected because of the fact that the bond dipole moment of C – H bond and that of C – Cl bond reinforce one another.
Replacement of another H atom by Cl increases the bond angle due to lone pair – lone pair repulsion between two Cl–atoms thereby reducing the dipole moment of the molecule. Increase in angle is again caused by the the introduction of the third Cl–atom.
When the fourth Cl–atom is introduced, the molecule (CCl4) again becomes symmetrical and dipole moment reduces to zero. So, CH3Cl will have the maximum dipole moment.
Statement -1: Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reactions.Statement-2:In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbocation is more resonance stabilized.- a)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
- b)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
- c)If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
- d)If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement -1: Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reactions.
Statement-2:In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbocation is more resonance stabilized.
a)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
b)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
c)
If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
d)
If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
 its in termediate carbocation is more stable than the one in benzene.
its in termediate carbocation is more stable than the one in benzene.The IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is- a)Benzene chloro ketone
- b)Benzoyl chloride
- c)Chloro phenyl ketone
- d)Benzene carbonyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is
a)
Benzene chloro ketone
b)
Benzoyl chloride
c)
Chloro phenyl ketone
d)
Benzene carbonyl chloride

|
Nandini Nair answered |
Carboxylic acids ar e named as oyl chlorides
In Carius method of estimation of halogens, 250 mg of an organic compound gave 141 mg of AgBr. The percentage of bromine in the compound is :(at. mass Ag =108; Br = 80)- a)48
- b)60
- c)24
- d)36
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Carius method of estimation of halogens, 250 mg of an organic compound gave 141 mg of AgBr. The percentage of bromine in the compound is :
(at. mass Ag =108; Br = 80)
a)
48
b)
60
c)
24
d)
36
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
First we have to find moles of br in rex. as 141/188
now mass of br in compound is 141*80/188
so %br=141*80*100/188*250=24
now mass of br in compound is 141*80/188
so %br=141*80*100/188*250=24
In the given conformation, if C2 is rotated about C2 – C3 bond anticlockwise by an angle of 120º then the conformation obtained is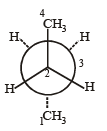
- a)fully eclipsed conformation
- b)partially eclipsed conformation
- c)gauche conformation
- d)staggered conformation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given conformation, if C2 is rotated about C2 – C3 bond anticlockwise by an angle of 120º then the conformation obtained is

a)
fully eclipsed conformation
b)
partially eclipsed conformation
c)
gauche conformation
d)
staggered conformation
|
|
Anand Kumar answered |
Option C is correct.
once go through some examples of gauche isomers.
once go through some examples of gauche isomers.
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is :- a)
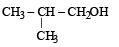
- b)
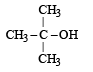
- c)
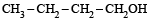
- d)
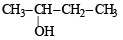
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is :
a)
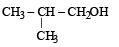
b)

c)
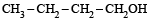
d)
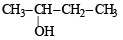
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
NOTE : The order of stability of carbonium ion is
tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
Tertiary carbonium ions (formed in b) are more stable because of electron repelling (+I effect) nature of CH3 group due to which the +ve charge gets dispersed and also due to hyperconjugation.
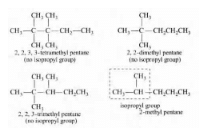
The number of isomers of C6H14 is - a)4
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of isomers of C6H14 is
a)
4
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
1) N-hexane
2)2 ,Methyl pentane
3)2,2 dimethyl butane
4)2,3 dimethyl butane
5)3 methyl pentane
In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is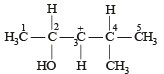
- a)CH3 at C-4
- b)H at C-4
- c)CH3 at C-2
- d)H at C-2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is

a)
CH3 at C-4
b)
H at C-4
c)
CH3 at C-2
d)
H at C-2
|
|
Akash Kumar answered |
As we know that the migratory aptitude of H-ion is more than CH3- ion.And we always have to form the most stable carbocation in case of rearrangement. Hence if we remove H-Ion form C4 linkage we will gate a +ve charge in the vicinity of a lone pair which is very stable due to back bonding.So option D is correct.
I hope u get it.
Among the following, the compound that can be most readily sulphonated is- a)benzene
- b)nitrobenzene
- c)toluene
- d)chlorobenzene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the compound that can be most readily sulphonated is
a)
benzene
b)
nitrobenzene
c)
toluene
d)
chlorobenzene

|
Sagar Mukherjee answered |
TIPS/FORMULAE :
–NO2, –Cl and –OH are electron-attracting or withdrawing group due to –M, –E and/or –I effects where as –CH3 show, +I effect (electron releasing).
Because of the + I effect of the CH3 group, toluene has the highest electron density in the o- and p- positions and hence can be most readily sulphonated.
Because of the + I effect of the CH3 group, toluene has the highest electron density in the o- and p- positions and hence can be most readily sulphonated.
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is:- a)2- methyl propene
- b)2-butene
- c)2- methyl -2- butene
- d)pr open e
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is:
a)
2- methyl propene
b)
2-butene
c)
2- methyl -2- butene
d)
pr open e

|
Sahana Joshi answered |
Correct answer is option (B) : 2-butene
When two groups attached to a double bonded carbon atom are same, the compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Compounds in which the two groups attached to a double bonded carbon are different, exhibit geometrical isomerism, thus, only 2-butene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
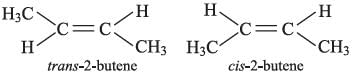
When two groups attached to a double bonded carbon atom are same, the compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Compounds in which the two groups attached to a double bonded carbon are different, exhibit geometrical isomerism, thus, only 2-butene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
The Cl—C—Cl angle in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about - a)120º and 109.5º
- b)90º and 109.5º
- c)109.5º and 90º
- d)109.5º and 120º
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Cl—C—Cl angle in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about
a)
120º and 109.5º
b)
90º and 109.5º
c)
109.5º and 90º
d)
109.5º and 120º

|
Anisha Deshpande answered |
The bond angle in sp3, sp2 and sp hybridization is respectively 109.28', 120º and 180º.
Tetrachloroethene being an alkene has sp2 hybridised C-atoms and hence the Cl – C – Cl angle is 120º, whereas in tetrachloromethane, carbon is sp3 hybridised, so the angle is 109º.28’.
Tetrachloroethene being an alkene has sp2 hybridised C-atoms and hence the Cl – C – Cl angle is 120º, whereas in tetrachloromethane, carbon is sp3 hybridised, so the angle is 109º.28’.
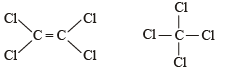
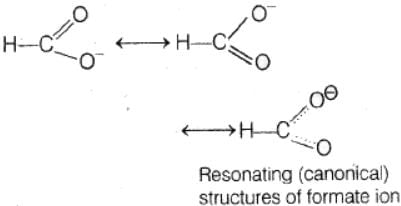
In the anion HCOO– the two carbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length. what is the reason for it ?
- a)The C = O bond is weaker than the C — O bond
- b)The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
- c)Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are hybridised
- d)The anion HCOO– has two resonating structures
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the anion HCOO– the two carbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length. what is the reason for it ?
a)
The C = O bond is weaker than the C — O bond
b)
The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
c)
Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are hybridised
d)
The anion HCOO– has two resonating structures

|
Nandita Basak answered |
The anion HCOO− has two resonating structures in which double bond occurs on both xygen atoms. So, the bond length of both the CO bonds is equal.

Arrangement of (CH3)3C –, (CH3)2CH –, CH3 – CH2 – when attached to benzyl or an unsaturated group in increasing order of inductive effect is- a)(CH3)3C – < (CH3)2CH – < CH3 – CH2
- b)CH3 –CH2– < (CH3)2 CH – < (CH3)3C –
- c)(CH3)2CH– <(CH3)3C –< CH3, –CH2
- d)(CH3)3C– < CH3 –CH2 –(CH3)2CH –
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrangement of (CH3)3C –, (CH3)2CH –, CH3 – CH2 – when attached to benzyl or an unsaturated group in increasing order of inductive effect is
a)
(CH3)3C – < (CH3)2CH – < CH3 – CH2
b)
CH3 –CH2– < (CH3)2 CH – < (CH3)3C –
c)
(CH3)2CH– <(CH3)3C –< CH3, –CH2
d)
(CH3)3C– < CH3 –CH2 –(CH3)2CH –

|
Anisha Deshpande answered |
Hyperconjugation effect increases in the order :
(CH3)3C−<(CH3)2CH−<CH3CH2−
The σ electrons of C—H bond of the alkyl group enter into partial conjugation with the attached unsaturated system or with the unshared p orbital.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
(CH3)3C−<(CH3)2CH−<CH3CH2−
The σ electrons of C—H bond of the alkyl group enter into partial conjugation with the attached unsaturated system or with the unshared p orbital.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
Which of the following represents the given mode of hybridisation sp2 – sp2 – sp – sp from left to right?- a)H2C = CH – C ≡ N
- b)HC ≡ C – C ≡ CH
- c)H2C = C = C = CH2
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the given mode of hybridisation sp2 – sp2 – sp – sp from left to right?
a)
H2C = CH – C ≡ N
b)
HC ≡ C – C ≡ CH
c)
H2C = C = C = CH2
d)

|
Notes Wala answered |
A has the following hybridization order:
Nitrogen atom has an sp hybridization because it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
Note: lone pair and negative charge on an atom can be converted to a bond while considering the hybridization.
B has the following hybridization order:
C has the following hybridization order:
D has the following hybridization order:
Hence A is the correct answer.
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives- a)an enantiomer of the substrate
- b)a product with opposite optical rotation
- c)a mixture of diastereomers
- d)a single stereoisomer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives
a)
an enantiomer of the substrate
b)
a product with opposite optical rotation
c)
a mixture of diastereomers
d)
a single stereoisomer

|
Manisha Mehta answered |
SN2 reactions proceed with inversion of configuration.
Since the attacking nucleophile is not necessarily the same as that of leaving group, the product cannot be enantiomer of the substrate and thus necessarily will not have opposite optical rotation. Moreover since only one product is obtained, we can not obtain diastereomers.
Since the attacking nucleophile is not necessarily the same as that of leaving group, the product cannot be enantiomer of the substrate and thus necessarily will not have opposite optical rotation. Moreover since only one product is obtained, we can not obtain diastereomers.
The structure 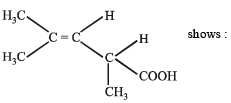
- a)geometrical isomersism
- b)optical isomerism
- c)geometrical & optical isomerism
- d)tautomerism.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure 

a)
geometrical isomersism
b)
optical isomerism
c)
geometrical & optical isomerism
d)
tautomerism.

|
Ravi Kumar answered |
Since there is one chiral carbon
so it will show optical isomerism
so it will show optical isomerism
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds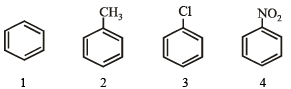
- a)1 > 2 > 3 > 4
- b)4 > 3 > 2 > 1
- c)2 > 1 > 3 > 4
- d)2 > 3 > 1 > 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds

a)
1 > 2 > 3 > 4
b)
4 > 3 > 2 > 1
c)
2 > 1 > 3 > 4
d)
2 > 3 > 1 > 4

|
Vikas Saini answered |
Because ch3 shows plus i effect which increases e- density while others shows -i effect
Due to the presence of an unpaired electron, free radicals are:- a)cations
- b)an ions
- c)chemically inactive
- d)chemically reactive
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Due to the presence of an unpaired electron, free radicals are:
a)
cations
b)
an ions
c)
chemically inactive
d)
chemically reactive

|
Mohit Patel answered |
(D) :- Free radicals are highly reactive due to presence of an unpaired electron. They readily try to pairup the odd electrons.
The bond order of in dividual carbon -carbon bonds in benzene is- a)one
- b)two
- c)between one and two
- d)one and two, alternately
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond order of in dividual carbon -carbon bonds in benzene is
a)
one
b)
two
c)
between one and two
d)
one and two, alternately

|
Pranav Pillai answered |
NOTE : The phenomenon of resonance gives identical bonding and hence identical bond lengths.
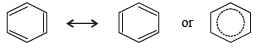
C – C bond order in benzene = 1.5
Out of the following, the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is- a)3-methyl-2-pentene
- b)4-methyl-1-pentene
- c)3-methyl-1-pentene
- d)2-methyl-2-pentene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following, the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is
a)
3-methyl-2-pentene
b)
4-methyl-1-pentene
c)
3-methyl-1-pentene
d)
2-methyl-2-pentene
|
|
Tanishq Saini answered |
For a compound to show optical isomer ism, presence of chiral carbon atom is a necessary condition.
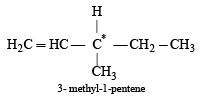
The products of combustion of an aliphatic thiol (RSH) at 298 K are- a)CO2(g), H2O(g) and SO2(g)
- b)CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
- c)CO2(l), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
- d)CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(l)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The products of combustion of an aliphatic thiol (RSH) at 298 K are
a)
CO2(g), H2O(g) and SO2(g)
b)
CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
c)
CO2(l), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
d)
CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(l)
|
|
Deepika Das answered |
Products of Combustion of Aliphatic Thiol (RSH)
The combustion of an aliphatic thiol (RSH) typically results in the formation of several products. In this case, the products are:
CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
Here's why:
- CO2(g): Carbon dioxide is a common product of combustion reactions involving organic compounds. It is formed when the carbon in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen during combustion.
- H2O(l): Water is also a common product of combustion reactions. In this case, the hydrogen in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen to form water.
- SO2(g): Sulfur dioxide is produced when sulfur in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen during combustion. It is a common product of combustion reactions involving sulfur-containing compounds.
Therefore, the correct combination of products for the combustion of an aliphatic thiol at 298 K is CO2(g), H2O(l), and SO2(g) as given in option B.
The combustion of an aliphatic thiol (RSH) typically results in the formation of several products. In this case, the products are:
CO2(g), H2O(l) and SO2(g)
Here's why:
- CO2(g): Carbon dioxide is a common product of combustion reactions involving organic compounds. It is formed when the carbon in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen during combustion.
- H2O(l): Water is also a common product of combustion reactions. In this case, the hydrogen in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen to form water.
- SO2(g): Sulfur dioxide is produced when sulfur in the aliphatic thiol combines with oxygen during combustion. It is a common product of combustion reactions involving sulfur-containing compounds.
Therefore, the correct combination of products for the combustion of an aliphatic thiol at 298 K is CO2(g), H2O(l), and SO2(g) as given in option B.
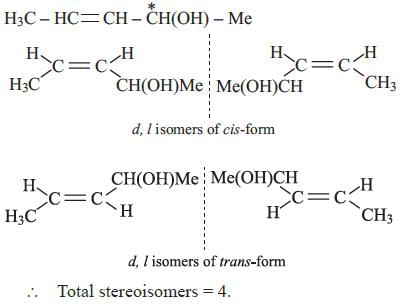
The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formulaCH3 – CH = CH – CH(OH) – Me is:- a)2
- b)4
- c)6
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formula
CH3 – CH = CH – CH(OH) – Me is:
a)
2
b)
4
c)
6
d)
3

|
Siddharth Chaudhary answered |
(B) : The given compound has a C = C group and one chiral (*) carbon,

Which of the following molecules, in pure form, is (are) unstable at room temperature ?- a)
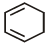
- b)
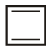
- c)
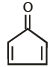
- d)
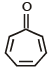
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules, in pure form, is (are) unstable at room temperature ?
a)

b)

c)
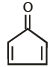
d)
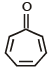
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
b and c, being antiaromatic, are unstable at room temperature.
Resonance structures of a molecule should have :- a)identical arrangement of atoms
- b)nearly the same energy content
- c)the same number of paired electrons
- d)identical bonding
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Resonance structures of a molecule should have :
a)
identical arrangement of atoms
b)
nearly the same energy content
c)
the same number of paired electrons
d)
identical bonding
|
|
Swara Joshi answered |
Resonating structures differ in bonding pattern.
Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant ?- a)CH3CHFCOOH
- b)FCH2CH2COOH
- c)BrCH2CH2COOH
- d)CH3CHBrCOOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant ?
a)
CH3CHFCOOH
b)
FCH2CH2COOH
c)
BrCH2CH2COOH
d)
CH3CHBrCOOH

|
Tejas Chawla answered |
TIPS/Formulae :
(i) The inductive effect decreases with increase in distance of halogen atom from the carboxylic group and hence the strength of acid proportionally decreases.
(ii) Th e acidity in cr eas es with th e in cr eas e in electronegativity of the halogen present.
Smallest dissociation constant means weakest acid, which is BrCH2 CH2COOH because here Br (less electronegative than F) is two carbon atoms away from – COOH.
(ii) Th e acidity in cr eas es with th e in cr eas e in electronegativity of the halogen present.
Smallest dissociation constant means weakest acid, which is BrCH2 CH2COOH because here Br (less electronegative than F) is two carbon atoms away from – COOH.
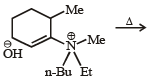 The alkene formed as a major product in the above elimination reaction is
The alkene formed as a major product in the above elimination reaction is- a)
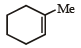
- b)
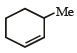
- c)
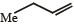
- d)CH2 = CH2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
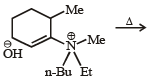
The alkene formed as a major product in the above elimination reaction is
a)
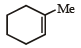
b)

c)
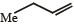
d)
CH2 = CH2
|
|
Vivek answered |

See, in this one, HYPERCONJUGATION will decide the major product. Hyperconjugation is dependent on the number of α-H's. See the carbon to which Me is attached. Check the number of H's α to this carbon in each option. The one with the max number of them will be the major product. It's B.
The bond between carbon atom (1) and carbon atom (2) in compound 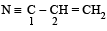 involves the hybrids as
involves the hybrids as- a)sp2 and sp2
- b)sp3 and sp
- c)sp and sp2
- d)sp and sp
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond between carbon atom (1) and carbon atom (2) in compound 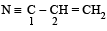 involves the hybrids as
involves the hybrids as
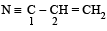 involves the hybrids as
involves the hybrids asa)
sp2 and sp2
b)
sp3 and sp
c)
sp and sp2
d)
sp and sp
|
|
Sravya Nair answered |
Car bon bonded with a triple bond (i.e. C1) is sp hybridised. Carbon bonded with a double bond (C2) is sp2 hybridised.
Out of the following compounds, which will have a zero dipole moment?- a)1, 1-dichloroethylene
- b)cis-1, 2-dichloroethylene
- c)trans-1, 2-dichloroethylene
- d)None of these compounds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following compounds, which will have a zero dipole moment?
a)
1, 1-dichloroethylene
b)
cis-1, 2-dichloroethylene
c)
trans-1, 2-dichloroethylene
d)
None of these compounds
|
|
Abhijeet Ingle answered |
The trans isomer has net dipole moment zero as constituent dipole moments cancel out each other
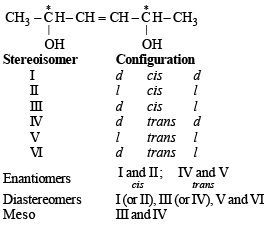
The correct statement(s) about the compoundH3C(HO)HC–CH = CH – CH(OH)CH3 (X) is(are)- a)The total number of stereoisomers possible for X is 6
- b)The total number of diastereomers possible for X is 3
- c)If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is trans, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 4
- d)If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is cis, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 2
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement(s) about the compound
H3C(HO)HC–CH = CH – CH(OH)CH3 (X) is(are)
a)
The total number of stereoisomers possible for X is 6
b)
The total number of diastereomers possible for X is 3
c)
If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is trans, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 4
d)
If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is cis, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 2
|
|
Sarthak Dasgupta answered |
Dipole moment is shown by :- a)1, 4-dichlorobenzene
- b)cis- 1, 2-dichloroethane
- c)trans -1, 2-dichloroethene
- d)trans- 1, 2-dichloro-2-pentene
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dipole moment is shown by :
a)
1, 4-dichlorobenzene
b)
cis- 1, 2-dichloroethane
c)
trans -1, 2-dichloroethene
d)
trans- 1, 2-dichloro-2-pentene
|
|
Nidhi Joshi answered |
1, 4-Dichlorobenzene (p-dichlorobenzene) and trans1, 2-dichloroethene have zero dipole moment because of their symmetrical structures.
In the compound CH2 = CH–CH2–CH2–C ≡ CH, the C2–C3 bond is of the type,- a)sp – sp2
- b)sp3 – sp3
- c)sp – sp3
- d)sp2 – sp3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the compound CH2 = CH–CH2–CH2–C ≡ CH, the C2–C3 bond is of the type,
a)
sp – sp2
b)
sp3 – sp3
c)
sp – sp3
d)
sp2 – sp3
|
|
Kaavya Pillai answered |
The compound CH2=CH is known as ethene or ethylene. It is an organic compound with the formula C2H4. Ethene is a colorless gas with a sweet odor and is commonly used in the production of plastics, solvents, and as a fuel.
Among the following compounds, the most acidic is- a)p-nitrophenol
- b)p-hydroxybenzoic acid
- c)o-hydroxybenzoic acid
- d)p-toluic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, the most acidic is
a)
p-nitrophenol
b)
p-hydroxybenzoic acid
c)
o-hydroxybenzoic acid
d)
p-toluic acid
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
will be most acidic due to hydrogen bonding .among B) and D) ...B) will be more acidic as -OH is slighlty e- withdrawing
so correct order should be - (C) o-hydroxybenzoic > (B) p-hydroxybenzoic > (D) p-toluic acid > (A) p-nitrophenol
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for a SN2 reaction is- a)RF > RCl > RBr > RI
- b)RF > RBr > RCl > RI
- c)RCl > RBr > RF > RI
- d)RI > RBr > RCl > RF
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for a SN2 reaction is
a)
RF > RCl > RBr > RI
b)
RF > RBr > RCl > RI
c)
RCl > RBr > RF > RI
d)
RI > RBr > RCl > RF
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Rate of reaction will be R – I > R – Br > R – Cl > R – F. because I– is the best, while F– is the poorest leaving groups among halide ions.
Molecule in which the distance between the two adjacent carbon atoms is largest is - a)Ethane
- b)Ethene
- c)Ethyne
- d)Benzene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecule in which the distance between the two adjacent carbon atoms is largest is
a)
Ethane
b)
Ethene
c)
Ethyne
d)
Benzene
|
|
Khaja Moinuddin answered |
Bond order is inversely proportional to the bond length
The order of stability of the following carbocations :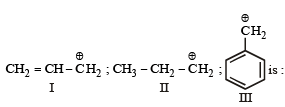
- a)III > II > I
- b)II > III > I
- c)I > II > III
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The order of stability of the following carbocations :
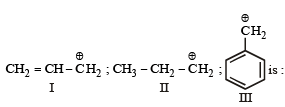
a)
III > II > I
b)
II > III > I
c)
I > II > III
d)
III > I > II

|
Roshni Chavan answered |
Correct Option (d) III > I > II
Explanation:
The order of stability of carbocation will be
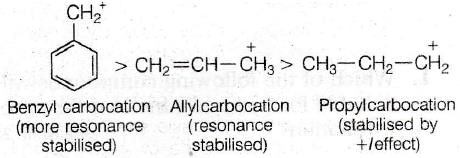
Explanation:
The order of stability of carbocation will be

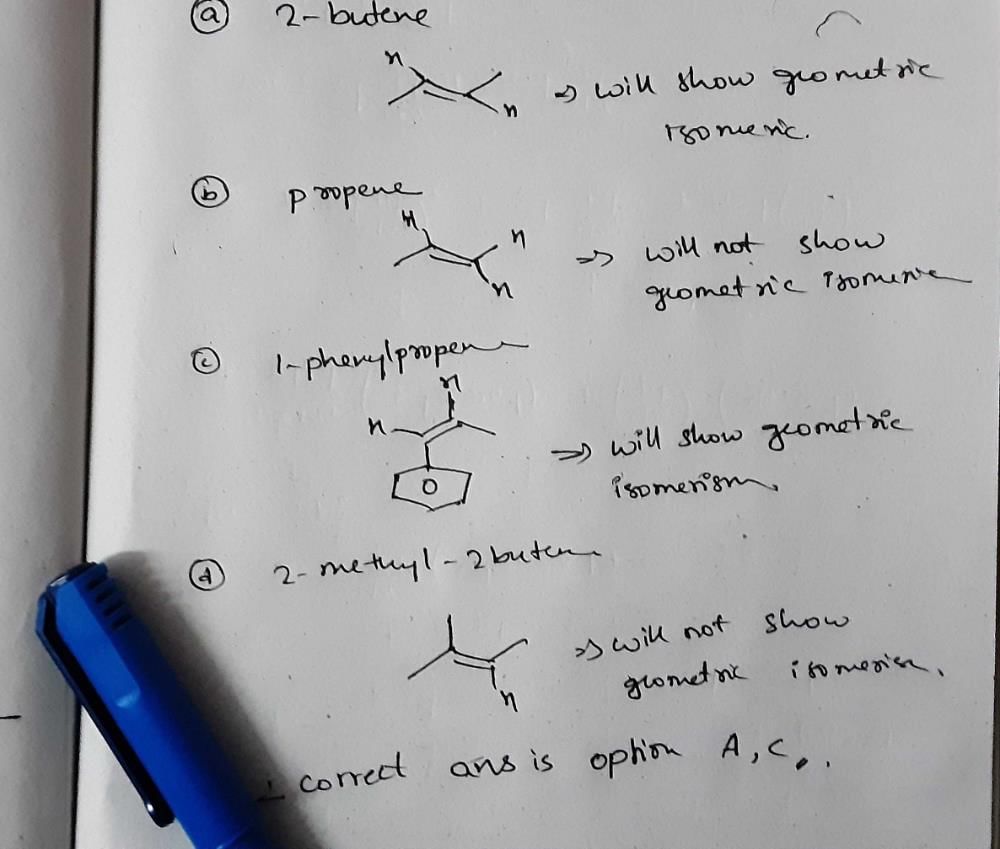
Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism ?- a)2 - Phenyl -1 - butene
- b)1, 1 - Diphenyl - 1 - propene
- c)1 - Phenyl - 2 - butene
- d)3 - Phenyl -1 - butene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism ?
a)
2 - Phenyl -1 - butene
b)
1, 1 - Diphenyl - 1 - propene
c)
1 - Phenyl - 2 - butene
d)
3 - Phenyl -1 - butene

|
Saikat Dasgupta answered |
Correct answer is option C: 1-phenyl-2-butene
1. Alkene in which different groups are attached with the double bonded carbon atoms, exhibit geometrical isomerism.
2. Alkene in which different groups are attached with the double bonded carbon atoms, exhibit geometrical isomerism.
1. Alkene in which different groups are attached with the double bonded carbon atoms, exhibit geometrical isomerism.
2. Alkene in which different groups are attached with the double bonded carbon atoms, exhibit geometrical isomerism.
The general formula CnH2nO2 could be for open chain- a)carboxylic acids
- b)diols
- c)dialdeh ydes
- d)diketon es
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The general formula CnH2nO2 could be for open chain
a)
carboxylic acids
b)
diols
c)
dialdeh ydes
d)
diketon es
|
|
Maulik Khanna answered |
General formula CnH2nO2 for carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids are a class of organic compounds that contain the carboxyl functional group (-COOH). The general formula for carboxylic acids is CnH2nO2, where 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
Explanation:
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl functional group (-COOH) attached to a carbon atom. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) bonded to the same carbon atom. The carbon atom is also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group.
The general formula CnH2nO2 represents the molecular formula of carboxylic acids. The 'n' in this formula represents the number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain. For example, if 'n' is 1, the formula becomes CH3COOH, which is the molecular formula for acetic acid.
Carboxylic acids can have both linear and branched carbon chains. The carbon chain can contain various functional groups and substituents, but the carboxyl group remains the characteristic functional group of carboxylic acids.
Examples:
1. Methanoic acid (formic acid) - CH2O2
2. Ethanoic acid (acetic acid) - C2H4O2
3. Propanoic acid - C3H6O2
4. Butanoic acid - C4H8O2
The general formula CnH2nO2 allows us to determine the molecular formula of any carboxylic acid based on the number of carbon atoms present in the carbon chain. This formula helps in identifying and classifying carboxylic acids based on their molecular composition.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - carboxylic acids.
Carboxylic acids are a class of organic compounds that contain the carboxyl functional group (-COOH). The general formula for carboxylic acids is CnH2nO2, where 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
Explanation:
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl functional group (-COOH) attached to a carbon atom. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) bonded to the same carbon atom. The carbon atom is also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group.
The general formula CnH2nO2 represents the molecular formula of carboxylic acids. The 'n' in this formula represents the number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain. For example, if 'n' is 1, the formula becomes CH3COOH, which is the molecular formula for acetic acid.
Carboxylic acids can have both linear and branched carbon chains. The carbon chain can contain various functional groups and substituents, but the carboxyl group remains the characteristic functional group of carboxylic acids.
Examples:
1. Methanoic acid (formic acid) - CH2O2
2. Ethanoic acid (acetic acid) - C2H4O2
3. Propanoic acid - C3H6O2
4. Butanoic acid - C4H8O2
The general formula CnH2nO2 allows us to determine the molecular formula of any carboxylic acid based on the number of carbon atoms present in the carbon chain. This formula helps in identifying and classifying carboxylic acids based on their molecular composition.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - carboxylic acids.
Read the following Statement-1(Asseration) and Statement -2 (Reason) and answer as per the options given below :Q. Statement -1: Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with ease.Statement -2:The carbon-halogen bond in aryl halides has partial double bond character.- a)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
- b)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
- c)If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
- d)If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following Statement-1(Asseration) and Statement -2 (Reason) and answer as per the options given below :
Q.
Statement -1: Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with ease.
Statement -2:The carbon-halogen bond in aryl halides has partial double bond character.
a)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
b)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
c)
If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
d)
If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
|
|
Anshul Choudhary answered |
Statement -1 is false beca use aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions. This is due to resonance, because of which the carbon–chlorine bond acquires partial double bond character, hence it becomes shorter and stronger and thus cannot be replaced by nucleophiles.
Which of the following is the strongest base ?- a)
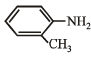
- b)
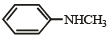
- c)
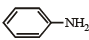
- d)
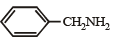
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the strongest base ?
a)
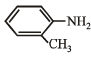
b)

c)

d)
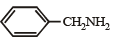
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Lone pair of electrons present on the nitrogen of benzyl amine is not involved in resonance
Among the following four structures I to IV,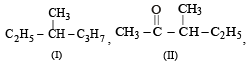
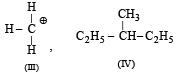 it is true that
it is true that- a)only I and II are chiral compounds
- b)only III is a chiral compound
- c)only II and IV are chiral compounds
- d)all four are chiral compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following four structures I to IV,
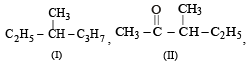
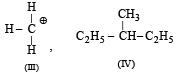
it is true that
a)
only I and II are chiral compounds
b)
only III is a chiral compound
c)
only II and IV are chiral compounds
d)
all four are chiral compounds
|
|
Sarika Bharti answered |
Option 'A' is correct because in compound I the carbon has all the 4 different or non identical groups. Similarly in compound II while compound III have 3 H atoms which is identical and similarly in compound IV the carbon atom have 2 ethyl group. That's why the correct option is 3.
In CH3CH2OH, the bond that undergoes heterolytic cleavage most readily is- a)C—C
- b)C—O
- c)C—H
- d)O—H
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In CH3CH2OH, the bond that undergoes heterolytic cleavage most readily is
a)
C—C
b)
C—O
c)
C—H
d)
O—H
|
|
Vivek answered |
Due to high difference in electronegativity, polarity of the bond is high. So it's easier to break C—O bond.
Chapter doubts & questions for Organic Chemistry — Some Basic Principles & Technique - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organic Chemistry — Some Basic Principles & Technique - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily