All questions of Environment and Ecology for RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Exam
Which of the following is NOT the major coral reef area?- a) Gulf of Mannar
- b) Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- c) Chilika Lake
- d) Gulf of Kutch
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT the major coral reef area?
a)
Gulf of Mannar
b)
Andaman & Nicobar Islands
c)
Chilika Lake
d)
Gulf of Kutch
|
|
Mansi Bajaj answered |
Major Coral Reef Areas
The major coral reef areas are crucial ecosystems that support a diverse range of marine life and play a significant role in maintaining biodiversity. These areas are vital for the health of the oceans and are often designated as protected marine areas to conserve their unique ecosystems.
Options
- Gulf of Mannar: Located between India and Sri Lanka, the Gulf of Mannar is one of the major coral reef areas in the Indian Ocean region.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are known for their rich coral reefs, which are an important part of the marine ecosystem in the region.
- Chilika Lake: Chilika Lake is not a major coral reef area. It is actually the largest brackish water lagoon in India and is known for its biodiversity, including various species of fish and birds.
- Gulf of Kutch: The Gulf of Kutch is another major coral reef area in India, located off the coast of Gujarat.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C - Chilika Lake, as it is not a major coral reef area.
Which one of the following is not a site for in-situ method of conservation of flora?- a)National Park
- b)Biosphere Reserve
- c)Botanical Garden
- d)Wildlife Sanctuary
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a site for in-situ method of conservation of flora?
a)
National Park
b)
Biosphere Reserve
c)
Botanical Garden
d)
Wildlife Sanctuary
|
|
Bhavya Gupta answered |
National Park:
- A National Park is an area set aside by a national government to protect the natural environment and the flora and fauna found within it.
- The primary objective of a National Park is to preserve the ecological integrity of the area and to provide a sanctuary for wildlife.
- In-situ conservation is a key aspect of National Parks, as they aim to protect the natural habitats and ecosystems in their original form.
- National Parks often have strict regulations and restrictions in place to ensure that the flora and fauna are not disturbed or harmed.
Biosphere Reserve:
- A Biosphere Reserve is a unique designation given to a specific area that is recognized internationally for its importance in terms of biodiversity conservation.
- Biosphere Reserves are intended to promote the conservation of ecosystems, genetic diversity, and sustainable development.
- They often encompass a variety of habitats, including forests, wetlands, mountains, and coastal areas, and are managed to balance conservation with sustainable use.
- In-situ conservation is a core component of Biosphere Reserves, as they aim to protect and sustain the natural ecosystems found within their boundaries.
- Biosphere Reserves also focus on research, education, and community involvement to promote conservation efforts.
Botanical Garden:
- A Botanical Garden is a curated collection of plants, both native and exotic, for scientific, educational, and ornamental purposes.
- While Botanical Gardens play an important role in ex-situ conservation, as they maintain living collections of plants outside their natural habitats, they can also contribute to in-situ conservation efforts.
- Many Botanical Gardens have sections dedicated to native plant species, where they are grown and displayed in their natural ecological settings.
- These gardens often serve as educational platforms to raise awareness about the importance of conserving local flora and its role in maintaining ecosystems.
Wildlife Sanctuary:
- A Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area that is established to conserve wildlife and their habitats.
- The primary focus of a Wildlife Sanctuary is the protection and conservation of wildlife species, including both flora and fauna.
- In-situ conservation is a key objective of Wildlife Sanctuaries, as they aim to preserve the natural habitats and ecosystems that support the wildlife populations.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries often have strict regulations in place to restrict human activities and minimize disturbances to the wildlife.
Botanical Garden is not a site for in-situ method of conservation of flora:
- While Botanical Gardens can contribute to in-situ conservation efforts through the display and cultivation of native plant species, their primary role is in ex-situ conservation.
- Botanical Gardens typically maintain collections of plants outside their natural habitats, often for research, education, and ornamental purposes.
- They may have conservation programs in place, but their main function is to provide a controlled environment for preserving plant species and studying their biology and ecology.
- In contrast, National Parks, Biosphere Reserves, and Wildlife Sanctuaries focus on the conservation of flora and fauna in their natural habitats, making them more suitable for in-situ conservation efforts.
- A National Park is an area set aside by a national government to protect the natural environment and the flora and fauna found within it.
- The primary objective of a National Park is to preserve the ecological integrity of the area and to provide a sanctuary for wildlife.
- In-situ conservation is a key aspect of National Parks, as they aim to protect the natural habitats and ecosystems in their original form.
- National Parks often have strict regulations and restrictions in place to ensure that the flora and fauna are not disturbed or harmed.
Biosphere Reserve:
- A Biosphere Reserve is a unique designation given to a specific area that is recognized internationally for its importance in terms of biodiversity conservation.
- Biosphere Reserves are intended to promote the conservation of ecosystems, genetic diversity, and sustainable development.
- They often encompass a variety of habitats, including forests, wetlands, mountains, and coastal areas, and are managed to balance conservation with sustainable use.
- In-situ conservation is a core component of Biosphere Reserves, as they aim to protect and sustain the natural ecosystems found within their boundaries.
- Biosphere Reserves also focus on research, education, and community involvement to promote conservation efforts.
Botanical Garden:
- A Botanical Garden is a curated collection of plants, both native and exotic, for scientific, educational, and ornamental purposes.
- While Botanical Gardens play an important role in ex-situ conservation, as they maintain living collections of plants outside their natural habitats, they can also contribute to in-situ conservation efforts.
- Many Botanical Gardens have sections dedicated to native plant species, where they are grown and displayed in their natural ecological settings.
- These gardens often serve as educational platforms to raise awareness about the importance of conserving local flora and its role in maintaining ecosystems.
Wildlife Sanctuary:
- A Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area that is established to conserve wildlife and their habitats.
- The primary focus of a Wildlife Sanctuary is the protection and conservation of wildlife species, including both flora and fauna.
- In-situ conservation is a key objective of Wildlife Sanctuaries, as they aim to preserve the natural habitats and ecosystems that support the wildlife populations.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries often have strict regulations in place to restrict human activities and minimize disturbances to the wildlife.
Botanical Garden is not a site for in-situ method of conservation of flora:
- While Botanical Gardens can contribute to in-situ conservation efforts through the display and cultivation of native plant species, their primary role is in ex-situ conservation.
- Botanical Gardens typically maintain collections of plants outside their natural habitats, often for research, education, and ornamental purposes.
- They may have conservation programs in place, but their main function is to provide a controlled environment for preserving plant species and studying their biology and ecology.
- In contrast, National Parks, Biosphere Reserves, and Wildlife Sanctuaries focus on the conservation of flora and fauna in their natural habitats, making them more suitable for in-situ conservation efforts.
In Nitrogen Cycle, soil nitrates are transformed into free nitrogen by:- a) Denitrifying bacteria
- b) Nitrifying bacteria
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Ammonifying bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Nitrogen Cycle, soil nitrates are transformed into free nitrogen by:
a)
Denitrifying bacteria
b)
Nitrifying bacteria
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Ammonifying bacteria

|
Lakshya Ias answered |
Denitrifying bacteria
Explanation: Denitrifying bacteria are microorganisms that convert nitrates in soil into free atmospheric nitrogen, depleting the soil of fertility and reducing agricultural productivity
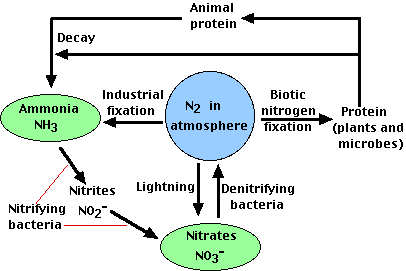
The two major components of Ecosystem are:- a)Herbs and Shrubs
- b)Biotic and Abiotic
- c)Plants and Animals
- d)Water and Air
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The two major components of Ecosystem are:
a)
Herbs and Shrubs
b)
Biotic and Abiotic
c)
Plants and Animals
d)
Water and Air
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
Abiotic Components: The Non-Living. Biotic factors in an ecosystem cannot survive without abiotic components, which include light, temperature, water, atmosphere and soil. In nearly all ecosystems, sunlight is the abiotic component that the rest of the ecosystem depends on, as it is the major source of energy.
Consider the following statements :
1. No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
2. Tourism is allowed in national parks.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?- a) Both 1 and 2
- b) Neither 1 nor 2
- c) 2 only
- d) 1 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements :
1. No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
2. Tourism is allowed in national parks.
1. No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
2. Tourism is allowed in national parks.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
a)
Both 1 and 2
b)
Neither 1 nor 2
c)
2 only
d)
1 only
|
|
Samarth Unni answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'C' which states that only statement 2 is correct. Let's analyze each statement separately to understand why.
Statement 1: No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
- Tiger reserves are designated areas that are created to protect the habitat of tigers and conserve their population.
- The primary objective of establishing tiger reserves is to promote the conservation of tigers and their prey species, and to eliminate human disturbances that can negatively impact their habitat.
- To achieve this objective, human activities are restricted within tiger reserves.
- These restrictions include prohibiting activities such as farming, livestock grazing, mining, logging, and any other form of human interference that can disrupt the ecosystem and disturb the tigers.
- The idea is to create a safe and undisturbed environment for tigers to thrive.
Therefore, statement 1 is correct. No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
Statement 2: Tourism is allowed in national parks.
- National parks are areas that are designated for the purpose of conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.
- While the primary objective of national parks is to preserve natural habitats and protect wildlife, they also serve as tourist destinations.
- Tourism in national parks is allowed, but it is regulated to minimize its impact on the environment and wildlife.
- The number of tourists, vehicular movement, and certain activities may be restricted or controlled to ensure the preservation of the park's ecology.
- Tourism in national parks can provide economic benefits to local communities and foster awareness and appreciation for nature and wildlife.
Therefore, statement 2 is correct. Tourism is allowed in national parks.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct as no human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves, while statement 2 is also correct as tourism is allowed in national parks.
The correct answer is option 'C' which states that only statement 2 is correct. Let's analyze each statement separately to understand why.
Statement 1: No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
- Tiger reserves are designated areas that are created to protect the habitat of tigers and conserve their population.
- The primary objective of establishing tiger reserves is to promote the conservation of tigers and their prey species, and to eliminate human disturbances that can negatively impact their habitat.
- To achieve this objective, human activities are restricted within tiger reserves.
- These restrictions include prohibiting activities such as farming, livestock grazing, mining, logging, and any other form of human interference that can disrupt the ecosystem and disturb the tigers.
- The idea is to create a safe and undisturbed environment for tigers to thrive.
Therefore, statement 1 is correct. No human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves.
Statement 2: Tourism is allowed in national parks.
- National parks are areas that are designated for the purpose of conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.
- While the primary objective of national parks is to preserve natural habitats and protect wildlife, they also serve as tourist destinations.
- Tourism in national parks is allowed, but it is regulated to minimize its impact on the environment and wildlife.
- The number of tourists, vehicular movement, and certain activities may be restricted or controlled to ensure the preservation of the park's ecology.
- Tourism in national parks can provide economic benefits to local communities and foster awareness and appreciation for nature and wildlife.
Therefore, statement 2 is correct. Tourism is allowed in national parks.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct as no human activity is allowed inside tiger reserves, while statement 2 is also correct as tourism is allowed in national parks.
In which one among following categories of the protected areas in the India are local people not allowed to collect and use the biomass ?- a) Biosphere reserves
- b) National parks
- c) Wild Sanctuaries
- d) Wetlands declared under Ramsar convection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one among following categories of the protected areas in the India are local people not allowed to collect and use the biomass ?
a)
Biosphere reserves
b)
National parks
c)
Wild Sanctuaries
d)
Wetlands declared under Ramsar convection
|
|
Bhavya Gupta answered |
Explanation:
In India, the protected areas are categorized into different types based on their conservation objectives and level of restrictions. These categories include Biosphere Reserves, National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Wetlands declared under the Ramsar Convention.
Among these categories, National Parks are the areas where local people are not allowed to collect and use biomass. Here's why:
National Parks:
1. National Parks are created with the primary objective of conserving the ecological integrity of an area and protecting the biodiversity within it.
2. These areas are specifically designated for the protection and preservation of wildlife, their habitats, and the natural landscape.
3. National Parks have strict regulations and guidelines, and their management is focused on minimizing human interference and preserving the natural ecosystem.
4. Local people are generally not allowed to collect or use biomass in National Parks to prevent any disturbance to the wildlife and their habitats.
5. This restriction helps in maintaining the natural balance and protects the flora and fauna from any human-induced damage.
6. National Parks are also important for scientific research, education, and promoting eco-tourism.
Other Categories:
1. Biosphere Reserves: These areas are designated for the conservation of biodiversity, sustainable development, and research. Local communities living in and around the Biosphere Reserves are encouraged to participate in the sustainable use of resources, including biomass.
2. Wildlife Sanctuaries: These areas are created to provide a safe haven for wildlife and their habitats. Some wildlife sanctuaries may allow limited use of biomass by local communities under specific regulations.
3. Wetlands declared under Ramsar Convention: Wetlands are critical ecosystems that provide numerous ecological services. While some restrictions may be in place for specific activities, such as hunting or fishing, the use of biomass by local communities in wetlands is often allowed, as long as it is sustainable and does not harm the ecosystem.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B: National Parks.
In India, the protected areas are categorized into different types based on their conservation objectives and level of restrictions. These categories include Biosphere Reserves, National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Wetlands declared under the Ramsar Convention.
Among these categories, National Parks are the areas where local people are not allowed to collect and use biomass. Here's why:
National Parks:
1. National Parks are created with the primary objective of conserving the ecological integrity of an area and protecting the biodiversity within it.
2. These areas are specifically designated for the protection and preservation of wildlife, their habitats, and the natural landscape.
3. National Parks have strict regulations and guidelines, and their management is focused on minimizing human interference and preserving the natural ecosystem.
4. Local people are generally not allowed to collect or use biomass in National Parks to prevent any disturbance to the wildlife and their habitats.
5. This restriction helps in maintaining the natural balance and protects the flora and fauna from any human-induced damage.
6. National Parks are also important for scientific research, education, and promoting eco-tourism.
Other Categories:
1. Biosphere Reserves: These areas are designated for the conservation of biodiversity, sustainable development, and research. Local communities living in and around the Biosphere Reserves are encouraged to participate in the sustainable use of resources, including biomass.
2. Wildlife Sanctuaries: These areas are created to provide a safe haven for wildlife and their habitats. Some wildlife sanctuaries may allow limited use of biomass by local communities under specific regulations.
3. Wetlands declared under Ramsar Convention: Wetlands are critical ecosystems that provide numerous ecological services. While some restrictions may be in place for specific activities, such as hunting or fishing, the use of biomass by local communities in wetlands is often allowed, as long as it is sustainable and does not harm the ecosystem.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B: National Parks.
Which one of the following is the characteristics climate of the tropical Savannah Region?- a) A definite dry and wet season
- b) Rainfall in the winter only
- c) Rainfall throughout the year
- d) An extremely short dry season
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the characteristics climate of the tropical Savannah Region?
a)
A definite dry and wet season
b)
Rainfall in the winter only
c)
Rainfall throughout the year
d)
An extremely short dry season

|
Sahana Bajaj answered |
A definite dry(winter) and wet(summer) season
Explanation: The Savanna biome has a wet/dry climate. Its Koppen climate group is Aw. The A stands for a tropical climate, and the w for a dry season in the winter.
The ‘Olive Ridley turtles’ are considered to be endangered because of their few remaining nesting sites in the world. In this context, which among the following Statement(s) is/are correct ?1.Their peculiar behavior of synchronized nesting in mass numbers is known as ‘Arribada’.
2.Gahirmatha Beach in Orissa is one of their few nesting grounds in the world.- a) Only 1
- b) Both 1 and 2
- c) Neither 1 nor 2
- d) Only 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ‘Olive Ridley turtles’ are considered to be endangered because of their few remaining nesting sites in the world. In this context, which among the following Statement(s) is/are correct ?
1.Their peculiar behavior of synchronized nesting in mass numbers is known as ‘Arribada’.
2.Gahirmatha Beach in Orissa is one of their few nesting grounds in the world.
2.Gahirmatha Beach in Orissa is one of their few nesting grounds in the world.
a)
Only 1
b)
Both 1 and 2
c)
Neither 1 nor 2
d)
Only 2

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
Both 1 and 2
Explanation: Olive Ridleys are omnivorous, meaning that they consume a varied diet from both plant and animal sources. Primary threat to the Olive Ridley comes from human predation in the nesting habitat.
The BOD helps to determine the :- a) Extent of organic pollution in waste water
- b) Filtering capacity of soil
- c) Number of bacteria in 100 ml sample of water
- d) Types of biota in ecosystem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The BOD helps to determine the :
a)
Extent of organic pollution in waste water
b)
Filtering capacity of soil
c)
Number of bacteria in 100 ml sample of water
d)
Types of biota in ecosystem
|
|
Avik Ghoshal answered |
Biological oxygen demand is a measure of the quantity of oxygen used by microorganisms (e.g., aerobic bacteria) in the oxidation of organic matter. Natural water bodies contain a certain level of organic substances that are acted upon and decomposed by microbes. Determining the BOD of the water body establishes the amount of organic content in it. The presence of more organic wastes increases the biological activity, thus leading to algal blooms. High BOD value indicates more microbial activity, indicating that the water body is polluted.
Van Mahotsav is celebrated every year in the month of- a) September
- b) July
- c) March
- d) August
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Van Mahotsav is celebrated every year in the month of
a)
September
b)
July
c)
March
d)
August
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
Van Mahotsava is an annual tree planting festival in the month of July. During this festival thousand of trees are planted all over India. In 1950, it was started by K. M. Munshi, the Union Minister for Agriculture and Food at that time. It was started to create awareness in the mind of the people for the conservation of forests and planting of new trees.
The following soil particles are arranged in the order of decreasing size:
- a)Clay Silt Sand Gravel
- b)Gravel Sand Silt Clay
- c)Gravel Clay Silt Sand
- d)Clay Sand Silt Gravel
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following soil particles are arranged in the order of decreasing size:
a)
Clay Silt Sand Gravel
b)
Gravel Sand Silt Clay
c)
Gravel Clay Silt Sand
d)
Clay Sand Silt Gravel
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Soil is made up of different-sized particles. Gravel size is (4 - 5mm). Sand is a naturally occurring, finely divided rock, comprising particles or granules ranging in size from 0.0625 (or 1⁄16) to 2 millimeters. Silt is of (0.05 - 0.002mm). Clay particles are very small – less than 0.002 mm.
Which state plans to become fully organic farming state by 2016 ?- a) Maharashtra
- b)Tamil Nadu
- c) Kerla
- d) Nagaland
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which state plans to become fully organic farming state by 2016 ?
a)
Maharashtra
b)
Tamil Nadu
c)
Kerla
d)
Nagaland
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Kerla
Explanation: Sikkim has become the first organic state of India
The ‘thickness’ of Stratospheric Ozone layer is measured in/on:- a) Beaufort Scale
- b) Dobson units
- c) Melson units
- d) Sieverts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ‘thickness’ of Stratospheric Ozone layer is measured in/on:
a)
Beaufort Scale
b)
Dobson units
c)
Melson units
d)
Sieverts

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
Dobson units
Explanation: Dobson units is a unit of measurement for the total amount of ozone in the atmosphere above a point on the earth's surface, one Dobson unit being equivalent to a layer of pure ozone 0.01 mm thick at standard temperature and pressure.
The relationship between water fern Azolla and cyanobacterium Anabaena is :- a) Symbiotic
- b) Proto-Cooperation
- c) Mutualistic
- d) Commensalism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The relationship between water fern Azolla and cyanobacterium Anabaena is :
a)
Symbiotic
b)
Proto-Cooperation
c)
Mutualistic
d)
Commensalism
|
|
Aruna Singh answered |
Anabaena Azollae maintains a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship with the water fern Azolla, which provides the cyanobacteria with a safe environment in exchange for nitrogen. ... When free living, A. Azollae only develops between 5-10% of its cells into heterocysts.
Which of the followings statements are correct about ecosystem?1) It comprises of biome only
2) It comprises of biome and habitat
3) It is an open system
4) It is an closed system- a) 1&4
- b) 1 & 3
- c) 2&4
- d) 2&3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the followings statements are correct about ecosystem?
1) It comprises of biome only
2) It comprises of biome and habitat
3) It is an open system
4) It is an closed system
2) It comprises of biome and habitat
3) It is an open system
4) It is an closed system
a)
1&4
b)
1 & 3
c)
2&4
d)
2&3
|
|
Nidhi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding Ecosystems
An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms and their physical environment. To determine which statements are correct, let’s analyze them one by one.
Statement 1: It comprises of biome only
- This statement is incorrect.
- A biome is a large ecological area on Earth’s surface, but an ecosystem includes various components beyond just biomes.
Statement 2: It comprises of biome and habitat
- This statement is correct.
- An ecosystem encompasses both biomes (large-scale ecological areas) and habitats (specific environments where organisms live).
Statement 3: It is an open system
- This statement is correct.
- Ecosystems are typically open systems as they exchange matter and energy with their surroundings. For instance, they receive sunlight, nutrients, and gases from the environment.
Statement 4: It is a closed system
- This statement is incorrect.
- Ecosystems are generally not closed systems because they interact with external factors, such as climate and human influence.
Correct Answer Explanation
Given the analysis:
- The correct statements are 2 and 3.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B (2, 3).
In summary, ecosystems include both biomes and habitats, and they operate as open systems due to their interactions with surrounding environments. Understanding these concepts is crucial for studying ecology and environmental science, especially in the context of UPSC examinations.
An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms and their physical environment. To determine which statements are correct, let’s analyze them one by one.
Statement 1: It comprises of biome only
- This statement is incorrect.
- A biome is a large ecological area on Earth’s surface, but an ecosystem includes various components beyond just biomes.
Statement 2: It comprises of biome and habitat
- This statement is correct.
- An ecosystem encompasses both biomes (large-scale ecological areas) and habitats (specific environments where organisms live).
Statement 3: It is an open system
- This statement is correct.
- Ecosystems are typically open systems as they exchange matter and energy with their surroundings. For instance, they receive sunlight, nutrients, and gases from the environment.
Statement 4: It is a closed system
- This statement is incorrect.
- Ecosystems are generally not closed systems because they interact with external factors, such as climate and human influence.
Correct Answer Explanation
Given the analysis:
- The correct statements are 2 and 3.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B (2, 3).
In summary, ecosystems include both biomes and habitats, and they operate as open systems due to their interactions with surrounding environments. Understanding these concepts is crucial for studying ecology and environmental science, especially in the context of UPSC examinations.
What would happen if phytoplankton of an ocean is completely destroyed for some reason?1.The ocean as a carbon sink would be adversely affected.
2.The food chains in the ocean would be adversely affected.
3.The density of ocean water would drastically decrease.Select the correct answer using the codes given below :- a) 1 and 2 only
- b) 2 only
- c) 3 only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What would happen if phytoplankton of an ocean is completely destroyed for some reason?
1.The ocean as a carbon sink would be adversely affected.
2.The food chains in the ocean would be adversely affected.
3.The density of ocean water would drastically decrease.
2.The food chains in the ocean would be adversely affected.
3.The density of ocean water would drastically decrease.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 only
c)
3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Sahana Bajaj answered |
1 and 2 only
Explanation:Density would increase
Soil acidification can occur due to
1. heavy rainfall
2. application of fertilizer
3. shifting cultivation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.- a) 1, 2 and 3
- b) 1 and 2 only
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1 and 3 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Soil acidification can occur due to
1. heavy rainfall
2. application of fertilizer
3. shifting cultivation
1. heavy rainfall
2. application of fertilizer
3. shifting cultivation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
1 and 2 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1 and 3 only
|
|
Mohit Goyal answered |
2 and 3 only
Explanation:heavy rain will increase the soil pH and thus reduce soil acidity.
What is ‘BOD’?- a)Biological Oxygen Demand
- b)Biochemical Oxygen Demand
- c)Biosphere Oxygen Demand
- d)Biomedical Oxygen Demand
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is ‘BOD’?
a)
Biological Oxygen Demand
b)
Biochemical Oxygen Demand
c)
Biosphere Oxygen Demand
d)
Biomedical Oxygen Demand
|
|
Nidhi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding BOD
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a critical parameter in environmental science and water quality assessment. It measures the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms while decomposing organic matter in water. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its significance:
Definition of BOD
- BOD stands for Biological Oxygen Demand.
- It quantifies the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic bacteria to break down organic material in a given water sample over a specific time frame, usually five days at 20°C.
Importance of BOD
- Water Quality Indicator: A high BOD indicates a high level of organic pollution, suggesting that the water body is polluted and may not support aquatic life.
- Wastewater Treatment: BOD is a crucial factor in designing wastewater treatment processes. It helps in determining the efficiency of treatment plants.
- Environmental Monitoring: Regular BOD testing is essential for monitoring the health of rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, ensuring they are safe for recreational use and aquatic ecosystems.
Comparison with Other Options
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD): Often confused with biochemical terminology, “biological” is the correct term that emphasizes the role of living organisms in oxygen consumption.
- Biosphere Oxygen Demand: This term does not accurately describe the measurement process or its application in water quality.
- Biomedical Oxygen Demand: This is not a recognized term in environmental science and does not relate to water quality assessment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, option ‘A’ is correct as BOD specifically refers to Biological Oxygen Demand, a vital metric in assessing water pollution and ecosystem health. Understanding BOD helps in effective environmental management and preservation of water resources.
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a critical parameter in environmental science and water quality assessment. It measures the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms while decomposing organic matter in water. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its significance:
Definition of BOD
- BOD stands for Biological Oxygen Demand.
- It quantifies the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic bacteria to break down organic material in a given water sample over a specific time frame, usually five days at 20°C.
Importance of BOD
- Water Quality Indicator: A high BOD indicates a high level of organic pollution, suggesting that the water body is polluted and may not support aquatic life.
- Wastewater Treatment: BOD is a crucial factor in designing wastewater treatment processes. It helps in determining the efficiency of treatment plants.
- Environmental Monitoring: Regular BOD testing is essential for monitoring the health of rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, ensuring they are safe for recreational use and aquatic ecosystems.
Comparison with Other Options
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD): Often confused with biochemical terminology, “biological” is the correct term that emphasizes the role of living organisms in oxygen consumption.
- Biosphere Oxygen Demand: This term does not accurately describe the measurement process or its application in water quality.
- Biomedical Oxygen Demand: This is not a recognized term in environmental science and does not relate to water quality assessment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, option ‘A’ is correct as BOD specifically refers to Biological Oxygen Demand, a vital metric in assessing water pollution and ecosystem health. Understanding BOD helps in effective environmental management and preservation of water resources.
The number of organisms that can be supported by the environment in a given area isknown as :- a) None of the above
- b) Population
- c) Pyramid of number or biomass
- d) Carrying Capacity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of organisms that can be supported by the environment in a given area isknown as :
a)
None of the above
b)
Population
c)
Pyramid of number or biomass
d)
Carrying Capacity

|
Charvi Banerjee answered |
Carrying Capacity
Explanation: carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals of a given species that an area's resources can sustain indefinitely without significantly depleting or degrading those resources. Determining the carrying capacities for most organisms is fairly straightforward. For humans carrying capacity is much more complicated. The definition is expanded to include not degrading our cultural and social environments and not harming the physical environment in ways that would adversely affect future generations.
Kedar valley disaster of June, 2013, was cause by heavy rains in the catchment area of a river, which was :- a) Bhagirathi
- b) Yamuna
- c) Alaknanda
- d) Mandakini
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Kedar valley disaster of June, 2013, was cause by heavy rains in the catchment area of a river, which was :
a)
Bhagirathi
b)
Yamuna
c)
Alaknanda
d)
Mandakini

|
Ujwal Sengupta answered |
Mandakini
Explanation: the Indian state of Uttarakhand and adjoining areas received heavy rainfall, which was about 375% more than the benchmark rainfall during a normal monsoon. This caused the melting of Chorabari Glacier at the height of 3800 metres, and eruption of the Mandakini River which led to heavy floods near Gobindghat, Kedar Dome, Rudraprayag district, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Western Nepal,
Which of the following States has the second highest percentage of mangrove cover?- a) Gujarat
- b) Orissa
- c) Andhra Pradesh
- d) West Bengal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following States has the second highest percentage of mangrove cover?
a)
Gujarat
b)
Orissa
c)
Andhra Pradesh
d)
West Bengal

|
Sahana Bajaj answered |
Gujarat
Explanation: West Bengal has highest
'World House Sparrow Day’ is celebrated on:
- a)22 May
- b)22 March
- c)20 Marc h
- d)20 May
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
'World House Sparrow Day’ is celebrated on:
a)
22 May
b)
22 March
c)
20 Marc h
d)
20 May

|
Charvi Banerjee answered |
20 March
Explanation: World Sparrow Day is an initiative of the Nature Forever Society to celebrate March 20, every year as World Sparrow Day. Sparrow is threatened by the destruction of Natural habitat and change in building code in urban area.
Which of the following is aare type(s) of biodiversity?- a) Ecosystem Diversity
- b) Genetic Diversity
- c) Species Diversity
- d) All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is aare type(s) of biodiversity?
a)
Ecosystem Diversity
b)
Genetic Diversity
c)
Species Diversity
d)
All of the above
|
|
Nidhi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the different species, genetic variations, and ecosystems. It is crucial for the stability of ecosystems and the overall health of the planet.
Types of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is categorized into three main types:
Why All Types Matter
Each type of biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance:
Conclusion
In summary, all three types of biodiversity—ecosystem, genetic, and species diversity—are interconnected and essential for the health and sustainability of our planet. Therefore, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'D': all of the above.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the different species, genetic variations, and ecosystems. It is crucial for the stability of ecosystems and the overall health of the planet.
Types of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is categorized into three main types:
- Ecosystem Diversity: This refers to the range of different habitats and ecosystems within a region. It includes forests, wetlands, grasslands, and oceans, each supporting unique communities of organisms.
- Genetic Diversity: Genetic diversity encompasses the variations in genes among individuals within a species. Higher genetic diversity enhances a species' ability to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases.
- Species Diversity: This involves the variety of species within a particular ecosystem or on the planet as a whole. It accounts for both the number of species and their relative abundance, which contributes to ecosystem resilience and function.
Why All Types Matter
Each type of biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance:
- The loss of ecosystem diversity can lead to habitat destruction and loss of species.
- Reduced genetic diversity may impair a species' ability to adapt and survive in the face of environmental changes.
- Declines in species diversity can destabilize ecosystems, affecting food webs and nutrient cycling.
Conclusion
In summary, all three types of biodiversity—ecosystem, genetic, and species diversity—are interconnected and essential for the health and sustainability of our planet. Therefore, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'D': all of the above.
Three of the following criteria have contributed to the recognition of Western Ghats-Sri Lanka and Indo-Burma regions as hotspots of biodiversity:A) Species richness
B) Vegetation density
C) Endemism
D) Ethno-botanical importance
E) Threat perception
F) Adaptation of flora and fauna to warm and humid conditionsWhich three of the above are correct criteria in this context?- a) 1, 3 and 5
- b) 2, 4 and 6
- c) 1, 2 and 6
- d) 3, 4 and 6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three of the following criteria have contributed to the recognition of Western Ghats-Sri Lanka and Indo-Burma regions as hotspots of biodiversity:
A) Species richness
B) Vegetation density
C) Endemism
D) Ethno-botanical importance
E) Threat perception
F) Adaptation of flora and fauna to warm and humid conditions
B) Vegetation density
C) Endemism
D) Ethno-botanical importance
E) Threat perception
F) Adaptation of flora and fauna to warm and humid conditions
Which three of the above are correct criteria in this context?
a)
1, 3 and 5
b)
2, 4 and 6
c)
1, 2 and 6
d)
3, 4 and 6
|
|
Subhankar Nambiar answered |
Biodiversity hotspot:
(i) To qualify as a biodiversity hotspot, a region must meet two strict criteria:
- It must have at least 1,500 vascular plants as endemics — which is to say, it must have a high percentage of plant life found nowhere else on the planet. A hotspot, in other words, is irreplaceable. Hence, statements 1 and 3 are correct.
- It must have 30% or less of its original natural vegetation. In other words, it must be threatened. Hence statement 5 is correct.
(ii) Around the world, 36 areas qualify as hotspots. They represent just 2.4% of Earth’s land surface, but they support more than half of the world’s plant species as endemics — i.e., species found no place else — and nearly 43% of bird, mammal, reptile and amphibian species as endemics.
(iii) Conservation International was a pioneer in defining and promoting the concept of hotspots.
(iv) In 1989, just one year after scientist Norman Myers wrote the paper that introduced the hotspots concept, Conservation International adopted the idea of protecting these incredible places as the guiding principle of our investments.
(i) To qualify as a biodiversity hotspot, a region must meet two strict criteria:
- It must have at least 1,500 vascular plants as endemics — which is to say, it must have a high percentage of plant life found nowhere else on the planet. A hotspot, in other words, is irreplaceable. Hence, statements 1 and 3 are correct.
- It must have 30% or less of its original natural vegetation. In other words, it must be threatened. Hence statement 5 is correct.
(ii) Around the world, 36 areas qualify as hotspots. They represent just 2.4% of Earth’s land surface, but they support more than half of the world’s plant species as endemics — i.e., species found no place else — and nearly 43% of bird, mammal, reptile and amphibian species as endemics.
(iii) Conservation International was a pioneer in defining and promoting the concept of hotspots.
(iv) In 1989, just one year after scientist Norman Myers wrote the paper that introduced the hotspots concept, Conservation International adopted the idea of protecting these incredible places as the guiding principle of our investments.
Arid Forest Research Institute is located in- a) Jabalpur
- b) Jaipur
- c) Jodhpur
- d) Bhopal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arid Forest Research Institute is located in
a)
Jabalpur
b)
Jaipur
c)
Jodhpur
d)
Bhopal

|
Prateek Nambiar answered |
Jodhpur
Explanation: The institute carries out scientific research in forestry in order to provide technologies to increase the vegetative cover and to conserve biodiversity in the hot arid and semi-arid region of Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Which among the following is not a tiger reserve- a) Norkek
- b) Sariska
- c) Ranthambore
- d) Bandipur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not a tiger reserve
a)
Norkek
b)
Sariska
c)
Ranthambore
d)
Bandipur

|
Ujwal Sengupta answered |
Norkek
Explanation: Norkek Biosphere Reserve, is a national park located at Western Garo Hills near Tura and William Nagar, Meghalaya
The “Red Data Books” published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contain lists of:1. Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots,
2. Threatened plant and animal species.
3. Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries.Select the correct answer using the codes given below:- a) 3 only
- b) 2 only
- c) 2 and 3
- d) 1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The “Red Data Books” published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contain lists of:
1. Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots,
2. Threatened plant and animal species.
3. Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries.
2. Threatened plant and animal species.
3. Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
3 only
b)
2 only
c)
2 and 3
d)
1 and 3
|
|
Partho Saini answered |
Answer:
The Red Data Books published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contain lists of endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots and threatened plant and animal species. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - 2 only.
Explanation:
The Red Data Books are comprehensive databases that provide information on the conservation status of various species. They are published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and are considered as a key reference for assessing the conservation status of plant and animal species worldwide.
The Red Data Books contain the following lists:
1. Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots: Biodiversity hotspots are regions that are rich in biodiversity but also face significant threats due to habitat loss, climate change, and other factors. These hotspots are home to a large number of endemic species, which are found nowhere else in the world. The Red Data Books list these endemic species to highlight their conservation significance and the need for their protection.
2. Threatened plant and animal species: The Red Data Books also list species that are considered threatened or at risk of extinction. These species are categorized into different categories such as critically endangered, endangered, vulnerable, etc., based on their population size, geographical range, and other factors. By listing these species, the Red Data Books draw attention to their conservation needs and help prioritize conservation efforts.
In addition to these two lists, the Red Data Books do not contain information about protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries. Therefore, option 'B' - 2 only is the correct answer.
It is important to note that the Red Data Books are regularly updated to reflect the latest scientific knowledge and changes in the conservation status of species. They play a crucial role in informing conservation policies, management plans, and conservation actions at various levels, from local to global.
The Red Data Books published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contain lists of endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots and threatened plant and animal species. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - 2 only.
Explanation:
The Red Data Books are comprehensive databases that provide information on the conservation status of various species. They are published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and are considered as a key reference for assessing the conservation status of plant and animal species worldwide.
The Red Data Books contain the following lists:
1. Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots: Biodiversity hotspots are regions that are rich in biodiversity but also face significant threats due to habitat loss, climate change, and other factors. These hotspots are home to a large number of endemic species, which are found nowhere else in the world. The Red Data Books list these endemic species to highlight their conservation significance and the need for their protection.
2. Threatened plant and animal species: The Red Data Books also list species that are considered threatened or at risk of extinction. These species are categorized into different categories such as critically endangered, endangered, vulnerable, etc., based on their population size, geographical range, and other factors. By listing these species, the Red Data Books draw attention to their conservation needs and help prioritize conservation efforts.
In addition to these two lists, the Red Data Books do not contain information about protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries. Therefore, option 'B' - 2 only is the correct answer.
It is important to note that the Red Data Books are regularly updated to reflect the latest scientific knowledge and changes in the conservation status of species. They play a crucial role in informing conservation policies, management plans, and conservation actions at various levels, from local to global.
An aquatic plant introduced from America to check pollution turned out to be a troublesome weed in Indian water bodies. The name of this ‘invasive alien species’ is :1. Eichhornia
2. Aegilops
3. Opuntia
4. Pistia- a) Eichhornia
- b) Aegilops
- c) Opuntia
- d) Pistia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An aquatic plant introduced from America to check pollution turned out to be a troublesome weed in Indian water bodies. The name of this ‘invasive alien species’ is :
1. Eichhornia
2. Aegilops
3. Opuntia
4. Pistia
2. Aegilops
3. Opuntia
4. Pistia
a)
Eichhornia
b)
Aegilops
c)
Opuntia
d)
Pistia

|
Nishanth Jain answered |
Eichhornia
Explanation: Eichhornia crassipes, commonly known as (common) water hyacinth, is an aquatic plant native to the Amazon basin, and is often considered a highly problematic invasive species outside its native range.
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 provides for various categories of protected areas. These include:
1. National parks
2. Wildlife sanctuaries
3. Biosphere reserve
4. Tiger reserves
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.- a) 1 and 2 only
- b) 1 and 3 only
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1, 2 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 provides for various categories of protected areas. These include:
1. National parks
2. Wildlife sanctuaries
3. Biosphere reserve
4. Tiger reserves
1. National parks
2. Wildlife sanctuaries
3. Biosphere reserve
4. Tiger reserves
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 4 only

|
Sahana Bajaj answered |
1, 2 and 4 only
Explanation: The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 has six schedules which give varying degrees of protection. Schedule I and part II of Schedule II provide absolute protection - offences under these are prescribed the highest penalties. Species listed in Schedule III and Schedule IV are also protected, but the penalties are much lower. Schedule V includes the animals which may be hunted. The plants in Schedule VI are prohibited from cultivation and planting.
Which one of the following statement is true?- a) Homo eructus had an Asian origin
- b) Australiopithecine had Australian origin
- c) Homosapiens originated in Europe
- d) Homosapiens originated in Africa
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is true?
a)
Homo eructus had an Asian origin
b)
Australiopithecine had Australian origin
c)
Homosapiens originated in Europe
d)
Homosapiens originated in Africa

|
Tushar Iyer answered |
Homosapiens originated in Africa
Explanation: Homo sapiens evolved to anatomically modern humans solely in Africa, between 200,000 and 100,000 years ago, with members of one branch leaving Africa by 60,000 years ago and over time replacing earlier human populations such as Neanderthals and Homo erectus.
In percentage terms, which State/UT has the highest forest coverage in India?- a) Madhya Pradesh
- b) Lakshadweep
- c) Arunachal Pradesh
- d) Mizoram
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In percentage terms, which State/UT has the highest forest coverage in India?
a)
Madhya Pradesh
b)
Lakshadweep
c)
Arunachal Pradesh
d)
Mizoram

|
Geetika Bajaj answered |
Mizoram
Explanation: Mizoram (88.93%) Lakshadweep (84.56%) A&N islands (81.84%) Arunachal Pradesh (80.30%) Nagaland (78.21%)
Match the following tiger reserves with their respective states1. Sanjay Dubri ———— i. Uttar Pradesh
2. Palamau —————– ii. Jharkhand
3. Namdapha —————- iii.Madhya Pradesh
4. Arnangarh ————— iv. Arunachal Pradesh
5. Dampa ——————- v. Mizoram- a) 1-iii, 2-i, 3-v, 4-ii, 5-iv
- b) 1-i, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-iii, 5-v
- c) 1-iii, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-v
- d) 1-ii, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-v
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following tiger reserves with their respective states
1. Sanjay Dubri ———— i. Uttar Pradesh
2. Palamau —————– ii. Jharkhand
3. Namdapha —————- iii.Madhya Pradesh
4. Arnangarh ————— iv. Arunachal Pradesh
5. Dampa ——————- v. Mizoram
2. Palamau —————– ii. Jharkhand
3. Namdapha —————- iii.Madhya Pradesh
4. Arnangarh ————— iv. Arunachal Pradesh
5. Dampa ——————- v. Mizoram
a)
1-iii, 2-i, 3-v, 4-ii, 5-iv
b)
1-i, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-iii, 5-v
c)
1-iii, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-v
d)
1-ii, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-v

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
1-iii, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-v
Explanation: National park is an area which is strictly reserved for the betterment of the wildlife & biodiversity, and where activities like developmental, forestry, poaching, hunting and grazing on cultivation are not permitted. Their boundaries are well marked and circumscribed.
Which of the following are required for the formation of Ground-level ozone ( GLO) ?
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Volatile Organic Compounds
3. Sunlight
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.- a) 1 and 3 only
- b) 1, 2 and 3
- c) 1 and 2 only
- d) 2 and 3 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are required for the formation of Ground-level ozone ( GLO) ?
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Volatile Organic Compounds
3. Sunlight
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Volatile Organic Compounds
3. Sunlight
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a)
1 and 3 only
b)
1, 2 and 3
c)
1 and 2 only
d)
2 and 3 only

|
Nishanth Jain answered |
2 and 3 only
Explanation: Ground-level ozone (GLO) is a harmful agent.
Man causes soil erosion through
1. use of improper ploughing methods.
2. leaving roots of crop in the field after harvest.
3. practicing trash farming.
4. use of heavy machines.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.- a) 1 and 4 only
- b) 1, 2 and 3 only
- c) 1, 3 and 4 only
- d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Man causes soil erosion through
1. use of improper ploughing methods.
2. leaving roots of crop in the field after harvest.
3. practicing trash farming.
4. use of heavy machines.
1. use of improper ploughing methods.
2. leaving roots of crop in the field after harvest.
3. practicing trash farming.
4. use of heavy machines.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a)
1 and 4 only
b)
1, 2 and 3 only
c)
1, 3 and 4 only
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4 only

|
Geetika Bajaj answered |
1, 3 and 4 only
National Green Tribunal Act was passed in the year - a)2008
- b)2009
- c)2010
- d)2011
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
National Green Tribunal Act was passed in the year
a)
2008
b)
2009
c)
2010
d)
2011

|
Pritam Shah answered |
2010
Explanation: National Green Tribunal Act 2010 for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources including enforcement of any legal right relating to environment and giving relief and compensation for damages to persons and property and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto. It is a specialized body equipped with the necessary expertise to handle environmental disputes involving multi-disciplinary issues.
In which year was the National Institute for Disaster Management officially established ?- a) 2010
- b) 2013
- c) 2006
- d) 1995
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which year was the National Institute for Disaster Management officially established ?
a)
2010
b)
2013
c)
2006
d)
1995

|
Tushar Iyer answered |
1995
Explanation: The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) was constituted under an Act of Parliament with a vision to play the role of a premier institute for capacity development in India and the region. NIDM has been assigned nodal responsibilities for human resource development, capacity building, training, research, documentation and policy advocacy in the field of disaster management.
Consider the following statements1. Red sandalwood is found in dry deciduous forest2. It was declared as an Endangered species by the IUCN, because of overexploitation for its timber.Which of the above statements are correct?- a) None
- b) Only 2
- c) Only 1
- d) Both
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements
1. Red sandalwood is found in dry deciduous forest
2. It was declared as an Endangered species by the IUCN, because of overexploitation for its timber.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
None
b)
Only 2
c)
Only 1
d)
Both

|
Geetika Bajaj answered |
Both
Explanation: Red sandalwood is endemic to the southern Eastern Ghats mountain range of South India. The sandalwood is a root parasite so you have to provide other plants for it to grow along with, especially by the time it is 8" high.
Montreal protocol is associated with- a) development of coastal areas
- b) protection of stratospheric ozone layer
- c) protection of Himalayas
- d) protection of wildlife
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Montreal protocol is associated with
a)
development of coastal areas
b)
protection of stratospheric ozone layer
c)
protection of Himalayas
d)
protection of wildlife

|
Shounak Chaudhary answered |
protection of stratospheric ozone layer
Explanation: The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer was finally agreed upon on 16 September 1987 at the Headquarters of the International Civil Aviation Organization in Montreal. The Montreal Protocol stipulates that the production and consumption of compounds that deplete ozone in the stratosphere--chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform--are to be phased out by 2000 (2005 for methyl chloroform). Scientific theory and evidence suggest that, once emitted to the atmosphere, these compounds could significantly deplete the stratospheric ozone layer that shields the planet from damaging UV-B radiation.Man-made chlorines, primarily chloroflourobcarbons (CFCs), contribute to the thinning of the ozone layer and allow larger quantities of harmful ultraviolet rays to reach the earth.
Under which IUCN protected area management National Park falls?- a) Category II
- b) Category III
- c) Category I
- d) Category IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Under which IUCN protected area management National Park falls?
a)
Category II
b)
Category III
c)
Category I
d)
Category IV

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
Category II
Explanation: Category Ia — Strict Nature ReserveCategory Ib — Wilderness AreaCategory II — National ParkCategory III — Natural Monument or FeatureCategory IV — Habitat/Species Management AreaCategory V — Protected Landscape/SeascapeCategory VI – Protected Area with sustainable use of natural resources
Which of the following colours of light travels slowest in glass ?- a) Violet
- b) Green
- c) Red
- d) All travel with the same speed.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following colours of light travels slowest in glass ?
a)
Violet
b)
Green
c)
Red
d)
All travel with the same speed.

|
Shounak Malik answered |
Red
The colours of the spectrum of white light are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red (VIBGYOR). The white light is a mixture of different colours. Each colour is associated with light of a particular wavelength. Red light has longer wavelengths(and least speed and frequency) than the blue light. The angle of deviation by a prism is not the same for all the wavelength (colours) of light. Hence the prism disperses white light into its constituent colours. The red is deviated least and the violet most.
‘Earth day’ is celebrated on- a) 22 April
- b) 22 March
- c) 5 June
- d) 22 May
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Earth day’ is celebrated on
a)
22 April
b)
22 March
c)
5 June
d)
22 May

|
Ujwal Sengupta answered |
22 April
Explanation: Earth Day is an annual event created to celebrate the planet's environment and raise public awareness about pollution. The first Earth Day was in 1970. Nelson, after seeing the damage done by a 1969 massive oil spill in Santa Barbara, California, was inspired to organize a national "teach-in" that focused on educating the public about the environment.
Chapter doubts & questions for Environment and Ecology - RAS RPSC Prelims Preparation - Notes, Study Material & Tests 2025 is part of RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Environment and Ecology - RAS RPSC Prelims Preparation - Notes, Study Material & Tests in English & Hindi are available as part of RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









