All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Mock Test Series for SSC JE Mechanical Engineering 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Design of Machine Elements for Mechanical Engineering Exam
Which of the following is an absorption type dynamometer ?- a)Prony brake dynamometer
- b)Epicyclic-train dynamometer
- c)Torsion dynamometer
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an absorption type dynamometer ?
a)
Prony brake dynamometer
b)
Epicyclic-train dynamometer
c)
Torsion dynamometer
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
A dynamometer is a device used for measuring the torque and brake power required to operate a driven machine. It has a device to measure the frictional resistance.
Following are the two types of dynamometers, used for measuring the brake power of an engine.
1. Absorption dynamometers: The entire energy or power produced by the engine is absorbed by the friction resistances of the brake and is transformed into heat, during the process of measurement.
Example: Prony brake dynamometer, Rope brake dynamometer, Hydraulic dynamometer
2. Transmission dynamometers: The energy is not wasted in friction but is used for doing work. The energy or power produced by the engine is transmitted through the dynamometer to some other machines where the power developed is suitably measured.
Example: Epicyclic-train dynamometer, Belt transmission dynamometer, Torsion dynamometer.
The crest diameter of a screw thread is same as _____- a)Major diameter
- b)Minor diameter
- c)Pitch diameter
- d)Core diameter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
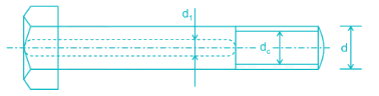
The crest diameter of a screw thread is same as _____
a)
Major diameter
b)
Minor diameter
c)
Pitch diameter
d)
Core diameter
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Screw thread is a continuous helical groove of specified cross-section produced on the external or internal surface. A screw thread formed on a cylinder is known as straight or parallel screw thread, while screw thread formed on a cone or frustum is known as the tapered screw thread.
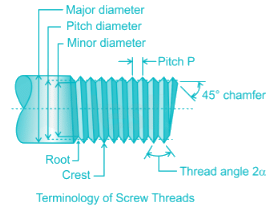
Crest: Crest of the thread is the top most surface joining the two sides.
Root: Root of the thread is the bottom of the groove between the two flanks.
Pitch: Pitch of a thread is the distance measured parallel to the axis from a point on a thread to the corresponding points on adjacent thread forms in the same axial plane and on the same side of the axis.
Major diameter: It is an imaginary largest diameter of the thread which would touch the crests of an internal or external thread. It is also called crest diameter.
Minor diameter: It is an imaginary smallest diameter of the thread which would touch the roots of an external thread.
Pitch diameter: It is a theoretical diameter between the major and minor diameter of screw threads.
The pressure distribution in the uniform wear theory is ________.- a)directly proportional to radius
- b)directly proportional to the square of radius
- c)inversely proportional to radius
- d)inversely proportional to the square of radius
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure distribution in the uniform wear theory is ________.
a)
directly proportional to radius
b)
directly proportional to the square of radius
c)
inversely proportional to radius
d)
inversely proportional to the square of radius

|
Srestha Datta answered |
Let p be the normal intensity of pressure at a distance r from the axis of the clutch.
Since the intensity of pressure varies inversely with the distance in the uniform wear theory,
∴ p.r = C (a constant)
The maximum efficiency of a screw jack having square threads and friction angle of 30° will be:- a)11%
- b)20%
- c)30%
- d)33%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum efficiency of a screw jack having square threads and friction angle of 30° will be:
a)
11%
b)
20%
c)
30%
d)
33%
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The maximum efficiency of screw jack is:
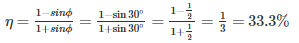
Which of the following is a permanent fastening ?- a)Bolts
- b)Keys
- c)Screws
- d)Rivets
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a permanent fastening ?
a)
Bolts
b)
Keys
c)
Screws
d)
Rivets

|
Raghavendra Goyal answered |
The rivets are used to make permanent fastening between the plates such as in structural work,ship building, bridges, tanks and boiler shells.
A screwed joint is mainly composed of two elements i.e. a bolt and nut. The screwed joints are widely used where the machine parts are required to be readily connected or disconnected without damage to the machine or the fastening.
A key is a piece of mild steel inserted between the shaft and hub or boss of the pulley to connect these together in order to prevent relative motion between them. It is always inserted parallel to the axis of the shaft. Keys are used as temporary fastenings and are subjected to considerable crushing and shearing stresses.
Which key transmits power through frictional resistance only- a)Woodruff
- b)Kennedy
- c)Sunk
- d)Saddle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which key transmits power through frictional resistance only
a)
Woodruff
b)
Kennedy
c)
Sunk
d)
Saddle
|
|
Sai Reddy answered |
Saddle key is a key that fits in the key way of the hub only. In this case there is no keyway provided on the shaft and friction between shaft, key and hub prevents relative motion between the shaft and the hub and power is transmitted by means of friction only.
In a multiple V belt drive, when a single belt is damaged, it is preferable to change the complete set to _____.- a)Reduce vibration
- b)Reduce slip
- c)Ensure uniform loading
- d)Ensure proper alignment
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a multiple V belt drive, when a single belt is damaged, it is preferable to change the complete set to _____.
a)
Reduce vibration
b)
Reduce slip
c)
Ensure uniform loading
d)
Ensure proper alignment

|
Shalini Deshpande answered |
Misalignment and improper belt tensioning can cause sheaves to wear prematurely, and when that happens, a formerly flat groove sidewall can take on a concave shape and the surface that interacts with the belt can be damaged. Eroded sheave sidewalls can reduce V-belt drive efficiency up to 12 percent. So to avoid it, when a single belt is damaged, it is preferable to change the complete set to ensure proper alignment.
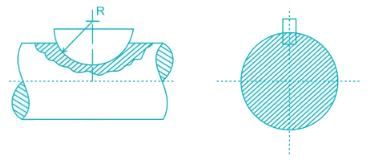
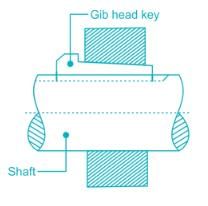
A key made from a cylindrical disc having segmental cross-section, is known as- a)wood-ruff key
- b)feather key
- c)flat saddle key
- d)gib head key
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A key made from a cylindrical disc having segmental cross-section, is known as
a)
wood-ruff key
b)
feather key
c)
flat saddle key
d)
gib head key

|
Subham Unni answered |
The woodruff key is an easily adjustable key. It is a piece from a cylindrical disc having segmental cross-section. This key is largely used in machine tool and automobile construction.
A key attached to one member of a pair and which permits relative axial movement is known as feather key. It is a special type of parallel key which transmits a turning moment and also permits axial movement.
A flat saddle key is a taper key which fits in a keyway in the hub and is flat on the shaft. A hollow saddle key is a taper key which fits in a keyway in the hub and the bottom of the key is shaped to fit the curved surface of the shaft.
Gib-head key is a rectangular sunk key with a head at one end known as gib head. It is usually provided to facilitate the removal of key.
Function of cage in ball bearing is:- a)to reduce friction
- b)to facilitate slipping of balls
- c)to prevent the lubricant from flowing out
- d)to maintain the balls at a fixed distance apart
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Function of cage in ball bearing is:
a)
to reduce friction
b)
to facilitate slipping of balls
c)
to prevent the lubricant from flowing out
d)
to maintain the balls at a fixed distance apart

|
Nayanika Joshi answered |
Function of Cage in Ball Bearing
The cage, also known as the ball bearing retainer or separator, is an essential component of a ball bearing. It is a device that separates and maintains a fixed distance between the balls, allowing them to roll smoothly and evenly within the bearing raceways. The function of the cage in a ball bearing is to:
1. Maintain the Balls at a Fixed Distance Apart:
The primary function of the cage in a ball bearing is to hold the balls at a fixed distance from each other. It ensures that the balls are evenly spaced and distributed around the bearing raceways. By keeping the balls in a specific arrangement, the cage prevents any contact or collision between them, which could lead to increased friction, wear, and damage.
2. Prevent Ball Slippage:
The cage also plays a crucial role in preventing the balls from slipping or sliding. It provides a confined space for the balls to roll within, guiding their movement and preventing them from tangling or getting displaced. This ensures that the balls maintain their intended positions and do not deviate from the proper load distribution, allowing for efficient and smooth operation of the bearing.
3. Reduce Friction:
While the primary function of the cage is not to reduce friction, it indirectly contributes to minimizing friction within the ball bearing. By maintaining a fixed distance between the balls, the cage helps to distribute the applied load evenly across the bearing raceways. This reduces excessive contact, friction, and wear between the balls and the raceways, resulting in smoother rotation and improved efficiency of the bearing.
4. Retain Lubricant:
The cage also helps to retain the lubricant within the bearing. It acts as a barrier, preventing the lubricant from flowing out of the bearing and ensuring that it remains in contact with the rolling elements. The lubricant plays a critical role in reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing corrosion within the bearing. By retaining the lubricant, the cage helps to maintain the optimal operating conditions and prolong the lifespan of the ball bearing.
In summary, the cage in a ball bearing functions to maintain the balls at a fixed distance apart, prevent ball slippage, reduce friction, and retain the lubricant. It plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation, longevity, and efficiency of the bearing.
The cage, also known as the ball bearing retainer or separator, is an essential component of a ball bearing. It is a device that separates and maintains a fixed distance between the balls, allowing them to roll smoothly and evenly within the bearing raceways. The function of the cage in a ball bearing is to:
1. Maintain the Balls at a Fixed Distance Apart:
The primary function of the cage in a ball bearing is to hold the balls at a fixed distance from each other. It ensures that the balls are evenly spaced and distributed around the bearing raceways. By keeping the balls in a specific arrangement, the cage prevents any contact or collision between them, which could lead to increased friction, wear, and damage.
2. Prevent Ball Slippage:
The cage also plays a crucial role in preventing the balls from slipping or sliding. It provides a confined space for the balls to roll within, guiding their movement and preventing them from tangling or getting displaced. This ensures that the balls maintain their intended positions and do not deviate from the proper load distribution, allowing for efficient and smooth operation of the bearing.
3. Reduce Friction:
While the primary function of the cage is not to reduce friction, it indirectly contributes to minimizing friction within the ball bearing. By maintaining a fixed distance between the balls, the cage helps to distribute the applied load evenly across the bearing raceways. This reduces excessive contact, friction, and wear between the balls and the raceways, resulting in smoother rotation and improved efficiency of the bearing.
4. Retain Lubricant:
The cage also helps to retain the lubricant within the bearing. It acts as a barrier, preventing the lubricant from flowing out of the bearing and ensuring that it remains in contact with the rolling elements. The lubricant plays a critical role in reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing corrosion within the bearing. By retaining the lubricant, the cage helps to maintain the optimal operating conditions and prolong the lifespan of the ball bearing.
In summary, the cage in a ball bearing functions to maintain the balls at a fixed distance apart, prevent ball slippage, reduce friction, and retain the lubricant. It plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation, longevity, and efficiency of the bearing.
What is the stress to which a metal is subjected indefinitely to the stress reversal without rupture called?- a)Endurance limit
- b)Safe stress
- c)Yield point
- d)Ultimate stress
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the stress to which a metal is subjected indefinitely to the stress reversal without rupture called?
a)
Endurance limit
b)
Safe stress
c)
Yield point
d)
Ultimate stress
|
|
Mrinalini Sharma answered |
Endurance limit (Se), also known as fatigue limit is the stress level below which a specimen can withstand cyclic stress indefinitely without exhibiting fatigue failure.
Which if the following key is under compression rather than in being shear when under load?- a)Saddle
- b)Barth
- c)Feather
- d)Kennedy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which if the following key is under compression rather than in being shear when under load?
a)
Saddle
b)
Barth
c)
Feather
d)
Kennedy

|
Meghana Desai answered |
A key is a machine member employed at the interface of a pair of mating male and female circular cross-sectioned members to prevent relative angular motion between these mating members. The key fits into mating grooves in the shaft and mating member called the keyway and transmit torque by shear across the key.
Barth key is a modification of rectangular key which has two beveled surfaces. The beveled surface ensures that the key will fit tightly. This key is usually under compression rather than shear.
Ball bearing type screws are found in following application- a)Screw jack
- b)Aeroplane engines
- c)Crane
- d)Steering mechanism
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ball bearing type screws are found in following application
a)
Screw jack
b)
Aeroplane engines
c)
Crane
d)
Steering mechanism

|
Sankar Dasgupta answered |
Ball screw is also called as ball bearing screw or recirculating ballscrew. It is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. It consists of a screw spindle, a nut, balls and integrated ball return mechanism.
Ball screws are used in aircraft and missiles to move control surfaces, and in automobile power steering to translate rotary motion from an electric motor to axial motion of the steering rack. They are also used in machine tools, robots and precision assembly equipment.
In a bolt of uniform strength- a)There are many free threads under the nut
- b)The run out angle of thread is not more than 15 degree
- c)The shank is turned down to a diameter equal to the diameter of the root of threads
- d)There is rounded circumferential grove in the shank immediately below the threads
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a bolt of uniform strength
a)
There are many free threads under the nut
b)
The run out angle of thread is not more than 15 degree
c)
The shank is turned down to a diameter equal to the diameter of the root of threads
d)
There is rounded circumferential grove in the shank immediately below the threads
|
|
Kritika Joshi answered |
In normal situations, where bolts are subjected to shock or impact loads,the stress in the threaded part of the bolt will be higher than that in the shank. Hence a great portion of the energy will be absorbed at the region of the threaded part which may fracture the threaded portion because of its small length.
If the shank of the bolt is turned down to a diameter equal or even slightly less than the core diameter of the thread then shank of the bolt will undergo a higher stress. This means that a shank will absorb a large portion of the energy, thus relieving the material at the sections near the thread. The bolt, in this way, becomes stronger and lighter and it increases the shock absorbing capacity of the bolt because of an increased modulus of resilience. This gives us bolts of uniform strength.
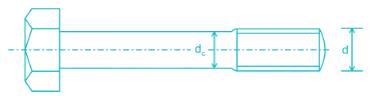
Bolt of Uniform Strength with Reduced Shank Diameter
A second alternative method of obtaining the bolts of uniform strength is to drill an axial hole through the head as far as the thread portion such that the area of the shank becomes equal to the root area of the thread.
Bolt of Uniform Strength with Drilled Hole
The valve rod in a steam engine is connected to an eccentric rod by- a)Cotter joint
- b)Bolted joint
- c)Knuckle joint
- d)Universal coupling
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The valve rod in a steam engine is connected to an eccentric rod by
a)
Cotter joint
b)
Bolted joint
c)
Knuckle joint
d)
Universal coupling

|
Divya Mehta answered |
A knuckle joint is used to connect two rods under tensile load. This joint permits angular misalignment of the rods and may take compressive load if it is guided. The automotive engine piston is connected to the small end of connecting rod by means of piston pin. This is one major application of knuckle joint. The valve rod in a steam engine is connected to an eccentric rod by Knuckle joint.
Rivet nominal pitch is:- a)=2d
- b)=5d
- c)=4d
- d)=3d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rivet nominal pitch is:
a)
=2d
b)
=5d
c)
=4d
d)
=3d
|
|
Dipika Bose answered |
Pitch is the distance between two adjacent rows of rivet parallel to the direction of application of force. The minimum pitch will be 2.5 times the gross diameter.
Minimum pitch should not be less than 2.5 times the nominal diameter of the rivet.
As a thumb rule pitch equal to 3 times the nominal diameter of the rivet is adopted.
Maximum pitch shall not exceed 32 times the thickness of the thinner outside plate or 300 mm whichever is less.
A lead screw with half nuts in a lathe, free to rotate in both directions has- a)V - threads
- b)Whitworth threads
- c)Buttress threads
- d)Acme threads
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A lead screw with half nuts in a lathe, free to rotate in both directions has
a)
V - threads
b)
Whitworth threads
c)
Buttress threads
d)
Acme threads
|
|
Kajal Tiwari answered |
Lead screw is large screw with a few threads per inch used for cutting threads. It has ACME threads with included angle of 29o for easy engagement and disengagement of half nut.
Which of the following is self-aligning bearing?- a)Conical
- b)Spherical
- c)Rectangular
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is self-aligning bearing?
a)
Conical
b)
Spherical
c)
Rectangular
d)
None of these
|
|
Stuti Bajaj answered |
A spherical plain bearing is a bearing that permits angular rotation about a central point in two orthogonal directions. The outer surface of the inner ring and the inner surface of the outer ring are spherical and are collectively considered the raceway and they slide against each other. The centre point of the sphere in the outer ring raceway is at the bearing axis. Therefore, the bearings are self-aligning and insensitive to misalignment of the shaft relative to the housing, which can be caused, for example, by shaft deflection. Spherical roller bearings are designed to accommodate heavy radial loads, as well as heavy axial loads in both directions.
The centre to centre distance between two consecutive rivets in a row is called- a)Pitch
- b)Backlash
- c)Margin
- d)Centre distance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The centre to centre distance between two consecutive rivets in a row is called
a)
Pitch
b)
Backlash
c)
Margin
d)
Centre distance
|
|
Amrita Chauhan answered |
Pitch: This is the distance between two centres of the consecutive rivets in a single row.
Back Pitch: This is the shortest distance between two successive rows in a multiple riveted joint.
Diagonal pitch: This is the distance between the centers of rivets in adjacent rows of zigzag riveted joint.
Margin or marginal pitch: This is the distance between the centre of the rivet hole to the nearest edge of the plate.
In a plate clutch axial force is 4 kN. The inside radius of contact surface is 50 mm and the outside radius is 100 mm. For uniform pressure the mean radius of friction surface will be- a)78 mm
- b)60 mm
- c)75 mm
- d)80 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a plate clutch axial force is 4 kN. The inside radius of contact surface is 50 mm and the outside radius is 100 mm. For uniform pressure the mean radius of friction surface will be
a)
78 mm
b)
60 mm
c)
75 mm
d)
80 mm

|
Dipanjan Ghosh answered |
For Uniform pressure theory
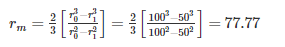
For Uniform wear theory the mean radius of friction surface is given as
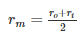
Thread angle of BSW thread in degree is- a)55
- b)60
- c)47.5
- d)29
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
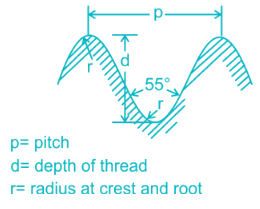
Thread angle of BSW thread in degree is
a)
55
b)
60
c)
47.5
d)
29
|
|
Raj Kumar answered |
The principal features of the British Standard Whitworth (BSW) thread form are that the angle between the thread flanks is 55 degrees and the thread have radii at both the roots and the crests of the thread.
Which of the following is a positive clutch?- a)Centrifugal clutch
- b)Dog clutch
- c)Single plate clutch
- d)Cone clutch
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a positive clutch?
a)
Centrifugal clutch
b)
Dog clutch
c)
Single plate clutch
d)
Cone clutch
|
|
Sahil Majumdar answered |
Positive Clutch: Dog clutch
A positive clutch is a type of clutch that transmits power from the engine to the transmission without any slippage. In other words, the clutch is fully engaged and the power is transmitted without any loss. The following are the types of positive clutches:
Centrifugal Clutch:
The centrifugal clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses centrifugal force to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in small engines such as go-karts, lawn mowers, and chainsaws.
Single Plate Clutch:
The single plate clutch is a type of positive clutch that has only one friction plate. It is commonly used in cars and trucks.
Cone Clutch:
The cone clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses conical friction surfaces to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in industrial machinery.
Dog Clutch:
The dog clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses two or more pairs of teeth to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in manual transmissions and racing cars. The teeth on the clutch engage with corresponding slots in the transmission gears, providing a positive and instantaneous engagement.
In summary, the dog clutch is the only positive clutch among the given options. It provides instantaneous and positive engagement, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
A positive clutch is a type of clutch that transmits power from the engine to the transmission without any slippage. In other words, the clutch is fully engaged and the power is transmitted without any loss. The following are the types of positive clutches:
Centrifugal Clutch:
The centrifugal clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses centrifugal force to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in small engines such as go-karts, lawn mowers, and chainsaws.
Single Plate Clutch:
The single plate clutch is a type of positive clutch that has only one friction plate. It is commonly used in cars and trucks.
Cone Clutch:
The cone clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses conical friction surfaces to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in industrial machinery.
Dog Clutch:
The dog clutch is a type of positive clutch that uses two or more pairs of teeth to engage the clutch. It is commonly used in manual transmissions and racing cars. The teeth on the clutch engage with corresponding slots in the transmission gears, providing a positive and instantaneous engagement.
In summary, the dog clutch is the only positive clutch among the given options. It provides instantaneous and positive engagement, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
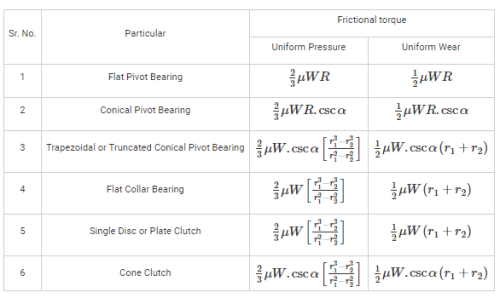
The frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is same as that of ________ bearing.- a)Conical pivot
- b)Flat pivot
- c)Trapezoidal pivot
- d)Flat collar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is same as that of ________ bearing.
a)
Conical pivot
b)
Flat pivot
c)
Trapezoidal pivot
d)
Flat collar

|
Sankar Rane answered |
Frictional torque in a disc or plate clutch compared to a flat collar bearing
Introduction:
A clutch is a mechanical device used to transmit torque from one shaft to another shaft, typically in an automotive system. One type of clutch is the disc or plate clutch, which consists of a set of friction plates that are pressed together to transmit torque. On the other hand, a flat collar bearing is a type of bearing that supports a rotating shaft with a flat collar. Both the disc or plate clutch and the flat collar bearing rely on friction to transmit torque. In this context, let's compare the frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch to that of a flat collar bearing.
Frictional torque in a disc or plate clutch:
- A disc or plate clutch consists of a set of friction plates, typically made of a high-friction material such as organic or metallic material.
- When the clutch is engaged, the friction plates are pressed together, creating frictional contact.
- The frictional torque in a disc or plate clutch is generated by the frictional forces between the contacting surfaces of the plates.
- The frictional torque is proportional to the normal force between the plates and the coefficient of friction between the contacting surfaces.
- The frictional torque can be calculated using the equation: T = μ * R * F, where T is the torque, μ is the coefficient of friction, R is the effective radius of the contact surface, and F is the normal force.
Frictional torque in a flat collar bearing:
- A flat collar bearing consists of a flat collar that supports a rotating shaft.
- The frictional torque in a flat collar bearing is also generated by the frictional forces between the contacting surfaces of the collar and the shaft.
- The frictional torque is proportional to the normal force between the collar and the shaft and the coefficient of friction between the contacting surfaces.
- The frictional torque can be calculated using the equation: T = μ * R * F, where T is the torque, μ is the coefficient of friction, R is the effective radius of the contact surface, and F is the normal force.
Comparison:
- From the above explanations, it is clear that the frictional torque in both a disc or plate clutch and a flat collar bearing can be calculated using the same equation: T = μ * R * F.
- The factors affecting the frictional torque, such as the coefficient of friction, effective radius, and normal force, are similar for both the clutch and the bearing.
- Therefore, the frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is the same as that of a flat collar bearing.
Conclusion:
The frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is the same as that of a flat collar bearing. Both the clutch and the bearing rely on friction to transmit torque, and the factors affecting the frictional torque are similar for both.
Introduction:
A clutch is a mechanical device used to transmit torque from one shaft to another shaft, typically in an automotive system. One type of clutch is the disc or plate clutch, which consists of a set of friction plates that are pressed together to transmit torque. On the other hand, a flat collar bearing is a type of bearing that supports a rotating shaft with a flat collar. Both the disc or plate clutch and the flat collar bearing rely on friction to transmit torque. In this context, let's compare the frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch to that of a flat collar bearing.
Frictional torque in a disc or plate clutch:
- A disc or plate clutch consists of a set of friction plates, typically made of a high-friction material such as organic or metallic material.
- When the clutch is engaged, the friction plates are pressed together, creating frictional contact.
- The frictional torque in a disc or plate clutch is generated by the frictional forces between the contacting surfaces of the plates.
- The frictional torque is proportional to the normal force between the plates and the coefficient of friction between the contacting surfaces.
- The frictional torque can be calculated using the equation: T = μ * R * F, where T is the torque, μ is the coefficient of friction, R is the effective radius of the contact surface, and F is the normal force.
Frictional torque in a flat collar bearing:
- A flat collar bearing consists of a flat collar that supports a rotating shaft.
- The frictional torque in a flat collar bearing is also generated by the frictional forces between the contacting surfaces of the collar and the shaft.
- The frictional torque is proportional to the normal force between the collar and the shaft and the coefficient of friction between the contacting surfaces.
- The frictional torque can be calculated using the equation: T = μ * R * F, where T is the torque, μ is the coefficient of friction, R is the effective radius of the contact surface, and F is the normal force.
Comparison:
- From the above explanations, it is clear that the frictional torque in both a disc or plate clutch and a flat collar bearing can be calculated using the same equation: T = μ * R * F.
- The factors affecting the frictional torque, such as the coefficient of friction, effective radius, and normal force, are similar for both the clutch and the bearing.
- Therefore, the frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is the same as that of a flat collar bearing.
Conclusion:
The frictional torque transmitted by a disc or plate clutch is the same as that of a flat collar bearing. Both the clutch and the bearing rely on friction to transmit torque, and the factors affecting the frictional torque are similar for both.
A key that has curved bottom to match the shaft. This key is known as________- a)Sunk key
- b)Feather key
- c)Flat saddle key
- d)Hollow saddle key
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A key that has curved bottom to match the shaft. This key is known as________
a)
Sunk key
b)
Feather key
c)
Flat saddle key
d)
Hollow saddle key

|
Megha Choudhury answered |
The sunk keys are provided half in the keyway of the shaft and half in the keyway of the hub or boss of the pulley.
A key attached to one member of a pair and which permits relative axial movement is known as feather key. It is a special type of parallel key which transmits a turning moment and permits axial movement.
A flat saddle key is a taper key which fits in a keyway in the hub and is flat on the shaft. It is likely to slip round the shaft under load. Therefore, it is used for comparatively light loads.
A hollow saddle key is a taper key which fits in a keyway in the hub and the bottom of the key is shaped to fit the curved surface of the shaft. Since hollow saddle keys hold on by friction, therefore these are suitable for light loads. It is usually used as a temporary fastening in fixing and setting eccentrics, cams etc.
For longitudinal joint in boiler, the type of joint used is- a)Lap joint with one ring one slopping the other
- b)Butt joint with single cover plate
- c)Butt joint with double cover plate
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For longitudinal joint in boiler, the type of joint used is
a)
Lap joint with one ring one slopping the other
b)
Butt joint with single cover plate
c)
Butt joint with double cover plate
d)
Any of the above

|
Arya Menon answered |
The longitudinal joint in a boiler shell is usually Butt joint with two cover plates this joint is more efficient than lap joint. It is also stiffer and helps to maintain circularity of the shell.
The type of riveted joint shown in figure is: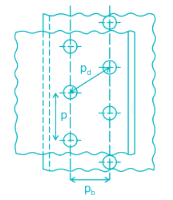
- a)Double riveted lap joint (Chain riveting)
- b)Double riveted lap joint (Zig-zag riveting)
- c)Double riveted butt joint ((Chain riveting)
- d)Triple riveted lap joint (Zig-zag riveting)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of riveted joint shown in figure is:

a)
Double riveted lap joint (Chain riveting)
b)
Double riveted lap joint (Zig-zag riveting)
c)
Double riveted butt joint ((Chain riveting)
d)
Triple riveted lap joint (Zig-zag riveting)

|
Rajdeep Gupta answered |
A lap joint is that in which one plate overlaps the other and the two plates are then riveted together.
A butt joint is that in which the main plates are kept in alignment butting (i.e. touching) each other and a cover plate(i.e. strap) is placed either on one side or on both sides of the main plates.
A n-riveted joint is that in which there is n number of rows of rivets in a lap joint and there is a n number of rows of rivets on each side in a butt joint.
The given figure shows Double riveted lap joint.
When the rivets in the various rows are opposite to each other, as shown in figure then the joint is said to be chain riveted. On the other hand, if the rivets in the adjacent rows are staggered in such a way that every rivet is in the middle of the two rivets of the opposite row, then the joint is said to be zig-zag riveted.
Which of the following is Trapezoidal thread?- a)Acme
- b)Square
- c)Buttress
- d)All options are correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is Trapezoidal thread?
a)
Acme
b)
Square
c)
Buttress
d)
All options are correct

|
Milan Saha answered |
Trapezoidal thread
A trapezoidal thread is a type of thread commonly used in mechanical engineering applications. It is characterized by its trapezoidal shape, with both the thread flanks and the top being inclined at a certain angle.
Characteristics of Trapezoidal Threads
- Trapezoidal threads have a relatively large thread angle, typically 30 degrees. This angle allows for a larger contact area between the mating threads, resulting in increased load-carrying capacity and improved resistance to wear.
- The flanks of trapezoidal threads are inclined at the thread angle, which provides self-locking characteristics. This means that the thread can resist axial forces and prevent unintended loosening or tightening of the threaded components.
- Trapezoidal threads have a flat top, which allows for efficient transfer of torque between the threaded components. This makes them suitable for applications that require high torque transmission, such as power transmission systems.
Comparison with Other Thread Types
- Acme threads: Acme threads are similar to trapezoidal threads in terms of their trapezoidal shape and self-locking characteristics. However, the thread angle of Acme threads is typically 29 degrees instead of 30 degrees for trapezoidal threads. Both thread types are commonly used in power transmission and linear motion systems.
- Square threads: Square threads have a square-shaped profile, with both the flanks and the top being perpendicular to the thread axis. Unlike trapezoidal threads, square threads do not have self-locking characteristics. They are commonly used in applications that require high efficiency in power transmission, such as lead screws.
- Buttress threads: Buttress threads have an asymmetrical shape, with one flank being inclined at a large angle and the other flank being perpendicular to the thread axis. They are primarily used in applications that require high load-carrying capacity in one direction, such as jack screws and vise mechanisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trapezoidal threads are a type of thread commonly used in mechanical engineering applications. They are characterized by their trapezoidal shape, self-locking characteristics, and efficient torque transmission. While other thread types such as Acme, square, and buttress threads also have their own advantages and applications, the correct answer to the given question is that trapezoidal threads are specifically associated with the trapezoidal shape.
A trapezoidal thread is a type of thread commonly used in mechanical engineering applications. It is characterized by its trapezoidal shape, with both the thread flanks and the top being inclined at a certain angle.
Characteristics of Trapezoidal Threads
- Trapezoidal threads have a relatively large thread angle, typically 30 degrees. This angle allows for a larger contact area between the mating threads, resulting in increased load-carrying capacity and improved resistance to wear.
- The flanks of trapezoidal threads are inclined at the thread angle, which provides self-locking characteristics. This means that the thread can resist axial forces and prevent unintended loosening or tightening of the threaded components.
- Trapezoidal threads have a flat top, which allows for efficient transfer of torque between the threaded components. This makes them suitable for applications that require high torque transmission, such as power transmission systems.
Comparison with Other Thread Types
- Acme threads: Acme threads are similar to trapezoidal threads in terms of their trapezoidal shape and self-locking characteristics. However, the thread angle of Acme threads is typically 29 degrees instead of 30 degrees for trapezoidal threads. Both thread types are commonly used in power transmission and linear motion systems.
- Square threads: Square threads have a square-shaped profile, with both the flanks and the top being perpendicular to the thread axis. Unlike trapezoidal threads, square threads do not have self-locking characteristics. They are commonly used in applications that require high efficiency in power transmission, such as lead screws.
- Buttress threads: Buttress threads have an asymmetrical shape, with one flank being inclined at a large angle and the other flank being perpendicular to the thread axis. They are primarily used in applications that require high load-carrying capacity in one direction, such as jack screws and vise mechanisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trapezoidal threads are a type of thread commonly used in mechanical engineering applications. They are characterized by their trapezoidal shape, self-locking characteristics, and efficient torque transmission. While other thread types such as Acme, square, and buttress threads also have their own advantages and applications, the correct answer to the given question is that trapezoidal threads are specifically associated with the trapezoidal shape.
Two shafts show axes are not in the same straight line and are not parallel but intersect each other. Which of the following couplings can be used for this type of shafts?- a)Flexible coupling
- b)Universal coupling
- c)Oldham’s coupling
- d)Rigid coupling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two shafts show axes are not in the same straight line and are not parallel but intersect each other. Which of the following couplings can be used for this type of shafts?
a)
Flexible coupling
b)
Universal coupling
c)
Oldham’s coupling
d)
Rigid coupling

|
Sankar Rane answered |
Flexible couplings are usually used to transmit torque from one shaft to another when the two shafts are slightly misaligned. They can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment up to 3° and some parallel misalignment.
Universal coupling is a rigid coupling that connects two shafts, whose axes intersect if extended.
Oldham’s coupling is used to connect two parallel shafts whose axes are at a small distance apart.
The most suitable bearing for carrying very heavy loads with slow speed is _____.- a)Hydrodynamic bearing
- b)Ball bearing
- c)Roller bearing
- d)Hydrostatic bearing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most suitable bearing for carrying very heavy loads with slow speed is _____.
a)
Hydrodynamic bearing
b)
Ball bearing
c)
Roller bearing
d)
Hydrostatic bearing

|
Harshad Iyer answered |
A bearing is said to be hydrostatic bearing if it has a static fluid (liquid or air) along the surface of the shaft/journal where the fluid will be supplied externally and the pressure is generally maintained by an external pump; thus enabling non-contacting operation and the ability to support a load. Hydrostatic bearings can support large loads without journal rotation and provide large (accurate and controllable) direct stiffness as well as damping (energy dissipation) coefficients.
In case of hydrodynamic bearing the pressure is developed by the high speed journal at higher rpm, this helps the movement of thin film of lubricant. For Journal bearings mostly converging fluids are employed.
Welder joint as compare to riveted joint has ____ strength.- a)zero
- b)more
- c)less
- d)same
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Welder joint as compare to riveted joint has ____ strength.
a)
zero
b)
more
c)
less
d)
same
|
|
Meera Bose answered |
Welded joint is permanent joint and riveted joint has semi-permanent joint. Strength of welded joint is more than rivet joint.
The important factor to be considered while selecting a bearing is- a)applied load
- b)operating speed range
- c)required bearing capacity
- d)All option is correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The important factor to be considered while selecting a bearing is
a)
applied load
b)
operating speed range
c)
required bearing capacity
d)
All option is correct

|
Abhay Kapoor answered |
Important factors to be considered:
(1) Dimensional limitation: Allowable space for bearings is generally limited.
(2) Applied loads: The characteristic, magnitudes & direction of loads is important.
(3) Rotational speed: It depends upon bearing type, size, tolerance, cage type, load lubrication & cooling condition,
(4) Bearing tolerances
(5) Rigidity
(6) Misalignment of inner & outer races
(7) Noise & torque levels
(8) Installation of disassembly.
In hydrostatic bearing, pressure to lubricant is supplied by- a)External sources
- b)Partially external and partially from rotation of journal
- c)Not supplied by external sources
- d)Shaft driven pump
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In hydrostatic bearing, pressure to lubricant is supplied by
a)
External sources
b)
Partially external and partially from rotation of journal
c)
Not supplied by external sources
d)
Shaft driven pump
|
|
Gaurav Kapoor answered |
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces.
They can be broadly classified into two types:
Fluid dynamic bearings/ hydrodynamic bearings: are externally pressurized fluid bearings, where the fluid is usually oil, water or air, and the pressurization is done by a pump.
Hydrodynamic bearings: are rely on the high speed of the journal (the part of the shaft resting on the fluid) to pressurize the fluid in a wedge between the faces.
The ‘Crowning’ of the flat pulley is generally done:- a)To reduce the belt friction
- b)To prevent the belt joint from damaging the belt surface
- c)To prevent the belt from running off the pulley
- d)In case of cross belt drive only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ‘Crowning’ of the flat pulley is generally done:
a)
To reduce the belt friction
b)
To prevent the belt joint from damaging the belt surface
c)
To prevent the belt from running off the pulley
d)
In case of cross belt drive only

|
Partho Jain answered |
The rim of the pulley of a flat belt drive is slightly crowned to prevent the slipping off the belt from the pulley.
The function of cutting oil when threading a pipe is to- a)provide cooling action
- b)lubricate the dies
- c)help remove chips
- d)All options are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of cutting oil when threading a pipe is to
a)
provide cooling action
b)
lubricate the dies
c)
help remove chips
d)
All options are correct

|
Divya Mehta answered |
The primary functions of cutting fluids in machining are:
- Lubricating the cutting process primarily at low cutting speeds
- Cooling the workpiece primarily at high cutting speeds
- Flushing chips away from the cutting zone
- To protect the machine tool and workpiece against corrosion
Chapter doubts & questions for Design of Machine Elements - Mock Test Series for SSC JE Mechanical Engineering 2026 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Design of Machine Elements - Mock Test Series for SSC JE Mechanical Engineering 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series for SSC JE Mechanical Engineering 2026
3 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily