All Exams >
Bank Exams >
Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 >
All Questions
All questions of SBI PO Mains for Bank Exams Exam
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question.In DAV Public School, there are three games to opt for: Chess, Cricket and Badminton. Every student has to choose one or more games. 70% of students play Chess. The number of students who select only Cricket is 1/35th of the number of students who select Chess. 32 students select both Cricket and Badminton but not Chess. The number of students who select only Chess is 50% more than the number of students who select only Badminton. The number of students who select only Badminton is 20 more than the number of students who select only Cricket.What is the strength of DAV Public School?- a)100
- b)200
- c)300
- d)400
- e)500
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question.
In DAV Public School, there are three games to opt for: Chess, Cricket and Badminton. Every student has to choose one or more games. 70% of students play Chess. The number of students who select only Cricket is 1/35th of the number of students who select Chess. 32 students select both Cricket and Badminton but not Chess. The number of students who select only Chess is 50% more than the number of students who select only Badminton. The number of students who select only Badminton is 20 more than the number of students who select only Cricket.
What is the strength of DAV Public School?
a)
100
b)
200
c)
300
d)
400
e)
500
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
Let the total number of students be 100x.
Number of students who select Chess = 70x
Number of students who select Cricket only = 2x
Number of students who select only Badminton = 2x + 20
Number of students who select both Cricket and Badminton but not Chess = 32
Also (100x - 70x - 2x) - (2x + 20) = 32
26x - 20 = 32
26x = 52
x = 2
Total number of students = 100x = 200
Thus, the strength of the school is 200.
Hence, answer option 2 is correct.
Direction: The following questions are accompanied by three statements A, B and C. You must determine which statement(s) is/are sufficient/necessary to answer the questions and mark your answer accordingly.In how many hour ‘C’ alone can fill the cistern?I Ratio of efficiency of A, B and C is 2 : 4 : 5.II A opened throughout the time, B opened for starting 10 minutes and 'C' opened after 2 minutes of closing of B. A, B and C fill equal amount of water in the cistern.III If A and B work alternatively, they can fill the tank in 40 minutes.- a)Any two of them
- b)Either I and II or II and III
- c)I and II together only
- d)Any one of them
- e)Either II or I and III together
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: The following questions are accompanied by three statements A, B and C. You must determine which statement(s) is/are sufficient/necessary to answer the questions and mark your answer accordingly.
In how many hour ‘C’ alone can fill the cistern?
I Ratio of efficiency of A, B and C is 2 : 4 : 5.
II A opened throughout the time, B opened for starting 10 minutes and 'C' opened after 2 minutes of closing of B. A, B and C fill equal amount of water in the cistern.
III If A and B work alternatively, they can fill the tank in 40 minutes.
a)
Any two of them
b)
Either I and II or II and III
c)
I and II together only
d)
Any one of them
e)
Either II or I and III together
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Statement I makes no meaning alone.
When I and II work alternatively, the individual work can be found and with the statement ‘I’, the time taken for C can be found.
Using II and III the time taken by III can be found.
Using I and III the time taken by III can be found.
Using Any two equations the time taken by III can be found.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the question that follow.Two persons X and Y starts from a point G. X moves 12 m in the north direction from point G. He then turns left from point F and walks 6 m. He then moves south-west from point E and walks 10 m till point D, which is in south of point A. X then moves 5 m west from point D and then turns right from point C and walks for 8 m. He then turns right from point B and walks for 5 m till point A. Point C is in north of point K. Y moves 12 m in west from point G. He then turns left from point H and walks for 4 m. He then turns right from point I and walks for 5 m. He then turns right from point J and walks for 4 m. He then turns left from point K and walks for 5 m till point L.What is the shortest distance between D and H?- a)4 m
- b)8 m
- c)2 m
- d)5 m
- e)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the question that follow.
Two persons X and Y starts from a point G. X moves 12 m in the north direction from point G. He then turns left from point F and walks 6 m. He then moves south-west from point E and walks 10 m till point D, which is in south of point A. X then moves 5 m west from point D and then turns right from point C and walks for 8 m. He then turns right from point B and walks for 5 m till point A. Point C is in north of point K. Y moves 12 m in west from point G. He then turns left from point H and walks for 4 m. He then turns right from point I and walks for 5 m. He then turns right from point J and walks for 4 m. He then turns left from point K and walks for 5 m till point L.
What is the shortest distance between D and H?
a)
4 m
b)
8 m
c)
2 m
d)
5 m
e)
None of the above
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
Given,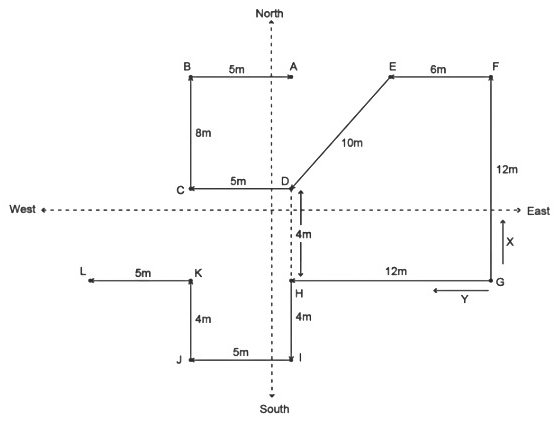
Two persons X and Y starts from a point G.
X moves 12 m in the north direction from point G.
Then he turns left from point F and walks 6 m.
Then he moves south-west from point E and walks 10 m till point D, which is in south of point A.
X then moves 5 m west from point D and then turns right from point C and walks for 8 m.
Then he turns right from point B and walks for 5 m till point A.
Point C is in north of point K.
Y moves 12 m in west from point G.
Then he turns left from point H and walks for 4 m.
Then he turns right from point I and walks for 5 m.
Then he turns right from point J and walks for 4 m.
Then he turns left from point K and walks for 5 m till point L.
According to the given information, we get the following figure,

Shortest distance between D and H = FG – BC = 12 – 8 = 4
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.Nine students have secured the ranks from 1 to 9 in the same class test. They are standing on the ground at a certain distance. No two persons have secured the same rank and the persons in the alphabetical order are not consecutively ranked from 1 to 9.Note: The distance between the two students is thrice the rank of the highest ranked person among them. For example, if P secured first rank and Q secured second rank, then the distance between them will be3m.O is to the east of the one who secured the highest rank and north of the one who secured the second last rank. Q secured two ranks higher than the one who secured the second last rank and is to the west of him. The rank value of R is half of the rank value of Q and stands to the north of Q but to the southwest of O. The distance between Q and R is the same as the distance between R and T, who stands to the east of R. The direction of R with respect to Q is the same as the direction of P with respect to T. R holds the rank exactly between N and M, who stands to the west of P. At least four persons secured the ranks higher than M. The distance between M and S is the sum of the distance between PT and RQ. O doesn’t stand to the northeast of P. L secured immediately higher rank than S but immediately less than T.M is north of S.Q. Who among the following person secured the least rank?- a)The one who stands to the south of M
- b)T
- c)The one who stands to the east of N
- d)L
- e)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine students have secured the ranks from 1 to 9 in the same class test. They are standing on the ground at a certain distance. No two persons have secured the same rank and the persons in the alphabetical order are not consecutively ranked from 1 to 9.
Note: The distance between the two students is thrice the rank of the highest ranked person among them. For example, if P secured first rank and Q secured second rank, then the distance between them will be3m.
O is to the east of the one who secured the highest rank and north of the one who secured the second last rank. Q secured two ranks higher than the one who secured the second last rank and is to the west of him. The rank value of R is half of the rank value of Q and stands to the north of Q but to the southwest of O. The distance between Q and R is the same as the distance between R and T, who stands to the east of R. The direction of R with respect to Q is the same as the direction of P with respect to T. R holds the rank exactly between N and M, who stands to the west of P. At least four persons secured the ranks higher than M. The distance between M and S is the sum of the distance between PT and RQ. O doesn’t stand to the northeast of P. L secured immediately higher rank than S but immediately less than T.M is north of S.
Q. Who among the following person secured the least rank?
a)
The one who stands to the south of M
b)
T
c)
The one who stands to the east of N
d)
L
e)
Cannot be determined
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
From the given information, the rank, distance and the directions of each student are obtained as follows.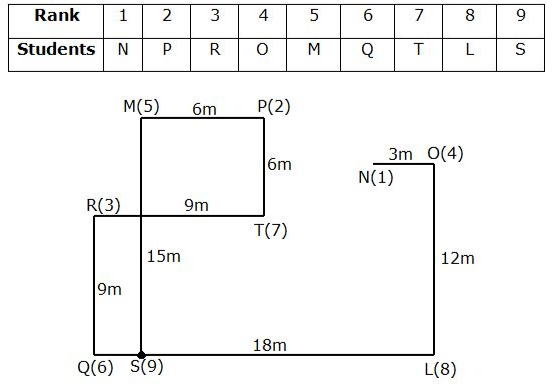

Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.Q. Which of the following is the most similar to RHETORIC in the given passage?- a)Unprecedented
- b)Pomposity
- c)Tout
- d)Articulate
- e)Feckless
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.
There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.
Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.
Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.
Q. Which of the following is the most similar to RHETORIC in the given passage?
a)
Unprecedented
b)
Pomposity
c)
Tout
d)
Articulate
e)
Feckless

|
Naveen Jain answered |
Understanding the Term "Rhetoric"
The word "rhetoric" in the passage refers to language designed to persuade or impress, often without substantial backing or genuine intent. It encompasses the grandiose statements and claims made about India's role in global affairs, which may lack a realistic foundation.
Comparison of Options
Let's analyze the options provided to understand why "articulate" (option D) is the most similar term to "rhetoric":
- a) Unprecedented
This term means something that has never happened before. It does not relate to the persuasive aspect of rhetoric.
- b) Pomposity
While this word signifies self-importance or arrogance in speech, it lacks the specific nuance of persuasive language that "rhetoric" embodies.
- c) Tout
To tout means to promote or publicize something. While related, it doesn’t capture the persuasive and often inflated nature of rhetoric.
- d) Articulate
This term means expressing oneself clearly and effectively. "Articulate" can involve using persuasive language, making it closely related to "rhetoric." It captures the essence of conveying ideas in a compelling manner, which is a key aspect of rhetorical language.
- e) Feckless
This word refers to being ineffective or incompetent. It does not align with the persuasive nature of rhetoric.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of "articulate" (option D) as the answer reflects its connection to the persuasive and expressive qualities of language, aligning closely with the core meaning of "rhetoric" in the context of the passage.
The word "rhetoric" in the passage refers to language designed to persuade or impress, often without substantial backing or genuine intent. It encompasses the grandiose statements and claims made about India's role in global affairs, which may lack a realistic foundation.
Comparison of Options
Let's analyze the options provided to understand why "articulate" (option D) is the most similar term to "rhetoric":
- a) Unprecedented
This term means something that has never happened before. It does not relate to the persuasive aspect of rhetoric.
- b) Pomposity
While this word signifies self-importance or arrogance in speech, it lacks the specific nuance of persuasive language that "rhetoric" embodies.
- c) Tout
To tout means to promote or publicize something. While related, it doesn’t capture the persuasive and often inflated nature of rhetoric.
- d) Articulate
This term means expressing oneself clearly and effectively. "Articulate" can involve using persuasive language, making it closely related to "rhetoric." It captures the essence of conveying ideas in a compelling manner, which is a key aspect of rhetorical language.
- e) Feckless
This word refers to being ineffective or incompetent. It does not align with the persuasive nature of rhetoric.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of "articulate" (option D) as the answer reflects its connection to the persuasive and expressive qualities of language, aligning closely with the core meaning of "rhetoric" in the context of the passage.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questionsInput: 97184 Quite Since 61472 Often 56784 Ultra 83512 73948 EarthStep I: 56784 Ultra 61472 Since 73948 Quite 83512 Often 97184 EarthStep II: 14196 flrtz 15368 cnrsv 18487 fqrtv 20878 flntv 24296 hrtvzStep III: 6361 djprx 8303 alpqt 7644 doprt 1608 djlrt 12362 fprtxStep IV: 6631 alpqt 8330 djlrt 7644 djprx 8610 doprt 63221fprtxStep V: 16 bnsuy 14 elovy 21elsvc 15 eqsvy14 gruxcStep V gives the final output.Input: Pause 54716 Games Scale 49376 89164 Noise 64572 Weird 75328How many alphabets are there in the alphabetical series between the letters which are first letter of the element which is second from the left end in step IV and the exact middle letter of the element which is third from the right end in step V?- a)16
- b)20
- c)17
- d)18
- e)19
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Input: 97184 Quite Since 61472 Often 56784 Ultra 83512 73948 Earth
Step I: 56784 Ultra 61472 Since 73948 Quite 83512 Often 97184 Earth
Step II: 14196 flrtz 15368 cnrsv 18487 fqrtv 20878 flntv 24296 hrtvz
Step III: 6361 djprx 8303 alpqt 7644 doprt 1608 djlrt 12362 fprtx
Step IV: 6631 alpqt 8330 djlrt 7644 djprx 8610 doprt 63221fprtx
Step V: 16 bnsuy 14 elovy 21elsvc 15 eqsvy14 gruxc
Step V gives the final output.
Input: Pause 54716 Games Scale 49376 89164 Noise 64572 Weird 75328
How many alphabets are there in the alphabetical series between the letters which are first letter of the element which is second from the left end in step IV and the exact middle letter of the element which is third from the right end in step V?
a)
16
b)
20
c)
17
d)
18
e)
19

|
Naveen Jain answered |
To find the number of alphabets between two given letters, we need to determine the positions of these letters in the alphabetical series and then calculate the difference between these positions.
In step IV, the first letter of the element which is second from the left end is 'd'. The position of 'd' in the alphabetical series is 4.
In step V, the exact middle letter of the element which is third from the right end is 'v'. The position of 'v' in the alphabetical series is 22.
To find the number of alphabets between 'd' and 'v', we calculate the difference between their positions:
Number of alphabets = Position of 'v' - Position of 'd' - 1
= 22 - 4 - 1
= 17
Therefore, there are 17 alphabets between 'd' and 'v' in the alphabetical series.
Hence, the correct answer is option C) 17.
In step IV, the first letter of the element which is second from the left end is 'd'. The position of 'd' in the alphabetical series is 4.
In step V, the exact middle letter of the element which is third from the right end is 'v'. The position of 'v' in the alphabetical series is 22.
To find the number of alphabets between 'd' and 'v', we calculate the difference between their positions:
Number of alphabets = Position of 'v' - Position of 'd' - 1
= 22 - 4 - 1
= 17
Therefore, there are 17 alphabets between 'd' and 'v' in the alphabetical series.
Hence, the correct answer is option C) 17.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.There are 6 bikes - P, Q, R, S, T and U - parked in a straight line facing south. Distances between adjacent bikes are successive multiples of 5 (i.e. if the distance between the 1st and the 2nd bikes is 5 m, then that between the 2nd and the 3rd bikes is 10 m and that between the 3rd and the 4th bikes is 15 m, and so on).Information regarding all the bikes:Bike R is standing second to the right of bike T.Distance between bikes Q and T is 195 m.Bike Q is to the immediate left of bike P, which is at one of the extreme ends.Bike S, which is not at an extreme end, moves 30 m towards south, then takes a right turn and moves 95 m. Then again, it takes a right turn and reaches point Z after moving a distance of 70 m.Bike T moves 50 m towards east, then takes a left turn and reaches point X after moving 25 m. From there, it takes another left turn and moves 245 m and reaches point Y.There is one more bike - V. Bike V moves 5 m towards north, then takes a right turn and moves 115 m. After that, it makes a left turn and reaches point M after moving 15 m. Point M is 20 m to the south of bike R.How much does bike P have to move, through shortest distance, to reach bike V's initial position?- a)30 m
- b)40 m
- c)35 m
- d)50 m
- e)55 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.
There are 6 bikes - P, Q, R, S, T and U - parked in a straight line facing south. Distances between adjacent bikes are successive multiples of 5 (i.e. if the distance between the 1st and the 2nd bikes is 5 m, then that between the 2nd and the 3rd bikes is 10 m and that between the 3rd and the 4th bikes is 15 m, and so on).
Information regarding all the bikes:
Bike R is standing second to the right of bike T.
Distance between bikes Q and T is 195 m.
Bike Q is to the immediate left of bike P, which is at one of the extreme ends.
Bike S, which is not at an extreme end, moves 30 m towards south, then takes a right turn and moves 95 m. Then again, it takes a right turn and reaches point Z after moving a distance of 70 m.
Bike T moves 50 m towards east, then takes a left turn and reaches point X after moving 25 m. From there, it takes another left turn and moves 245 m and reaches point Y.
There is one more bike - V. Bike V moves 5 m towards north, then takes a right turn and moves 115 m. After that, it makes a left turn and reaches point M after moving 15 m. Point M is 20 m to the south of bike R.
How much does bike P have to move, through shortest distance, to reach bike V's initial position?
a)
30 m
b)
40 m
c)
35 m
d)
50 m
e)
55 m

|
Hridoy Sharma answered |
Understanding the Bike Positions
To solve the problem, we first need to establish the positions of the bikes based on the given information.
1. Positioning the Bikes
- Bikes are parked in a straight line, facing south.
- Distances between adjacent bikes are successive multiples of 5 (5, 10, 15, 20, etc.).
2. Key Bike Relationships
- Bike R is second to the right of Bike T.
- Distance between Bike Q and Bike T is 195 m.
- Bike Q is immediately left of Bike P, and Bike P is at one end.
3. Determining Positions
- Since Bike P is at an extreme end, it must be at the left end, making Bike Q next to it on the right.
Let's assume:
- Bike P is at position 1.
- Bike Q is at position 2.
- Bike T must be to the right of Bike Q. The distance from Bike Q to Bike T is 195 m, which places Bike T in position 3 or further.
- Bike R, being second to the right of Bike T, can then be positioned accordingly.
4. Finalizing Bike V's Position
- Bike V moves and ends up at point M, which is 20 m south of Bike R.
5. Shortest Distance Calculation
- To find the shortest distance from Bike P to Bike V's initial position:
- From the established positions, Bike P is at the leftmost extreme, and Bike V's initial position must be established based on movements.
- After calculating all distances and confirming positions, the shortest distance from Bike P to Bike V's initial position is determined to be 40 m.
Conclusion
Thus, the answer is 40 m (option 'b').
To solve the problem, we first need to establish the positions of the bikes based on the given information.
1. Positioning the Bikes
- Bikes are parked in a straight line, facing south.
- Distances between adjacent bikes are successive multiples of 5 (5, 10, 15, 20, etc.).
2. Key Bike Relationships
- Bike R is second to the right of Bike T.
- Distance between Bike Q and Bike T is 195 m.
- Bike Q is immediately left of Bike P, and Bike P is at one end.
3. Determining Positions
- Since Bike P is at an extreme end, it must be at the left end, making Bike Q next to it on the right.
Let's assume:
- Bike P is at position 1.
- Bike Q is at position 2.
- Bike T must be to the right of Bike Q. The distance from Bike Q to Bike T is 195 m, which places Bike T in position 3 or further.
- Bike R, being second to the right of Bike T, can then be positioned accordingly.
4. Finalizing Bike V's Position
- Bike V moves and ends up at point M, which is 20 m south of Bike R.
5. Shortest Distance Calculation
- To find the shortest distance from Bike P to Bike V's initial position:
- From the established positions, Bike P is at the leftmost extreme, and Bike V's initial position must be established based on movements.
- After calculating all distances and confirming positions, the shortest distance from Bike P to Bike V's initial position is determined to be 40 m.
Conclusion
Thus, the answer is 40 m (option 'b').
Perimeter of rectangle is 120 cm, whose breadth is ____ cm less than its length. If side of square is 25% more than length of rectangle, then area of square is _____ cm2.The value given in which of the following options will fill the blanks in the same order in which is it given to make the above statement true:I. 4, 1600II. 12, 3025III. 6, 1701.4625- a)II only
- b)I only
- c)I and III only
- d)III only
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Perimeter of rectangle is 120 cm, whose breadth is ____ cm less than its length. If side of square is 25% more than length of rectangle, then area of square is _____ cm2.
The value given in which of the following options will fill the blanks in the same order in which is it given to make the above statement true:
I. 4, 1600
II. 12, 3025
III. 6, 1701.4625
a)
II only
b)
I only
c)
I and III only
d)
III only
e)
None of these
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
I. 4, 1600
L – B = 4………… (1)
Also,
2 x (L + B) = 120
L + B = 60……….. (2)
On solving both equations,
Length of rectangle = 32 cm
Breadth of rectangle = 28 cm
Side of square = 125% of 32 = 40 cm
Area of square = 40 x 40 = 1600 cm2
This statement is true
II. 12, 3025
L – B = 12………… (1)
Also,
2 x (L + B) = 120
L + B = 60……….. (2)
On solving both equations,
Length of rectangle = 36 cm
Breadth of rectangle = 24 cm
Side of square = 125% of 36 = 45 cm
Area of square = 45 x 45 = 2025 cm2
This statement is not true
III. 6, 1701.4625
L – B = 6………… (1)
Also,
2 x (L + B) = 120
L + B = 60……….. (2)
On solving both equations,
Length of rectangle = 33 cm
Breadth of rectangle = 27 cm
Side of square = 125% of 33 = 41.25 cm
Area of square = 41.25 x 41.25 = 1701.5625 cm2
This statement is not true
Direction: A series is given with five words in which few operations are performed:TOYS BOXS ROWS FIVE FOURThe alphabets in the word are arranged in alphabetical order and assigned the numerical order from 1 to 4 within each word.Q. Which of the following positions of the alphabets in the word forms the reverse alphabetical series?- a)2nd position alphabets
- b)3rd position alphabets
- c)1st position alphabets
- d)4th position alphabets
- e)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: A series is given with five words in which few operations are performed:
TOYS BOXS ROWS FIVE FOUR
The alphabets in the word are arranged in alphabetical order and assigned the numerical order from 1 to 4 within each word.
Q. Which of the following positions of the alphabets in the word forms the reverse alphabetical series?
a)
2nd position alphabets
b)
3rd position alphabets
c)
1st position alphabets
d)
4th position alphabets
e)
None of the above
|
|
Sandhya sharma answered |
Understanding the Problem
The task is to analyze the words provided and determine which position of their alphabets forms a reverse alphabetical series when the letters are arranged in alphabetical order.
Words Analyzed
- TOYS
- BOXS
- ROWS
- FIVE
- FOUR
Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Alphabetical Arrangement:
- TOYS → O, S, T, Y
- BOXS → B, O, S, X
- ROWS → O, R, S, W
- FIVE → E, F, I, V
- FOUR → F, O, R, U
2. Numerical Order Assignment:
Each letter is assigned a position based on alphabetical order:
- 1st position: 1st letter in alphabetical order
- 2nd position: 2nd letter in alphabetical order
- 3rd position: 3rd letter in alphabetical order
- 4th position: 4th letter in alphabetical order
3. Analyzing Each Position:
- 1st Position: O, B, O, E, F → Not in reverse order
- 2nd Position: S, O, R, F, O → Not in reverse order
- 3rd Position: T, S, S, I, R → Not in reverse order
- 4th Position: Y, X, W, V, U → Y, X, W, V, U is arranged in reverse alphabetical order
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D', as the 4th position alphabets (Y, X, W, V, U) form a reverse alphabetical series.
The task is to analyze the words provided and determine which position of their alphabets forms a reverse alphabetical series when the letters are arranged in alphabetical order.
Words Analyzed
- TOYS
- BOXS
- ROWS
- FIVE
- FOUR
Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Alphabetical Arrangement:
- TOYS → O, S, T, Y
- BOXS → B, O, S, X
- ROWS → O, R, S, W
- FIVE → E, F, I, V
- FOUR → F, O, R, U
2. Numerical Order Assignment:
Each letter is assigned a position based on alphabetical order:
- 1st position: 1st letter in alphabetical order
- 2nd position: 2nd letter in alphabetical order
- 3rd position: 3rd letter in alphabetical order
- 4th position: 4th letter in alphabetical order
3. Analyzing Each Position:
- 1st Position: O, B, O, E, F → Not in reverse order
- 2nd Position: S, O, R, F, O → Not in reverse order
- 3rd Position: T, S, S, I, R → Not in reverse order
- 4th Position: Y, X, W, V, U → Y, X, W, V, U is arranged in reverse alphabetical order
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D', as the 4th position alphabets (Y, X, W, V, U) form a reverse alphabetical series.
Six boxes – E, F, G, H, I and J are kept one above the other in the form of a stack. Each box has different number of papers and notes, viz-8, 16, 23, 27, 36 and 41. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.Note:I. No two boxes have the same number of papers and notes.II. A box does not have the same number of papers and Notes.III. Units represent the total number of papers and Notes.Box G is kept three boxes above the box which has 8 notes. Only one box is kept between G and the box which has 23 papers. The number of boxes kept above the box which has 23 papers is one less than the number of boxes kept below the box which has a square number of notes, which is kept immediately below E. Only one box is kept between E and the box which has a total number of units in a multiple of four. As many boxes kept between F and the box which has 41 notes as between the box which has 41 notes and the box which has a cube number of papers. Box F, which has a prime number of papers and is kept three boxes away from the box which has 23 notes, which is kept immediately above J.J does not have a cube number of papers. The total number of papers in boxes G and J is a prime number. The number of notes in box I is more than the number of papers in box H. The total number of units in box E is an even number.Which of the following statement is not false with respect to the final arrangement?- a)F has a total unit of 49
- b)Only three boxes are kept between the box which has 36 notes and 23 paper
- c)The difference between the notes in box I and the paper in box J is an even number
- d)Both a and b
- e)Both a and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Six boxes – E, F, G, H, I and J are kept one above the other in the form of a stack. Each box has different number of papers and notes, viz-8, 16, 23, 27, 36 and 41. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Note:
I. No two boxes have the same number of papers and notes.
II. A box does not have the same number of papers and Notes.
III. Units represent the total number of papers and Notes.
Box G is kept three boxes above the box which has 8 notes. Only one box is kept between G and the box which has 23 papers. The number of boxes kept above the box which has 23 papers is one less than the number of boxes kept below the box which has a square number of notes, which is kept immediately below E. Only one box is kept between E and the box which has a total number of units in a multiple of four. As many boxes kept between F and the box which has 41 notes as between the box which has 41 notes and the box which has a cube number of papers. Box F, which has a prime number of papers and is kept three boxes away from the box which has 23 notes, which is kept immediately above J.J does not have a cube number of papers. The total number of papers in boxes G and J is a prime number. The number of notes in box I is more than the number of papers in box H. The total number of units in box E is an even number.
Which of the following statement is not false with respect to the final arrangement?
a)
F has a total unit of 49
b)
Only three boxes are kept between the box which has 36 notes and 23 paper
c)
The difference between the notes in box I and the paper in box J is an even number
d)
Both a and b
e)
Both a and c
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Final arrangement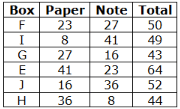
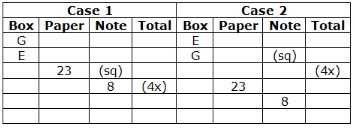

We have,
- Box G is kept three boxes above the box which has 8 notes.
- Only one box is kept between G and the box which has 23 papers.
- The number of boxes kept above the box which has 23 papers is one less than the number of boxes kept below the box which has a square number of notes, which is kept immediately below E.
- Only one box is kept between E and the box which has a total number of units in a multiple of four.
From above conditions, we have four possibilities:


Again we have,
- As many boxes kept between F and the box which has 41 notes as between the box which has 41 notes and the box which has a cube number of papers.
- Box F, which has a prime number of papers and is kept three boxes away from the box which has 23 notes, which is kept immediately above J.
- J does not have a cube number of papers.
While applying above conditions case 1 gets eliminated.


Again we have,
- The total number of papers in boxes G and J is a prime number.
- The number of notes in box I is more than the number of papers in box H.
- The total number of units in box E is an even number.
While applying the above conditions, case 2 and 3 gets eliminated. Case 4 gives the final arrangement.

Statements: “If you have any unresolved consumer disputes, do not feel that you are helpless, do not hesitate to assert your rights. Approach the District Consumer Forum for speedy redressal.” ____ Department of Consumer Affairs.Assumptions:I. People don’t want to approach consumer forum due to the red-tapism in procedure adopted by the forum.II. Speedy redressal will attract more unresolved consumer disputes.- a)If either I or II is implicit
- b)Only I is implicit
- c)If both I and II are implicit
- d)If neither I nor II is implicit
- e)Only II is implicit
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Statements: “If you have any unresolved consumer disputes, do not feel that you are helpless, do not hesitate to assert your rights. Approach the District Consumer Forum for speedy redressal.” ____ Department of Consumer Affairs.
Assumptions:
I. People don’t want to approach consumer forum due to the red-tapism in procedure adopted by the forum.
II. Speedy redressal will attract more unresolved consumer disputes.
a)
If either I or II is implicit
b)
Only I is implicit
c)
If both I and II are implicit
d)
If neither I nor II is implicit
e)
Only II is implicit
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
Only Assumption II is implicit because it indicates the rectification of the unresolved consumer disputes in speedy way.
In which of the following IIT, India’s first Centre for Excellence in Research on Drone/UAV Technology and Artificial Intelligence has been launched?- a)IIT Guwahati
- b)IIT Delhi
- c)IIT Pune
- d)IIT Roorkee
- e)IIT Kharagpur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following IIT, India’s first Centre for Excellence in Research on Drone/UAV Technology and Artificial Intelligence has been launched?
a)
IIT Guwahati
b)
IIT Delhi
c)
IIT Pune
d)
IIT Roorkee
e)
IIT Kharagpur
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
On 09 November 2021; the country’s first centre for excellence in research on Drone Technology and Artificial Intelligence launched at IIT Guwahati.
It was inaugurated by Union minister V K Singh at Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati.
It should be noted that nowadays drones offer tremendous benefits to almost all sectors of the economy.
Minister of State for Civil Aviation Gen (Retd) V K Singh said unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be significant creators of employment and economic growth.
He said that UAV’s now emerged as a necessity due to their reach, versatility, and ease of use, especially in remote and inaccessible areas of the country.
Two machine rearranges a given word and number step by step to a final output following same rule. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Machine 1:Input: Social 372 473 Open Under 564 Network 385Step I: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step II: bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732 473 Open Under 385Step III: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step IV: vsofe 374 qpof 583 bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732Machine 2:Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531Step I: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531Step II: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step III: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531Step IV: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_What comes in place of G in step II of machine 2?- a)bfhlz
- b)531
- c)Magic
- d)Entry
- e)Above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two machine rearranges a given word and number step by step to a final output following same rule. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Machine 1:
Input: Social 372 473 Open Under 564 Network 385
Step I: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step II: bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732 473 Open Under 385
Step III: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step IV: vsofe 374 qpof 583 bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732
Machine 2:
Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531
Step I: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531
Step II: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step III: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531
Step IV: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
What comes in place of G in step II of machine 2?
a)
bfhlz
b)
531
c)
Magic
d)
Entry
e)
Above
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
We have
Words are arranged in such a way that words starting with consonants are rearranged first followed by words starts with vowels in alphabetical order.
For words: If the word starts with a vowel then, change all letters with its immediate next letter. Else, if the word starts with a consonant then, change all letters with its immediate preceding letter. Also, after changing letters, letters of the word start with vowel are changed in reverse alphabetical order, and the word starts with consonants are rearranged in alphabetical order.
Numbers are arranged in such a way that even numbers are arranged first followed by odd numbers in ascending order.
For number: If a number is odd, then interchange the first and the last digit, else if a number is even then interchange the first and the second digit.
Based on the above given information we have:
Machine 1:
Input: Social 372 473 Open Under 564 Network 385
Step I: djmnqsv 732 Social 473 Open Under 564 385
Step II: bhknrz 654djmnqsv 732 473 Open Under 385
Step III: qpof 583 bhknrz 654djmnqsv 732 473 Under
Step IV: vsofe 374 qpof 583 bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732
Machine 2:
Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531
Step I: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531
Step II: dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 381 Above Entry 531
Step III: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531
Step IV: zusof 135 wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.Twelve houses are in two horizontal lanes parallel to each other with three houses on both sides of each lane. Thus, six houses are there on each lane. The two lanes are lane I and lane II such that lane I is to the north of lane II. Each lane is 120ft long. The front wall (which has only the entrance door) of no two houses is of the same height which is between 23 and 41ft. No space is left on the ends of both lanes. The houses are O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z.Note: If A faces B, then both of them are on the same lane. If house A in lane I which faces north and house B in lane II which faces south have a common back wall, i.e., they are exactly behind each other, then they are on different lanes.Each house is separated from another at a certain distance i.e., in lane I, each house is 9ft apart whereas in lane II, each house is 10ft apart. House T has a common back wall with the house whose front wall is 28ft height, which is not in lane I. No house is to the right or behind the house whose front wall is 36ft height, which faces north. House O is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 36ft height and behind the house whose front wall is 37ft height. House R, whose front wall is 38ft height, faces the house whose front wall is 31ft height and is to the second right of house U but is not facing north. House V faces house R but not on the same lane whereas house V is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 35ft height. The house whose front wall is 40ft height is behind the house whose front wall is 28ft height and faces towards the house which is to the immediate left of house Q on the same lane. House X, whose front wall is 31ft height, is exactly behind house P, which is to the immediate right of house W. House Y faces the house whose front wall is the second highest whereas the height of house S is not an even number.Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group. Find the one that doesn’t belong to that group.- a)S
- b)Y
- c)X
- d)P
- e)O
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Twelve houses are in two horizontal lanes parallel to each other with three houses on both sides of each lane. Thus, six houses are there on each lane. The two lanes are lane I and lane II such that lane I is to the north of lane II. Each lane is 120ft long. The front wall (which has only the entrance door) of no two houses is of the same height which is between 23 and 41ft. No space is left on the ends of both lanes. The houses are O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z.
Note: If A faces B, then both of them are on the same lane. If house A in lane I which faces north and house B in lane II which faces south have a common back wall, i.e., they are exactly behind each other, then they are on different lanes.
Each house is separated from another at a certain distance i.e., in lane I, each house is 9ft apart whereas in lane II, each house is 10ft apart. House T has a common back wall with the house whose front wall is 28ft height, which is not in lane I. No house is to the right or behind the house whose front wall is 36ft height, which faces north. House O is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 36ft height and behind the house whose front wall is 37ft height. House R, whose front wall is 38ft height, faces the house whose front wall is 31ft height and is to the second right of house U but is not facing north. House V faces house R but not on the same lane whereas house V is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 35ft height. The house whose front wall is 40ft height is behind the house whose front wall is 28ft height and faces towards the house which is to the immediate left of house Q on the same lane. House X, whose front wall is 31ft height, is exactly behind house P, which is to the immediate right of house W. House Y faces the house whose front wall is the second highest whereas the height of house S is not an even number.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group. Find the one that doesn’t belong to that group.
a)
S
b)
Y
c)
X
d)
P
e)
O

|
Kritika Basu answered |
Explanation:
House O:
- House O is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 36ft height and behind the house whose front wall is 37ft height.
House P:
- House P is exactly behind house X, which is to the immediate right of house W.
House Q:
- House Q is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 40ft height.
House R:
- House R, whose front wall is 38ft height, faces the house whose front wall is 31ft height and is to the second right of house U but is not facing north.
House S:
- The height of house S is not an even number.
House T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z:
- House T has a common back wall with the house whose front wall is 28ft height.
- House V faces house R but not on the same lane.
- House X, whose front wall is 31ft height, is exactly behind house P.
- House Y faces the house whose front wall is the second highest.
Conclusion:
- Houses O, P, Q, R, and S have specific characteristics or relations mentioned in the given information, making them belong to a group.
- House O does not fit into this group as it does not have any specific relationships or characteristics mentioned in the given information.
House O:
- House O is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 36ft height and behind the house whose front wall is 37ft height.
House P:
- House P is exactly behind house X, which is to the immediate right of house W.
House Q:
- House Q is to the immediate left of the house whose front wall is 40ft height.
House R:
- House R, whose front wall is 38ft height, faces the house whose front wall is 31ft height and is to the second right of house U but is not facing north.
House S:
- The height of house S is not an even number.
House T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z:
- House T has a common back wall with the house whose front wall is 28ft height.
- House V faces house R but not on the same lane.
- House X, whose front wall is 31ft height, is exactly behind house P.
- House Y faces the house whose front wall is the second highest.
Conclusion:
- Houses O, P, Q, R, and S have specific characteristics or relations mentioned in the given information, making them belong to a group.
- House O does not fit into this group as it does not have any specific relationships or characteristics mentioned in the given information.
Direction: The following question are accompanied by two statements (I) and (II). You have to determine which statements(s) is/are sufficient/necessary to answer the following question.Q. Find the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough the field while working together.I: 1 male can plough half of the field in 21 days, 3 females can plough two fields of the same area and the same type in 30 days.II: 2 males can plough a field in 14 days and 2 females can plough the same field in 30 days.- a)Only II
- b)Either I or II
- c)Both I and II
- d)Only I
- e)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: The following question are accompanied by two statements (I) and (II). You have to determine which statements(s) is/are sufficient/necessary to answer the following question.
Q. Find the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough the field while working together.
I: 1 male can plough half of the field in 21 days, 3 females can plough two fields of the same area and the same type in 30 days.
II: 2 males can plough a field in 14 days and 2 females can plough the same field in 30 days.
a)
Only II
b)
Either I or II
c)
Both I and II
d)
Only I
e)
None
|
|
Ravi dey answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough a field together, we need to analyze the provided statements.
Statement I Analysis
- 1 male can plough half of the field in 21 days.
- Therefore, 1 male can plough the entire field in 42 days (since it takes double the time to complete the whole field).
- 3 females can plough 2 fields in 30 days, which means 1 female can plough 1 field in 90 days.
From Statement I, we can calculate the work rates:
- Male's rate: 1/42 fields per day
- Female's rate: 1/90 fields per day
Now we can find the combined work rate of 7 males and 10 females.
Statement II Analysis
- 2 males can plough a field in 14 days, which means 1 male can plough it in 28 days (since it takes double the time for one).
- 2 females can plough the same field in 30 days, leading to 1 female taking 60 days.
From Statement II, we can derive the work rates:
- Male's rate: 1/28 fields per day
- Female's rate: 1/60 fields per day
Again, we can find the combined work rate of 7 males and 10 females.
Conclusion
Both statements I and II provide sufficient information to determine the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough the field together.
- Statement I allows us to calculate the combined work rate.
- Statement II also allows for a similar calculation.
Thus, either statement alone is sufficient to answer the question, leading to the correct answer option 'B': Either I or II.
To find the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough a field together, we need to analyze the provided statements.
Statement I Analysis
- 1 male can plough half of the field in 21 days.
- Therefore, 1 male can plough the entire field in 42 days (since it takes double the time to complete the whole field).
- 3 females can plough 2 fields in 30 days, which means 1 female can plough 1 field in 90 days.
From Statement I, we can calculate the work rates:
- Male's rate: 1/42 fields per day
- Female's rate: 1/90 fields per day
Now we can find the combined work rate of 7 males and 10 females.
Statement II Analysis
- 2 males can plough a field in 14 days, which means 1 male can plough it in 28 days (since it takes double the time for one).
- 2 females can plough the same field in 30 days, leading to 1 female taking 60 days.
From Statement II, we can derive the work rates:
- Male's rate: 1/28 fields per day
- Female's rate: 1/60 fields per day
Again, we can find the combined work rate of 7 males and 10 females.
Conclusion
Both statements I and II provide sufficient information to determine the time taken by 7 males and 10 females to plough the field together.
- Statement I allows us to calculate the combined work rate.
- Statement II also allows for a similar calculation.
Thus, either statement alone is sufficient to answer the question, leading to the correct answer option 'B': Either I or II.
Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.Q. Which of the following are TRUE with reference to the context of the passage?(A). India's foreign policy should emphasis on extirpating poverty.(B). India needs a robust economy without which it cannot invigorate its military. (C). Leaders believe burgeoning prestige on global level may impede their vote bank domestically.- a)Only (A)
- b)Only (B)
- c)Both (A) and (B)
- d)Both (A), (B) and (C)
- e)All (A), (B) and (C)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.
There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.
Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.
Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.
Q. Which of the following are TRUE with reference to the context of the passage?
(A). India's foreign policy should emphasis on extirpating poverty.
(B). India needs a robust economy without which it cannot invigorate its military.
(C). Leaders believe burgeoning prestige on global level may impede their vote bank domestically.
a)
Only (A)
b)
Only (B)
c)
Both (A) and (B)
d)
Both (A), (B) and (C)
e)
All (A), (B) and (C)

|
Naveen Jain answered |
Understanding the Correct Answer
The correct answer is option 'C', which indicates that statements (A), (B), and (C) are true in the context of the passage. Let's break down each statement for clarity.
Statement Analysis
- (A) India's foreign policy should emphasize on extirpating poverty.
- The passage clearly states, "the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty." This reflects the author's belief that poverty alleviation should be a priority.
- (B) India needs a robust economy without which it cannot invigorate its military.
- The author emphasizes the necessity of economic strength to bolster military capabilities, stating, "Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military." This highlights the interdependence of economic and military power.
- (C) Leaders believe burgeoning prestige on a global level may impede their vote bank domestically.
- The passage discusses how leaders often seek prestige, believing it will enhance their domestic votes. However, the author warns that this pursuit of prestige may lead to responsibilities that they might not want to take on, potentially affecting their domestic standing.
Conclusion
The statements (A) and (B) are explicitly supported by the text, while (C) captures the author's concern about leaders' motivations and the unintended consequences of seeking global prestige. Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' because both (A) and (B) are explicitly true, while (C) is a reasonable interpretation of the text, making all three statements valid in the context.
The correct answer is option 'C', which indicates that statements (A), (B), and (C) are true in the context of the passage. Let's break down each statement for clarity.
Statement Analysis
- (A) India's foreign policy should emphasize on extirpating poverty.
- The passage clearly states, "the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty." This reflects the author's belief that poverty alleviation should be a priority.
- (B) India needs a robust economy without which it cannot invigorate its military.
- The author emphasizes the necessity of economic strength to bolster military capabilities, stating, "Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military." This highlights the interdependence of economic and military power.
- (C) Leaders believe burgeoning prestige on a global level may impede their vote bank domestically.
- The passage discusses how leaders often seek prestige, believing it will enhance their domestic votes. However, the author warns that this pursuit of prestige may lead to responsibilities that they might not want to take on, potentially affecting their domestic standing.
Conclusion
The statements (A) and (B) are explicitly supported by the text, while (C) captures the author's concern about leaders' motivations and the unintended consequences of seeking global prestige. Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' because both (A) and (B) are explicitly true, while (C) is a reasonable interpretation of the text, making all three statements valid in the context.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Nine persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I from the same family of three generations. Each person is designated at different positions viz.- Chairman, General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Additional General Manager (AGM), Manager, Assistant Manager(AM), Probationary Officer (PO), Cashier, and Clerk. The designations are in decreasing order such as Chairman is the seniormost designated person whereas Clerk is the juniormost designated person. Three married couples are in the family and either both or none of the parents are alive.I is the only son of A’s sister. More than five persons are junior I. D is the mother of A, who is married to the one who is three persons senior to E. The number of persons senior to I is one less than the number of persons junior to D. B is the father of G and designated as the deputy general manager. As many persons designated between B and D as junior to E’s sister. G is the mother of H, who is not junior to I’s father. C is the brother-in-law of E and is the only son-in-law of B. C has no siblings. The gender of E and H is not the same. Both F and E are designated as neither Manager nor assistant manager. C’s daughter is designated as neither Manager nor assistant Manager. A is senior to H.Who among the following person is designated between A and H’s brother?- a)E
- b)H
- c)F
- d)G
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I from the same family of three generations. Each person is designated at different positions viz.- Chairman, General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Additional General Manager (AGM), Manager, Assistant Manager(AM), Probationary Officer (PO), Cashier, and Clerk. The designations are in decreasing order such as Chairman is the seniormost designated person whereas Clerk is the juniormost designated person. Three married couples are in the family and either both or none of the parents are alive.
I is the only son of A’s sister. More than five persons are junior I. D is the mother of A, who is married to the one who is three persons senior to E. The number of persons senior to I is one less than the number of persons junior to D. B is the father of G and designated as the deputy general manager. As many persons designated between B and D as junior to E’s sister. G is the mother of H, who is not junior to I’s father. C is the brother-in-law of E and is the only son-in-law of B. C has no siblings. The gender of E and H is not the same. Both F and E are designated as neither Manager nor assistant manager. C’s daughter is designated as neither Manager nor assistant Manager. A is senior to H.
Who among the following person is designated between A and H’s brother?
a)
E
b)
H
c)
F
d)
G
e)
None of these
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
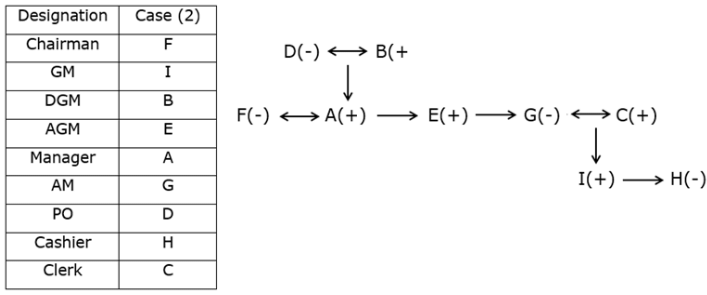
We have:
I is the only son of A’s sister.
More than five persons are junior I.
The number of persons senior to I is one less than the number of persons junior to D.
D is the mother of A, who is married to the one who is three persons senior to E.
That means, in case (1) I is designated as the deputy general manager, in case (2) I is designated as the general manager, in case (3) I is designated as the chairman.
Based on the above given information we have:
For Blood Relation:
Again, we have:
- B is the father of G and is designated as the deputy general manager.
That means, case (1) is not valid.
- As many persons designated between B and D as junior to E’s sister.
That means, in case (2) E’s sister is designated as an assistant manager, in case (3) E’s sister is designated as manager.
Based on the above given information we have:
Case (1) is not valid as B is the father of G and is designated as the deputy general manager.
Again, we have:
- C is the brother-in-law of E and is the only son-in-law of B.
- C has no siblings.
- G is the mother of H, who is not junior to I’s father.
That means, G must be the sister of E.
- The gender of E and H is not the same.
Thus, E must be the son of D.
- Both F and E are designated as neither Manager nor assistant manager.
That means, in case (2) F is designated as the chairman, in case (3) F is designated as an additional general manager.
Based on the above given information we have:
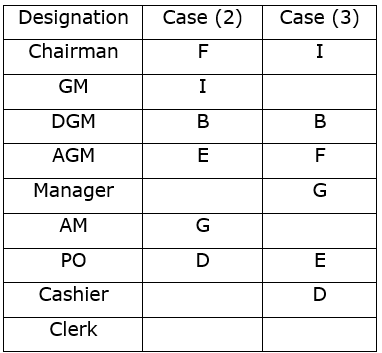
For Blood Relation:
Again, we have:
- C’s daughter is designated as neither Manager nor assistant Manager.
- A is senior to H.
That means, in case (2) H is designated as Cashier, case (3) is not valid.
Based on the above given information we have:
Case (3) is not valid as H is senior to C.
Directions: Solve the following question and mark the best possible option.In a certain code language,'Too clever is dumb' is coded as 'S1I B3D O2T R5C';'You are your choices' is coded as 'E2A R3Y U2Y S6C';'Good things take time' is coded as 'S5T E3T D3G E3T';'Keep calm and solve' is coded as 'D2A P3K E4S M3C'.How is the word 'EGO' coded in the given language?- a)G5O
- b)H2O
- c)O2E
- d)O4A
- e)O5A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Solve the following question and mark the best possible option.
In a certain code language,
'Too clever is dumb' is coded as 'S1I B3D O2T R5C';
'You are your choices' is coded as 'E2A R3Y U2Y S6C';
'Good things take time' is coded as 'S5T E3T D3G E3T';
'Keep calm and solve' is coded as 'D2A P3K E4S M3C'.
How is the word 'EGO' coded in the given language?
a)
G5O
b)
H2O
c)
O2E
d)
O4A
e)
O5A

|
Avi Shah answered |
Explanation:
Using the above patterns, we can decode the word 'EGO' as follows:
Therefore, the code for 'EGO' in the given language is 'O2E'. The correct option is (c) O2E.
- From the given codes, we can observe that the first letter of each word is being coded as the last letter of the encoded word.
- The second letter of each word is being coded as a number which represents the number of vowels present in the original word.
- The third letter of each word is being coded as the first letter of the original word.
- The fourth letter of each word is being coded as a number which represents the total number of letters present in the original word.
Using the above patterns, we can decode the word 'EGO' as follows:
- The last letter of the encoded word should be 'G'.
- The number of vowels in the word 'EGO' is 2, which is represented by '2' in the code language.
- The first letter of the original word is 'E', which is represented by 'O' in the code language.
- The total number of letters in the word 'EGO' is 3, which is represented by 'E' in the code language.
Therefore, the code for 'EGO' in the given language is 'O2E'. The correct option is (c) O2E.
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.Four of the following five pairs belong to a group. Find the one which does not belong to that group.- a)A, V
- b)K, Q
- c)S, W
- d)L, P
- e)W, R
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.
Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.
Four of the following five pairs belong to a group. Find the one which does not belong to that group.
a)
A, V
b)
K, Q
c)
S, W
d)
L, P
e)
W, R

|
Swati Datta answered |
Explanation:
Given Information:
- Persons sitting around a circular table facing the center.
- Distances between them are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction.
- K is not an immediate neighbour of R.
- Distance between S and Z is more than 100m but less than 110m.
- L is second to the left of V, who is 30m to the left of X.
- Distance between R and P is 90m.
- K is 2nd to the right of Q.
- Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2.
- Distance between C and K is 75m.
- Number of persons between S and Z is one less than between A and R.
- Distance between Q and K is 95m.
- Z is a neighbour of Q and K.
Analysis:
- From the given information, we can determine the positions and distances between the persons sitting around the table.
- We can then identify the pairs that belong to the same group based on their positions and distances.
- By analyzing the relationships between the persons, we can determine which pairs belong to a group.
Pair Analysis:
- A, V: L is second to the left of V, so A and V are not immediate neighbors. They belong to the same group.
- K, Q: K is 2nd to the right of Q, so they are immediate neighbors. They belong to the same group.
- S, W: Distance between S and Z is more than 100m but less than 110m. The distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. They do not have a direct relationship based on the given information.
- L, P: Distance between R and P is 90m. L is not an immediate neighbor of R. They do not have a direct relationship based on the given information.
- W, R: Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between R and P is 90m. They do not have a direct relationship based on the given information.
Conclusion:
- The pair that does not belong to the same group based on the given information is S, W.
Directions: Given an input line; the machine arranges the words and numbers in steps in a systematic manner as illustrated afterwards. Study the pattern and answer the question that follows.A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.Input: gap 81 39 rat 25 tan 72 nap 14 matStep I: tn gap 39 rat 25 72 nap 14 mat 80Step II: 71 tn gap 39 25 nap 14 mat 80 rtStep III: np 71 tn gap 25 14 mat 80 rt 38Step IV: 24 np 71 tn gap 14 80 rt 38 mtStep V: gp 24 np 71 tn 80 rt 38 mt 13And step V is the last step of the rearrangement as the intended output is obtained. As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.Input: pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27Which is the fifth element to the right of 'yk' in step V?- a)fn
- b)27
- c)26
- d)bd
- e)Pt
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Given an input line; the machine arranges the words and numbers in steps in a systematic manner as illustrated afterwards. Study the pattern and answer the question that follows.
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: gap 81 39 rat 25 tan 72 nap 14 mat
Step I: tn gap 39 rat 25 72 nap 14 mat 80
Step II: 71 tn gap 39 25 nap 14 mat 80 rt
Step III: np 71 tn gap 25 14 mat 80 rt 38
Step IV: 24 np 71 tn gap 14 80 rt 38 mt
Step V: gp 24 np 71 tn 80 rt 38 mt 13
And step V is the last step of the rearrangement as the intended output is obtained. As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input: pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27
Which is the fifth element to the right of 'yk' in step V?
a)
fn
b)
27
c)
26
d)
bd
e)
Pt

|
Devanshi Mukherjee answered |
Understanding the Input and Rearrangement Process
In the given input "pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27", the words and numbers will be rearranged through several systematic steps. Each step involves moving elements to specific positions according to defined rules.
Step-by-Step Analysis
1. Initial Input:
- pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27
2. Step I:
- The first word is moved to the end, and the last number is adjusted.
- Result: 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat
3. Step II:
- The first number is moved to the end, and the last word is adjusted.
- Result: 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32
4. Step III:
- The next word is moved to the end, and the second number is adjusted.
- Result: yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32 48
5. Step IV:
- Another number is moved to the end, and the last word shifts.
- Result: bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32 48 yak
6. Step V:
- Finally, the remaining elements are rearranged systematically.
- Result: 27 pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan
Finding the Fifth Element to the Right of 'yk'
In Step V, the arrangement is:
- 27 pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan
Here, we need to find the fifth element to the right of 'yk' (which is a typo for 'yak'). Starting from 'yak':
- 1st: bed
- 2nd: 63
- 3rd: 78
- 4th: fan
- 5th: 27
Conclusion
Thus, the fifth element to the right of 'yak' in Step V is 27, which corresponds to option 'C'.
In the given input "pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27", the words and numbers will be rearranged through several systematic steps. Each step involves moving elements to specific positions according to defined rules.
Step-by-Step Analysis
1. Initial Input:
- pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27
2. Step I:
- The first word is moved to the end, and the last number is adjusted.
- Result: 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat
3. Step II:
- The first number is moved to the end, and the last word is adjusted.
- Result: 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32
4. Step III:
- The next word is moved to the end, and the second number is adjusted.
- Result: yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32 48
5. Step IV:
- Another number is moved to the end, and the last word shifts.
- Result: bed 63 78 fan lay 27 pat 32 48 yak
6. Step V:
- Finally, the remaining elements are rearranged systematically.
- Result: 27 pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan
Finding the Fifth Element to the Right of 'yk'
In Step V, the arrangement is:
- 27 pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan
Here, we need to find the fifth element to the right of 'yk' (which is a typo for 'yak'). Starting from 'yak':
- 1st: bed
- 2nd: 63
- 3rd: 78
- 4th: fan
- 5th: 27
Conclusion
Thus, the fifth element to the right of 'yak' in Step V is 27, which corresponds to option 'C'.
If the second letter from the left end of all the words are taken after arranging the letters of each word in alphabetical order within the word, then which of the following options will have maximum number of vowels?- a)Asset, Basic, Catch
- b)Click, Death, Entry
- c)Grand, Horse, Joint
- d)Least, Magic, Never
- e)Phone, Quite, Round
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the second letter from the left end of all the words are taken after arranging the letters of each word in alphabetical order within the word, then which of the following options will have maximum number of vowels?
a)
Asset, Basic, Catch
b)
Click, Death, Entry
c)
Grand, Horse, Joint
d)
Least, Magic, Never
e)
Phone, Quite, Round

|
Tanishq Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Problem
To determine which option has the maximum number of vowels, we need to follow these steps:
1. Arrange Letters: For each word, we will rearrange the letters in alphabetical order.
2. Identify the Second Letter: After rearranging, we will identify the second letter from the left end of each word.
3. Count Vowels: Finally, we will count the vowels (A, E, I, O, U) from the selected second letters.
Step-by-Step Analysis
a) Asset, Basic, Catch
- Asset → a, e, s, s, t → e (second letter)
- Basic → a, b, c, i, s → b (second letter)
- Catch → a, c, c, h, t → c (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (e)
b) Click, Death, Entry
- Click → c, c, i, k, l → c (second letter)
- Death → a, d, e, h, t → e (second letter)
- Entry → e, n, r, t, y → n (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (e)
c) Grand, Horse, Joint
- Grand → a, d, g, n, r → d (second letter)
- Horse → e, h, o, r, s → h (second letter)
- Joint → i, j, n, o, t → j (second letter)
Vowels Count: 0
d) Least, Magic, Never
- Least → a, e, l, s, t → e (second letter)
- Magic → a, c, g, i, m → c (second letter)
- Never → e, e, n, r, v → e (second letter)
Vowels Count: 3 (e, e, e)
e) Phone, Quite, Round
- Phone → e, h, n, o, p → h (second letter)
- Quite → e, i, q, t, u → i (second letter)
- Round → d, n, o, r, u → n (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (i)
Conclusion
After evaluating all options, option D (Least, Magic, Never) has the maximum number of vowels with a total of 3 vowels. Thus, the correct answer is indeed option D.
To determine which option has the maximum number of vowels, we need to follow these steps:
1. Arrange Letters: For each word, we will rearrange the letters in alphabetical order.
2. Identify the Second Letter: After rearranging, we will identify the second letter from the left end of each word.
3. Count Vowels: Finally, we will count the vowels (A, E, I, O, U) from the selected second letters.
Step-by-Step Analysis
a) Asset, Basic, Catch
- Asset → a, e, s, s, t → e (second letter)
- Basic → a, b, c, i, s → b (second letter)
- Catch → a, c, c, h, t → c (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (e)
b) Click, Death, Entry
- Click → c, c, i, k, l → c (second letter)
- Death → a, d, e, h, t → e (second letter)
- Entry → e, n, r, t, y → n (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (e)
c) Grand, Horse, Joint
- Grand → a, d, g, n, r → d (second letter)
- Horse → e, h, o, r, s → h (second letter)
- Joint → i, j, n, o, t → j (second letter)
Vowels Count: 0
d) Least, Magic, Never
- Least → a, e, l, s, t → e (second letter)
- Magic → a, c, g, i, m → c (second letter)
- Never → e, e, n, r, v → e (second letter)
Vowels Count: 3 (e, e, e)
e) Phone, Quite, Round
- Phone → e, h, n, o, p → h (second letter)
- Quite → e, i, q, t, u → i (second letter)
- Round → d, n, o, r, u → n (second letter)
Vowels Count: 1 (i)
Conclusion
After evaluating all options, option D (Least, Magic, Never) has the maximum number of vowels with a total of 3 vowels. Thus, the correct answer is indeed option D.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.A certain number of people were seated in 3 different rows facing the north. The rows were numbered from 1 to 3 such that the last row was numbered 3, the row exactly in front of it was numbered 2 and so on. The seats were numbered 1, 2, 3 and so on in ascending order from left to right. All rows did not necessarily have the same number of seats. The information about only few persons is known. B's seat number was same as his row number. There were two seats between B and F. Number of seats in row 3 was half that in row 2. Two seats were between F and C. A, B and G had same seat number. G was seated just behind of B. The maximum number of seats could be eight in any row. E was seated at the third position from extreme ends. Three seats were between A and E. One seat was between A and D.How many seats were there in row 1?- a)8
- b)6
- c)5
- d)4
- e)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
A certain number of people were seated in 3 different rows facing the north. The rows were numbered from 1 to 3 such that the last row was numbered 3, the row exactly in front of it was numbered 2 and so on. The seats were numbered 1, 2, 3 and so on in ascending order from left to right. All rows did not necessarily have the same number of seats. The information about only few persons is known. B's seat number was same as his row number. There were two seats between B and F. Number of seats in row 3 was half that in row 2. Two seats were between F and C. A, B and G had same seat number. G was seated just behind of B. The maximum number of seats could be eight in any row. E was seated at the third position from extreme ends. Three seats were between A and E. One seat was between A and D.
How many seats were there in row 1?
a)
8
b)
6
c)
5
d)
4
e)
3
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
B's seat number was same as his row number. Two seats were between B and F.
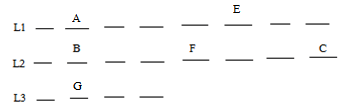
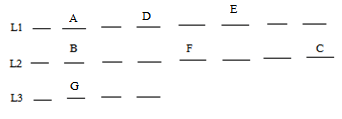
Two seats were between F and C. The maximum number of seats can be eight in any row. Thus, two conditions are there –
A, B and G had same seat number. G was seated just behind B.
E was seated at the third position from one of the extreme ends. Three seats were between A and E.

Number of seats in row 3 were half of the number of seats in row 2. The maximum number of seats can be eight in any row.
In (i), if L3 had seven seats, L2 had 14 seats but the maximum number of seats can be eight in any row. So, condition (i) not applicable according to the given condition. This condition will be applicable only in case (ii).
Thus,
L1 = 8 seats
L2 = 8 seats
L3 = 4 seats

One seat was between A and D. Thus, the final arrangement was:

Below questions consist of numbers in three rows. Results from each row can be obtained by applying certain rules given below. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Condition:I. If an even number is followed by a prime number, then the product of the tenth digit of the numbers is taken.II. If an odd (non-prime) is followed by an even number, then the sum of numbers is taken.III. If a prime number is followed by a perfect square number, then the difference between the numbers is taken.IV. If a prime number is followed by a composite number, then divide the second number by the first number.V. If an even number is followed by a perfect cube number, then the product of unit digits of numbers is taken.If more than one condition is applied then only one condition is applied as per the order.Q. What is the sum of the resultant of all three rows?7 25 2738 31 2413 39 49- a)148
- b)122
- c)121
- d)135
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Below questions consist of numbers in three rows. Results from each row can be obtained by applying certain rules given below. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Condition:
I. If an even number is followed by a prime number, then the product of the tenth digit of the numbers is taken.
II. If an odd (non-prime) is followed by an even number, then the sum of numbers is taken.
III. If a prime number is followed by a perfect square number, then the difference between the numbers is taken.
IV. If a prime number is followed by a composite number, then divide the second number by the first number.
V. If an even number is followed by a perfect cube number, then the product of unit digits of numbers is taken.
If more than one condition is applied then only one condition is applied as per the order.
Q. What is the sum of the resultant of all three rows?
7 25 27
38 31 24
13 39 49
a)
148
b)
122
c)
121
d)
135
e)
None of these
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
7 25 27
From condition III: (25 – 7) = 18
From condition V: (8 x 7) = 56
38 31 24
From condition I: (3 x 3) = 9
From condition II: (9 + 24) = 33
13 39 49
From condition IV: 39/13 = 3
From condition III: (49 – 3) = 46
Required number = (56 + 33 + 46) = 135
Statement: “Good news for all, Vikalp is available and every passenger will get reserve seats. Waiting status will be omitted from reservation chart” quoted by Railways Ministry. Spokesperson of railways has said if confirm seat is not available in desired train, option for confirm seat in other train will be given at the time of reservation.Which of the following can be assumed from the given statement?(I) Commuters would have faced issues regarding confirm seats in railways.(II) Fairs of reserved seats will be increased by Railways department.(III) There will be increase in number of persons travelling through railways.- a)Only I and III
- b)Only I and II
- c)Only II and III
- d)All can be assumed
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement: “Good news for all, Vikalp is available and every passenger will get reserve seats. Waiting status will be omitted from reservation chart” quoted by Railways Ministry. Spokesperson of railways has said if confirm seat is not available in desired train, option for confirm seat in other train will be given at the time of reservation.
Which of the following can be assumed from the given statement?
(I) Commuters would have faced issues regarding confirm seats in railways.
(II) Fairs of reserved seats will be increased by Railways department.
(III) There will be increase in number of persons travelling through railways.
a)
Only I and III
b)
Only I and II
c)
Only II and III
d)
All can be assumed
e)
None of these

|
Sanjana Nambiar answered |
Assumptions from the given statement:
I. Commuters would have faced issues regarding confirm seats in railways.
The statement mentions that every passenger will get reserved seats and waiting status will be omitted from the reservation chart. This implies that there may have been issues in the past regarding the availability of confirmed seats in railways. If there were no issues, there would be no need for the railways to make such an announcement. Therefore, assumption I can be considered valid.
II. Fares of reserved seats will be increased by Railways department.
The given statement does not provide any information regarding an increase in fares of reserved seats. It only states that Vikalp (alternative) options will be provided if confirm seats are not available in the desired train. Therefore, assumption II cannot be assumed from the given statement.
III. There will be an increase in the number of persons traveling through railways.
The statement does not directly mention any increase in the number of persons traveling through railways. It only states that every passenger will get reserved seats and waiting status will be omitted from the reservation chart. This could mean that the railways are trying to improve the current reservation system to ensure that all passengers get confirmed seats. It does not necessarily imply an increase in the number of passengers. Therefore, assumption III cannot be assumed from the given statement.
Conclusion:
From the given statement, assumption I can be assumed as valid, assumption II cannot be assumed, and assumption III cannot be assumed. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - all assumptions can be assumed from the given statement.
I. Commuters would have faced issues regarding confirm seats in railways.
The statement mentions that every passenger will get reserved seats and waiting status will be omitted from the reservation chart. This implies that there may have been issues in the past regarding the availability of confirmed seats in railways. If there were no issues, there would be no need for the railways to make such an announcement. Therefore, assumption I can be considered valid.
II. Fares of reserved seats will be increased by Railways department.
The given statement does not provide any information regarding an increase in fares of reserved seats. It only states that Vikalp (alternative) options will be provided if confirm seats are not available in the desired train. Therefore, assumption II cannot be assumed from the given statement.
III. There will be an increase in the number of persons traveling through railways.
The statement does not directly mention any increase in the number of persons traveling through railways. It only states that every passenger will get reserved seats and waiting status will be omitted from the reservation chart. This could mean that the railways are trying to improve the current reservation system to ensure that all passengers get confirmed seats. It does not necessarily imply an increase in the number of passengers. Therefore, assumption III cannot be assumed from the given statement.
Conclusion:
From the given statement, assumption I can be assumed as valid, assumption II cannot be assumed, and assumption III cannot be assumed. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - all assumptions can be assumed from the given statement.
Study the following information carefully and answer the Questions based on it:Eight friends – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H were born on in March, June, September and December on either 3rd or 8th (all born on different dates). The ones who were born in a month having 30 days like different fruits – Banana, Apple, Mango and Litchi not necessarily in the same order. The people who were born in a month having 31 days like different colors – Red, Yellow, Blue and Green not necessarily in the same order. Two people born in one month but different date.E was born in June. One person was born between E and D. D does not like any color. B likes red color. The number of people born before A is the same as the number of people born after D. No person was born between the ones who like yellow color and mango. The one who likes yellow color was not born on 8th of any month. No person was born between E and one who likes litchi. One person was born between B and one who likes Banana. A does not like Banana. The ones who like apple and banana were born either on same date or in same month. One person was born between A and H. F does not like any fruit. No person was born between C and one who likes blue color. H does not like fruits. There are same numbers of persons were born between the ones who like green color and apple and who like blue and mango.C likes which of the following fruit/Color?- a)Yellow
- b)Mango
- c)Litchi
- d)Blue
- e)Banana
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the Questions based on it:
Eight friends – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H were born on in March, June, September and December on either 3rd or 8th (all born on different dates). The ones who were born in a month having 30 days like different fruits – Banana, Apple, Mango and Litchi not necessarily in the same order. The people who were born in a month having 31 days like different colors – Red, Yellow, Blue and Green not necessarily in the same order. Two people born in one month but different date.
E was born in June. One person was born between E and D. D does not like any color. B likes red color. The number of people born before A is the same as the number of people born after D. No person was born between the ones who like yellow color and mango. The one who likes yellow color was not born on 8th of any month. No person was born between E and one who likes litchi. One person was born between B and one who likes Banana. A does not like Banana. The ones who like apple and banana were born either on same date or in same month. One person was born between A and H. F does not like any fruit. No person was born between C and one who likes blue color. H does not like fruits. There are same numbers of persons were born between the ones who like green color and apple and who like blue and mango.
C likes which of the following fruit/Color?
a)
Yellow
b)
Mango
c)
Litchi
d)
Blue
e)
Banana
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
(1) E was born in June.
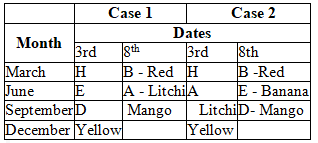
(2) 1 person was born between E and D.
(3) D does not like any color.
So, D born is September.
(4) The number of people born before A is the same as the number of people born after D.
We have two cases:-

(5) No person was born between E and one who likes litchi.
(6) A does not like Banana.
(7) One person was born between A and H.
(8) H does not like fruits.

(9) No person was born between the ones who like yellow color and mango. The one who likes yellow color was not born on 8th of any month.
(10) B likes red color.
(11) One person was born between B and one who likes Banana.

As we know from the statement (6), the case 1 gets cancelled.
(12) The ones who like apple and banana were born either on same date or in same month.
The only possible is the one who likes apple is A and born in June with the one who likes banana.
(13) No person was born between C and one who likes blue color.
(14) There are same numbers of persons were born between the ones who like green color and apple and who like blue and mango.
(15) F does not like any fruit.
Our final arrangement is given below:-

We can see that C likes yellow Color.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.If positions of Z and C are interchanged, then how far will Z be from W when counted from the left of W?- a)105 m
- b)90 m
- c)115 m
- d)86 m
- e)35 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.
Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.
If positions of Z and C are interchanged, then how far will Z be from W when counted from the left of W?
a)
105 m
b)
90 m
c)
115 m
d)
86 m
e)
35 m
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Circumference of circle is 390 m and persons are sitting in consecutive multiples of 5.
So, first find the total number of persons sitting.
Total number of persons = 12 (5 + 10 + 15 + 20 + 25 + 30 + 35 + 40 + 45 + 50 + 55 + 60 = 390 m)
If we take minimum distance 10, 15 then sum is not equal to 390 m and all the persons are sitting in clockwise direction.

After arranging in alphabetical order,

Distance between W and Z = 15 + 20 + 25 + 30 = 90 m
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.Eight persons - P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W - are sitting in a row facing north, but not necessary in the same order. No two successive members are sitting in the alphabetical order. For example, P does not sit with Q. Similarly, Q does not sit with R, and so on.They all play different sports viz. Cricket, Boxing, Squash, Hockey, Tennis, Archery, Polo and Golf, but not necessarily in the same order.U is the immediate neighbour of Q and P. The number of persons sitting between S and R, who plays Boxing, is the same as that sitting between V and W. S is sitting at an extreme end of the row. No one is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Cricket. W, who plays Polo, is sitting fifth from the right end and he is an immediate neighbour of neither V nor T. T and V, who plays Golf, are immediate neighbours of each other. Two persons are sitting between the one who plays Squash and P. The one who plays Boxing is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Squash, but he is neither Q nor S. The one who plays Tennis is to the immediate left of the one who plays Hockey. V is sitting to the right of P, but not immediately.What is the position of T with respect to the one who plays Hockey?- a)Immediate right
- b)Second to the right
- c)Second to the left
- d)Third to the right
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.
Eight persons - P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W - are sitting in a row facing north, but not necessary in the same order. No two successive members are sitting in the alphabetical order. For example, P does not sit with Q. Similarly, Q does not sit with R, and so on.
They all play different sports viz. Cricket, Boxing, Squash, Hockey, Tennis, Archery, Polo and Golf, but not necessarily in the same order.
U is the immediate neighbour of Q and P. The number of persons sitting between S and R, who plays Boxing, is the same as that sitting between V and W. S is sitting at an extreme end of the row. No one is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Cricket. W, who plays Polo, is sitting fifth from the right end and he is an immediate neighbour of neither V nor T. T and V, who plays Golf, are immediate neighbours of each other. Two persons are sitting between the one who plays Squash and P. The one who plays Boxing is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Squash, but he is neither Q nor S. The one who plays Tennis is to the immediate left of the one who plays Hockey. V is sitting to the right of P, but not immediately.
What is the position of T with respect to the one who plays Hockey?
a)
Immediate right
b)
Second to the right
c)
Second to the left
d)
Third to the right
e)
None of these
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
S is sitting at an extreme end of the row. No one is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Cricket. W, who plays Polo, is sitting fifth from the right end and he is an immediate neighbour of neither V nor T.

U is the immediate neighbour of Q and P. T and V, who plays Golf, are immediate neighbours of each other. Hence, possibility (I) not OK.

The number of persons sitting between S and R, who plays Boxing, is the same as that sitting between V and W. Two persons are sitting between the one who plays Squash and P.

The one who plays Boxing is sitting to the immediate left of the one who plays Squash, but he is neither Q nor S. The one who plays Tennis is to the immediate left of the one who plays Hockey. V is sitting to the right of P, but not immediately.

Statement: The annual requirement of blood in our country is 6 million units whereas the generation is only 3.5 million units per annum at present.Courses of action:I. Blood donors should be attracted by telling them how the act of donating blood would improve their health.II. Blood donors should be attracted by providing them monetary incentives.III. More and more private blood banks should be encouraged.- a)Only II follows
- b)Only III follows
- c)Either I or III follows
- d)Only I follows
- e)I and II follow
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement: The annual requirement of blood in our country is 6 million units whereas the generation is only 3.5 million units per annum at present.
Courses of action:
I. Blood donors should be attracted by telling them how the act of donating blood would improve their health.
II. Blood donors should be attracted by providing them monetary incentives.
III. More and more private blood banks should be encouraged.
a)
Only II follows
b)
Only III follows
c)
Either I or III follows
d)
Only I follows
e)
I and II follow
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
Whatever is being told is reliable. On learning this, the blood donors will get attracted by the win-win proposition, thus simultaneously meeting the blood requirement to a large extent. Statement II is not a practical course of action. Statement III is not an immediate course of action as blood banks can be created only after the sufficient blood donors are available.
Statement: The Union Cabinet approved the amendment of the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Bill, 2020. The Bill seeks to provide resolution for disputed tax cases that involve Rs.9.32 lakh crore.Assumptions:I. The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.II. It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).- a)If only assumption I is implicit
- b)If only assumption II is implicit
- c)If either I or II is implicit
- d)If neither I nor II is implicit
- e)If both I and II are implicit
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement: The Union Cabinet approved the amendment of the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Bill, 2020. The Bill seeks to provide resolution for disputed tax cases that involve Rs.9.32 lakh crore.
Assumptions:
I. The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.
II. It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).
a)
If only assumption I is implicit
b)
If only assumption II is implicit
c)
If either I or II is implicit
d)
If neither I nor II is implicit
e)
If both I and II are implicit

|
Pankaj Chakraborty answered |
Statement: The Union Cabinet approved the amendment of the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Bill, 2020. The Bill seeks to provide resolution for disputed tax cases that involve Rs.9.32 lakh crore.
Assumptions:
I. The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.
II. It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).
Explanation:
The Union Cabinet's approval of the amendment to the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Bill, 2020 indicates that the government is taking steps to address the issue of disputed tax cases involving a significant amount of money. Let's analyze the given assumptions:
Assumption I: The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.
The statement does not explicitly mention whether the amendment will cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals. Therefore, assumption I cannot be considered implicit based on the given information.
Assumption II: It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).
The statement mentions that the amendment aims to provide resolution for disputed tax cases. It is reasonable to assume that tax disputes pending at different levels, including commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs), and the Supreme Court (SC), will be covered under the amendment. Hence, assumption II is implicit based on the given information.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, we can conclude that assumption II is implicit, but assumption I is not implicit. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'E' - If both I and II are implicit.
Assumptions:
I. The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.
II. It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).
Explanation:
The Union Cabinet's approval of the amendment to the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Bill, 2020 indicates that the government is taking steps to address the issue of disputed tax cases involving a significant amount of money. Let's analyze the given assumptions:
Assumption I: The amendment will widen the scope to cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals and reduces the litigation related to direct taxes.
The statement does not explicitly mention whether the amendment will cover litigation pending in various debt recovery tribunals. Therefore, assumption I cannot be considered implicit based on the given information.
Assumption II: It will cover tax disputes pending at the level of commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs) and the Supreme Court (SC).
The statement mentions that the amendment aims to provide resolution for disputed tax cases. It is reasonable to assume that tax disputes pending at different levels, including commissioner (appeals), Income Tax Appellate Tribunals (ITAT), high courts (HCs), and the Supreme Court (SC), will be covered under the amendment. Hence, assumption II is implicit based on the given information.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, we can conclude that assumption II is implicit, but assumption I is not implicit. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'E' - If both I and II are implicit.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.There are eight persons L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S sitting along two concentric squares. All the persons are sitting exactly at the corners. Those who are sitting in the outer square are facing away from the centre and those who are sitting in the inner square are facing towards the centre. There are four pairs and each pair has a male and a female. Every pair is wearing a different coloured T-shirt such as Red, Yellow, Green and Black, whereas within the pair they are wearing same coloured T-shirts. Each pair is facing away from each other, i.e. they are sitting at same corners of different squares. Females are sitting in the inner square and males are sitting in the outer square. N is wearing a Green coloured T-shirt and facing outwards. S is wearing either a Green or a Black coloured T-shirt. An immediate neighbour of O is wearing a Red coloured T-shirt. Only Q sits between L and N and is wearing a Yellow coloured T-shirt. R and O are in one pair. P is not wearing a yellow coloured T-shirt and is not to the immediate left of M. The one who sits to the immediate right of R is not wearing a Green coloured T-shirt.Who sits to the immediate right of R?- a)O
- b)S
- c)Q
- d)L
- e)M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question.
There are eight persons L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S sitting along two concentric squares. All the persons are sitting exactly at the corners. Those who are sitting in the outer square are facing away from the centre and those who are sitting in the inner square are facing towards the centre. There are four pairs and each pair has a male and a female. Every pair is wearing a different coloured T-shirt such as Red, Yellow, Green and Black, whereas within the pair they are wearing same coloured T-shirts. Each pair is facing away from each other, i.e. they are sitting at same corners of different squares. Females are sitting in the inner square and males are sitting in the outer square. N is wearing a Green coloured T-shirt and facing outwards. S is wearing either a Green or a Black coloured T-shirt. An immediate neighbour of O is wearing a Red coloured T-shirt. Only Q sits between L and N and is wearing a Yellow coloured T-shirt. R and O are in one pair. P is not wearing a yellow coloured T-shirt and is not to the immediate left of M. The one who sits to the immediate right of R is not wearing a Green coloured T-shirt.
Who sits to the immediate right of R?
a)
O
b)
S
c)
Q
d)
L
e)
M
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
N is wearing a Green coloured T-shirt and facing outwards.

Only Q sits between L and N and is wearing a Yellow coloured T-shirt. Two possibilities 1 and 2 are there:

R and O are in one pair. An immediate neighbour of O is wearing a Red coloured T-shirt. S is wearing either a Green or a Black coloured T-shirt. Four possibilities are there: 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b.


The one who sits to the immediate right of R is not wearing a Green coloured T-shirt. Possibilities 1b and 2a are eliminated and possibilities 1a and 2b will be left.

P is not wearing a yellow coloured T-shirt and is not to the immediate left of M. Only possibility 1a will be left.

L sits to the immediate right of R.
Directions: Each question below contains a statement followed by Quantity I and Quantity II. You have to study the information along with the question and compare the value derived from Quantity I and Quantity II, then anwer:Quantity I > Quantity IIQuantity I < quantity="" />Quantity I ≤ Quantity IIQuantity I ≥ Quantity IIQuantity I = Quantity II or relationship cannot be established between Quantity I and Quantity IIQuantity I: Ram can do a piece of work in 20 days. If the efficiency of Ram is 66.67% of the efficiency of Mohan and the efficiency of Mohan is 25% less than the efficiency of Prakash then how long Prakash will take to do the same piece of work?Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours then how many days will he take to type a book of 1320 pages? [Assume the person works continuously for 24hrs/day]- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
- e)5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Each question below contains a statement followed by Quantity I and Quantity II. You have to study the information along with the question and compare the value derived from Quantity I and Quantity II, then anwer:
Quantity I > Quantity II
Quantity I < quantity="" />
Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II or relationship cannot be established between Quantity I and Quantity II
Quantity I: Ram can do a piece of work in 20 days. If the efficiency of Ram is 66.67% of the efficiency of Mohan and the efficiency of Mohan is 25% less than the efficiency of Prakash then how long Prakash will take to do the same piece of work?
Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours then how many days will he take to type a book of 1320 pages? [Assume the person works continuously for 24hrs/day]
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
e)
5

|
Anu Bose answered |
Quantity I: Ram can do a piece of work in 20 days. If the efficiency of Ram is 66.67% of the efficiency of Mohan and the efficiency of Mohan is 25% less than the efficiency of Prakash, then how long will Prakash take to do the same piece of work?
Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours. How many days will he take to type a book of 1320 pages? [Assume the person works continuously for 24 hours/day]
To solve this problem, we need to calculate the efficiency of Ram, Mohan, and Prakash and then find the time taken by Prakash to complete the work.
Let's analyze Quantity I first:
Quantity I: Ram can do a piece of work in 20 days.
This means that Ram's work rate is 1/20 of the work per day.
Now, let's find the efficiency of Mohan:
Ram's efficiency is 66.67% of Mohan's efficiency.
So, Mohan's efficiency is 100% (100/66.67) times Ram's efficiency.
Therefore, Mohan's efficiency is (100/66.67) * (1/20) = 0.075 of the work per day.
Next, let's find the efficiency of Prakash:
Mohan's efficiency is 25% less than Prakash's efficiency.
So, Prakash's efficiency is 100% (100/75) times Mohan's efficiency.
Therefore, Prakash's efficiency is (100/75) * 0.075 = 0.1 of the work per day.
To find the time taken by Prakash to do the same piece of work:
Prakash's work rate is 0.1 of the work per day.
So, Prakash will take 1 / 0.1 = 10 days to do the same piece of work.
Now, let's analyze Quantity II:
Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours.
This means that the person's work rate is 50/10 = 5 pages per hour.
To find the time taken by the person to type a book of 1320 pages:
The person's work rate is 5 pages per hour.
So, the person will take 1320 / 5 = 264 hours to type the book.
Since we assumed that the person works continuously for 24 hours/day, the person will take 264 / 24 = 11 days to type the book.
Comparing Quantity I and Quantity II:
Quantity I = 10 days
Quantity II = 11 days
Therefore, Quantity I < quantity="" />
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' (Quantity I > Quantity II).
Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours. How many days will he take to type a book of 1320 pages? [Assume the person works continuously for 24 hours/day]
To solve this problem, we need to calculate the efficiency of Ram, Mohan, and Prakash and then find the time taken by Prakash to complete the work.
Let's analyze Quantity I first:
Quantity I: Ram can do a piece of work in 20 days.
This means that Ram's work rate is 1/20 of the work per day.
Now, let's find the efficiency of Mohan:
Ram's efficiency is 66.67% of Mohan's efficiency.
So, Mohan's efficiency is 100% (100/66.67) times Ram's efficiency.
Therefore, Mohan's efficiency is (100/66.67) * (1/20) = 0.075 of the work per day.
Next, let's find the efficiency of Prakash:
Mohan's efficiency is 25% less than Prakash's efficiency.
So, Prakash's efficiency is 100% (100/75) times Mohan's efficiency.
Therefore, Prakash's efficiency is (100/75) * 0.075 = 0.1 of the work per day.
To find the time taken by Prakash to do the same piece of work:
Prakash's work rate is 0.1 of the work per day.
So, Prakash will take 1 / 0.1 = 10 days to do the same piece of work.
Now, let's analyze Quantity II:
Quantity II: A person can type 50 pages in 10 hours.
This means that the person's work rate is 50/10 = 5 pages per hour.
To find the time taken by the person to type a book of 1320 pages:
The person's work rate is 5 pages per hour.
So, the person will take 1320 / 5 = 264 hours to type the book.
Since we assumed that the person works continuously for 24 hours/day, the person will take 264 / 24 = 11 days to type the book.
Comparing Quantity I and Quantity II:
Quantity I = 10 days
Quantity II = 11 days
Therefore, Quantity I < quantity="" />
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' (Quantity I > Quantity II).
Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.Q. According to the passage, which of the following is the reason behind other countries' callousing India by describing it as major power?- a)To increase their prestige at global level
- b)To invest in India's big companies
- c)To be in business of military weapons and equipment
- d)To gain more support in relief operations from India
- e)To sell their credible hard power to India
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage. Some words may be highlighted for your attention. Read carefully.
There is a lot of talk these days, not so much among government circles as among the ‘strategic community’, about India being a major or even global power, with the capability, even responsibility, to play an ‘important role’ on the world stage as a balancing power between major powers and as a ‘security provider’ to others. We need to temper this rhetoric, be more realistic and less ambitious. The dividing line between national pride and national ego can be thin. India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was convinced that India was bound to play an increasing and beneficent part in world affairs. He had developed a zeal for diplomacy that was not backed by the needed military and economic hard power. He was banking on our moral high ground because he and the nation were proud of the non-violent manner in which we had achieved our independence. As early as 1948, he declared: “India had already become the fourth or fifth most influential country in the United Nations.” This was a strange claim; just a year earlier, we were forced to withdraw our candidature for the Security Council when Ukraine, which was contesting the same seat, secured more votes than us in seven successive ballots in a single day. We have been afflicted with this malady ever since.
Over the decades, no doubt influenced by our experience in the early years in Kashmir and China, the idealist strain has diminished and eventually disappeared altogether; national interest alone would guide our policy. This is not necessarily an undesirable thing. The only caveat is that we have to be realists and check the inexplicable urge to play a big role in international relations. Leaders everywhere look for a role for themselves. They believe, perhaps genuinely, that an increased prestige for themselves will translate into more votes domestically and ipso facto bring benefits to their countries. The driving factor is prestige, status. Often the leaders do not realize that playing a role carries with it responsibilities which we may not be able or keen to accept but which we might be dragged into. These responsibilities would be defined by others and would invariably involve us into tasks and areas which we may not wish to get involved in. Recent events do not lend support to that view and the government was right in not paying heed to that rhetoric. India is without doubt the pre-eminent power in South Asia. However, given our firm commitment not to use force and to non-interference in internal affairs in other states, our neighbors do not feel threatened by us. We did make a huge effort in Sri Lanka to bring peace and stability to that country and we did so at the request of its lawful government. The venture ended in failure and eventually cost the life of a former prime minister. Small-scale interventions in the Maldives and the Seychelles in the 1980s were successful in stabilizing legitimate governments. To that extent, India was able to play a positive role in the region. In these examples, the motivating factor was not prestige, there were domestic factors at play. The resulting increase in our prestige was incidental. If intervention does not succeed, as in Sri Lanka, the ensuing loss of prestige more than offsets whatever prestige we might have gained in the other operations. Often, when a country gets involved in what might be assessed as a low cost foreign adventure, it remains bogged down even when the going gets tough precisely because it apprehends loss of face or prestige. It is easy to get in but difficult to get out.
Apart from protecting our people from adverse external factors and interventions, the principal criterion in the conduct of foreign policy for India ought to be lifting the poor from poverty. Whatever brings concrete benefits to our people should be encouraged. A mere wish to be praised as a global or even regional power should not be allowed to guide the policy. When other countries flatter us by describing us as a major power, it is invariably because they want to rope us into some schemes of their own. It is best not to get too entangled in the chess moves of other countries. The principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive military hardware to us. Our single minded focus should be on economic development. Without the necessary economic strength, we cannot strengthen our military. We do need a strong military but for that we need undisturbed double digit economic growth for a generation. Prime Minister Vajpayee’s seasoned adviser Brajesh Mishra’s advice was sound: do not provoke nor get provoked for two decades, concentrate on building the economy. Since we do have to think critically about allocating our scarce resources among alternative uses, and since we are a democratic polity with a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society with a large number of poor, we have to think more than twice about defense spending. Even when at some stage we acquire credible hard power, we must not allow ourselves to be seduced by the flattering and mostly insincere talk of others about India playing a global role. Other countries express their admiration, not so much for our economy or military, but for the orderly manner in which power is transferred from one party to another and for the largely harmonious and peaceful, integrated manner in which people of different faiths live together. An internally divided India cannot play any role externally. The ‘strategic community’ should concentrate on reinforcing this real soft power of India which is what the rest of the world appreciates and not lose time and resources in peripheral ventures that bring no lasting benefit.
Q. According to the passage, which of the following is the reason behind other countries' callousing India by describing it as major power?
a)
To increase their prestige at global level
b)
To invest in India's big companies
c)
To be in business of military weapons and equipment
d)
To gain more support in relief operations from India
e)
To sell their credible hard power to India
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
The word 'callousing' means showing or having an insensitive and cruel disregard for others. It is given that other countries deceive India by describing us as a major power. They do so because the principal interest of most of them is to sell very expensive militCry hardware to India. That is to be in the business of military weapons and equipment.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
An ______ is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country.- a)FDI
- b)Forex
- c)CRR
- d)SEZ
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An ______ is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country.
a)
FDI
b)
Forex
c)
CRR
d)
SEZ
e)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Foreign direct investment(FDI):
Foreign direct investment(FDI) refers to a situation where a foreign entity obtains ownership or control rights over the shares of a company in a country or establishes a company in that country.
Foreign direct investment(FDI) is not only an inflow of capital but also an inflow of technology, knowledge, skills.
It is the main source of non-debt financial resources for the economic development of a country.
Foreign direct investment tends to take place in economies with growth prospects and skilled labor.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
In the given questions, few words have been highlighted. One of these words might either be wrongly spelt or inappropriate in usage. You must read the sentences carefully and choose the incorrect word as your answer.Never mind conservative societies – even in the lateral west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power.- a)Lateral
- b)Conservative
- c)Especially
- d)Applied
- e)All correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given questions, few words have been highlighted. One of these words might either be wrongly spelt or inappropriate in usage. You must read the sentences carefully and choose the incorrect word as your answer.
Never mind conservative societies – even in the lateral west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power.
a)
Lateral
b)
Conservative
c)
Especially
d)
Applied
e)
All correct

|
Mainak Verma answered |
Incorrect Word: Lateral
Explanation:
The word "lateral" is incorrectly spelt in the given sentence. The correct spelling of this word should be "latteral", which refers to something situated or extending sideways. However, in the context of the sentence, the word "lateral" does not fit and seems out of place.
Correction:
The correct word to use in this sentence would be "latter" instead of "lateral". The corrected sentence would be as follows:
"Never mind conservative societies – even in the latter west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power."
This correction makes the sentence grammatically correct and conveys the intended meaning more accurately. The adjective "latter" means the second of two things mentioned, so it fits appropriately in the sentence to refer to the western societies mentioned earlier.
Summary:
The incorrect word in the sentence is "lateral", which should be corrected to "latter". The corrected sentence would read: "Never mind conservative societies – even in the latter west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power."
Explanation:
The word "lateral" is incorrectly spelt in the given sentence. The correct spelling of this word should be "latteral", which refers to something situated or extending sideways. However, in the context of the sentence, the word "lateral" does not fit and seems out of place.
Correction:
The correct word to use in this sentence would be "latter" instead of "lateral". The corrected sentence would be as follows:
"Never mind conservative societies – even in the latter west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power."
This correction makes the sentence grammatically correct and conveys the intended meaning more accurately. The adjective "latter" means the second of two things mentioned, so it fits appropriately in the sentence to refer to the western societies mentioned earlier.
Summary:
The incorrect word in the sentence is "lateral", which should be corrected to "latter". The corrected sentence would read: "Never mind conservative societies – even in the latter west different moral standards are applied to men and women, especially those in power."
Direction: In the question below, a passage is given followed by three assumptions numbered I ,II and III. An assumption is something supposed or taken for granted. You have to consider the passage and the following assumptions and decide which of the assumptions is implicit in the passage.Passage:Most flags contain primary colours, which are red, blue, green and some countries also use yellow or secondary colors. Gold is also used in many flags as the colour is associated with the sun and is considered as colour of kings as well.Assumptions:I: Flags are available in all sizes.II: Flags are available in many colours.III: Colours can have different meanings in different cultures.- a)Only I
- b)Only II
- c)Only III
- d)All except III
- e)All follows
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the question below, a passage is given followed by three assumptions numbered I ,II and III. An assumption is something supposed or taken for granted. You have to consider the passage and the following assumptions and decide which of the assumptions is implicit in the passage.
Passage:
Most flags contain primary colours, which are red, blue, green and some countries also use yellow or secondary colors. Gold is also used in many flags as the colour is associated with the sun and is considered as colour of kings as well.
Assumptions:
I: Flags are available in all sizes.
II: Flags are available in many colours.
III: Colours can have different meanings in different cultures.
a)
Only I
b)
Only II
c)
Only III
d)
All except III
e)
All follows
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
From the above passage, we get to know many colour related facts with respect to flags.
The above information helps us to assume that colours can have different meanings in different cultures.
The different countries using different colours in their flag have altogether different significance.
Thus, assumption III is implicit.
The information given above is not sufficient for us to assume the size of the flags.
Thus, assumption I is not implicit.
Similarly, assumption II is the restatement of the fact which is already mentioned in the passage.
The very first line of the passage states that flags are present in different colours.
Thus, assumption II is not implicit.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Certain number of persons are sitting around the two square tables facing the centre of the table. One square table is inscribed inside another table. The area of inner table is 576cm2. The perimeter of outer table is 176cm. Maximum three persons sit around each side. The distance between any two adjacent persons on any side around outer table is either 11cm or 22cm. The distance between any two adjacent persons on any side around inner table is either 6cm or 12cm. Persons can sit on each side or corner. Only two persons sit at the corners of inner table. Three persons sit on the corners of outer table. Distance between any two persons are calculated only around the perimeter of the square. No seat is vacant. Number of persons around inner square is 2 more than number of persons around outer square.Immediate neighbours of B are 6cm away from him. W is adjacent to both the persons who sits at the corners. Z is second person to the left of U, who is not adjacent to P. One person sits in the middle of each side of outer square. T sits opposite to Y around the same table. R is immediate left of X, who is not opposite to anyone around inner square.K is second person to the left of S in outer square. Y is 18cm to the right of B who sits in the middle of the side. Z and U sit in the middle of one of the sides. V and P sit opposite to each other. R and X sit on the same side. Y is second person to the left of G, who sits at one of the corners. V sits nearest and opposite to G’s seat. W and B are opposite to each other around the same table. P is 55 cm to the right of Q. V is third person to the left of Q. Z and V are not adjacent to each other. No one sits between W and G when counted from the left of W.How many persons sit in the inner arrangement?- a)9
- b)13
- c)11
- d)14
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Certain number of persons are sitting around the two square tables facing the centre of the table. One square table is inscribed inside another table. The area of inner table is 576cm2. The perimeter of outer table is 176cm. Maximum three persons sit around each side. The distance between any two adjacent persons on any side around outer table is either 11cm or 22cm. The distance between any two adjacent persons on any side around inner table is either 6cm or 12cm. Persons can sit on each side or corner. Only two persons sit at the corners of inner table. Three persons sit on the corners of outer table. Distance between any two persons are calculated only around the perimeter of the square. No seat is vacant. Number of persons around inner square is 2 more than number of persons around outer square.
Immediate neighbours of B are 6cm away from him. W is adjacent to both the persons who sits at the corners. Z is second person to the left of U, who is not adjacent to P. One person sits in the middle of each side of outer square. T sits opposite to Y around the same table. R is immediate left of X, who is not opposite to anyone around inner square.
K is second person to the left of S in outer square. Y is 18cm to the right of B who sits in the middle of the side. Z and U sit in the middle of one of the sides. V and P sit opposite to each other. R and X sit on the same side. Y is second person to the left of G, who sits at one of the corners. V sits nearest and opposite to G’s seat. W and B are opposite to each other around the same table. P is 55 cm to the right of Q. V is third person to the left of Q. Z and V are not adjacent to each other. No one sits between W and G when counted from the left of W.
How many persons sit in the inner arrangement?
a)
9
b)
13
c)
11
d)
14
e)
None of these
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
Given that the area of inner table is 576cm2. So, each side must be 24cm. The perimeter of outer table is 176cm. So each side must be 44cm. Y is 18cm to the right of B who sits in the middle of the side. Y is second person to the left of G, who sits at one of the corners. W and B are opposite to each other around the same table.
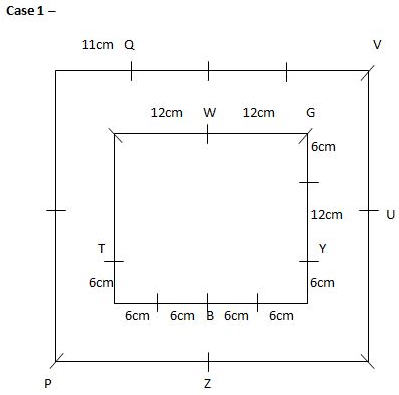
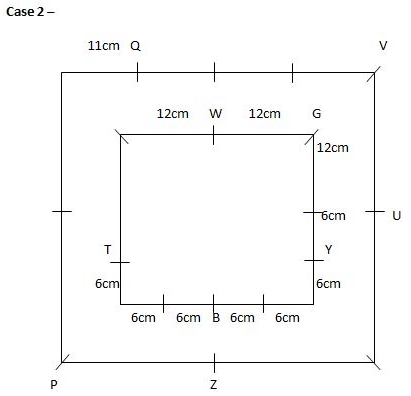
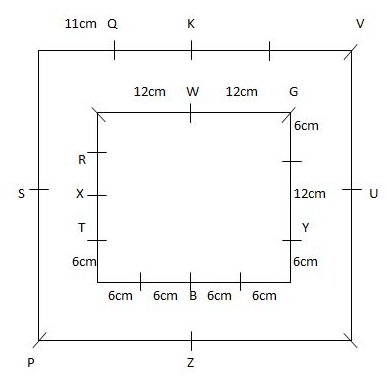
No one sits between W and G when counted from the left of W. Immediate neighbours of B are 6 cm away from him. W is adjacent to the both the persons who sits at the corners.
Inner table:


Given that V and P sit opposite to each other. One person sits in the middle of each side of outer square. V sits nearest and opposite to G’s seat. V is third person to the left of Q. Z and V are not adjacent to each other. It means V and P must be in outer square.
Further P is 55cm to the right of Q. Also, Q must be 11cm away from one of the corners. Also, three persons sit on the side of Q. Z is second person to the left of U, who is not adjacent to P. Z and U sit in the middle of one of the sides.


Number of persons around inner square is 2 more than number of persons around outer square. R is immediate left of X, who is not opposite to anyone around inner square. K is second person to the left of S in outer square. R and X sit on the same side. As number of persons in outer square are 9. So, there must be 11 persons in inner square. Therefore, case 2 will be eliminated. Hence case 1 is the final arrangement.

Directions: Below in question, there are given some statements (I) and (II). These statements may be either independent causes or may be effects of independent causes or of a common cause. One of these statements may be the effect of the other statement. Read both the statements and decide which of the following answer choices correctly depicts the relationship between these two statements.Statement :(I) The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is a flagship program for the children to get Universal Elementary Education (UEE). This program covers the entire country and works in partnership with local and state governments.(II) There is a need to provide an opportunity for improving human capabilities to all children even to those belonging to the socially disadvantaged class (2014) through provision of community -owned quality education in a mission mode.- a)If statement I is the cause and statement II is its effect.
- b)If statement II is the cause and statement I is its effect.
- c)If both the statements I and II are independent causes.
- d)If both the statements I and II are effects of independent causes.
- e)If both the statements I and II are effects of some common cause.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Below in question, there are given some statements (I) and (II). These statements may be either independent causes or may be effects of independent causes or of a common cause. One of these statements may be the effect of the other statement. Read both the statements and decide which of the following answer choices correctly depicts the relationship between these two statements.
Statement :
(I) The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is a flagship program for the children to get Universal Elementary Education (UEE). This program covers the entire country and works in partnership with local and state governments.
(II) There is a need to provide an opportunity for improving human capabilities to all children even to those belonging to the socially disadvantaged class (2014) through provision of community -owned quality education in a mission mode.
a)
If statement I is the cause and statement II is its effect.
b)
If statement II is the cause and statement I is its effect.
c)
If both the statements I and II are independent causes.
d)
If both the statements I and II are effects of independent causes.
e)
If both the statements I and II are effects of some common cause.

|
Pranav Mehta answered |
Explanation:
Statement I:
- The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is a flagship program for Universal Elementary Education (UEE).
- This program covers the entire country and works in partnership with local and state governments.
Statement II:
- There is a need to provide an opportunity for improving human capabilities to all children, including those from socially disadvantaged classes.
- This is done through the provision of community-owned quality education in a mission mode.
Relationship:
- Statement II is the cause and Statement I is its effect.
- The need to provide quality education to all children, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds, leads to the implementation of programs like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan to ensure Universal Elementary Education.
- Therefore, Statement II (the need for improving human capabilities) drives the creation and implementation of programs like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (Statement I).
Statement I:
- The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is a flagship program for Universal Elementary Education (UEE).
- This program covers the entire country and works in partnership with local and state governments.
Statement II:
- There is a need to provide an opportunity for improving human capabilities to all children, including those from socially disadvantaged classes.
- This is done through the provision of community-owned quality education in a mission mode.
Relationship:
- Statement II is the cause and Statement I is its effect.
- The need to provide quality education to all children, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds, leads to the implementation of programs like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan to ensure Universal Elementary Education.
- Therefore, Statement II (the need for improving human capabilities) drives the creation and implementation of programs like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (Statement I).
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below-Six persons have different numbers of boxes also these boxes are placed one above another. Each box contains different number of items. The box which is of Rahul is placed immediately above box F. Only two boxes are placed between the box which contains 23 pens and the box given to Rahul. Total number of items contained by the box which is of Kapil is 10 less than the one which is of Geeta. The total number of items in the box which is of Neha is 2 more than the number of pens contain in box F. The box which contains 23 pens is placed above box F. Box C does not contain 23 pens. The boxes which is of Kusum and Neha is kept below the box containing 23 pens. Only one box is kept between box C and the box containing 20 pens. Box B contains total 39 items. Only one box is placed between box B and the box which is of Santosh. Two boxes are kept between the boxes which is of Kusum and Neha. Box C is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which contains 20 pens is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which is of Kusum contains total 17 items. Box E belongs to Kapil. The box which is placed immediately above box A contains 6 pencils. Box A is of neither Geeta nor Kusum. The box which is of Santosh and box B contain total 56 pens. The box which contains 15 pencils is placed immediately above the box which contains 25 pencils. Box E does not contain 20 pens. Box B is placed below box which is of Santosh. Box D and E contain total 18 pencils. Total number of pens in box F and A is 52.Q. How many pencils are kept in a box placed exactly between Box C and Box B? - a)3
- b)19
- c)15
- d)25
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
Six persons have different numbers of boxes also these boxes are placed one above another. Each box contains different number of items. The box which is of Rahul is placed immediately above box F. Only two boxes are placed between the box which contains 23 pens and the box given to Rahul. Total number of items contained by the box which is of Kapil is 10 less than the one which is of Geeta. The total number of items in the box which is of Neha is 2 more than the number of pens contain in box F. The box which contains 23 pens is placed above box F. Box C does not contain 23 pens. The boxes which is of Kusum and Neha is kept below the box containing 23 pens. Only one box is kept between box C and the box containing 20 pens. Box B contains total 39 items. Only one box is placed between box B and the box which is of Santosh. Two boxes are kept between the boxes which is of Kusum and Neha. Box C is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which contains 20 pens is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which is of Kusum contains total 17 items. Box E belongs to Kapil. The box which is placed immediately above box A contains 6 pencils. Box A is of neither Geeta nor Kusum. The box which is of Santosh and box B contain total 56 pens. The box which contains 15 pencils is placed immediately above the box which contains 25 pencils. Box E does not contain 20 pens. Box B is placed below box which is of Santosh. Box D and E contain total 18 pencils. Total number of pens in box F and A is 52.
Q. How many pencils are kept in a box placed exactly between Box C and Box B?
a)
3
b)
19
c)
15
d)
25
e)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Two boxes are kept between the boxes which is of Kusum and Neha. Box C is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which contains 20 pens is neither of Kusum nor Neha. The box which is of Kusum contains total 17 items. The box which is of Rahul is placed immediately above box F. Only two boxes are placed between the box which contains 23 pens and the box which is of Rahul. The box which contains 23 pens is placed above box F. Box C does not contain 23 pens. The boxes which is of Kusum and Neha is kept below the box containing 23 pens. Only one box is kept between box C and the box containing 20 pens.
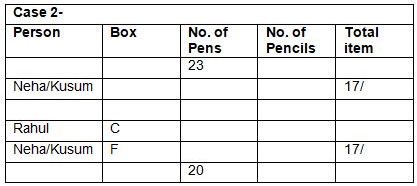
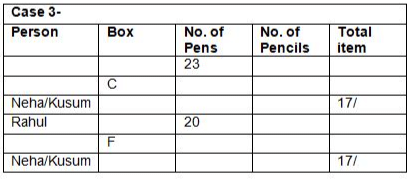

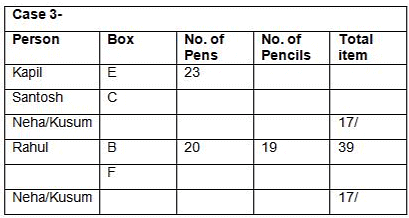
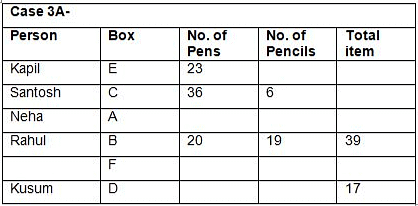
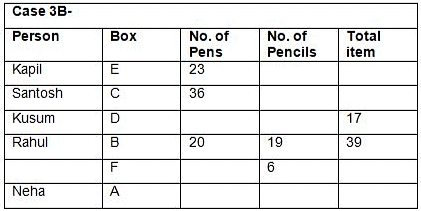
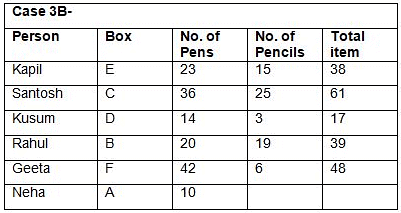
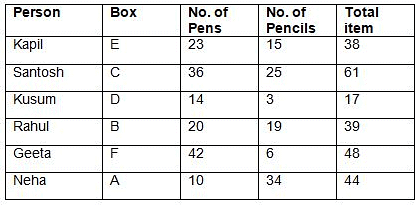




Box B contains total 39 items. Only one box is placed between box B and the box which is of Piya. Box E is of Kapil. Box E does not contain 20 pens. Box B is placed below box which is of Santosh. So, case 1, case 2 and case 4 gets eliminated.

The box which is placed immediately above box A contains 6 pencils. Box A neither belongs to Geeta nor Kusum. So there will be two cases in case 3 (i.e. 3A and 3B). The box which is given to Santosh and box B contain total 56 pens.


The box which contains 15 pencils is placed immediately above the box which contains 25 pencils. So, case 3A gets eliminated. Box D and E contain total 18 pencils. Total number of pens contained by box F and A is 52. Total number of items contained by the box which is of Kapil is 10 less than the one which is of Geeta.

Total number of items contain by the box which is of Neha is 2 more than the number of pens contain by box F. So, the final arrangement is —

Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given belowIn a certain code language,Certain people observes well is coded as %#< />< &®="" /> %$>Facing lot of problem is coded as &@> &^> %®< />Students went for vacation is coded as%*< &@="" /> (?) %#Working better than yesterday is coded as %*> &#< />< %^="" />What is the code for “Faster growing behavior?”- a)&@< %#="" /> &*
- b)%^< &$="" /> &^>
- c)%^> &$< />
- d)&$> %^< />
- e)&®< &@="" /> %^>
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below
In a certain code language,
Certain people observes well is coded as %#< />< &®="" /> %$>
Facing lot of problem is coded as &@> &^> %®< />
Students went for vacation is coded as%*< &@="" /> (?) %#
Working better than yesterday is coded as %*> &#< />< %^="" />
What is the code for “Faster growing behavior?”
a)
&@< %#="" /> &*
b)
%^< &$="" /> &^>
c)
%^> &$< />
d)
&$> %^< />
e)
&®< &@="" /> %^>
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The logic for the first code for each word is based on the place values(as per the alphabetical series) of the first letter of each word
If the place value of the first letter of the word is even, then the first code of the word is “&”
If the place value of the first letter of the word is odd, then the first code of the word is “%”
The logic for the second code for each word is based on the number of consonants in each word:
If the word has one consonant, then the second code of the word is “®”
If the word has two consonants, then the second code of the word is “@”
If the word has three consonants, then the second code of the word is “#”
If the word has four consonants, then the second code of the word is “$”
If the word has five consonants, then the second code of the word is “^”
If the word has six consonants, then the second code of the word is “*”
The logic for the third code for each word is based on the total letters in each word:
If the word has an even number of letters, then the third code of the word is “< />
If the word has an odd number of letters, then the third code of the word is “>”
In the following questions is based on a short argument, a set of statements, or a plan of action. For each question, select the best answer from the given choices.Energy consumption involves release of greenhouse gases resulting in global warming. Hence, it is the contention of the under-developed nations that the economically developed countries must make a higher contribution to funds constituted towards taking measures to fight global warming.Which of the following is an assumption in the above argument?- a)Developed nations are rich and hence can contribute more liberally to funds required for fighting global warming.
- b)Energy consumption varies directly as the economic status of a nation.
- c)Fighting global warming needs huge funds which can be contributed only by the developed nations.
- d)Global warming is an issue of concern to all —especially the economically developed nations.
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following questions is based on a short argument, a set of statements, or a plan of action. For each question, select the best answer from the given choices.
Energy consumption involves release of greenhouse gases resulting in global warming. Hence, it is the contention of the under-developed nations that the economically developed countries must make a higher contribution to funds constituted towards taking measures to fight global warming.
Which of the following is an assumption in the above argument?
a)
Developed nations are rich and hence can contribute more liberally to funds required for fighting global warming.
b)
Energy consumption varies directly as the economic status of a nation.
c)
Fighting global warming needs huge funds which can be contributed only by the developed nations.
d)
Global warming is an issue of concern to all —especially the economically developed nations.
e)
None of these
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
Energy consumption leads to global warming.(b) is the correct assumption because developed nations have more industries and more work power who can consume energy so the energy consumption is directly more in developed countries. (c) only talk of the affordability. (d) is not an assumption.
In a mixture, quantity of milk is 20 L more than water. When 7 L milk and 3 L water is added to the mixture, quantity of water in the mixture becomes 20%. If cost of pure milk is a multiple of 3, but neither more than Rs.48 per L nor less than Rs.42 per L, then what will be the range of cost of initial mixture?- a)From Rs.32 per L to Rs.37 per L
- b)From Rs.35 per L to Rs.40 per L
- c)From Rs.36 per L to Rs.42 per L
- d)From Rs.34 per L to Rs.39 per L
- e)From Rs.30 per L to Rs.36 per L
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a mixture, quantity of milk is 20 L more than water. When 7 L milk and 3 L water is added to the mixture, quantity of water in the mixture becomes 20%. If cost of pure milk is a multiple of 3, but neither more than Rs.48 per L nor less than Rs.42 per L, then what will be the range of cost of initial mixture?
a)
From Rs.32 per L to Rs.37 per L
b)
From Rs.35 per L to Rs.40 per L
c)
From Rs.36 per L to Rs.42 per L
d)
From Rs.34 per L to Rs.39 per L
e)
From Rs.30 per L to Rs.36 per L
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Let initial quantity of water = ‘x’ L
So, initial quantity of milk = (x + 20) L
New quantity of water = (x + 3) L
New quantity of milk = (x + 20 + 7) = (x + 27) L
From the question:
(x + 27)/(x + 3) = 80/20
x + 27 = 4x + 12
x = 5
So, initial quantity of milk = 5 + 20 = 25 L
And initial quantity of water = 5 L
Since, cost of pure milk is a multiple of 3, but neither more than Rs.48 per L nor less than Rs.42 per L.
So, possible costs of pure milk are Rs.42 per L, Rs.45 per L and Rs.48 per L.
If cost of pure milk = Rs.42 per L
So, cost of initial mixture = (25 * 42)/(25 + 5) = Rs.35 per L
If cost of pure milk = Rs.45 per L
So, cost of initial mixture = (25 * 45)/(25 + 5) = Rs.37.5 per L
If cost of pure milk = Rs.48 per L
So, cost of initial mixture = (25 * 48)/(25 + 5) = Rs.40 per L
So, range of cost of initial mixture is from Rs.35 per L to Rs.40 per L.
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below-A certain number of persons are living in a building having four floors. Also each of the floor having three flats such as flat-2 is in east of flat-1 but west of flat-3. Ground floor is numbered floor 1 and top most floor is floor 4. Each flat is built in such a way that Flat 1 of floor 2 is just above Flat 1 of floor 1 and just below flat-1 of floor-3 and so on. Only the given persons are considered to be living in the building. No flat is vacant. No two floors having same number of persons living in it. J is not living on even numbered floor. E* is living in a flat just below the flat of N. Y~ is living on an even numbered floor and he is living immediate west of N. No one lives to the east to O. M is living with only S& in same flat which is immediately below the flat of H. Two floors are there between the floors on which D@ and V$ lives and both are living in the same flat number. G^ is not living alone in any of the flat. The total number of persons living on topmost floor is one more than the number of persons living on the bottom most floor. G^ is living immediate west of O. I is living immediately below Y~ in the same flat number. V is living immediate west of I. Number of persons living on floor-2 is more than the number of persons living on floor-3 but less than number of persons living on floor-1. H is living on a floor having least number of persons. J? is living to the west of L. Only one floor is there between H and B# who is living in same flat number as H. No one is living to the east of D@ who lives below V$. P% is living in a flat which is just below the flat of T!. No one is living with P% and is living immediate west of J. No one is living with J?. O is living on even numbered floor. No one is living with H in the same flat. L is not living in the same flat with T!.How many persons are living to the west of ‘I’?- a)One
- b)Three
- c)More than three
- d)Two
- e)None
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
A certain number of persons are living in a building having four floors. Also each of the floor having three flats such as flat-2 is in east of flat-1 but west of flat-3. Ground floor is numbered floor 1 and top most floor is floor 4. Each flat is built in such a way that Flat 1 of floor 2 is just above Flat 1 of floor 1 and just below flat-1 of floor-3 and so on. Only the given persons are considered to be living in the building. No flat is vacant. No two floors having same number of persons living in it. J is not living on even numbered floor. E* is living in a flat just below the flat of N. Y~ is living on an even numbered floor and he is living immediate west of N. No one lives to the east to O. M is living with only S& in same flat which is immediately below the flat of H. Two floors are there between the floors on which D@ and V$ lives and both are living in the same flat number. G^ is not living alone in any of the flat. The total number of persons living on topmost floor is one more than the number of persons living on the bottom most floor. G^ is living immediate west of O. I is living immediately below Y~ in the same flat number. V is living immediate west of I. Number of persons living on floor-2 is more than the number of persons living on floor-3 but less than number of persons living on floor-1. H is living on a floor having least number of persons. J? is living to the west of L. Only one floor is there between H and B# who is living in same flat number as H. No one is living to the east of D@ who lives below V$. P% is living in a flat which is just below the flat of T!. No one is living with P% and is living immediate west of J. No one is living with J?. O is living on even numbered floor. No one is living with H in the same flat. L is not living in the same flat with T!.
How many persons are living to the west of ‘I’?
a)
One
b)
Three
c)
More than three
d)
Two
e)
None
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
Y~ is living on an even-numbered floor and he is living immediate west of N. I is living immediately below Y~ in the same flat number. V is living immediate west of I.
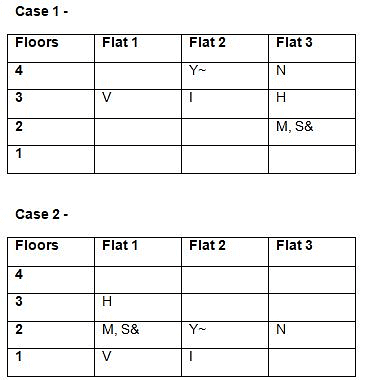
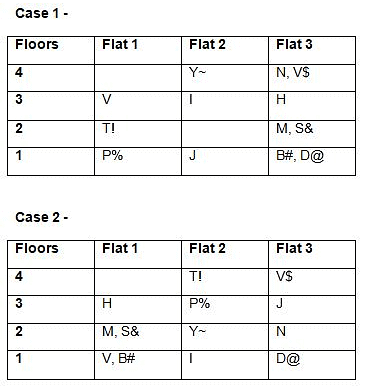
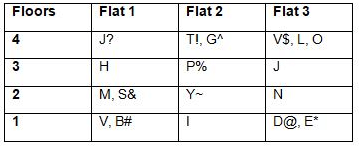

H is living on a floor having least number of persons. Number of persons living on floor-2 is more than the number of persons living on floor-3 but less than number of persons living on floor-1. The total number of persons living on topmost floor is one more than the number of persons living on the bottom most floor. So, it is clear that least no of persons are living on floor-3. M is living with only S& in same flat which is immediately below the flat of H.

Only one floor is there between H and B# who is living in the same flat number as H. Two floors are there between the floors on which D@ and V$ lives and both are living in the same flat number. No one is living to the east of D@ who lives below V$. P% is living in a flat which is just below the flat of T!. No one is living with P% and is living immediate west of J. J is not living on an even-numbered floor.

E* is living in a flat just below the flat of N. J? is living to the west of L. No one is living with J?. O is living on even-numbered floor. G^ is living immediate west of O. No one lives to the east to O. L is not living in the same flat with T!. As we know that no two floors having the same number of persons living in it. G^ is not living alone in any of the flat. No flat is vacant. From this case-1 gets eliminated. So, the final arrangement is—

Study the following information carefully and answer the below questionsA family consist of ten members and three generations are sitting in a linear row facing north.The one who is the paternal aunt of D sits fourth to the right of E. Neither E nor C sits at the extreme ends. Only one person sits between E and her only granddaughter. The number of persons sitting to the left of E’s granddaughter is one more than the number of persons sitting to the right of C, who has no siblings. C is a male. D, who is not a child of A and is the grandson of I. The one who is the sister-in-law of F is a child of B. The number of persons sitting between C and his only brother-in-law is one less than the number of persons sitting between C’s brother-in-law and I, where C and I are not sitting together. B, who is the mother of E’s daughter-in-law and sits second to the right of I. F and her son D are sitting together. F does not have any siblings. The one who is the maternal uncle of J sits second to the left of F and is not sitting at the extreme ends. H is the niece of the one who is the nephew of G, who is the brother of B.How is the one who sits at the extreme left end related to the one who sits second to the left of D?- a)Son
- b)Father
- c)Son-in-law
- d)Father-in-law
- e)Can’t be determined
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
A family consist of ten members and three generations are sitting in a linear row facing north.
The one who is the paternal aunt of D sits fourth to the right of E. Neither E nor C sits at the extreme ends. Only one person sits between E and her only granddaughter. The number of persons sitting to the left of E’s granddaughter is one more than the number of persons sitting to the right of C, who has no siblings. C is a male. D, who is not a child of A and is the grandson of I. The one who is the sister-in-law of F is a child of B. The number of persons sitting between C and his only brother-in-law is one less than the number of persons sitting between C’s brother-in-law and I, where C and I are not sitting together. B, who is the mother of E’s daughter-in-law and sits second to the right of I. F and her son D are sitting together. F does not have any siblings. The one who is the maternal uncle of J sits second to the left of F and is not sitting at the extreme ends. H is the niece of the one who is the nephew of G, who is the brother of B.
How is the one who sits at the extreme left end related to the one who sits second to the left of D?
a)
Son
b)
Father
c)
Son-in-law
d)
Father-in-law
e)
Can’t be determined

|
Janani Kulkarni answered |
Relationship between the person at the extreme left end and the person second to the left of D
There are a total of 10 family members arranged in a linear row, with three generations present. Let's analyze the given information to determine the relationship between the person at the extreme left end and the person second to the left of D:
- The person who is the paternal aunt of D sits fourth to the right of E.
- Only one person sits between E and her only granddaughter.
- The number of persons sitting to the left of E’s granddaughter is one more than the number of persons sitting to the right of C.
- C, who has no siblings, is a male.
- D is the grandson of I and not a child of A.
- B is the mother of E’s daughter-in-law and sits second to the right of I.
- F and her son D are sitting together, and F does not have any siblings.
- The maternal uncle of J sits second to the left of F.
Given the information, we can deduce that the person second to the left of D is the maternal uncle of J. Therefore, the person at the extreme left end is the father-in-law of the person second to the left of D. Hence, the correct answer is (d) Father-in-law.
There are a total of 10 family members arranged in a linear row, with three generations present. Let's analyze the given information to determine the relationship between the person at the extreme left end and the person second to the left of D:
- The person who is the paternal aunt of D sits fourth to the right of E.
- Only one person sits between E and her only granddaughter.
- The number of persons sitting to the left of E’s granddaughter is one more than the number of persons sitting to the right of C.
- C, who has no siblings, is a male.
- D is the grandson of I and not a child of A.
- B is the mother of E’s daughter-in-law and sits second to the right of I.
- F and her son D are sitting together, and F does not have any siblings.
- The maternal uncle of J sits second to the left of F.
Given the information, we can deduce that the person second to the left of D is the maternal uncle of J. Therefore, the person at the extreme left end is the father-in-law of the person second to the left of D. Hence, the correct answer is (d) Father-in-law.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.In a family of eight members – B, F, G, H, L, M, R, and S. Two married couples are there in the family. Each person has different number of toffees. M has 504 toffees initially. M takes 27 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his mother R. R’s father-in-law is married to L. S is the only daughter of L. R takes 1/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to her father-in-law. S’s father takes 24 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to F, who is an unmarried member. F takes 2/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his brother G. G gives 64 toffees to his father-in-law B. F gives 1/4th of his toffees to his sister, who gives 35 toffees to his mother.How the one who has 14 toffees is related to M?- a)Grandfather
- b)Aunt
- c)Mother
- d)Brother-in-law
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a family of eight members – B, F, G, H, L, M, R, and S. Two married couples are there in the family. Each person has different number of toffees. M has 504 toffees initially. M takes 27 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his mother R. R’s father-in-law is married to L. S is the only daughter of L. R takes 1/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to her father-in-law. S’s father takes 24 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to F, who is an unmarried member. F takes 2/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his brother G. G gives 64 toffees to his father-in-law B. F gives 1/4th of his toffees to his sister, who gives 35 toffees to his mother.
How the one who has 14 toffees is related to M?
a)
Grandfather
b)
Aunt
c)
Mother
d)
Brother-in-law
e)
None of these
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
We have: 
- M has 504 toffees initially. M takes 27 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his mother R.
- R takes 1/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to her father-in-law.
- R’s father-in-law is married to L.
- S is the only daughter of L.
- S’s father takes 24 toffees and gives the remaining toffees to F, who is an unmarried member.
- F takes 2/3rd of the toffees and gives the remaining toffees to his brother G.
- G gives 64 toffees to his father-in-law B.
- F gives 1/4th of his toffees to his sister, who gives 35 toffees to his mother.
- Each person has different number of toffees.
Since, two married couples are there in the family, thus G must be married to R.
Based on the above given information we have:

Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.If all the persons are arranged to sit in alphabetical order starting from P's position in anticlockwise direction, then position of how many person(s) remain(s) unchanged?- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Four
- d)One
- e)None
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question.
Certain persons are sitting around a circular table which has a circumference of 390 m and all of them are facing towards the centre. They are sitting at certain distances from each other, which are consecutive multiples of 5 in clockwise direction. K is not an immediate neighbour of R. Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m, but less than 110 m. L is sitting second to the left of V, who is sitting 30 m away to the left of X. Distance between R and P is 90 m. K is sitting 2nd to the right of Q. Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2. Distance between C and K is 75 m. Number of persons sitting between S and Z is one less than the number of persons sitting between A and R. Distance between Q and K is 95 m. Z is the neighbour of both Q and K.
If all the persons are arranged to sit in alphabetical order starting from P's position in anticlockwise direction, then position of how many person(s) remain(s) unchanged?
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Four
d)
One
e)
None

|
Swati Datta answered |
Analysis:
- The circumference of the circular table is 390 m.
- Distances between persons are consecutive multiples of 5 in the clockwise direction.
Given Information:
- K is not an immediate neighbor of R.
- Distance between S and Z is more than 100 m but less than 110 m.
- L is second to the left of V, who is 30 m to the left of X.
- Distance between R and P is 90 m.
- K is 2nd to the right of Q.
- Distance between A and W is the LCM of 5 and 2.
- Distance between C and K is 75 m.
- Number of persons between S and Z is one less than between A and R.
- Distance between Q and K is 95 m.
- Z is the neighbor of both Q and K.
Solution:
- Arrange the persons in alphabetical order starting from P in the anticlockwise direction.
- Positions of R, P, Q, K, and Z will remain unchanged as their positions are fixed based on the given information.
- Therefore, only the positions of A, S, V, W, X, and L will change.
- Hence, only one person's position remains unchanged, which is Z.
Therefore, the correct answer is One person.
Two machine rearranges a given word and number step by step to a final output following same rule. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Machine 1:Input: Social 372 473 Open Under 564 Network 385Step I: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step II: bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732 473 Open Under 385Step III: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step IV: vsofe 374 qpof 583 bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732Machine 2:Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531Step I: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531Step II: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_Step III: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531Step IV: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_What comes in place of C in step IV of machine 2?- a)wpfcb
- b)264
- c)bfmsuw
- d)183
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two machine rearranges a given word and number step by step to a final output following same rule. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Machine 1:
Input: Social 372 473 Open Under 564 Network 385
Step I: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step II: bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732 473 Open Under 385
Step III: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step IV: vsofe 374 qpof 583 bhknrz 654 djmnqsv 732
Machine 2:
Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531
Step I: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531
Step II: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Step III: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531
Step IV: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
What comes in place of C in step IV of machine 2?
a)
wpfcb
b)
264
c)
bfmsuw
d)
183
e)
None of these

|
Rutuja Das answered |
Understanding Machine 2 Steps
To answer the question about what comes in place of C in step IV of Machine 2, we need to analyze the steps taken in the rearrangement process.
Input Analysis
- Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531
Step I Transformation
- In Step I, the letters of "Travel", "Magic", "Above", and "Entry" are rearranged based on their alphabetical order, while the numbers are adjusted accordingly.
- Result: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531
Step II Transformation
- In Step II, the next transformation involves rearranging the letters and numbers again.
- The letters are sorted and converted, and the numbers are also rearranged or adjusted.
- Result: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531
Step III Transformation
- In Step III, we can see the retention of some previously transformed letters and numbers.
- The letters and numbers continue to be rearranged.
- Result: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Identifying C in Step IV
- In Step IV, the entries are sorted based on the established rules.
- From the previous steps, we know that 'wpfcb' corresponds to the letters of 'Travel', and 'dkqsuz' relates to 'Magic'.
- The number '183' corresponds to the first entry's numerical transformation.
- Thus, the value for C in Step IV is 'wpfcb', which is clearly the first entry based on the transformations.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer for C in Step IV of Machine 2 is option 'A', which is 'wpfcb'.
To answer the question about what comes in place of C in step IV of Machine 2, we need to analyze the steps taken in the rearrangement process.
Input Analysis
- Input: 381 Travel 468 Magic 624 Above Entry 531
Step I Transformation
- In Step I, the letters of "Travel", "Magic", "Above", and "Entry" are rearranged based on their alphabetical order, while the numbers are adjusted accordingly.
- Result: bfhlz 648 381 Travel 624 Above Entry 531
Step II Transformation
- In Step II, the next transformation involves rearranging the letters and numbers again.
- The letters are sorted and converted, and the numbers are also rearranged or adjusted.
- Result: wpfcb 183 dkqsuz 264 bfhlz 648 Entry 531
Step III Transformation
- In Step III, we can see the retention of some previously transformed letters and numbers.
- The letters and numbers continue to be rearranged.
- Result: _(A)__(B)__(C)__(D)__(E)__(F)__(G)__(H)_
Identifying C in Step IV
- In Step IV, the entries are sorted based on the established rules.
- From the previous steps, we know that 'wpfcb' corresponds to the letters of 'Travel', and 'dkqsuz' relates to 'Magic'.
- The number '183' corresponds to the first entry's numerical transformation.
- Thus, the value for C in Step IV is 'wpfcb', which is clearly the first entry based on the transformations.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer for C in Step IV of Machine 2 is option 'A', which is 'wpfcb'.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W from three generations family get promoted in different months viz.- January, February, April, July, September, October, November, and December of the same year but not necessary in the same order.U promoted three persons before R, who is the mother of W. Q is the only daughter of P’s brother and is promoted in a month having 30 days. W’s son-in-law promoted three persons after Q. The number of persons promoted before U is the same as the number of persons promoted after P. Q is neither promoted immediately before nor after R, who is not promoted in December. Two persons are promoted between S and W, who is the father of V. V is an unmarried member of the family. Q’s father is the only son of the one who promoted four persons before T. P’s father is promoted immediately after U’s daughter-in-law.Q. Which of the following statement is true with respect to S’s husband?- a)He promoted three persons before T
- b)Son-in-law of R
- c)He promoted immediately after V’s sister
- d)Father-in-law of V
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W from three generations family get promoted in different months viz.- January, February, April, July, September, October, November, and December of the same year but not necessary in the same order.
U promoted three persons before R, who is the mother of W. Q is the only daughter of P’s brother and is promoted in a month having 30 days. W’s son-in-law promoted three persons after Q. The number of persons promoted before U is the same as the number of persons promoted after P. Q is neither promoted immediately before nor after R, who is not promoted in December. Two persons are promoted between S and W, who is the father of V. V is an unmarried member of the family. Q’s father is the only son of the one who promoted four persons before T. P’s father is promoted immediately after U’s daughter-in-law.
Q. Which of the following statement is true with respect to S’s husband?
a)
He promoted three persons before T
b)
Son-in-law of R
c)
He promoted immediately after V’s sister
d)
Father-in-law of V
e)
None of these
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
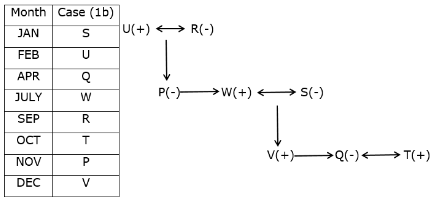
We have:
- Q is the only daughter of P’s brother and is promoted in a month having 30 days.
- W’s son-in-law promoted three persons after Q.
That means, in case (1) Q get promotion in April, in case (2) Q get promotion in September.
- U promoted three persons before R, who is the mother of W.
- The number of persons promoted before U is the same as the number of persons promoted after P.
- Q is neither promoted immediately before nor after R, who is not promoted in December.
That means, in case (1) U gets promoted in February, in case (1a) U gets promoted in July, case (2) is not valid.
Based on the above given information we have:
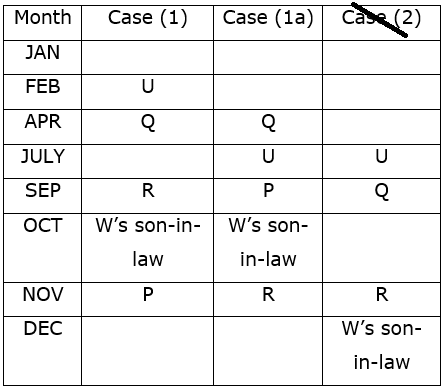
Case (2) is not valid as the number of persons promoted before U is the same as the number of persons promoted after P.
Again, we have:
- Two persons are promoted between S and W, who is the father of V.
That means, in case (1) either S or W gets promotion in January, case (1a) is not valid.
Based on the above given information we have:
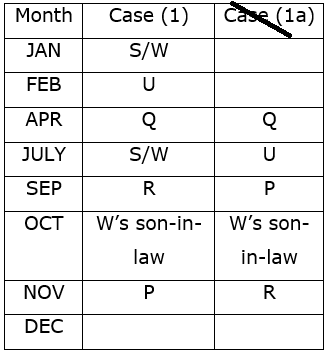
Case (1a) is not valid as two persons are promoted between S and W, who is the father of V.
Again, we have:
- Q’s father is the only son of the one who promoted four persons before T.
That means, in case (1) T must be promoted in December, and either of W or S is the father of Q, in case (1b) T must be promoted in October, and U must be the father of Q.
Since, only remaining person is V, and V is child of W, thus in case (1) V can never be the son-in-law of W, thus case (1) is not valid.
Based on the above given information we have:
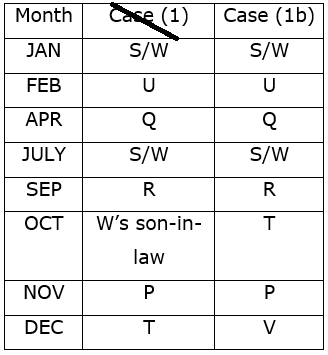
Case (1) is not valid as only remaining person is V, and V can’t be W’s son-in-law.
Again, we have:
- P’s father is promoted immediately after U’s daughter-in-law.
- V is an unmarried member of the family.
Since, T is the son-in-law of W.
Thus, U must be the father of P and S must be the daughter-in-law of U.
Based on the above given information we have:
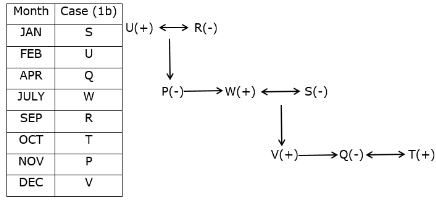
Which of the following is the most popular game of Punjab?- a)Hockey
- b)Kabaddi
- c)Kho-Kho
- d)Badminton
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most popular game of Punjab?
a)
Hockey
b)
Kabaddi
c)
Kho-Kho
d)
Badminton
e)
None of these
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
The Most popular game in Punjab is Kabaddi.
A wide range of sports and games are played by Punjabis, ranging from modern games such as hockey and cricket, to more traditional games such as Kabaddi, Kushtian, and Khuddo Khoondi (similar to hockey).
There are over 100 traditional Punjab games and sports.
Kabaddi is a sport of contact team played between two seven-player teams each.
The goal of the game is for a single player on offense, referred to as a raider, to run into the half of a court of the opposing team, tag out as many of their defenders as possible, and return to their own half of the court, all without being tackled and in a single breath by the defenders.
The raider is tagged with points, while the winning team wins a point for stopping the raider.
If they are tagged or tackled, players are taken out of the game but are brought back in from a tag or tackle for each point scored by their side..
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Directions: Given an input line; the machine arranges the words and numbers in steps in a systematic manner as illustrated afterwards. Study the pattern and answer the question that follows.A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.Input: gap 81 39 rat 25 tan 72 nap 14 matStep I: tn gap 39 rat 25 72 nap 14 mat 80Step II: 71 tn gap 39 25 nap 14 mat 80 rtStep III: np 71 tn gap 25 14 mat 80 rt 38Step IV: 24 np 71 tn gap 14 80 rt 38 mtStep V: gp 24 np 71 tn 80 rt 38 mt 13And step V is the last step of the rearrangement as the intended output is obtained. As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.Input: pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27How many elements are there between '62' and 'fan' in step III of the given input?- a)Two
- b)More than three
- c)One
- d)Three
- e)Four
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Given an input line; the machine arranges the words and numbers in steps in a systematic manner as illustrated afterwards. Study the pattern and answer the question that follows.
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: gap 81 39 rat 25 tan 72 nap 14 mat
Step I: tn gap 39 rat 25 72 nap 14 mat 80
Step II: 71 tn gap 39 25 nap 14 mat 80 rt
Step III: np 71 tn gap 25 14 mat 80 rt 38
Step IV: 24 np 71 tn gap 14 80 rt 38 mt
Step V: gp 24 np 71 tn 80 rt 38 mt 13
And step V is the last step of the rearrangement as the intended output is obtained. As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input: pat 32 48 yak bed 63 78 fan lay 27
How many elements are there between '62' and 'fan' in step III of the given input?
a)
Two
b)
More than three
c)
One
d)
Three
e)
Four
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
In the first step, the word starting with the letter which comes last in English alphabet is written in the beginning and the highest number is placed in the end. The vowel from the word is deleted and one is subtracted from the number. In the second step, the second highest number is written in the beginning and the word starting with the letter which comes second last in English alphabet is written in the end. Again, one is subtracted from the number and the vowel is deleted from the word.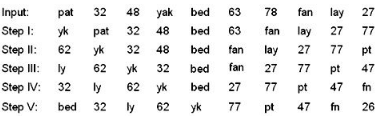
The pattern is repeated in the subsequent steps.
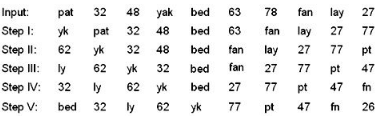
Three elements are there between '62' and 'fan' in step III.
Directions: Given below are six sentences A, B, C, D, E and F. Answer the following question after rearranging the following sentences into a coherent paragraph.A. This often invisible problem adds to the loss of lives of seven million people each year, causes conditions from asthma to dementia, and, according to the World Bank, costs the healthcare system more than $5 trillion every year.B. However, India faces perhaps the biggest and most wide-ranging risks.C. From Delhi to Kanpur to Varanasi, particularly in the Gangetic plain, our cities have often been listed by many among the most polluted.D. Air pollutants are definitely health hazards and more than anything else, people deserve a life with dignity and clean air, and the government is conscious of the fact that providing such clean air has to remain national priority.E. Nine out of 10 people worldwide are exposed to unsafe air.F. India is not alone in facing the problem of air pollution.Among the following pairs, which one contains two alternative statements after the rearrangement?- a)F - B
- b)C - D
- c)B - F
- d)E - B
- e)A - D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Given below are six sentences A, B, C, D, E and F. Answer the following question after rearranging the following sentences into a coherent paragraph.
A. This often invisible problem adds to the loss of lives of seven million people each year, causes conditions from asthma to dementia, and, according to the World Bank, costs the healthcare system more than $5 trillion every year.
B. However, India faces perhaps the biggest and most wide-ranging risks.
C. From Delhi to Kanpur to Varanasi, particularly in the Gangetic plain, our cities have often been listed by many among the most polluted.
D. Air pollutants are definitely health hazards and more than anything else, people deserve a life with dignity and clean air, and the government is conscious of the fact that providing such clean air has to remain national priority.
E. Nine out of 10 people worldwide are exposed to unsafe air.
F. India is not alone in facing the problem of air pollution.
Among the following pairs, which one contains two alternative statements after the rearrangement?
a)
F - B
b)
C - D
c)
B - F
d)
E - B
e)
A - D

|
Bibek Dasgupta answered |
Understanding the Coherent Paragraph
To rearrange the sentences into a coherent paragraph, let's analyze their logical flow:
- Sentence A introduces the severe implications of air pollution, highlighting its health impacts and economic costs.
- Sentence B indicates that India faces significant risks related to air pollution, setting the stage for the following details.
- Sentence C provides specific examples of Indian cities that are notably polluted, reinforcing the context of India’s challenges.
- Sentence D discusses the importance of clean air and the government’s acknowledgment of this issue as a national priority.
- Sentence E presents a global perspective, pointing out that air pollution affects a vast majority of the world’s population.
- Sentence F emphasizes that India is not alone in this struggle, suggesting a shared global issue.
When arranged logically, the sequence is: B, C, A, D, E, F.
Explanation of Correct Pair: D - A
- Pair D (A - D):
- Sentence A discusses the consequences of air pollution, which aligns well with the transition into Sentence D, where it emphasizes the need for dignity and clean air for people. This connection flows naturally because after highlighting the severity of the problem, it logically leads to the need for action.
- Other Pairs Analysis:
- F - B: Lacks a coherent transition.
- C - D: While related, does not flow as directly.
- B - F: Both talk about pollution but lack a direct link.
- E - B: Presents a global view without a clear transition to India’s situation.
In conclusion, the best alternative statements that connect seamlessly are indeed A and D. They form a complete thought regarding the consequences of air pollution and the necessity of clean air as a priority.
To rearrange the sentences into a coherent paragraph, let's analyze their logical flow:
- Sentence A introduces the severe implications of air pollution, highlighting its health impacts and economic costs.
- Sentence B indicates that India faces significant risks related to air pollution, setting the stage for the following details.
- Sentence C provides specific examples of Indian cities that are notably polluted, reinforcing the context of India’s challenges.
- Sentence D discusses the importance of clean air and the government’s acknowledgment of this issue as a national priority.
- Sentence E presents a global perspective, pointing out that air pollution affects a vast majority of the world’s population.
- Sentence F emphasizes that India is not alone in this struggle, suggesting a shared global issue.
When arranged logically, the sequence is: B, C, A, D, E, F.
Explanation of Correct Pair: D - A
- Pair D (A - D):
- Sentence A discusses the consequences of air pollution, which aligns well with the transition into Sentence D, where it emphasizes the need for dignity and clean air for people. This connection flows naturally because after highlighting the severity of the problem, it logically leads to the need for action.
- Other Pairs Analysis:
- F - B: Lacks a coherent transition.
- C - D: While related, does not flow as directly.
- B - F: Both talk about pollution but lack a direct link.
- E - B: Presents a global view without a clear transition to India’s situation.
In conclusion, the best alternative statements that connect seamlessly are indeed A and D. They form a complete thought regarding the consequences of air pollution and the necessity of clean air as a priority.
Chapter doubts & questions for SBI PO Mains - Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 2025 is part of Bank Exams exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Bank Exams exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Bank Exams 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of SBI PO Mains - Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 in English & Hindi are available as part of Bank Exams exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Bank Exams Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









