All Exams >
JEE >
Online MCQ Tests for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Surface Chemistry for JEE Exam
The name aquadag is given to the colloidal sol of:- a)Copper in water
- b)platinum in water
- c)graphite in water
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The name aquadag is given to the colloidal sol of:
a)
Copper in water
b)
platinum in water
c)
graphite in water
d)
none of the above

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Aquadag is the name of a water-based colloidal graphite coating which is a colloidal solution of graphite in water.
Catalyst only- a)Decreases activation energy
- b)increases activation energy
- c)Brings about equilibrium
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Catalyst only
a)
Decreases activation energy
b)
increases activation energy
c)
Brings about equilibrium
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Catalyst is a substance which changes the rate of reaction without affecting the overall energetics of the reaction.
Which of the following will have the highest coagulating power for As2S3 colloids?- a)Al3+
- b)Na+
- c)PO43-
- d)PO42-
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have the highest coagulating power for As2S3 colloids?
a)
Al3+
b)
Na+
c)
PO43-
d)
PO42-
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
AS2S3 is an anionic sol (negative sol) hence coagulation will depend on coagulating power of cation , which is directly proportional to the valency of the cation (Hardy-Schulze rule).
Hence positive ions having maximum amount of charge will have more coagulation thus, Al3+ have maximum coagulating power.
Hence positive ions having maximum amount of charge will have more coagulation thus, Al3+ have maximum coagulating power.
Adsorption is a- a)Reduction process
- b)Surface phenomenon
- c)Colligative property
- d)Oxidation process
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorption is a
a)
Reduction process
b)
Surface phenomenon
c)
Colligative property
d)
Oxidation process
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. ... Adsorption is a surface phenomenon, while absorption involves the whole volume of the material.
During the adsorption of Krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature - a)ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
- b)ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
- c)ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
- d)ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During the adsorption of Krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature
a)
ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
b)
ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
c)
ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
d)
ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Correct answer is option A
During the adsorption of krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature.
ΔH<0 and ΔS<0.
Since adsorption is an exothermic process, the enthalpy change is negative. Heat is given out during the process.
The krypton gas adsorbed on activated charcoal is more ordered than unadsorbed krypton gas. Hence, the process occurs with a decrease in entropy.
In other words, the entropy change is negative for the process.
During the adsorption of krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature.
ΔH<0 and ΔS<0.
Since adsorption is an exothermic process, the enthalpy change is negative. Heat is given out during the process.
The krypton gas adsorbed on activated charcoal is more ordered than unadsorbed krypton gas. Hence, the process occurs with a decrease in entropy.
In other words, the entropy change is negative for the process.
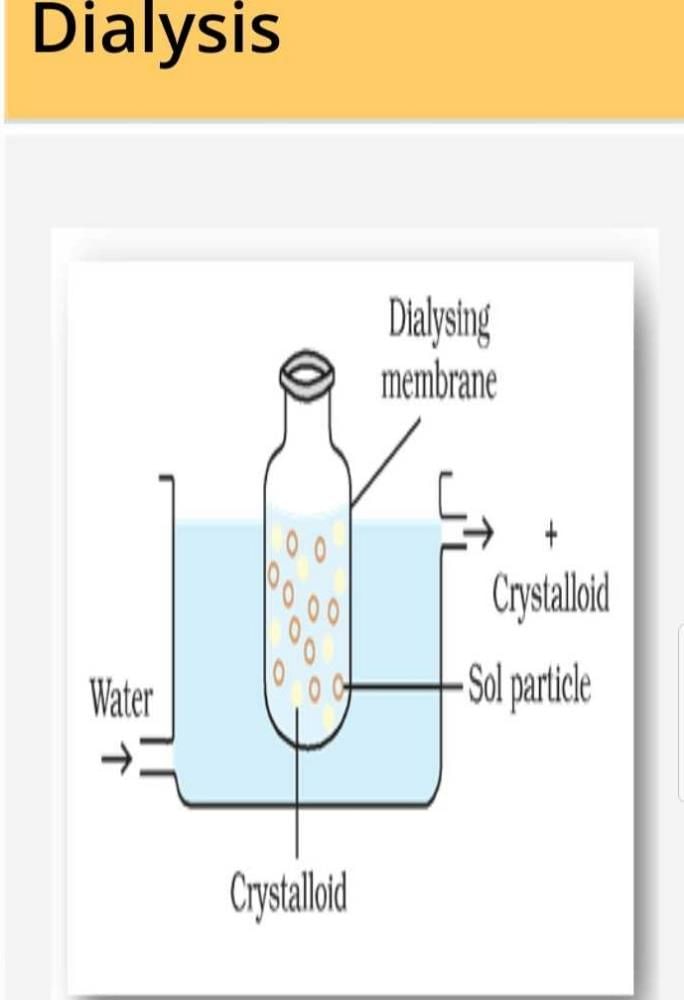
Blood is purified by:- a)Dialysis
- b)Filtration
- c)Coagulation
- d)Electro-osmosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood is purified by:
a)
Dialysis
b)
Filtration
c)
Coagulation
d)
Electro-osmosis
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make substances that keep your body healthy. Dialysis replaces some of these functions when your kidneys no longer work.
An example of colloid in which both phase and medium are solid is?- a)milk
- b)cheese
- c)cake
- d)marble
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of colloid in which both phase and medium are solid is?
a)
milk
b)
cheese
c)
cake
d)
marble

|
Ashu Bhardwaj answered |
Cake batter an emulsion ,cheese a gel ,solid in liquid malai,milk emulsion, so marble is left
Why are enzymes highly specific?- a)They are nitrogenous material
- b)They have active site on their surface
- c)They are biological catalyst
- d)They are very active
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are enzymes highly specific?
a)
They are nitrogenous material
b)
They have active site on their surface
c)
They are biological catalyst
d)
They are very active
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Enzymes are highly selective catalysts, meaning that each enzyme only speeds up a specific reaction. The molecules that an enzyme works with are called substrates. The substrates bind to a region on the enzyme called the active site. There are two theories explaining the enzyme-substrate interaction.
Water-in-oil emulsions is also called as:- a)Aqueous emulsion
- b)Oily emulsion
- c)Alcoholic emulsion
- d)Electrophoresis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water-in-oil emulsions is also called as:
a)
Aqueous emulsion
b)
Oily emulsion
c)
Alcoholic emulsion
d)
Electrophoresis

|
Osheen Bishnoi answered |
Water in oil emulsion is also called oily emulsion
Which of the following is the reason for adsorption?- a)internal core molecules are experiencing more inward force
- b)surface molecules are experiencing more inward force
- c)internal core molecules are experiencing less inward force
- d)surface molecules are experiencing less inward force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the reason for adsorption?
a)
internal core molecules are experiencing more inward force
b)
surface molecules are experiencing more inward force
c)
internal core molecules are experiencing less inward force
d)
surface molecules are experiencing less inward force
|
|
Om Desai answered |
There is an unbalanced attractive force of adsorbent are responsible for attracting the adsorbate particles on its surface.
What kind of forces exists between adsorbate and adsorbent in physisorption?- a)hydrogen bond
- b)ionic bond
- c)covalent bond
- d)London force
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What kind of forces exists between adsorbate and adsorbent in physisorption?
a)
hydrogen bond
b)
ionic bond
c)
covalent bond
d)
London force
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Physisorption is defined as adsorption in which force between adsorbate and adsorbent is physical van der Waals force also known as London force.
In Rosenmund reduction, barium sulphate:- a)Lowers the melting point of catalysts
- b)Promotes the catalyst
- c)Lowers the melting point of reactants
- d)Poisons the catalyst
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Rosenmund reduction, barium sulphate:
a)
Lowers the melting point of catalysts
b)
Promotes the catalyst
c)
Lowers the melting point of reactants
d)
Poisons the catalyst
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
The rosenmund reaction is catalyzed by palladium on barium sulfate. Barium sulfate reduces the activity of palladium due to its low surface area meaning it decreases the reducing power of palladium in order to prevent over-reduction of the acid.
Which one of the following is not applicable to chemisorption ?- a)Its heat of adsorption is high
- b)It takes place at high temperature
- c)It is reversible
- d)It forms mono-molecular layers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not applicable to chemisorption ?
a)
Its heat of adsorption is high
b)
It takes place at high temperature
c)
It is reversible
d)
It forms mono-molecular layers
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Chemisorption is irreversible in nature because in chemisorption there are strong covalent bond are formed which do not brake easily to separate the reactants because of this it has high heat of adsorption, takes place at high temperatures and forms monolayers.
Homogeneous catalyst is the one- a)Which has same phase as that of products
- b)which makes reactants homogeneous
- c)Which has same phase as that of reactants
- d)Which is homogeneous at room temperature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Homogeneous catalyst is the one
a)
Which has same phase as that of products
b)
which makes reactants homogeneous
c)
Which has same phase as that of reactants
d)
Which is homogeneous at room temperature
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
A catalyst helps speed up reactions. These catalysts can be homogeneous, in the same phase, or heterogeneous, in different phases. A homogeneous catalyst mixes the catalyst with the reactants, allowing it to speed up the reaction. One type of homogeneous catalyst, an autocatalyst, is part of one of the reactants.
Any two immiscible liquids when mixed form an:- a)Aerosol
- b)Emulsion
- c)Gel
- d)Sol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Any two immiscible liquids when mixed form an:
a)
Aerosol
b)
Emulsion
c)
Gel
d)
Sol
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
An emulsion is a colloid of two or more immiscible liquids where one liquid contains a dispersion of the other liquids.
Examples: Oil and water mixtures are emulsions when shaken together. The oil will form drops and disperse throughout the water. So, curd is not an emulsion.
Foam is a substance where air or gas bubbles are trapped inside a solid or liquid.
Examples: Styrofoam, whipped cream, soap bubbles. So, mist is not a foam.
An aerosol is a colloid of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or not. An Example of natural aerosol is fog. Examples of artificial aerosols are dust, particulates, air pollutants and smoke.
Solid sol is a type of colloid of the form of one solid dispersed in another continuous solid. So, cake is not solid sol.
An emulsion is a colloid of two or more immiscible liquids where one liquid contains a dispersion of the other liquids.
Examples: Oil and water mixtures are emulsions when shaken together. The oil will form drops and disperse throughout the water. So, curd is not an emulsion.
Foam is a substance where air or gas bubbles are trapped inside a solid or liquid.
Examples: Styrofoam, whipped cream, soap bubbles. So, mist is not a foam.
An aerosol is a colloid of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or not. An Example of natural aerosol is fog. Examples of artificial aerosols are dust, particulates, air pollutants and smoke.
Solid sol is a type of colloid of the form of one solid dispersed in another continuous solid. So, cake is not solid sol.
Study the following reactions.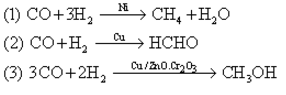 Which characteristic of catalyst is represented by them.?
Which characteristic of catalyst is represented by them.?- a)energy specific
- b)shape selectivity
- c)activity
- d)selectivity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following reactions.
Which characteristic of catalyst is represented by them.?
a)
energy specific
b)
shape selectivity
c)
activity
d)
selectivity

|
Busy answered |
Yess..ans is selectivity...bcs u can see that reactants in each rxns are same...but the products depend on the type of catalyst used in the particular rxn....so that's y ans is selectivity...
The adsorbent used to adsorb the dye particles in the dying industry is- a)Activated charcoal
- b)Silica gel
- c)Alumina gel
- d)Alum
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The adsorbent used to adsorb the dye particles in the dying industry is
a)
Activated charcoal
b)
Silica gel
c)
Alumina gel
d)
Alum
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Alum has pores on it which adsorbs the color of dye and makes the solution colorless.
Hence D is correct.
Hence D is correct.
Why shoes, purses and leather items have silica gel pouches kept in them?
a)for good fragranceb)for insect repellantc)for adsorption of moistured)for all the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Solids, particularly in a finely divided state, have a large surface area and so silica gel is a good adsorbent and keeps the leather dry and free of moisture.
Which of the following is the best example of shape selective catalysis?- a)finely divided nickel
- b)zeolites
- c)palladium
- d)platinum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the best example of shape selective catalysis?
a)
finely divided nickel
b)
zeolites
c)
palladium
d)
platinum
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Zeolites (ZSM-5 preparation of gasoline from methanol).
Which one of the following is lyophilic colloid ?- a)Milk
- b)Gum
- c)Fog
- d)Blood
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is lyophilic colloid ?
a)
Milk
b)
Gum
c)
Fog
d)
Blood
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Colloidal sols formed by mixing substances in a suitable dispersion medium are called lyophilic sols. These are quite stable. They are also known as reversible sols because the dispersion medium can be separated from the colloid by means of physical methods like evaporation. For e.g. gum, gelatin, starch, rubber etc.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a plot between:- a)x/m and T
- b)x/m and p
- c)P and T
- d)V and T
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a plot between:
a)
x/m and T
b)
x/m and p
c)
P and T
d)
V and T
|
|
Mihir Yadav answered |
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a relationship between the amount of adsorbate x/m (adsorbate per unit mass of the adsorbent) and the pressure p (or concentration) at a constant temperature. This is represented by the equation:
x/m = k * p^(1/n)
where k and n are constants that depend on the nature of the adsorbent-adsorbate system and the temperature.
Explanation:
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a model that describes the adsorption of a gas or a solute onto a solid surface at equilibrium. It was first proposed by Fritz Freundlich in 1906.
The plot between x/m and p is called the Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Here, x/m represents the amount of adsorbate per unit mass of the adsorbent, and p represents the pressure (or concentration) of the adsorbate in the gas (or liquid) phase.
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm assumes that the adsorption process occurs on a heterogeneous surface, where the adsorbate molecules are adsorbed onto active sites of different energies. This results in a non-linear relationship between the amount of adsorbate and the pressure (or concentration).
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is represented by a logarithmic plot of x/m versus log p. The slope of this plot is equal to 1/n, and the intercept is equal to log k. The constant k is related to the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent, while n is related to the degree of heterogeneity of the surface.
Applications of Freundlich adsorption isotherm:
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is widely used in various fields, such as:
1. Environmental science: To study the adsorption of pollutants on soil, water, and air.
2. Materials science: To design and optimize adsorbent materials for gas separation, catalysis, and energy storage.
3. Chemical engineering: To model and simulate adsorption processes in industrial applications, such as gas purification, chromatography, and ion exchange.
In conclusion, the Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a useful tool for understanding and predicting the adsorption behavior of gases and solutes on solid surfaces. The plot between x/m and p (or c) provides valuable insights into the adsorption mechanism and the properties of the adsorbent-adsorbate system.
x/m = k * p^(1/n)
where k and n are constants that depend on the nature of the adsorbent-adsorbate system and the temperature.
Explanation:
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a model that describes the adsorption of a gas or a solute onto a solid surface at equilibrium. It was first proposed by Fritz Freundlich in 1906.
The plot between x/m and p is called the Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Here, x/m represents the amount of adsorbate per unit mass of the adsorbent, and p represents the pressure (or concentration) of the adsorbate in the gas (or liquid) phase.
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm assumes that the adsorption process occurs on a heterogeneous surface, where the adsorbate molecules are adsorbed onto active sites of different energies. This results in a non-linear relationship between the amount of adsorbate and the pressure (or concentration).
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is represented by a logarithmic plot of x/m versus log p. The slope of this plot is equal to 1/n, and the intercept is equal to log k. The constant k is related to the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent, while n is related to the degree of heterogeneity of the surface.
Applications of Freundlich adsorption isotherm:
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is widely used in various fields, such as:
1. Environmental science: To study the adsorption of pollutants on soil, water, and air.
2. Materials science: To design and optimize adsorbent materials for gas separation, catalysis, and energy storage.
3. Chemical engineering: To model and simulate adsorption processes in industrial applications, such as gas purification, chromatography, and ion exchange.
In conclusion, the Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a useful tool for understanding and predicting the adsorption behavior of gases and solutes on solid surfaces. The plot between x/m and p (or c) provides valuable insights into the adsorption mechanism and the properties of the adsorbent-adsorbate system.
Rotation at high speed makes the colloid settle down and the impurities remain in solution. What is this process called?- a)Ultra centrifugation
- b)Ultrafiltration
- c)Dialysis
- d)Mechanical dispersion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rotation at high speed makes the colloid settle down and the impurities remain in solution. What is this process called?
a)
Ultra centrifugation
b)
Ultrafiltration
c)
Dialysis
d)
Mechanical dispersion
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The ultracentrifuge is a centrifuge optimized for spinning a rotor at very high speeds, capable of generating acceleration as high as 1 000 000 g (approx. 9 800 km/s2). There are two kinds of ultracentrifuges, the preparative and the analytical ultracentrifuge.
Ammonia is adsorbed by- a)Silica
- b)Water
- c)Charcoal
- d)Alcohol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ammonia is adsorbed by
a)
Silica
b)
Water
c)
Charcoal
d)
Alcohol

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
Charcoal act as an adsorbent.
Enzymes are- a)Substances made by chemists to activate washing powder
- b)Synthetic catalyst
- c)Catalyst found in organisms
- d)Very active vegetable catalyst
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes are
a)
Substances made by chemists to activate washing powder
b)
Synthetic catalyst
c)
Catalyst found in organisms
d)
Very active vegetable catalyst
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Enzymes are biological catalysts produced by all living organisms. They facilitate the biochemical reactions that enable microbes, plants and animals to function. Playing a crucial role in digestion, enzymes help to break down food components into simple molecules for absorption and assimilation.
The factors which are responsible for the stability of lyophilic sols are:
- a)Size of the colloidal particles
- b)Charge of the colloidal particles
- c)Charge and solvation of the colloidal particles
- d)Solvation of the colloidal particles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The factors which are responsible for the stability of lyophilic sols are:
a)
Size of the colloidal particles
b)
Charge of the colloidal particles
c)
Charge and solvation of the colloidal particles
d)
Solvation of the colloidal particles

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Charge and solvation of the colloidal particles
Lyophilic sols are colloidal solutions in which the dispersed particles have a strong attraction to the solvent. The stability of lyophilic sols is due to the charge and solvation of the colloidal particles. The particles carry a charge and are surrounded by a layer of solvent molecules, known as the solvation layer. This solvation layer acts as a barrier between the particles, preventing them from coming into contact and aggregating. The charge of the particles also helps to repel them and keep them dispersed.
The size of the colloidal particles is not a direct factor in the stability of lyophilic sols. The charge and solvation of the particles are more important in maintaining stability.
Solvation of the colloidal particles is one of the factors that contribute to the stability of lyophilic sols, but not the only one, it should be combined with the charge of the colloidal particles.
Which of the following statements about physical adsorption is not correct ?- a)It is usually monolayer
- b)It is reversible in nature
- c)It involves van der Weals interactions between adsorbent and adsorbate
- d)It involves small value of adsorption
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about physical adsorption is not correct ?
a)
It is usually monolayer
b)
It is reversible in nature
c)
It involves van der Weals interactions between adsorbent and adsorbate
d)
It involves small value of adsorption
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Physical adsorption is a multilayer phenomenon
In which of the following systems, the dispersed phase and dispersion medium are both solid?- a)Foam
- b)Dust storm
- c)Paints
- d)Colored glass
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following systems, the dispersed phase and dispersion medium are both solid?
a)
Foam
b)
Dust storm
c)
Paints
d)
Colored glass
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The dispersion medium may be a gas, a liquid, or a solid and the dispersed phase may also be any of these, with the exception of one gas in another. ... A system of solid substance or water-insoluble liquid colloidally dispersed in liquid water is called a hydrosol.
Which phenomenon is represented by the following diagram ?
- a)adsorption
- b)absorption
- c)desorption
- d)sorption
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phenomenon is represented by the following diagram ?
a)
adsorption
b)
absorption
c)
desorption
d)
sorption
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where concentration of the molecules, is more on the surface than in the core.
Milk is an emulsion in which:- a)Acid particles are dispersed in water
- b)Base particles are dispersed in water
- c)Water particles are dispersed in liquid fat
- d)Liquid fat particles are dispersed in water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Milk is an emulsion in which:
a)
Acid particles are dispersed in water
b)
Base particles are dispersed in water
c)
Water particles are dispersed in liquid fat
d)
Liquid fat particles are dispersed in water
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
An emulsion is a temporarily stable mixture of immiscible fluids, such as oil and water, achieved by finely dividing one phase into very small droplets. Common emulsions can be oil suspended in water or aqueous phase (o/w) or water suspended in oil (w/o).
Which one is not true about catalyst ?- a)The catalyst is unchanged at the end of the reaction
- b)A small quantity of catalyst is often sufficient to bring about considerable amount of reaction
- c)The catalyst accelerates the reaction
- d)In a reversible recation the catalyst alters the equilibrium position
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not true about catalyst ?
a)
The catalyst is unchanged at the end of the reaction
b)
A small quantity of catalyst is often sufficient to bring about considerable amount of reaction
c)
The catalyst accelerates the reaction
d)
In a reversible recation the catalyst alters the equilibrium position
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
The catalyst is unchanged chemically at the end of a reaction. During the reaction between the chemical intermediates and the reactants, the catalyst is regenerated.
The catalyst accelerated the reaction. A catalyst is a substance which speeds up a reaction but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
In a reversible reaction, the catalyst does not alter the equilibrium position but increases the rate by decreasing activation energy and temperature.
A small amount of catalyst is often sufficient to bring about a large change in reaction. Catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant, forming chemical intermediates that are able to react more readily with each other or with another reactant to form the desired end product.
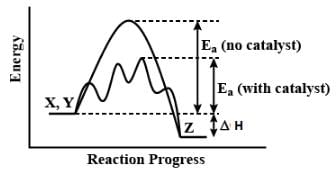
The catalyst accelerated the reaction. A catalyst is a substance which speeds up a reaction but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
In a reversible reaction, the catalyst does not alter the equilibrium position but increases the rate by decreasing activation energy and temperature.
A small amount of catalyst is often sufficient to bring about a large change in reaction. Catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant, forming chemical intermediates that are able to react more readily with each other or with another reactant to form the desired end product.

When body temperature is high, doctors advice consumption of light food. This is because- a)At high temperature, body is weak
- b)The body temperature can increase further
- c)At high temperature certain enzymes get denatured and cannot function well
- d)At high temperature coenzymes are not available
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When body temperature is high, doctors advice consumption of light food. This is because
a)
At high temperature, body is weak
b)
The body temperature can increase further
c)
At high temperature certain enzymes get denatured and cannot function well
d)
At high temperature coenzymes are not available
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
As the temperature increases, so does the rate of reaction. But very high temperatures denature enzymes. The graph shows the typical change in an enzyme's activity with increasing temperature. The enzyme activity gradually increases with temperature up to around 37degC, or body temperature.
A dispersion of AgCl in water is:- a)hydrophobic sol
- b)an emulsion
- c)an aerosol
- d)hydrophilic colloid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A dispersion of AgCl in water is:
a)
hydrophobic sol
b)
an emulsion
c)
an aerosol
d)
hydrophilic colloid
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
AgCl beinga covalent molecule is insoluble in water and hence hydrophobic.
Adsorbate is represented by which spheres in the following diagram.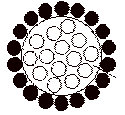
- a)White
- b)Black
- c)both
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorbate is represented by which spheres in the following diagram.
a)
White
b)
Black
c)
both
d)
none
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Black spheres adhering on the surface represent adsorbate.
Which substance is added to water containing suspended impurities to coagulate the suspended impurities and make water fit for drinking purposes.- a)Milk of magnesia
- b)KCl
- c)NaCl
- d)Alum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which substance is added to water containing suspended impurities to coagulate the suspended impurities and make water fit for drinking purposes.
a)
Milk of magnesia
b)
KCl
c)
NaCl
d)
Alum

|
Aadhar Academy answered |
The correct answer is Option D
When alum is added to raw water it reacts with the bicarbonates alkalinities present in water and forms a gelatinous precipitate.
It neutralizes all the suspended impurities of water resulting in their coagulation.
When alum is added to raw water it reacts with the bicarbonates alkalinities present in water and forms a gelatinous precipitate.
It neutralizes all the suspended impurities of water resulting in their coagulation.
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided in how many categories?- a)1
- b)2
- c)6
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided in how many categories?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
6
d)
4
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided into two categories, namely, lyophilic and lyophobic:
1. Lyophilic colloids: The colloidal solution in which the particles of the dispersed phase have a greater affinity for the dispersion medium are called lyophilic colloids. The common example of lyophilic colloids are glue, gelatin, starch, protein, rubber, etc.
2. Lyophobic colloids: The colloidal solutions in which the particles of the dispersed phase have no affinity or love rather have hatred for the dispersion medium are called lyophobic colloids.
In heterogenous catalysis of a gaseous reactants over solid catalyst- a)Reaction occurs on the surface of catalyst
- b)Reaction occurs when gases diffuse towards the surface of catalyst
- c)Reaction starts when gases are about to desorb from the catalyst surface
- d)Reaction occurs before adsorption of reactants
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In heterogenous catalysis of a gaseous reactants over solid catalyst
a)
Reaction occurs on the surface of catalyst
b)
Reaction occurs when gases diffuse towards the surface of catalyst
c)
Reaction starts when gases are about to desorb from the catalyst surface
d)
Reaction occurs before adsorption of reactants
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Catalysts may be gases, liquids, or solids. In homogeneous catalysis, the catalyst is molecularly dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactants. In heterogeneous catalysis the reacta
Which of the following metal solution cannot be prepared by Bredig’s arc method?
- a)Platinum
- b)Gold
- c)Copper sol
- d)Potassium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following metal solution cannot be prepared by Bredig’s arc method?
a)
Platinum
b)
Gold
c)
Copper sol
d)
Potassium

|
Manisha Choudhary answered |
Bredig's arc method is a method of preparation of the colidal solution of metals such as silver, gold, platinum etc. Copper sol is not prepared using Bredig's arc method.
Why is the emulsion stable with the egg yolk?- a)Due to presence of fat in it.
- b)Due to presence of lecithin in it.
- c)Due to presence of albumin in it.
- d)Due to presence of proteins in it.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is the emulsion stable with the egg yolk?
a)
Due to presence of fat in it.
b)
Due to presence of lecithin in it.
c)
Due to presence of albumin in it.
d)
Due to presence of proteins in it.
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
Explanation:
Emulsion is a mixture of two immiscible liquids, where one liquid is dispersed in the other liquid in the form of small droplets. An emulsifying agent is required to stabilize the emulsion and prevent the separation of the two liquids. Egg yolk is one such emulsifying agent.
Presence of Lecithin:
Egg yolk contains a phospholipid called lecithin, which is a natural emulsifier. Lecithin has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which makes it capable of forming a stable emulsion by reducing the surface tension at the interface between the two immiscible liquids. The hydrophilic head of lecithin binds with water molecules, while the hydrophobic tail binds with oil droplets. This creates a stable emulsion, which does not separate easily.
Role of Lecithin in Emulsification:
Lecithin molecules form a protective barrier around the oil droplets, preventing them from coalescing and forming larger droplets. The emulsion remains stable due to the presence of lecithin, which prevents the oil droplets from coming together and separating from the water phase. This makes egg yolk an excellent emulsifying agent for making mayonnaise, hollandaise sauce, and other emulsified sauces.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the presence of lecithin in egg yolk makes it an excellent emulsifying agent. Lecithin molecules form a stable emulsion by reducing the surface tension at the interface between the two immiscible liquids. This makes egg yolk a popular ingredient in the food industry for preparing emulsified sauces, dressings, and other products that require stable emulsions.
Emulsion is a mixture of two immiscible liquids, where one liquid is dispersed in the other liquid in the form of small droplets. An emulsifying agent is required to stabilize the emulsion and prevent the separation of the two liquids. Egg yolk is one such emulsifying agent.
Presence of Lecithin:
Egg yolk contains a phospholipid called lecithin, which is a natural emulsifier. Lecithin has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which makes it capable of forming a stable emulsion by reducing the surface tension at the interface between the two immiscible liquids. The hydrophilic head of lecithin binds with water molecules, while the hydrophobic tail binds with oil droplets. This creates a stable emulsion, which does not separate easily.
Role of Lecithin in Emulsification:
Lecithin molecules form a protective barrier around the oil droplets, preventing them from coalescing and forming larger droplets. The emulsion remains stable due to the presence of lecithin, which prevents the oil droplets from coming together and separating from the water phase. This makes egg yolk an excellent emulsifying agent for making mayonnaise, hollandaise sauce, and other emulsified sauces.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the presence of lecithin in egg yolk makes it an excellent emulsifying agent. Lecithin molecules form a stable emulsion by reducing the surface tension at the interface between the two immiscible liquids. This makes egg yolk a popular ingredient in the food industry for preparing emulsified sauces, dressings, and other products that require stable emulsions.
The relation between extent of adsorbtion (x/m) and pressure at constant temperature is called as:- a)isochore
- b)isomer
- c)isobar
- d)isotherm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The relation between extent of adsorbtion (x/m) and pressure at constant temperature is called as:
a)
isochore
b)
isomer
c)
isobar
d)
isotherm
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Freundlich adsorption isotherm gives an empirical relationship between the quantity of gas adsorbed by the unit mass of solid adsorbent (x/m) and pressure at a specific temperature.
Which of the following statement is correct about Langmuir’s adsorption ?- a)It is not specific in nature
- b)It occurs at low temperature
- c)It is reversible in nature
- d)It forms monolayer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is correct about Langmuir’s adsorption ?
a)
It is not specific in nature
b)
It occurs at low temperature
c)
It is reversible in nature
d)
It forms monolayer
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Adsorbed molecules do not interact. All adsorption occurs through the same mechanism. At the maximum adsorption, only a monolayer is formed: molecules of adsorbate do not deposit on other, already adsorbed, molecules of adsorbate, only on the free surface of the adsorbent.
Which of the following is not exhibited by sols?- a)Flocculation
- b)Tyndall effect
- c)Paramagnetism
- d)Absorption
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not exhibited by sols?
a)
Flocculation
b)
Tyndall effect
c)
Paramagnetism
d)
Absorption
|
|
Shalini Choudhary answered |
Absorption, Tyndall effect and flocculation all are related to sol but paramagnetism is not represented by sol.
The basic principle of Cottrell precipitator is- a)Peptization
- b)Neutralization of charge on colloids
- c)Le Chatelier’s principle
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic principle of Cottrell precipitator is
a)
Peptization
b)
Neutralization of charge on colloids
c)
Le Chatelier’s principle
d)
None of these

|
Ashwin Yadav answered |
It is used for decreasing air pollution by neutralizing the colloid.
Statement-1 : All colloidal dispersions give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling pointelevation. Statement-2 : Tydall effect is due to scattering of light from the surface of colloidal particles.- a)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : All colloidal dispersions give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling pointelevation.
Statement-2 : Tydall effect is due to scattering of light from the surface of colloidal particles.
a)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
The Tyndall effect is seen due to light scattering by particles in a colloid or particles in a fine suspension. So, solution particles show the Tyndall effect due to the scattering of light and scattering is directly proportional to the size of sol particles.
Also, colloidal particles have a high molar mass so, their mole fraction is very less causing low colligative properties and hence, all colloidal dispersion give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling point elevation.
Also, colloidal particles have a high molar mass so, their mole fraction is very less causing low colligative properties and hence, all colloidal dispersion give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling point elevation.
Which gas will be adsorbed on a solid to greater extent.- a)A gas having non polar molecule
- b)A gas having highest critical temperature (Tc)
- c)A gas having lowest critical temperature.
- d)A gas having highest critical pressure.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gas will be adsorbed on a solid to greater extent.
a)
A gas having non polar molecule
b)
A gas having highest critical temperature (Tc)
c)
A gas having lowest critical temperature.
d)
A gas having highest critical pressure.
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
A gas with high critical temperature has high vander waal force due to which they are more easily liquefiable & hence more easily adsorb as adsorption decreases their energy
When do particles aggregate to form micelles?- a)below craft temperature
- b)below CMC
- c)low concentration
- d)high concentration and above craft temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When do particles aggregate to form micelles?
a)
below craft temperature
b)
below CMC
c)
low concentration
d)
high concentration and above craft temperature
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
In high concentration, particles aggregate to form micelles; it happens above Tk called kraft’s temperature and critical micelle concentration (CMC). If the concentration is low and it forms a true solution.
In high concentration, particles aggregate to form micelles; it happens above Tk called kraft’s temperature and critical micelle concentration (CMC). If the concentration is low and it forms a true solution.
100 mL of a colloidal solution is completely precipitated by addition of 5 mL of 1 M Nacl solution . Calculate the coagulation value of Nacl . - a)200
- b)100
- c)50
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
100 mL of a colloidal solution is completely precipitated by addition of 5 mL of 1 M Nacl solution . Calculate the coagulation value of Nacl .
a)
200
b)
100
c)
50
d)
25
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Coagulation value is the millimoles of an electrolyte that must be added to 1 L of a colloidal solution for complete coagulation .Therefore , 5 mL of 1 M NaCl = 1/1000 X 5=0.005 OR 5 m moles .
100 mL of a colloidal solution require NaCl for complete coagulation = 50 m moles
Therefore , Coagulation value of NaCl = 50
The formation of micelles takes places above a particular temperature, called as:- a)CMC
- b)Kraft temperature
- c)Boiling point
- d)Specific temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The formation of micelles takes places above a particular temperature, called as:
a)
CMC
b)
Kraft temperature
c)
Boiling point
d)
Specific temperature

|
Syed Hussain answered |
Above this concentration only the surfactants form micelles and micelle formation takes place. To reach this concentration, a temperature is required which is called Critical Micelle temperature or Kraft temperature
A catalyst has no effect on- a)Energy of reactants
- b)Energy of products
- c)Enthalpy change of a reaction
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A catalyst has no effect on
a)
Energy of reactants
b)
Energy of products
c)
Enthalpy change of a reaction
d)
All of the above
|
|
Sanaya Kumar answered |
Effect of Catalyst on a Chemical Reaction
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction. It does so by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, thus making the reaction occur faster. However, a catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products or the enthalpy change of the reaction. The explanation for this is as follows:
Energy of Reactants and Products
The energy of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction depends on the nature and identity of the reactants and products. The catalyst does not affect the nature of the reactants or products, so it has no effect on their energy. The catalyst only affects the rate at which the reactants are converted to products.
Enthalpy Change of a Reaction
The enthalpy change of a reaction is the difference between the energy of the products and the energy of the reactants. It is a measure of the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. The catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products, so it has no effect on the enthalpy change of the reaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a catalyst only affects the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. It does not affect the energy of the reactants or products or the enthalpy change of the reaction. Therefore, option D, "All of the above" is the correct answer.
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction. It does so by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, thus making the reaction occur faster. However, a catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products or the enthalpy change of the reaction. The explanation for this is as follows:
Energy of Reactants and Products
The energy of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction depends on the nature and identity of the reactants and products. The catalyst does not affect the nature of the reactants or products, so it has no effect on their energy. The catalyst only affects the rate at which the reactants are converted to products.
Enthalpy Change of a Reaction
The enthalpy change of a reaction is the difference between the energy of the products and the energy of the reactants. It is a measure of the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. The catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products, so it has no effect on the enthalpy change of the reaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a catalyst only affects the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. It does not affect the energy of the reactants or products or the enthalpy change of the reaction. Therefore, option D, "All of the above" is the correct answer.
Chapter doubts & questions for Surface Chemistry - Online MCQ Tests for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Surface Chemistry - Online MCQ Tests for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup