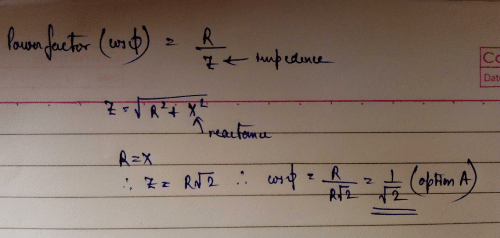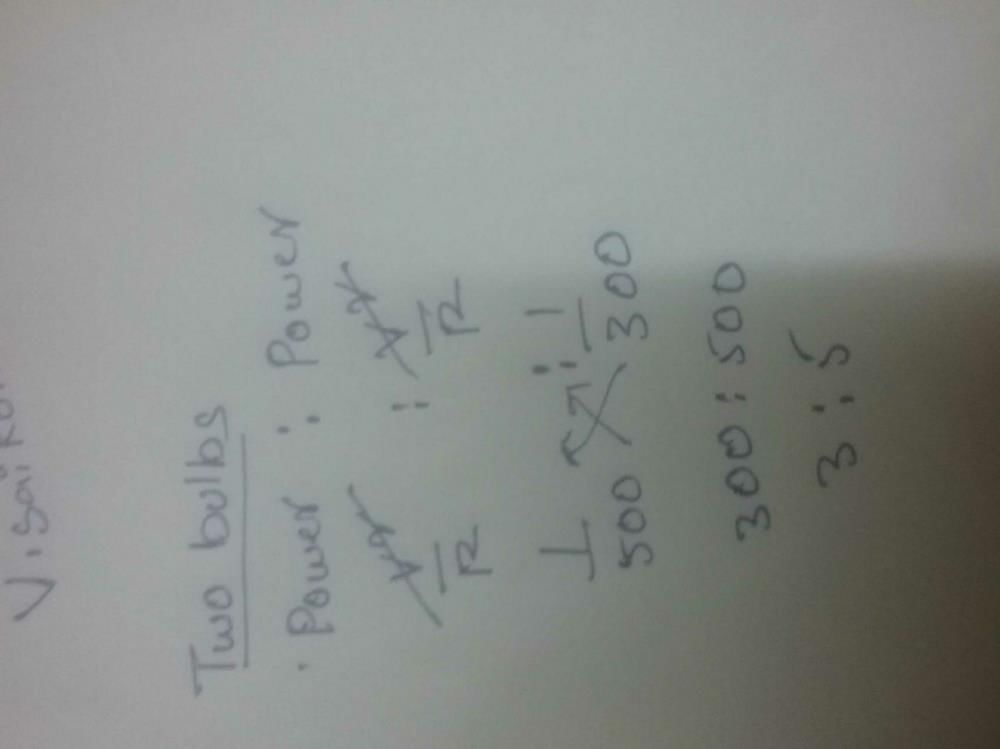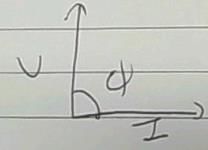All Exams >
JEE >
Online MCQ Tests for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Alternating Currents for JEE Exam
Alternating current is represented by- a)
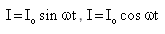
- b)
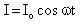
- c)
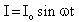
- d)
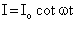
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Alternating current is represented by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Alternating current is an electric current which periodically reverses direction, as opposed to direct current which flows only in one direction. And it can be easily represented by the periodic function.
So, I = Io sin wt or I = lo cos wt.
So, I = Io sin wt or I = lo cos wt.
The average power dissipation in pure resistive circuit is:- a)
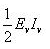
- b)
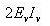
- c)
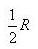
- d)
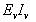
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The average power dissipation in pure resistive circuit is:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Power=IV
Where I=Vrms value of current=IV
And V=Vrms value of voltage=EV
Therefore, P=EVIV
Where I=Vrms value of current=IV
And V=Vrms value of voltage=EV
Therefore, P=EVIV
Find the instantaneous voltage for an a.c. supply of 200V and 75 hertz- a)E = 282.8 sin 50πt
- b)E = 282.8 sin 150πt
- c)E = 282.8 sin 75πt
- d)E = 282.8 sin 100πt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the instantaneous voltage for an a.c. supply of 200V and 75 hertz
a)
E = 282.8 sin 50πt
b)
E = 282.8 sin 150πt
c)
E = 282.8 sin 75πt
d)
E = 282.8 sin 100πt
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Answer :- b
Solution :- f = 75hz
w=2πf
= 2 * π * 75
= 150π
E(max) = (2)^½ E(rms)
E(max) = 1.414 * 200
= 282.8V
E(ins) = E(max)sinwt
E(ins) = 282.8 sin 150πt
Which is more dangerous?- a)220 V a.c
- b)220 V d.c
- c)Both 220 V a.c. and 220 V d.c
- d)Both 220 V a.c. and 220 V d.c. are not dangerous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is more dangerous?
a)
220 V a.c
b)
220 V d.c
c)
Both 220 V a.c. and 220 V d.c
d)
Both 220 V a.c. and 220 V d.c. are not dangerous

|
Gargey Dudhe answered |
Because in DC the potential difference is max 220 V but in AC the potential difference is greater than 220V .So AC is more dangerous than DC.pls upvote and follow me.
In an inductance the current- a)is in phase
- b)leads the voltage
- c)lags the voltage
- d)builds very fast
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an inductance the current
a)
is in phase
b)
leads the voltage
c)
lags the voltage
d)
builds very fast
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In an inductor, current lags behind the input voltage by a phase difference of π/2.
Current and voltage are in the same phase in the resistor whereas current leads the voltage by π/2 in a capacitor.
So, the circuit must contain an inductor only.
Current and voltage are in the same phase in the resistor whereas current leads the voltage by π/2 in a capacitor.
So, the circuit must contain an inductor only.
RMS value of ac i = i1 cos wt + i2 sin wt will be- a)
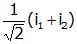
- b)
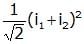
- c)
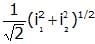
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RMS value of ac i = i1 cos wt + i2 sin wt will be
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
I=(I1)cosωt+(I2)sinωt
(I2)mean=I12cos2ωt+I22sin2ωt+I1I2cosωtsinωt
I12×(1/2)×i22×(1/2)+2I1I2×0
Irms=√(i2)mean=√(I12+I22/2)=(1/√2)( I12+I22)1/2
(I2)mean=I12cos2ωt+I22sin2ωt+I1I2cosωtsinωt
I12×(1/2)×i22×(1/2)+2I1I2×0
Irms=√(i2)mean=√(I12+I22/2)=(1/√2)( I12+I22)1/2
Three bulbs of 40, 60 and 100 watt are connected in series with the source of 200 volt. Then which of the bulb will be glowing the most –- a)100 watt
- b)60 watt
- c)40 watt
- d)All are glowing equally
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three bulbs of 40, 60 and 100 watt are connected in series with the source of 200 volt. Then which of the bulb will be glowing the most –
a)
100 watt
b)
60 watt
c)
40 watt
d)
All are glowing equally
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
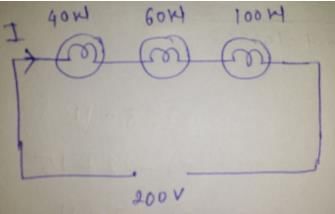
Resistance= (voltage)2/Power
Resistance of 40 W bulb= (200)2/40=1000 ohm
Resistance of 60 W bulb=(200)2/60=666.67 ohm
Resistance of 100 w bulb=(200)2/100=400 ohm
Total resistance= 1000+666.67+400=2066.67 ohm (addition because series circuit)
Now, we calculate current flowing in the bulbs (as we know this is series circuit so same current will flow in the circuit)
Current (I)= Voltage/total resistance=200/2066.67=0.0967 A
Now we find the power consumed by each bulb,
power consumed by 40 W bulb=I2R=(0.0967)2x1000=9.35 W
Power consumed by 60 W bulb=I2xR=(0.0967)2x666.67=6.23 W
Power consumed by 100 W bulb=I2R=(0.0967)2x400=3.74 W
From the above results, we can say that power consumed by a 40 W bulb is more as compared to other bulbs so 40 W glows brighter than other bulbs.
The only component that dissipates energy in ac circuit is:- a)Capacitor
- b)Inductor
- c)Resistors
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The only component that dissipates energy in ac circuit is:
a)
Capacitor
b)
Inductor
c)
Resistors
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The only component that dissipates energy in ac circuit is the resistor because Pure Inductive and pure capacitive circuits have no power loss.
What is the relationship between Em and E0- a)Em=-0.537 E0
- b)Em=-0.737 E0
- c)Em=-0.637 E0
- d)Em=-0.707 E0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relationship between Em and E0
a)
Em=-0.537 E0
b)
Em=-0.737 E0
c)
Em=-0.637 E0
d)
Em=-0.707 E0
|
|
Om Desai answered |
peak value Em=2E0/π
so 2/π value is 0.637
therefore,
Em=-0.637 E0
so 2/π value is 0.637
therefore,
Em=-0.637 E0
The domestic power supply is at 220 volt. The amplitude of emf will be- a)220 V
- b)110 V
- c)311 V
- d)None of this
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The domestic power supply is at 220 volt. The amplitude of emf will be
a)
220 V
b)
110 V
c)
311 V
d)
None of this

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
We know: Vrms=Vo/√2
Substituting values (Here RMS Voltage is 220 V)
We get: Maximum V (or amplitude) =311V
Substituting values (Here RMS Voltage is 220 V)
We get: Maximum V (or amplitude) =311V
The average value or alternating current for half cycle in terms of I0 is- a)
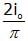
- b)
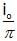
- c)
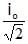
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The average value or alternating current for half cycle in terms of I0 is
a)
b)
c)
d)
0
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
For alternating current average value is taken for half cycles only,
Let, I=I0sinωt where ω=2π/T

=[(I0/ω) cosωt]oT/2 x 2/T
Iavg=2Io/ π
Let, I=I0sinωt where ω=2π/T

=[(I0/ω) cosωt]oT/2 x 2/T
Iavg=2Io/ π
Admittance is reciprocal of- a)Susceptance
- b)Reactance
- c)Impedance
- d)Capacitance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Admittance is reciprocal of
a)
Susceptance
b)
Reactance
c)
Impedance
d)
Capacitance

|
Aashika Packiaselvam. answered |
Look.. Impendenc means a kind of opposition to a steady electric current ie. resistance. While admittance is a measure to how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. Here by looking at the definition itself, we can clearly say that they are inverse of each other.
What is value of power factor if Ø = 90°- a)0
- b)0.5
- c)1
- d)infinite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is value of power factor if Ø = 90°
a)
0
b)
0.5
c)
1
d)
infinite
|
|
Sidharth Gupta answered |
Power factor = cos(angle ) that is in this case 90 so cos90 is zero
An ac circuit, the current is given by i = 4 sin (100pt + 30º) ampere. The current becomes maximum first time (after t = 0) at t equal to- a)(1/200) sec
- b)(1/300) sec
- c)(1/50) sec
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An ac circuit, the current is given by i = 4 sin (100pt + 30º) ampere. The current becomes maximum first time (after t = 0) at t equal to
a)
(1/200) sec
b)
(1/300) sec
c)
(1/50) sec
d)
None of the above
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
i=4sin(100πt+ π/6)
For I to be maximum
di/dt=0
therefore,4x100π(cos(100πt+π/6)=0
therefore, ωs(100πt+ π/6)=0
for the first time cosθ=0 at π/2
⇒ 100πt+ π/6= π/2
⇒ 100πt= π/3
⇒ πt= π/300
T=1/300
For I to be maximum
di/dt=0
therefore,4x100π(cos(100πt+π/6)=0
therefore, ωs(100πt+ π/6)=0
for the first time cosθ=0 at π/2
⇒ 100πt+ π/6= π/2
⇒ 100πt= π/3
⇒ πt= π/300
T=1/300
Power in an ac circuit is equal to- a)Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current
- b)Instantaneous voltage X current at an instant
- c)Voltage at an instant X Instantaneous current
- d)Both b and c
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Power in an ac circuit is equal to
a)
Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current
b)
Instantaneous voltage X current at an instant
c)
Voltage at an instant X Instantaneous current
d)
Both b and c

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Explanation:
Power in an AC circuit is equal to Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current:
- In an AC circuit, both voltage and current vary with time, and power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
- Power in an AC circuit is given by the product of the instantaneous voltage and the instantaneous current at any given moment.
- This means that at any instant, the power being dissipated or consumed in the circuit can be calculated by multiplying the instantaneous voltage and current values at that particular moment.
- Mathematically, the formula for power in an AC circuit is P = V(t) * I(t), where P is power, V(t) is the instantaneous voltage, and I(t) is the instantaneous current at a given time t.
- Therefore, the correct answer is A: Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current.
Power in an AC circuit is equal to Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current:
- In an AC circuit, both voltage and current vary with time, and power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
- Power in an AC circuit is given by the product of the instantaneous voltage and the instantaneous current at any given moment.
- This means that at any instant, the power being dissipated or consumed in the circuit can be calculated by multiplying the instantaneous voltage and current values at that particular moment.
- Mathematically, the formula for power in an AC circuit is P = V(t) * I(t), where P is power, V(t) is the instantaneous voltage, and I(t) is the instantaneous current at a given time t.
- Therefore, the correct answer is A: Instantaneous voltage X Instantaneous current.
Given the instantaneous value of current from a.c. source is I = 8 sin 623t. Find the r.m.s value of current- a)5.656 A
- b)8 A
- c)2.848 A
- d)1.414 A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the instantaneous value of current from a.c. source is I = 8 sin 623t. Find the r.m.s value of current
a)
5.656 A
b)
8 A
c)
2.848 A
d)
1.414 A
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Compare the given eqn. with the standard from I=I0sinωt
I0=8, Irms=I0/√2=8/√2=5.656A
I0=8, Irms=I0/√2=8/√2=5.656A
A coil of inductance 0.1 H is connected to an alternating voltage generator of voltage E = 100 sin (100t) volt. The current flowing through the coil will be- a)I = 10
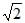 sin (100t) A
sin (100t) A - b)I = 10
 cos (100t) A
cos (100t) A - c)I = _10 sin (100t) A
- d)I = _10 cos (100t) A
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A coil of inductance 0.1 H is connected to an alternating voltage generator of voltage E = 100 sin (100t) volt. The current flowing through the coil will be
a)
I = 10 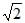 sin (100t) A
sin (100t) A
b)
I = 10  cos (100t) A
cos (100t) A
c)
I = _10 sin (100t) A
d)
I = _10 cos (100t) A
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
L =0.14
E=100sin(100t)
⇒XL=wL=100×0.1
=10Ω
⇒io=Eo/XL=100/10=10A
⇒i=iosin(100t− π/2)
⇒i=−iosin[(π/2)−100]
So we get
⇒i=−10cos(100t)A
therefore, option D is correct.
E=100sin(100t)
⇒XL=wL=100×0.1
=10Ω
⇒io=Eo/XL=100/10=10A
⇒i=iosin(100t− π/2)
⇒i=−iosin[(π/2)−100]
So we get
⇒i=−10cos(100t)A
therefore, option D is correct.
In a series LCR what will be phase difference between voltage drop across inductor and capacitor- a)0
- b)90
- c)180
- d)45
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a series LCR what will be phase difference between voltage drop across inductor and capacitor
a)
0
b)
90
c)
180
d)
45

|
Rajendri Rani answered |
Because In C-R circuit current lead by π/2 and in L-R circuit voltage lead by π/2 so after drawing the phasor diagram and current will be same so the phase difference is 2π
In an L.C.R series circuit R = 1W, XL = 1000W and XC = 1000W. A source of 100 m.volt is connected in the circuit the current in the circuit is- a)100 m.Amp
- b)1 m.Amp
- c)0.1 m.Amp
- d)10 m.Amp
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an L.C.R series circuit R = 1W, XL = 1000W and XC = 1000W. A source of 100 m.volt is connected in the circuit the current in the circuit is
a)
100 m.Amp
b)
1 m.Amp
c)
0.1 m.Amp
d)
10 m.Amp
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |

R=1W
XL=1000W
XC=1000W
Z= Z= √ (R2+(XL-XC)2)
=√(12+(1000-1000)2)
Z=1W
I=V/Z=100/1
I=1000A
If a capacitor of capacitance 9.2F has a voltage of 22.5V across it. Calculate the energy of the capacitor.- a)5062.5 J
- b) 2328.75 J
- c)50.625 J
- d)50625 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a capacitor of capacitance 9.2F has a voltage of 22.5V across it. Calculate the energy of the capacitor.
a)
5062.5 J
b)
2328.75 J
c)
50.625 J
d)
50625 J
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
We know that,
ω=(1/2)CV2
After putting the values,
=(1/2)x9.2x22.5x22.5
=2328.75J
Hence option B is the answer.
ω=(1/2)CV2
After putting the values,
=(1/2)x9.2x22.5x22.5
=2328.75J
Hence option B is the answer.
What is the unit of Capacitive Reactance Xc?- a)Ohm
- b)Ohm2
- c)Ohm-1
- d)mhO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the unit of Capacitive Reactance Xc?
a)
Ohm
b)
Ohm2
c)
Ohm-1
d)
mhO
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The opposition offered by a capacitor for the flow of A.C is called capacitive reactance.
Xc = 1/wC
it's SI unit is ohm
Xc = 1/wC
it's SI unit is ohm
Power factor of an L-R series circuit is 0.6 and that of a C_R series circuit is 0.5. If the element (L, C, and R) of the two circuits are joined in series the power factor of this circuit is found to be 1. The ratio of the resistance in the L-R circuit to the resistance in the C-R circuit is- a)6/5
- b)5/6
- c)
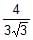
- d)
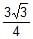
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Power factor of an L-R series circuit is 0.6 and that of a C_R series circuit is 0.5. If the element (L, C, and R) of the two circuits are joined in series the power factor of this circuit is found to be 1. The ratio of the resistance in the L-R circuit to the resistance in the C-R circuit is
a)
6/5
b)
5/6
c)
d)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
cosϕ1=0.6=5/3
tanϕ1=4/3= XC/R2…(1)
cosϕ1=0.5=1/2
tanϕ2=√3= R2/XC…(2)
From (1) and (2)3√3/4=R1/R2
tanϕ1=4/3= XC/R2…(1)
cosϕ1=0.5=1/2
tanϕ2=√3= R2/XC…(2)
From (1) and (2)3√3/4=R1/R2
The current amplitude in a pure inductor in a radio receiver is to be 250 μA when the voltage amplitude is 3.60 V at a frequency of 1.60 MHz (at the upper end of the AM broadcast band). If the voltage amplitude is kept constant, what will be the current amplitude through this inductor at 16.0 MHz?- a)20.0 μA
- b)33.0 μA
- c).35.0 μA
- d)25.0 μA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The current amplitude in a pure inductor in a radio receiver is to be 250 μA when the voltage amplitude is 3.60 V at a frequency of 1.60 MHz (at the upper end of the AM broadcast band). If the voltage amplitude is kept constant, what will be the current amplitude through this inductor at 16.0 MHz?
a)
20.0 μA
b)
33.0 μA
c)
.35.0 μA
d)
25.0 μA
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
I0=250μA, v0=3.6v . v=1.6x106 Hz
Here,
(Reactance of inductance) XL=ωL
XL=2πv X L
v0/I0=2πv x L
3.6/2.5x10-4=2πx1.6x10-6 x L
0.14x104-6=L
L=0.14x10-2H
Now for v=16.0x106Hz
XL=2πv X L
=2πx16x106x14x10-4
XL=1407x102Ω
Now,
v0=I0 x XL
3.6/1407x102=I0 [∵v0=kept constant.]
I0=0.00256x10-2
I0=25.6μA
Here,
(Reactance of inductance) XL=ωL
XL=2πv X L
v0/I0=2πv x L
3.6/2.5x10-4=2πx1.6x10-6 x L
0.14x104-6=L
L=0.14x10-2H
Now for v=16.0x106Hz
XL=2πv X L
=2πx16x106x14x10-4
XL=1407x102Ω
Now,
v0=I0 x XL
3.6/1407x102=I0 [∵v0=kept constant.]
I0=0.00256x10-2
I0=25.6μA
Find the series resonance frequency when L = 0.09 H, C = 25 F- a)10.6 s-1
- b)0.106 s-1
- c)1.66 s-1
- d)1.06 s-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the series resonance frequency when L = 0.09 H, C = 25 F
a)
10.6 s-1
b)
0.106 s-1
c)
1.66 s-1
d)
1.06 s-1
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
ω=1/√LC
ω=1√0.09x25
ω=0.666
ω=2πf
f=0.666/(2 x 3.14)
f=0.106 s-1
ω=1√0.09x25
ω=0.666
ω=2πf
f=0.666/(2 x 3.14)
f=0.106 s-1
Let f = 50 Hz, and C = 100 mF in an AC circuit containing a capacitor only. If the peak value of the current in the circuit is 1.57 A at t = 0. The expression for the instantaneous voltage across the capacitor will be- a) E = 50 sin (100 pt – p/2)
- b)E = 100 sin (50 pt)
- c)E = 50 sin 100 pt
- d)E = 50 sin (100 pt + p/2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Let f = 50 Hz, and C = 100 mF in an AC circuit containing a capacitor only. If the peak value of the current in the circuit is 1.57 A at t = 0. The expression for the instantaneous voltage across the capacitor will be
a)
E = 50 sin (100 pt – p/2)
b)
E = 100 sin (50 pt)
c)
E = 50 sin 100 pt
d)
E = 50 sin (100 pt + p/2)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Peak value of voltage
V0=i0XC =i0/2πvC
=>1.57/(2x3.14x50x100x10-6)
Hence if equation of current i = io sin ω t then in capacitive circuit voltage is
V=V0 (ωt - π/2)
=>50[sin2π x50t- (π/2)]
=50[100πt-(π/2)]
V0=i0XC =i0/2πvC
=>1.57/(2x3.14x50x100x10-6)
Hence if equation of current i = io sin ω t then in capacitive circuit voltage is
V=V0 (ωt - π/2)
=>50[sin2π x50t- (π/2)]
=50[100πt-(π/2)]
In a series resonant L_C_R circuit, if L is increased by 25% and C is decreased by 20%, then the resonant frequency will- a)Increase by 10%
- b)Decrease by 10%
- c)Remain unchanged
- d)Increase by 2.5%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a series resonant L_C_R circuit, if L is increased by 25% and C is decreased by 20%, then the resonant frequency will
a)
Increase by 10%
b)
Decrease by 10%
c)
Remain unchanged
d)
Increase by 2.5%
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
v0=1/2π√(LC)
⇒In this question,
L’=L+25% of L
=L+(L/4)=5L/4
And C’=C-20% of C
=C-(C/5)=4C/5
Hence, v0=1/2π√(L’C’)
=1/2π√[(5L/4) x (4C/5)]
=1/2π√(LC)=v0
The answer is option C, remains unchanged.
⇒In this question,
L’=L+25% of L
=L+(L/4)=5L/4
And C’=C-20% of C
=C-(C/5)=4C/5
Hence, v0=1/2π√(L’C’)
=1/2π√[(5L/4) x (4C/5)]
=1/2π√(LC)=v0
The answer is option C, remains unchanged.
Virtual value or effective value of a.c. is- a)-0.637I0
- b)-0.707I0
- c)0.637I0
- d)0.707I0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Virtual value or effective value of a.c. is
a)
-0.637I0
b)
-0.707I0
c)
0.637I0
d)
0.707I0
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
R.M.S. value or effective value or virtual value of Alternating current is given by
Irms = eo/√2 = 𝐼𝑝𝑒𝑎𝑘/√2 = 0.707 Io.
Irms = eo/√2 = 𝐼𝑝𝑒𝑎𝑘/√2 = 0.707 Io.
A hair dryer meant for 110V 60Hz is to be used in India . If 220 V is the supply voltage in India , the turns ratio for a transformer would be- a)step-down 2.5:1
- b)step-up 1:2
- c)step-down 3:1
- d)step-down 2:1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hair dryer meant for 110V 60Hz is to be used in India . If 220 V is the supply voltage in India , the turns ratio for a transformer would be
a)
step-down 2.5:1
b)
step-up 1:2
c)
step-down 3:1
d)
step-down 2:1
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Here Vp=220V Vs=110V
As we know the relation between V and n,
As,
Ve/Vs=np/ns ->220/110
Np/ns=2/1=2:1
Therefore, no. of turns in primary is greater than no. of turns in secondary,
Hence, it is a step-down transformer.
As we know the relation between V and n,
As,
Ve/Vs=np/ns ->220/110
Np/ns=2/1=2:1
Therefore, no. of turns in primary is greater than no. of turns in secondary,
Hence, it is a step-down transformer.
The effective value of current i = 2 sin 100p t + 2 sin (100pt + 30º) is- a)
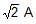
- b)
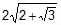
- c)4
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The effective value of current i = 2 sin 100p t + 2 sin (100pt + 30º) is
a)
b)
c)
4
d)
None

|
Learners Habitat answered |
cosθ=sin(90o−θ)
sinα+sinβ=2sin (α+β/2)cos (α−β/2)
i=2sin100πt+2cos(100πt+30o)
=2sin100πt+2sin(90o−(100πt+30o))
=2sin100πt+2sin(60o−100πt)
=2 x 2 x sin [{(100−100)πt+60o }/2] x cox[(100+100)πt−60o/2]
=4 x sin30o∗cos(100πt−30o)
=4x(1/2) x cos(100πt−30o)
=2cos(100πt−30o)
therefore, Io=2A
Irms=2 / √2= √2A
sinα+sinβ=2sin (α+β/2)cos (α−β/2)
i=2sin100πt+2cos(100πt+30o)
=2sin100πt+2sin(90o−(100πt+30o))
=2sin100πt+2sin(60o−100πt)
=2 x 2 x sin [{(100−100)πt+60o }/2] x cox[(100+100)πt−60o/2]
=4 x sin30o∗cos(100πt−30o)
=4x(1/2) x cos(100πt−30o)
=2cos(100πt−30o)
therefore, Io=2A
Irms=2 / √2= √2A
Capacitive reactance of the capacitor depends upon- a)Capacitance of condenser
- b)Frequency
- c)Both a and b
- d)Neither a nor b
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Capacitive reactance of the capacitor depends upon
a)
Capacitance of condenser
b)
Frequency
c)
Both a and b
d)
Neither a nor b

|
Adi Adi answered |
The formula for capacitive reactance (Xc) is Xc=1/(wC) so it clearly depends upon both frequency and capacitance.
In an a.c. circuit voltage V and current i are given by V = 100 sin 100 t volts, i = 100 sin (100t + p/3) mA. The power dissipated in the circuit is :- a)104 W
- b)10 W
- c) 2.5 W
- d)5 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an a.c. circuit voltage V and current i are given by V = 100 sin 100 t volts, i = 100 sin (100t + p/3) mA. The power dissipated in the circuit is :
a)
104 W
b)
10 W
c)
2.5 W
d)
5 W
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Vrms = 100/√2 V
Irms = 100/√2 mA
= 10-1/√2 A
π/3 = 30º
Average power = Vrms×Irms× cos
= (100/√2)×(10-1√2)× cos 30º
= 10/2×(1/2)
= 10/4
= 2.5W
Irms = 100/√2 mA
= 10-1/√2 A
π/3 = 30º
Average power = Vrms×Irms× cos
= (100/√2)×(10-1√2)× cos 30º
= 10/2×(1/2)
= 10/4
= 2.5W
Find the total voltage applied in a series RLC circuit when i=3mA, VL=30V, VC=18V and R=1000 ohms.
13.95V
2 32.67V
3 6.67V
4 51V
2
3
4
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Explanation: Total voltage= VR+VL+VC.
VR=1000x3x10-3=3V.
Therefore, total voltage = 30+18+3=51V.
VR=1000x3x10-3=3V.
Therefore, total voltage = 30+18+3=51V.
Ratio 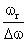 is equal to
is equal to- a)C
- b)L
- c)R
- d)Q
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ratio 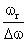 is equal to
is equal to
a)
C
b)
L
c)
R
d)
Q

|
Shubham Rajput answered |
It is Q i.e. quality factor
A 1.0 mH inductance, a10μF capacitance and a 5.0 ohm resistance are connected series to an a.c. source. It is found that inductor and the capacitor show equal reactance. The reactance should be nearest to:- a)10 ohm
- b)32 ohm
- c)3.2 ohm
- d)100 ohm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 1.0 mH inductance, a10μF capacitance and a 5.0 ohm resistance are connected series to an a.c. source. It is found that inductor and the capacitor show equal reactance. The reactance should be nearest to:
a)
10 ohm
b)
32 ohm
c)
3.2 ohm
d)
100 ohm
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
From the formula we get,
XL=XC
ωL=1/ωC
⇒ω2=1/LC
⇒ω=1/√Lc
⇒ω=1/√10-3x10-5
⇒ω=104
We also know that,
XL=ωL
⇒XL=104x10-3
⇒XL=10 Ω
Therefore,XL=XC=10Ω
XL=XC
ωL=1/ωC
⇒ω2=1/LC
⇒ω=1/√Lc
⇒ω=1/√10-3x10-5
⇒ω=104
We also know that,
XL=ωL
⇒XL=104x10-3
⇒XL=10 Ω
Therefore,XL=XC=10Ω
L/R has dimensions same as that of- a)Reactance
- b)Capacitance
- c)Resistance
- d)Time
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
L/R has dimensions same as that of
a)
Reactance
b)
Capacitance
c)
Resistance
d)
Time
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
First of all we have to find out dimension of L and R .
We know, relation L answer energy is E = 1/2Li^2
so, dimension of L = dimension of energy/dimension of i2
= [ML2T⁻2]/[A2] = [ML2T⁻2A⁻2]
Similarly we know, relation between R and energy is E = i2Rt
So, dimension of R = dimension of E/dimension of i2t
= [ML2T⁻2][A2T] = [ML2T⁻2A⁻2]
Now, dimension of L/R = dimension of L/dimension of R
= [ML2T⁻2A⁻2][ML2T⁻2A⁻2] = [T]
Hence, answer is [T]
A pure resistance R, pure capacitance C and pure inductance L are connected in series and the impedance of the circuit at resonance is Z0. If they are connected in parallel to each other, the maximum impedance at resonance will be:- a)Less than R
- b)dependent on the values of C and L
- c)Equal to Z0
- d)More than R
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A pure resistance R, pure capacitance C and pure inductance L are connected in series and the impedance of the circuit at resonance is Z0. If they are connected in parallel to each other, the maximum impedance at resonance will be:
a)
Less than R
b)
dependent on the values of C and L
c)
Equal to Z0
d)
More than R
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
If series LCR circuit is present then z={R2+(xl-xc)2}1/2
if resonance is present then XC=CL or VC=CL then Z= Zo
if LCR circuit is in parallel form then in which circuit resonance is also present firstly 1/Z ={(1/R)2+ ((1/xc) –(1/xl))2}1/2 and in resonance conditions XC=CL according to this Z= Zo then option C is the correct answer
if resonance is present then XC=CL or VC=CL then Z= Zo
if LCR circuit is in parallel form then in which circuit resonance is also present firstly 1/Z ={(1/R)2+ ((1/xc) –(1/xl))2}1/2 and in resonance conditions XC=CL according to this Z= Zo then option C is the correct answer
An ac-circuit having supply voltage E consists of a resistor of resistance 3W and an inductor of reactance 4W as shown in the figure. The voltage across the inductor at t = p/w is 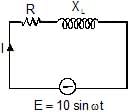
- a)2 volts
- b)10 volts
- c)zero
- d)4.8 volts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An ac-circuit having supply voltage E consists of a resistor of resistance 3W and an inductor of reactance 4W as shown in the figure. The voltage across the inductor at t = p/w is
a)
2 volts
b)
10 volts
c)
zero
d)
4.8 volts

|
EduRev Support answered |
Here,
XL = 4 Ω
R = 3 Ω
Z = √(XL2 + R2)=√(42 + 32)
= 5 Ω
E0 = 10 V
In the LR circuit current in the ckt is given by
I = (E0/Z)sin(ωt - Φ)
Φ = tan-1(XL/R)
=> Φ = tan-1(4/3)
I = (E0/Z)sin(ωt - Φ)
= (10/5) sin(ωt - Φ)
I at t = T/2
= 2sin(ωT/2 – Φ)
= 2sin(π - Φ)
= 2sin(tan-1(4/3))
= 2×0.8
= 1.6 A
Potential difference across the resistor = 1.6×R
= 1.6×3
= 4.8 V
Potential difference across the inductor = 1.6XL
= 1.6×4 = 6.4 V
XL = 4 Ω
R = 3 Ω
Z = √(XL2 + R2)=√(42 + 32)
= 5 Ω
E0 = 10 V
In the LR circuit current in the ckt is given by
I = (E0/Z)sin(ωt - Φ)
Φ = tan-1(XL/R)
=> Φ = tan-1(4/3)
I = (E0/Z)sin(ωt - Φ)
= (10/5) sin(ωt - Φ)
I at t = T/2
= 2sin(ωT/2 – Φ)
= 2sin(π - Φ)
= 2sin(tan-1(4/3))
= 2×0.8
= 1.6 A
Potential difference across the resistor = 1.6×R
= 1.6×3
= 4.8 V
Potential difference across the inductor = 1.6XL
= 1.6×4 = 6.4 V
If a resistor is connected across the voltage source and the frequency of voltage and current wave form is 50Hz, then what is frequency of instantaneous power- a)0 Hz.
- b)100 Hz.
- c) 50 Hz.
- d)150 Hz.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a resistor is connected across the voltage source and the frequency of voltage and current wave form is 50Hz, then what is frequency of instantaneous power
a)
0 Hz.
b)
100 Hz.
c)
50 Hz.
d)
150 Hz.

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
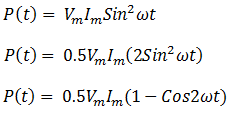 ]
]Therefore, frequency is doubled for the instantaneous power so, frequency of instantaneous power is 100Hz.
When an emf E = 7cos wt is applied across a circuit, the current is I = 5coswt. What is the power factor for the circuit?- a)infinite
- b)3/4
- c)zero
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When an emf E = 7cos wt is applied across a circuit, the current is I = 5coswt. What is the power factor for the circuit?
a)
infinite
b)
3/4
c)
zero
d)
1
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Since E and I are in the same phase.
Therefore, phase difference will be 0 and since power factor= cosx (where x= phase difference) and x =0
therefore, cos x or power factor will be =1
Therefore, phase difference will be 0 and since power factor= cosx (where x= phase difference) and x =0
therefore, cos x or power factor will be =1
Sinusoidal peak potential is 200 volt with frequency 50Hz. It is represented by the equation- a)E = 200 sin 50t
- b)E = 200 sin 314t
- c)E = 200
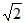 sin 50t
sin 50t - d)E =200
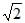 sin 314t
sin 314t
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sinusoidal peak potential is 200 volt with frequency 50Hz. It is represented by the equation
a)
E = 200 sin 50t
b)
E = 200 sin 314t
c)
E = 200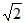 sin 50t
sin 50t
d)
E =200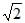 sin 314t
sin 314t

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Given peak potential is 200v
so, amplitude is 200
and frequency is 50Hz
so angular frequency is 2.πx50 = 314/sec
so the value is
E = 200sin(314t)
Hence option B is the correct answer.
so, amplitude is 200
and frequency is 50Hz
so angular frequency is 2.πx50 = 314/sec
so the value is
E = 200sin(314t)
Hence option B is the correct answer.
The percentage increase in the impedance of an ac circuit, when its power factor changes form 0.866 to 0.5 is (Resistance constant)- a)73.2%
- b)86.6%
- c)90.8%
- d)66.6%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage increase in the impedance of an ac circuit, when its power factor changes form 0.866 to 0.5 is (Resistance constant)
a)
73.2%
b)
86.6%
c)
90.8%
d)
66.6%
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Power factor (cosϕ)=R/Z1
For first case, power factor=0.866
Or, R/ Z1=0.866
Or,Z1=1.154R
For second case, power factor=>0.5
Cosϕ2=>R/Z2=>0.5, Z2=2R.
% increase=>[(Z2-Z1)/Z1] x100
So, [{(2R)-(1.154R)}/(1.154R)]x100=73.2%
So the correct answer is option A.
For first case, power factor=0.866
Or, R/ Z1=0.866
Or,Z1=1.154R
For second case, power factor=>0.5
Cosϕ2=>R/Z2=>0.5, Z2=2R.
% increase=>[(Z2-Z1)/Z1] x100
So, [{(2R)-(1.154R)}/(1.154R)]x100=73.2%
So the correct answer is option A.
The average power dissipation in pure inductance is:- a)
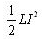
- b)2LI2
- c)zero
- d)
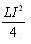
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The average power dissipation in pure inductance is:
a)
b)
2LI2
c)
zero
d)

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Zero .. power = Irms Vrms cosǿ... where ǿ is angle between volatage and current vector... For pure inductance circuit the ǿ=90.. thus power is zero as cos90 is 0
When Ø is the phase difference, what is the power factor?- a)tan Ø
- b)cosh Ø
- c)cos Ø
- d)sin Ø
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When Ø is the phase difference, what is the power factor?
a)
tan Ø
b)
cosh Ø
c)
cos Ø
d)
sin Ø
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
Cos Ø is called a power factor that indicates what fraction of [(Voltage V) x (Current I)] becomes the useful power. Most electric circuits have resistance and inductance. In such electric circuit, the current lags the voltage by the phase difference.
In an ac circuit, peak value of voltage is 423 volts. Its effective voltage is - a)400 volts
- b)323 volts
- c)300 volts
- d)340 volts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ac circuit, peak value of voltage is 423 volts. Its effective voltage is
a)
400 volts
b)
323 volts
c)
300 volts
d)
340 volts
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Effective voltage is also known as root mean square value of voltage of alternating current in an AC circuit.
we know, Erms=Epeak/ √2
where Erms denotes the rms voltage and Epeak peak voltage in an ac circuit.
here, peak voltage , Epeak =423 volts
so, effective voltage , Erms =423/√2 ≈ 300 volts
hence, effective voltage is 300 volts
The correct answer is option C.
we know, Erms=Epeak/ √2
where Erms denotes the rms voltage and Epeak peak voltage in an ac circuit.
here, peak voltage , Epeak =423 volts
so, effective voltage , Erms =423/√2 ≈ 300 volts
hence, effective voltage is 300 volts
The correct answer is option C.
In an L-R-C series circuit, the rms voltage across the resistor is 30.0 V, across the capacitor it is 90.0 V, and across the inductor it is 50.0 V. Rms voltage of the source is- a)60.0 V
- b)50.0 V
- c)65.0 V
- d)5.0 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an L-R-C series circuit, the rms voltage across the resistor is 30.0 V, across the capacitor it is 90.0 V, and across the inductor it is 50.0 V. Rms voltage of the source is
a)
60.0 V
b)
50.0 V
c)
65.0 V
d)
5.0 V
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
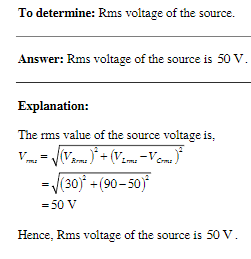
This Question Answer is
In a circuit an a.c. current and a d, c. current are supplied together. The expression of the instantaneous current is given as i = 3 + 6 sin wt. Then the rms value of the current is- a)3
- b)6
- c)
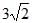
- d)
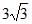
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a circuit an a.c. current and a d, c. current are supplied together. The expression of the instantaneous current is given as i = 3 + 6 sin wt. Then the rms value of the current is
a)
3
b)
6
c)
d)

|
Top Rankers answered |
Given,
Instantaneous current, i=3+6sinωt
irms=√[(1/T)0T(3+6sinωt)2dt]
irms=√(1/T) 0T(32+62sin2ωt+36sinωt) dt
irms=√(1/T) [0T32dt+∫0T62{(1/2) – (cos2ωt/2) dt+∫0T(36sinωt)dt]
irms=√9+(36/2) +0=3√3A
Hence, RMS value of current is 3√3A
Instantaneous current, i=3+6sinωt
irms=√[(1/T)0T(3+6sinωt)2dt]
irms=√(1/T) 0T(32+62sin2ωt+36sinωt) dt
irms=√(1/T) [0T32dt+∫0T62{(1/2) – (cos2ωt/2) dt+∫0T(36sinωt)dt]
irms=√9+(36/2) +0=3√3A
Hence, RMS value of current is 3√3A
Chapter doubts & questions for Alternating Currents - Online MCQ Tests for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Alternating Currents - Online MCQ Tests for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup