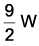All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern >
All Questions
All questions of NEET Practice Tests (Old NCERT) for NEET Exam
Which of the following options shows the correct respiratory tract of human beings?- a)Nose - Pharynx - Trachea - Larynx - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli
- b)Nose - Pharynx - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli
- c)Nose - Pharynx - Bronchi - Alveoli - Bronchioles - Larynx - Trachea
- d)Nose - Larynx - Pharynx - Trachea - Bronchioles - Bronchi - Alveoli
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options shows the correct respiratory tract of human beings?
a)
Nose - Pharynx - Trachea - Larynx - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli
b)
Nose - Pharynx - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli
c)
Nose - Pharynx - Bronchi - Alveoli - Bronchioles - Larynx - Trachea
d)
Nose - Larynx - Pharynx - Trachea - Bronchioles - Bronchi - Alveoli
|
|
Bijoy Rane answered |
Respiratory Tract in Human Beings
The respiratory system is responsible for respiration that involves the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide. The human respiratory tract consists of a series of organs and structures that work together to provide oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide.
The correct sequence of the respiratory tract in human beings is as follows:
- Nose: The respiratory tract starts with the nose, which is the primary organ for breathing. The nose filters, warms, and moistens the air before it enters the body.
- Pharynx: The air passes through the pharynx, which is a muscular tube that connects the nose and mouth to the larynx and esophagus.
- Larynx: The air then passes through the larynx, which is also known as the voice box. The larynx contains the vocal cords and helps in producing sound.
- Trachea: The air then enters the trachea, which is a tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi. The trachea is also known as the windpipe.
- Bronchi: The trachea divides into two bronchi, which are two branches that lead to the lungs.
- Bronchioles: The bronchi further divide into smaller branches, known as bronchioles.
- Alveoli: The bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by blood vessels. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the alveoli.
Therefore, the correct sequence of the respiratory tract in human beings is Nose - Pharynx - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli. Option B is the correct answer.
The respiratory system is responsible for respiration that involves the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide. The human respiratory tract consists of a series of organs and structures that work together to provide oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide.
The correct sequence of the respiratory tract in human beings is as follows:
- Nose: The respiratory tract starts with the nose, which is the primary organ for breathing. The nose filters, warms, and moistens the air before it enters the body.
- Pharynx: The air passes through the pharynx, which is a muscular tube that connects the nose and mouth to the larynx and esophagus.
- Larynx: The air then passes through the larynx, which is also known as the voice box. The larynx contains the vocal cords and helps in producing sound.
- Trachea: The air then enters the trachea, which is a tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi. The trachea is also known as the windpipe.
- Bronchi: The trachea divides into two bronchi, which are two branches that lead to the lungs.
- Bronchioles: The bronchi further divide into smaller branches, known as bronchioles.
- Alveoli: The bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by blood vessels. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the alveoli.
Therefore, the correct sequence of the respiratory tract in human beings is Nose - Pharynx - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi - Bronchioles - Alveoli. Option B is the correct answer.
Directions: In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choice given below.
Assertion (A): combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18g of water.
Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products.
- a)Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
- c)Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct
- d)Assertion is correct, reason is correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choice given below.
Assertion (A): combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18g of water.
Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products.
a)
Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
c)
Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct
d)
Assertion is correct, reason is correct.
|
|
Dishani Khanna answered |
Assertion and Reasoning
• Assertion (A): combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18g of water.
• Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products.
Explanation
• The assertion is correct. When methane is burned with oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water. The balanced equation is as follows:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
• Therefore, for every 16 g of methane burned, 18 g of water are produced.
• The reason is incorrect because it merely restates the assertion without providing any additional information.
• Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Conclusion
• The given assertion and reasoning deal with the combustion of methane and the resulting production of water.
• The assertion is correct, while the reasoning is incorrect.
• Assertion (A): combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18g of water.
• Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products.
Explanation
• The assertion is correct. When methane is burned with oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water. The balanced equation is as follows:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
• Therefore, for every 16 g of methane burned, 18 g of water are produced.
• The reason is incorrect because it merely restates the assertion without providing any additional information.
• Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Conclusion
• The given assertion and reasoning deal with the combustion of methane and the resulting production of water.
• The assertion is correct, while the reasoning is incorrect.
Product (A) is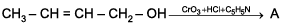
- a)CH3- C H = C H -C O O H
- b)CH3- CH = CH - CH2- OCH3
- c)CH3- C H = C H - CHO
- d)HOOC - CH = CH - COOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Product (A) is
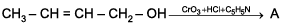
a)
CH3- C H = C H -C O O H
b)
CH3- CH = CH - CH2- OCH3
c)
CH3- C H = C H - CHO
d)
HOOC - CH = CH - COOH
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Weak oxidising agents like PCC, PDC etc. oxidise 1° alcohol to aldehyde.
Which among the following is a synthetic polymer?- a)Proteins
- b)Polysaccharides
- c)Natural rubber
- d)Phenol-formaldehyde resin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a synthetic polymer?
a)
Proteins
b)
Polysaccharides
c)
Natural rubber
d)
Phenol-formaldehyde resin
|
|
Aman Dasgupta answered |
Synthetic Polymer:
A synthetic polymer is a human-made polymer that is not found in nature. These polymers are made by linking together repeated units, called monomers, to form long chains. Phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer.
Explanation:
Phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer, which is made by the reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. It is commonly used as an adhesive and as a material for making molded products. The monomers used to make this polymer are not found in nature and are synthesized in a laboratory.
Proteins:
Proteins are natural polymers that are made up of amino acids. They are found in all living organisms and have a variety of functions, including structural support, enzymes, and hormones. Proteins are not synthetic polymers.
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides are natural polymers that are made up of monosaccharides (sugar molecules). They are found in plants and animals and have a variety of functions, including energy storage, structural support, and cell signaling. Polysaccharides are not synthetic polymers.
Natural rubber:
Natural rubber is a polymer that is found in the sap of certain plants, such as the rubber tree. It is a natural polymer and not a synthetic polymer.
In conclusion, among the given options, only phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer.
A synthetic polymer is a human-made polymer that is not found in nature. These polymers are made by linking together repeated units, called monomers, to form long chains. Phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer.
Explanation:
Phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer, which is made by the reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. It is commonly used as an adhesive and as a material for making molded products. The monomers used to make this polymer are not found in nature and are synthesized in a laboratory.
Proteins:
Proteins are natural polymers that are made up of amino acids. They are found in all living organisms and have a variety of functions, including structural support, enzymes, and hormones. Proteins are not synthetic polymers.
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides are natural polymers that are made up of monosaccharides (sugar molecules). They are found in plants and animals and have a variety of functions, including energy storage, structural support, and cell signaling. Polysaccharides are not synthetic polymers.
Natural rubber:
Natural rubber is a polymer that is found in the sap of certain plants, such as the rubber tree. It is a natural polymer and not a synthetic polymer.
In conclusion, among the given options, only phenol-formaldehyde resin is a synthetic polymer.
Which of the following is an example of green algae?- a)Chlorella
- b)Porphyra
- c)Batrachospermum
- d)Gelidium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of green algae?
a)
Chlorella
b)
Porphyra
c)
Batrachospermum
d)
Gelidium
|
|
Naveen Mehra answered |
Green algae is a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that belong to the kingdom Plantae. They are found in various aquatic and terrestrial habitats, including freshwater, saltwater, soil, and rocks. Chlorella is an example of green algae that is widely used as a nutritional supplement and food source for humans and animals. Let's discuss some of the characteristics of Chlorella that make it a green algae.
Characteristics of Chlorella:
1. Taxonomy: Chlorella belongs to the phylum Chlorophyta, which is a group of green algae that contains chloroplasts with chlorophyll a and b.
2. Cell structure: Chlorella is a unicellular organism with a spherical or oval-shaped cell that ranges from 2-10 microns in diameter. The cell wall of Chlorella is composed of cellulose and other polysaccharides.
3. Photosynthesis: Chlorella performs photosynthesis in the same way as higher plants. It uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and organic compounds, such as sugars and starches.
4. Nutrition: Chlorella is rich in nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It is often used as a dietary supplement for its potential health benefits, such as immune system support, detoxification, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion:
Chlorella is an example of green algae that has many uses and benefits for humans and animals. Its unique characteristics, such as cell structure, photosynthesis, and nutrition, make it a valuable resource in various fields, including biotechnology, agriculture, and medicine. Understanding the diversity and functions of green algae is essential for studying the evolution and ecology of plant life on Earth.
Characteristics of Chlorella:
1. Taxonomy: Chlorella belongs to the phylum Chlorophyta, which is a group of green algae that contains chloroplasts with chlorophyll a and b.
2. Cell structure: Chlorella is a unicellular organism with a spherical or oval-shaped cell that ranges from 2-10 microns in diameter. The cell wall of Chlorella is composed of cellulose and other polysaccharides.
3. Photosynthesis: Chlorella performs photosynthesis in the same way as higher plants. It uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and organic compounds, such as sugars and starches.
4. Nutrition: Chlorella is rich in nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It is often used as a dietary supplement for its potential health benefits, such as immune system support, detoxification, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion:
Chlorella is an example of green algae that has many uses and benefits for humans and animals. Its unique characteristics, such as cell structure, photosynthesis, and nutrition, make it a valuable resource in various fields, including biotechnology, agriculture, and medicine. Understanding the diversity and functions of green algae is essential for studying the evolution and ecology of plant life on Earth.
Select the incorrect match w.r.t. differential leukocyte count.- a)Neutrophils – 60-65%
- b)Basophils – 2-3%
- c)Lymphocytes – 20-25%
- d)Monocytes – 6-8%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect match w.r.t. differential leukocyte count.
a)
Neutrophils – 60-65%
b)
Basophils – 2-3%
c)
Lymphocytes – 20-25%
d)
Monocytes – 6-8%
|
|
Janani Kaur answered |
Incorrect Match in Differential Leukocyte Count
Explanation:
Differential leukocyte count is a laboratory test that is performed to identify the percentage of different types of white blood cells in the blood. This test helps to diagnose various medical conditions. The normal range of differential leukocyte count is as follows:
- Neutrophils – 60-65%
- Lymphocytes – 20-25%
- Monocytes – 6-8%
- Eosinophils – 1-3%
- Basophils – 0.5-1%
The incorrect match in differential leukocyte count is option B, which states that basophils are 2-3% of the total white blood cells. However, the correct percentage of basophils is 0.5-1%.
Summary:
- Differential leukocyte count is a laboratory test that helps to identify the percentage of different types of white blood cells in the blood.
- The normal range of differential leukocyte count includes neutrophils (60-65%), lymphocytes (20-25%), monocytes (6-8%), eosinophils (1-3%), and basophils (0.5-1%).
- The incorrect match in differential leukocyte count is option B, which states that basophils are 2-3% of the total white blood cells. The correct percentage of basophils is 0.5-1%.
Explanation:
Differential leukocyte count is a laboratory test that is performed to identify the percentage of different types of white blood cells in the blood. This test helps to diagnose various medical conditions. The normal range of differential leukocyte count is as follows:
- Neutrophils – 60-65%
- Lymphocytes – 20-25%
- Monocytes – 6-8%
- Eosinophils – 1-3%
- Basophils – 0.5-1%
The incorrect match in differential leukocyte count is option B, which states that basophils are 2-3% of the total white blood cells. However, the correct percentage of basophils is 0.5-1%.
Summary:
- Differential leukocyte count is a laboratory test that helps to identify the percentage of different types of white blood cells in the blood.
- The normal range of differential leukocyte count includes neutrophils (60-65%), lymphocytes (20-25%), monocytes (6-8%), eosinophils (1-3%), and basophils (0.5-1%).
- The incorrect match in differential leukocyte count is option B, which states that basophils are 2-3% of the total white blood cells. The correct percentage of basophils is 0.5-1%.
A block of mass 5 kg is moving in x-direction with a constant speed 20 m/s. Now it is subjected to a retarding force Fr = – 0.2 x J/m during its travel from x = 10 m to x = 20 m. Its final velocity will be nearly- a)19.7 m/s
- b)16.4 m/s
- c)14.3 m/s
- d)10 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 5 kg is moving in x-direction with a constant speed 20 m/s. Now it is subjected to a retarding force Fr = – 0.2 x J/m during its travel from x = 10 m to x = 20 m. Its final velocity will be nearly
a)
19.7 m/s
b)
16.4 m/s
c)
14.3 m/s
d)
10 m/s
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
DW = Fdx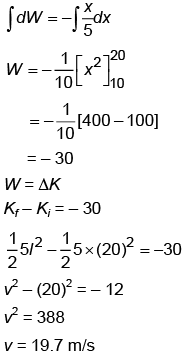
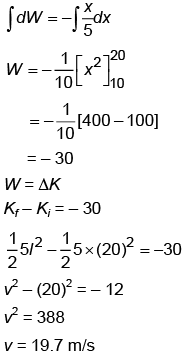
When the door of a refrigerator is kept open then the room temperature- a)Increases
- b)Decreases
- c)Neither increasing nor decreasing
- d)First increases then decreases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the door of a refrigerator is kept open then the room temperature
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Neither increasing nor decreasing
d)
First increases then decreases
|
|
Sounak Saini answered |
Impact of Open Refrigerator Door on Room Temperature
When the door of a refrigerator is kept open, it causes the following changes in the room temperature:
1. Heat Transfer:
- Refrigerators work by transferring heat from inside the fridge to the outside environment.
- When the door is open, the cold air inside the fridge escapes, and warm air from the room enters the fridge.
- This increases the amount of heat that the fridge needs to transfer to maintain its temperature, and as a result, the room temperature increases.
2. Energy Consumption:
- When the fridge has to work harder to maintain its temperature, it consumes more energy.
- This can cause an increase in electricity bills.
3. Food Spoilage:
- When the door of a refrigerator is kept open for a long time, it can cause the temperature inside the fridge to rise above the recommended level.
- This can lead to food spoilage and wastage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when the door of a refrigerator is kept open, it causes an increase in room temperature due to the transfer of heat from inside the fridge to the room. This can increase energy consumption, cause food spoilage, and lead to other negative consequences. Therefore, it is essential to keep the fridge door closed as much as possible to maintain its temperature and prevent unnecessary heat transfer.
When the door of a refrigerator is kept open, it causes the following changes in the room temperature:
1. Heat Transfer:
- Refrigerators work by transferring heat from inside the fridge to the outside environment.
- When the door is open, the cold air inside the fridge escapes, and warm air from the room enters the fridge.
- This increases the amount of heat that the fridge needs to transfer to maintain its temperature, and as a result, the room temperature increases.
2. Energy Consumption:
- When the fridge has to work harder to maintain its temperature, it consumes more energy.
- This can cause an increase in electricity bills.
3. Food Spoilage:
- When the door of a refrigerator is kept open for a long time, it can cause the temperature inside the fridge to rise above the recommended level.
- This can lead to food spoilage and wastage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when the door of a refrigerator is kept open, it causes an increase in room temperature due to the transfer of heat from inside the fridge to the room. This can increase energy consumption, cause food spoilage, and lead to other negative consequences. Therefore, it is essential to keep the fridge door closed as much as possible to maintain its temperature and prevent unnecessary heat transfer.
Ascaris is characterized by- a)Absence of true coelom but presence of metamerism.
- b)Presence of neither true coelom nor metamerism.
- c)Presence of true coelom and metamerism.
- d)Presence of true coelom but the absence of metamerism.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ascaris is characterized by
a)
Absence of true coelom but presence of metamerism.
b)
Presence of neither true coelom nor metamerism.
c)
Presence of true coelom and metamerism.
d)
Presence of true coelom but the absence of metamerism.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The body of Ascaris is elongated, cylindrical gradually tapering at both ends. There is no metameric segmentation. In Ascaris, between the body wall and visceral organs is a spacious fluid-filled cavity. They belong to the phylum Aschelminthes that have pseudocoelom as their body cavity.
Segmentation, also called metamerism, or metameric segmentation, in zoology, the condition of being constructed of a linear series of repeating parts, each being a metamere (body segment, or somite) and each being formed in sequence in the embryo, from anterior to posterior. E.g., animals of phylum Annelida.
An electric dipole of dipole moment 4×10−5 Cm is placed in a uniform electric field of 10−3 NC−1 making an angle of 30° with the direction of field. Determine the torque exerted by the electric field on the dipole.
- a)3 x 8−6 Nm
- b)2 x 10−8 Nm
- c)1 x 12−3 Nm
- d)3 x 10−7 Nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric dipole of dipole moment 4×10−5 Cm is placed in a uniform electric field of 10−3 NC−1 making an angle of 30° with the direction of field. Determine the torque exerted by the electric field on the dipole.
a)
3 x 8−6 Nm
b)
2 x 10−8 Nm
c)
1 x 12−3 Nm
d)
3 x 10−7 Nm
|
|
Devika Pillai answered |
The statement seems to be incomplete. Please provide the missing information so that I can assist you better.
The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by a convex lens of focal length 30 cm is 2 cm. If a concave lens of focal length 20 cm is placed between the convex lens and image at a distance of 26 cm from the convex lens, calculate the new size of the image.- a)1.25 cm
- b)2.5 cm
- c)1.05 cm
- d)2 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by a convex lens of focal length 30 cm is 2 cm. If a concave lens of focal length 20 cm is placed between the convex lens and image at a distance of 26 cm from the convex lens, calculate the new size of the image.
a)
1.25 cm
b)
2.5 cm
c)
1.05 cm
d)
2 cm
|
|
Anshika Roy answered |
Given:
- Object distance, u = infinity
- Focal length of convex lens, f1 = 30 cm
- Size of image formed by convex lens, v1 = 2 cm
- Focal length of concave lens, f2 = -20 cm (negative sign indicates concave lens)
- Distance between convex lens and concave lens, d = 26 cm
To find:
- Size of image formed by the combination of lenses, v2
We can use the lens formula:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
For the convex lens, when the object is at infinity:
1/f1 = 1/u + 1/v1
1/30 = 0 + 1/v1
v1 = 30 cm
Now, let's consider the combination of lenses. We can use the formula:
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2 - d/f1f2
where d is the distance between the two lenses.
Substituting the values:
1/f = 1/30 - 1/20 - 26/(30 x -20)
1/f = -1/60 - 13/600
1/f = -14/600
f = -42.86 cm
Note that the negative sign indicates that the combination of lenses acts like a concave lens.
Using the lens formula again, we can find the size of the image formed by the combination of lenses:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v2
1/-42.86 = 0 + 1/v2
v2 = -42.86 cm
Note that the negative sign indicates that the image is virtual. To find the size of the image, we can use the magnification formula:
m = -v2/v1
m = -(-42.86)/30
m = 1.43
The magnification is positive, which means that the image is upright. The size of the image is given by:
v2 = m x v1
v2 = 1.43 x 2 cm
v2 = 2.86 cm
Therefore, the new size of the image formed by the combination of lenses is 2.86 cm, which is closest to option (B) 2.5 cm.
- Object distance, u = infinity
- Focal length of convex lens, f1 = 30 cm
- Size of image formed by convex lens, v1 = 2 cm
- Focal length of concave lens, f2 = -20 cm (negative sign indicates concave lens)
- Distance between convex lens and concave lens, d = 26 cm
To find:
- Size of image formed by the combination of lenses, v2
We can use the lens formula:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
For the convex lens, when the object is at infinity:
1/f1 = 1/u + 1/v1
1/30 = 0 + 1/v1
v1 = 30 cm
Now, let's consider the combination of lenses. We can use the formula:
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2 - d/f1f2
where d is the distance between the two lenses.
Substituting the values:
1/f = 1/30 - 1/20 - 26/(30 x -20)
1/f = -1/60 - 13/600
1/f = -14/600
f = -42.86 cm
Note that the negative sign indicates that the combination of lenses acts like a concave lens.
Using the lens formula again, we can find the size of the image formed by the combination of lenses:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v2
1/-42.86 = 0 + 1/v2
v2 = -42.86 cm
Note that the negative sign indicates that the image is virtual. To find the size of the image, we can use the magnification formula:
m = -v2/v1
m = -(-42.86)/30
m = 1.43
The magnification is positive, which means that the image is upright. The size of the image is given by:
v2 = m x v1
v2 = 1.43 x 2 cm
v2 = 2.86 cm
Therefore, the new size of the image formed by the combination of lenses is 2.86 cm, which is closest to option (B) 2.5 cm.
Mark the wrong statement.- a)Ascariasis, Taeniasis and Enterobiasis are helminthic diseases.
- b)Measles, Mumps and Rubella are viral diseases.
- c)Malaria, Amoebiasis and Filariasis are protozoan diseases.
- d)Cholera, Diphtheria and Tetanus are bacterial diseases.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mark the wrong statement.
a)
Ascariasis, Taeniasis and Enterobiasis are helminthic diseases.
b)
Measles, Mumps and Rubella are viral diseases.
c)
Malaria, Amoebiasis and Filariasis are protozoan diseases.
d)
Cholera, Diphtheria and Tetanus are bacterial diseases.

|
Mukesh Chopade answered |
Ans is c)
* Malaria(Plamodium) & Amoebiasis(Entamoeba histolytica) are cause by protozoa, hence protozoal diseases.
* Filariasis/Elephantiasis(Wucheria bancrofti"' W. malayi) is caused by nematode (helminth), hence helminthic desease.
* Malaria(Plamodium) & Amoebiasis(Entamoeba histolytica) are cause by protozoa, hence protozoal diseases.
* Filariasis/Elephantiasis(Wucheria bancrofti"' W. malayi) is caused by nematode (helminth), hence helminthic desease.
Which of the following statements regarding pollen grains is/are false?A. The hard outer layer of pollen grains is made up of sporopollenin.B. A mature pollen grain contains vegetative cell and generative cell.C. The exine is the inner wall of a pollen grain that is made up of cellulose and pectin.- a)Only A
- b)Only A and B
- c)Only B
- d)Only C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding pollen grains is/are false?
A. The hard outer layer of pollen grains is made up of sporopollenin.
B. A mature pollen grain contains vegetative cell and generative cell.
C. The exine is the inner wall of a pollen grain that is made up of cellulose and pectin.
a)
Only A
b)
Only A and B
c)
Only B
d)
Only C

|
Hema answered |
B
Based on the location, muscles are classified as- a)Voluntary and involuntary
- b)Striated and smooth
- c)Skeletal, smooth and cardiac
- d)Skeletal, visceral and cardiac
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the location, muscles are classified as
a)
Voluntary and involuntary
b)
Striated and smooth
c)
Skeletal, smooth and cardiac
d)
Skeletal, visceral and cardiac
|
|
Rajveer Mehta answered |
Muscle Classification
Muscles are classified based on their location and function. The classification of muscles is as follows:
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and are responsible for the voluntary movement of the body. They are striated muscles, which means that they have a striped appearance when viewed under a microscope. Skeletal muscles are under conscious control, and we can contract and relax them at will. Examples include biceps, triceps, and quadriceps.
Visceral Muscles
Visceral muscles are also called smooth muscles. They are located in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. Visceral muscles are responsible for the involuntary movement of the body, such as the contraction of the stomach during digestion. They are not striated muscles and are not under conscious control.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles are found in the walls of the heart. They are striated muscles but are involuntary, meaning that we cannot consciously control their movements. Cardiac muscles are responsible for the regular contraction and relaxation of the heart, which pumps blood throughout the body.
Conclusion
Based on the location, muscles are classified into three main categories: skeletal, visceral, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are striated and are responsible for voluntary movement, while visceral muscles are smooth and are responsible for involuntary movement. Cardiac muscles are also striated but are involuntary and are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Muscles are classified based on their location and function. The classification of muscles is as follows:
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and are responsible for the voluntary movement of the body. They are striated muscles, which means that they have a striped appearance when viewed under a microscope. Skeletal muscles are under conscious control, and we can contract and relax them at will. Examples include biceps, triceps, and quadriceps.
Visceral Muscles
Visceral muscles are also called smooth muscles. They are located in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. Visceral muscles are responsible for the involuntary movement of the body, such as the contraction of the stomach during digestion. They are not striated muscles and are not under conscious control.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles are found in the walls of the heart. They are striated muscles but are involuntary, meaning that we cannot consciously control their movements. Cardiac muscles are responsible for the regular contraction and relaxation of the heart, which pumps blood throughout the body.
Conclusion
Based on the location, muscles are classified into three main categories: skeletal, visceral, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are striated and are responsible for voluntary movement, while visceral muscles are smooth and are responsible for involuntary movement. Cardiac muscles are also striated but are involuntary and are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
If repeated checks of blood pressure of an individual show pressures as 140/90, it is considered as- a)Hypotension
- b)Hypertension
- c)Bradycardia
- d)Heart block
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If repeated checks of blood pressure of an individual show pressures as 140/90, it is considered as
a)
Hypotension
b)
Hypertension
c)
Bradycardia
d)
Heart block
|
|
Gaurav Basu answered |
Explanation:
Hypertension:
- Hypertension is a condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently elevated.
- Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded as two numbers. The first number (systolic pressure) represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while the second number (diastolic pressure) represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
- A blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg indicates that the individual has hypertension. The systolic pressure of 140 mmHg and diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg fall within the range of Stage 1 hypertension according to the guidelines set by the American Heart Association.
- Untreated hypertension can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other cardiovascular issues.
- It is important for individuals with hypertension to work with their healthcare provider to manage their blood pressure through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.
Therefore, in the case of an individual whose blood pressure readings consistently show pressures of 140/90 mmHg, it is considered hypertension.
Hypertension:
- Hypertension is a condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently elevated.
- Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded as two numbers. The first number (systolic pressure) represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while the second number (diastolic pressure) represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
- A blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg indicates that the individual has hypertension. The systolic pressure of 140 mmHg and diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg fall within the range of Stage 1 hypertension according to the guidelines set by the American Heart Association.
- Untreated hypertension can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other cardiovascular issues.
- It is important for individuals with hypertension to work with their healthcare provider to manage their blood pressure through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.
Therefore, in the case of an individual whose blood pressure readings consistently show pressures of 140/90 mmHg, it is considered hypertension.
Select the incorrect statement.- a)Progesterone hormone maintains endometrium
- b)hCG hormone maintains corpus luteum in non-pregnant female
- c)Granulosa cells of follicle secrete estrogen hormone in presence of FSH
- d)Ruptured graafian follicle converts into corpus luteum in presence of LH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement.
a)
Progesterone hormone maintains endometrium
b)
hCG hormone maintains corpus luteum in non-pregnant female
c)
Granulosa cells of follicle secrete estrogen hormone in presence of FSH
d)
Ruptured graafian follicle converts into corpus luteum in presence of LH
|
|
Sanchita Saha answered |
Incorrect Statement: hCG hormone maintains corpus luteum in non-pregnant female.
Explanation:
• Corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine gland that develops from the ruptured Graafian follicle after ovulation.
• It secretes progesterone hormone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium and pregnancy.
• If fertilization and implantation do not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates and becomes the corpus albicans.
• However, if fertilization occurs, the developing embryo secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone that maintains the corpus luteum and prevents its degeneration.
• Therefore, the correct statement is that hCG hormone maintains the corpus luteum in pregnant females, not in non-pregnant females.
Summary:
• Progesterone hormone maintains endometrium.
• Granulosa cells of follicle secrete estrogen hormone in the presence of FSH.
• Ruptured Graafian follicle converts into corpus luteum in the presence of LH.
• Incorrect statement: hCG hormone maintains corpus luteum in non-pregnant females.
Explanation:
• Corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine gland that develops from the ruptured Graafian follicle after ovulation.
• It secretes progesterone hormone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium and pregnancy.
• If fertilization and implantation do not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates and becomes the corpus albicans.
• However, if fertilization occurs, the developing embryo secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone that maintains the corpus luteum and prevents its degeneration.
• Therefore, the correct statement is that hCG hormone maintains the corpus luteum in pregnant females, not in non-pregnant females.
Summary:
• Progesterone hormone maintains endometrium.
• Granulosa cells of follicle secrete estrogen hormone in the presence of FSH.
• Ruptured Graafian follicle converts into corpus luteum in the presence of LH.
• Incorrect statement: hCG hormone maintains corpus luteum in non-pregnant females.
Blood leaving the tissues has ________.- a)high pO2
- b)low pCO2
- c)high pCO2
- d)both high pCO2 and pO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood leaving the tissues has ________.
a)
high pO2
b)
low pCO2
c)
high pCO2
d)
both high pCO2 and pO2
|
|
Noushaba Mirza answered |
The blood in the body leaves the tissues becomes richer in CO2. The main artery(aorta) carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the organs. when this blood passes through the capillaries of body organs, it gives oxygen to the body cells. At the same time, CO2 produced during respiration enters the blood. Thus deoxygenated blood(carrying CO2) leaves tissues and enters vena cava, from where they are again passed to the lungs for oxygenation.
Given below are two statements:Statement I: The release of sperms into the seminiferous tubules is called spermiation.Statement II: Spermiogenesis is the process of formation of sperms from spermatogonia.In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- a)Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
- c)Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
- d)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The release of sperms into the seminiferous tubules is called spermiation.
Statement II: Spermiogenesis is the process of formation of sperms from spermatogonia.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
a)
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
c)
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
d)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
|
|
Maheshwar Iyer answered |
Statement I:
- Seminiferous tubules are the site of sperm production in testes.
- Spermiation is the process of release of mature spermatozoa from the seminiferous tubules into the lumen of the tubules.
- The released spermatozoa are transported through the rete testis, epididymis, and vas deferens to reach the urethra for ejaculation during sexual intercourse.
Statement II:
- Spermatogonia are the diploid cells that undergo meiosis to form haploid sperm cells.
- Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell production that involves meiosis, spermiogenesis, and spermiation.
- Spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of round spermatids into elongated and motile spermatozoa.
Explanation:
From the above statements, we can conclude that:
- Statement I is correct because spermiation is the process of release of mature spermatozoa from the seminiferous tubules into the lumen of the tubules.
- Statement II is incorrect because spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of round spermatids into elongated and motile spermatozoa, whereas sperm formation from spermatogonia involves meiosis and spermiogenesis.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
- Seminiferous tubules are the site of sperm production in testes.
- Spermiation is the process of release of mature spermatozoa from the seminiferous tubules into the lumen of the tubules.
- The released spermatozoa are transported through the rete testis, epididymis, and vas deferens to reach the urethra for ejaculation during sexual intercourse.
Statement II:
- Spermatogonia are the diploid cells that undergo meiosis to form haploid sperm cells.
- Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell production that involves meiosis, spermiogenesis, and spermiation.
- Spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of round spermatids into elongated and motile spermatozoa.
Explanation:
From the above statements, we can conclude that:
- Statement I is correct because spermiation is the process of release of mature spermatozoa from the seminiferous tubules into the lumen of the tubules.
- Statement II is incorrect because spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of round spermatids into elongated and motile spermatozoa, whereas sperm formation from spermatogonia involves meiosis and spermiogenesis.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Assertion (A): Classical Physics mainly includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics and Thermodynamics.Reason (R): The macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial and astronomical scales.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is also false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Classical Physics mainly includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics and Thermodynamics.
Reason (R): The macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial and astronomical scales.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is also false
|
|
Sahil Goyal answered |
Assertion (A): Classical Physics mainly includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics, and Thermodynamics.
Reason (R): The macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales.
To understand the given assertion-reason statement, let's examine each statement individually and then evaluate their relationship.
Classical Physics Subjects:
Classical Physics is a branch of physics that deals with the laws of motion and the behavior of macroscopic objects. It includes various subjects such as:
1. Mechanics: Mechanics is the study of the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. It encompasses both classical mechanics (Newtonian mechanics) and relativistic mechanics.
2. Electrodynamics: Electrodynamics is the study of the behavior of electric charges and electric currents. It includes topics such as electric fields, magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves, and electrical circuits.
3. Optics: Optics is the study of the behavior and properties of light. It involves the understanding of phenomena such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization of light.
4. Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between heat, work, and energy. It deals with concepts such as temperature, heat transfer, entropy, and the laws of thermodynamics.
All these subjects are part of classical physics and form the foundation of our understanding of the macroscopic world.
Macroscopic Domain:
The macroscopic domain refers to the scale at which objects and phenomena are observable and measurable without the need for microscopic or quantum-level analysis. It includes phenomena that can be observed and studied on laboratory scales, terrestrial scales (such as the Earth's atmosphere and geological processes), and astronomical scales (such as the motion of celestial bodies and the behavior of galaxies).
Evaluation of the Assertion-Reason Statement:
Assertion (A) states that classical physics mainly includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics, and Thermodynamics. This statement is true as discussed above.
Reason (R) states that the macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales. This statement is also true as the macroscopic domain encompasses phenomena that are observable and measurable on these scales.
Furthermore, the reason statement provides a correct explanation for the assertion. The subjects mentioned in the assertion are part of classical physics because they study phenomena that occur in the macroscopic domain.
Therefore, both the assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
In conclusion, classical physics includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics, and Thermodynamics, which study phenomena in the macroscopic domain. The reason for this is that the macroscopic domain encompasses phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales.
Reason (R): The macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales.
To understand the given assertion-reason statement, let's examine each statement individually and then evaluate their relationship.
Classical Physics Subjects:
Classical Physics is a branch of physics that deals with the laws of motion and the behavior of macroscopic objects. It includes various subjects such as:
1. Mechanics: Mechanics is the study of the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. It encompasses both classical mechanics (Newtonian mechanics) and relativistic mechanics.
2. Electrodynamics: Electrodynamics is the study of the behavior of electric charges and electric currents. It includes topics such as electric fields, magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves, and electrical circuits.
3. Optics: Optics is the study of the behavior and properties of light. It involves the understanding of phenomena such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization of light.
4. Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between heat, work, and energy. It deals with concepts such as temperature, heat transfer, entropy, and the laws of thermodynamics.
All these subjects are part of classical physics and form the foundation of our understanding of the macroscopic world.
Macroscopic Domain:
The macroscopic domain refers to the scale at which objects and phenomena are observable and measurable without the need for microscopic or quantum-level analysis. It includes phenomena that can be observed and studied on laboratory scales, terrestrial scales (such as the Earth's atmosphere and geological processes), and astronomical scales (such as the motion of celestial bodies and the behavior of galaxies).
Evaluation of the Assertion-Reason Statement:
Assertion (A) states that classical physics mainly includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics, and Thermodynamics. This statement is true as discussed above.
Reason (R) states that the macroscopic domain includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales. This statement is also true as the macroscopic domain encompasses phenomena that are observable and measurable on these scales.
Furthermore, the reason statement provides a correct explanation for the assertion. The subjects mentioned in the assertion are part of classical physics because they study phenomena that occur in the macroscopic domain.
Therefore, both the assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
In conclusion, classical physics includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics, and Thermodynamics, which study phenomena in the macroscopic domain. The reason for this is that the macroscopic domain encompasses phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scales.
Basmati rice is distinct for its unique aroma and flavour. How many documented varieties of Basmati are grown in our country?
- a)200
- b)27
- c)2,00,000
- d)127
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Basmati rice is distinct for its unique aroma and flavour. How many documented varieties of Basmati are grown in our country?
a)
200
b)
27
c)
2,00,000
d)
127
|
|
Deepak Mukherjee answered |
Varieties of Basmati Rice in India
Basmati rice is a long-grain rice variety that is known for its unique aroma and flavour. It is mainly grown in India and Pakistan. In India, there are several varieties of Basmati rice that are grown. Let's take a look at them.
Number of Varieties of Basmati Rice in India
Option (b) - 2,00,000 - is the correct answer.
Explanation of Answer
There are about 200,000 documented varieties of Basmati rice that are grown in India. However, only a few of them are commercially available. The following are some of the popular Basmati rice varieties grown in India:
1. Pusa Basmati 1121
2. Pusa Basmati 1
3. Taraori Basmati
4. Basmati 370
5. Haryana Basmati
6. Kasturi Basmati
7. Mahi Sugandha Basmati
8. Pusa Basmati 1509
9. Punjab Basmati 1
10. Pusa Basmati 6
Each of these varieties has its own unique characteristics in terms of grain length, cooking time, aroma, flavour, and texture. Some of them are more popular than others, depending on the region where they are grown and the preferences of consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are about 2,00,000 documented varieties of Basmati rice that are grown in India. However, only a few of them are commercially available. Each of these varieties has its own unique characteristics in terms of grain length, cooking time, aroma, flavour, and texture.
Basmati rice is a long-grain rice variety that is known for its unique aroma and flavour. It is mainly grown in India and Pakistan. In India, there are several varieties of Basmati rice that are grown. Let's take a look at them.
Number of Varieties of Basmati Rice in India
Option (b) - 2,00,000 - is the correct answer.
Explanation of Answer
There are about 200,000 documented varieties of Basmati rice that are grown in India. However, only a few of them are commercially available. The following are some of the popular Basmati rice varieties grown in India:
1. Pusa Basmati 1121
2. Pusa Basmati 1
3. Taraori Basmati
4. Basmati 370
5. Haryana Basmati
6. Kasturi Basmati
7. Mahi Sugandha Basmati
8. Pusa Basmati 1509
9. Punjab Basmati 1
10. Pusa Basmati 6
Each of these varieties has its own unique characteristics in terms of grain length, cooking time, aroma, flavour, and texture. Some of them are more popular than others, depending on the region where they are grown and the preferences of consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are about 2,00,000 documented varieties of Basmati rice that are grown in India. However, only a few of them are commercially available. Each of these varieties has its own unique characteristics in terms of grain length, cooking time, aroma, flavour, and texture.
Which of the following has highest number of atoms? (Atomic mass of Ag = 108 u)- a)2 g of butane (C4H10)
- b)2 g of nitrogen
- c)2 g of silver
- d)2 g of water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has highest number of atoms? (Atomic mass of Ag = 108 u)
a)
2 g of butane (C4H10)
b)
2 g of nitrogen
c)
2 g of silver
d)
2 g of water
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
2 g butane → moles = 2/58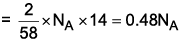
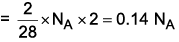
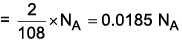
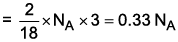
Number of atoms
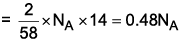
2 g nitrogen → moles = 2/58
Number of atoms
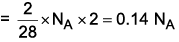
2 g silver → moles = 2/108
Number of atoms
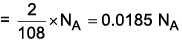
2 g water → moles = 2/18
Number of atoms
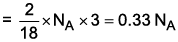
Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).Assertion (A): The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.Reason (R): A coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- a)(A) is false but (R) is true
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- c)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
- d)(A) is true but (R) is false
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.
Reason (R): A coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
a)
(A) is false but (R) is true
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
c)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
d)
(A) is true but (R) is false
|
|
Kaavya Chavan answered |
Assertion (A): The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.
Reason (R): A coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.
Explanation:
- Assertion (A) states that the stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring. This is true as the shear modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material and it determines how much a material will deform when a force is applied to it.
- Reason (R) states that a coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions. This statement is false as steel has a higher tensile strength than copper. Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand before breaking under tension.
- Therefore, option (D) is the correct answer as Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Conclusion:
- The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.
- A coil spring of copper does not have more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.
Reason (R): A coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.
Explanation:
- Assertion (A) states that the stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring. This is true as the shear modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material and it determines how much a material will deform when a force is applied to it.
- Reason (R) states that a coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions. This statement is false as steel has a higher tensile strength than copper. Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand before breaking under tension.
- Therefore, option (D) is the correct answer as Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Conclusion:
- The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.
- A coil spring of copper does not have more tensile strength than a steel spring of the same dimensions.
Which one is exclusive for Rods?- a)Retinal
- b)Rhodopsin
- c)Erythropsin
- d)Chloropsin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is exclusive for Rods?
a)
Retinal
b)
Rhodopsin
c)
Erythropsin
d)
Chloropsin
|
|
Pritam Choudhary answered |
Exclusive for Rods: Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin is a visual pigment found in the rods of the retina. It is responsible for the first step in the visual transduction process, which converts light into electrical signals that the brain can interpret.
Rhodopsin consists of two main components: opsin, a protein that acts as a receptor for light, and retinal, a light-sensitive molecule that undergoes a conformational change upon absorbing light.
Other Visual Pigments:
Retinal, Erythropsin, and Chloropsin are other visual pigments found in the retina, but they are not exclusive to rods.
Retinal is also found in cones, which are responsible for color vision, as well as in certain types of photosensitive cells in the skin.
Erythropsin is found in some fish and is responsible for detecting red light.
Chloropsin is found in some fish and is responsible for detecting green light.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, out of the given options, Rhodopsin is exclusive to rods and is responsible for the initial step in the visual transduction process.
Rhodopsin is a visual pigment found in the rods of the retina. It is responsible for the first step in the visual transduction process, which converts light into electrical signals that the brain can interpret.
Rhodopsin consists of two main components: opsin, a protein that acts as a receptor for light, and retinal, a light-sensitive molecule that undergoes a conformational change upon absorbing light.
Other Visual Pigments:
Retinal, Erythropsin, and Chloropsin are other visual pigments found in the retina, but they are not exclusive to rods.
Retinal is also found in cones, which are responsible for color vision, as well as in certain types of photosensitive cells in the skin.
Erythropsin is found in some fish and is responsible for detecting red light.
Chloropsin is found in some fish and is responsible for detecting green light.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, out of the given options, Rhodopsin is exclusive to rods and is responsible for the initial step in the visual transduction process.
Neuron with one axon and only one dendrite is called- a)Multipolar
- b)Bipolar
- c)Unipolar
- d)Apolar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Neuron with one axon and only one dendrite is called
a)
Multipolar
b)
Bipolar
c)
Unipolar
d)
Apolar
|
|
Nitya Shah answered |
Neuron with one axon and only one dendrite is called Bipolar.
A neuron is an essential building block of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting and processing information through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons consist of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon.
Bipolar neurons are a type of neuron that has one axon and one dendrite. Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
1. Structure of a Bipolar Neuron:
- Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite arising from opposite ends of the cell body.
- The cell body is located in the middle and contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for cellular functions.
2. Function of a Bipolar Neuron:
- Bipolar neurons are primarily involved in sensory processing, especially in the special senses such as vision, hearing, and olfaction.
- The dendrite receives sensory input from the environment or other neurons and transmits it towards the cell body.
- The axon carries the processed information away from the cell body to other neurons or effector cells.
3. Examples of Bipolar Neurons:
- Retinal bipolar cells: These neurons transmit visual information from photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) to ganglion cells in the retina.
- Olfactory bipolar cells: They relay olfactory information (smell) from olfactory receptor cells in the nasal epithelium to the olfactory bulb in the brain.
- Auditory bipolar cells: Found in the cochlea of the inner ear, they participate in the transmission of auditory signals to the brain.
4. Comparison with other types of neurons:
- Multipolar neurons have multiple dendrites and a single axon. They are the most common type of neurons and are involved in motor control and interneuronal communication.
- Unipolar neurons have a single process that branches into two, forming an axon and a dendrite. They are primarily found in the peripheral nervous system and are involved in sensory functions.
In summary, a neuron with one axon and one dendrite is called a bipolar neuron. These neurons play important roles in sensory processing and can be found in various sensory organs throughout the body.
A neuron is an essential building block of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting and processing information through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons consist of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon.
Bipolar neurons are a type of neuron that has one axon and one dendrite. Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
1. Structure of a Bipolar Neuron:
- Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite arising from opposite ends of the cell body.
- The cell body is located in the middle and contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for cellular functions.
2. Function of a Bipolar Neuron:
- Bipolar neurons are primarily involved in sensory processing, especially in the special senses such as vision, hearing, and olfaction.
- The dendrite receives sensory input from the environment or other neurons and transmits it towards the cell body.
- The axon carries the processed information away from the cell body to other neurons or effector cells.
3. Examples of Bipolar Neurons:
- Retinal bipolar cells: These neurons transmit visual information from photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) to ganglion cells in the retina.
- Olfactory bipolar cells: They relay olfactory information (smell) from olfactory receptor cells in the nasal epithelium to the olfactory bulb in the brain.
- Auditory bipolar cells: Found in the cochlea of the inner ear, they participate in the transmission of auditory signals to the brain.
4. Comparison with other types of neurons:
- Multipolar neurons have multiple dendrites and a single axon. They are the most common type of neurons and are involved in motor control and interneuronal communication.
- Unipolar neurons have a single process that branches into two, forming an axon and a dendrite. They are primarily found in the peripheral nervous system and are involved in sensory functions.
In summary, a neuron with one axon and one dendrite is called a bipolar neuron. These neurons play important roles in sensory processing and can be found in various sensory organs throughout the body.
Which of the following set contains non-reducing disaccharides?- a)Sucrose and maltose
- b)Maltose and lactose
- c)Lactose and trehalose
- d)Sucrose and trehalose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following set contains non-reducing disaccharides?
a)
Sucrose and maltose
b)
Maltose and lactose
c)
Lactose and trehalose
d)
Sucrose and trehalose
|
|
Lekshmi Nair answered |
Non-Reducing Disaccharides
Non-reducing disaccharides are a type of disaccharide that do not contain a free aldehyde or ketone group, which means they cannot be oxidized. Some common examples of non-reducing disaccharides are sucrose and trehalose.
Sucrose and Trehalose
Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose, while trehalose is a disaccharide made up of two glucose molecules. Both of these disaccharides are non-reducing, meaning they do not react with Benedict's reagent or Tollens' reagent.
Maltose and Lactose
Maltose is a disaccharide made up of two glucose molecules, while lactose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose. Both of these disaccharides are reducing, meaning they can react with Benedict's reagent or Tollens' reagent.
Conclusion
Therefore, the set that contains non-reducing disaccharides is sucrose and trehalose, which are made up of glucose and fructose and two glucose molecules, respectively.
Non-reducing disaccharides are a type of disaccharide that do not contain a free aldehyde or ketone group, which means they cannot be oxidized. Some common examples of non-reducing disaccharides are sucrose and trehalose.
Sucrose and Trehalose
Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose, while trehalose is a disaccharide made up of two glucose molecules. Both of these disaccharides are non-reducing, meaning they do not react with Benedict's reagent or Tollens' reagent.
Maltose and Lactose
Maltose is a disaccharide made up of two glucose molecules, while lactose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose. Both of these disaccharides are reducing, meaning they can react with Benedict's reagent or Tollens' reagent.
Conclusion
Therefore, the set that contains non-reducing disaccharides is sucrose and trehalose, which are made up of glucose and fructose and two glucose molecules, respectively.
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN → CH3CH2CH2CN + NaBr, will be fastest in- a)ethanol
- b)methanol
- c)N, N-dimethylformamide
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN → CH3CH2CH2CN + NaBr, will be fastest in
a)
ethanol
b)
methanol
c)
N, N-dimethylformamide
d)
Water
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The reaction given is a nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2) where cyanide ion (CN-) from sodium cyanide (NaCN) replaces the bromine atom (Br) in the 1-bromo-propane molecule (CH3CH2CH2Br) to form propionitrile (CH3CH2CH2CN) and sodium bromide (NaBr).
In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile (CN-) attacks the substrate (CH3CH2CH2Br) from the backside, and the leaving group (Br-) leaves from the same side. The rate of an SN2 reaction depends on the ability of the nucleophile to approach the substrate. Therefore, the reaction will be faster in a solvent that doesn't stabilize the nucleophile too much, so it remains reactive.
Polar aprotic solvents, like N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), do not have an acidic hydrogen atom and do not form strong hydrogen bonds with the nucleophile. This makes the nucleophile more available for the reaction, increasing the reaction rate. In contrast, polar protic solvents like water, methanol, and ethanol can form hydrogen bonds with the nucleophile, stabilizing it and decreasing its reactivity.
Therefore, the reaction will be fastest in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF).
In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile (CN-) attacks the substrate (CH3CH2CH2Br) from the backside, and the leaving group (Br-) leaves from the same side. The rate of an SN2 reaction depends on the ability of the nucleophile to approach the substrate. Therefore, the reaction will be faster in a solvent that doesn't stabilize the nucleophile too much, so it remains reactive.
Polar aprotic solvents, like N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), do not have an acidic hydrogen atom and do not form strong hydrogen bonds with the nucleophile. This makes the nucleophile more available for the reaction, increasing the reaction rate. In contrast, polar protic solvents like water, methanol, and ethanol can form hydrogen bonds with the nucleophile, stabilizing it and decreasing its reactivity.
Therefore, the reaction will be fastest in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF).
The drift velocity of the electrons in a current carrying conductor is of the order of:- a)10-4 ms
- b)10° ms
- c)104 ms
- d)108 ms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The drift velocity of the electrons in a current carrying conductor is of the order of:
a)
10-4 ms
b)
10° ms
c)
104 ms
d)
108 ms
|
|
Janani Yadav answered |
Drift Velocity of Electrons in a Current Carrying Conductor
Introduction:
In a current carrying conductor, electrons move from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal. The motion of the electrons is not constant but rather erratic. However, there is a net direction of motion that results in a current. The drift velocity is the average velocity of the electrons in the direction of the current.
Factors affecting the drift velocity:
The drift velocity of the electrons depends on various factors such as the electric field strength, the temperature of the conductor, and the number density of electrons in the conductor.
Formula for drift velocity:
The formula for drift velocity is given by:
vd = (eEτ)/m
Where,
vd = drift velocity
e = charge of an electron
E = electric field strength
τ = relaxation time of electrons
m = mass of an electron
Answer Explanation:
The drift velocity of the electrons in a current carrying conductor is of the order of 10^-4 m/s. This is because the electric field strength in a typical conductor is on the order of 10^5 V/m, and the relaxation time of electrons is on the order of 10^-14 s. Using the formula for drift velocity, we can calculate that the drift velocity of electrons is approximately 10^-4 m/s.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the drift velocity of electrons in a current carrying conductor is a function of various factors such as the electric field strength, temperature, and number density of electrons. However, the typical drift velocity in a conductor is on the order of 10^-4 m/s.
Introduction:
In a current carrying conductor, electrons move from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal. The motion of the electrons is not constant but rather erratic. However, there is a net direction of motion that results in a current. The drift velocity is the average velocity of the electrons in the direction of the current.
Factors affecting the drift velocity:
The drift velocity of the electrons depends on various factors such as the electric field strength, the temperature of the conductor, and the number density of electrons in the conductor.
Formula for drift velocity:
The formula for drift velocity is given by:
vd = (eEτ)/m
Where,
vd = drift velocity
e = charge of an electron
E = electric field strength
τ = relaxation time of electrons
m = mass of an electron
Answer Explanation:
The drift velocity of the electrons in a current carrying conductor is of the order of 10^-4 m/s. This is because the electric field strength in a typical conductor is on the order of 10^5 V/m, and the relaxation time of electrons is on the order of 10^-14 s. Using the formula for drift velocity, we can calculate that the drift velocity of electrons is approximately 10^-4 m/s.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the drift velocity of electrons in a current carrying conductor is a function of various factors such as the electric field strength, temperature, and number density of electrons. However, the typical drift velocity in a conductor is on the order of 10^-4 m/s.
Which of the following compound is essentially covalent in nature?- a)CaCl2
- b)SrCl2
- c)MgCl2
- d)BeCl2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound is essentially covalent in nature?
a)
CaCl2
b)
SrCl2
c)
MgCl2
d)
BeCl2
|
|
Shail Ghosh answered |
Covalent nature of compounds
Compounds are of two types based on their nature: covalent and ionic. Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, whereas ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The type of bond formed between atoms in a compound determines its nature.
Essentially covalent compound
An essentially covalent compound is a compound that has a high degree of covalent character. In other words, the sharing of electrons between atoms is so strong that the compound behaves as if it were a purely covalent compound. Essentially covalent compounds usually have low melting and boiling points, and they are poor conductors of electricity.
BeCl2 as an essentially covalent compound
Out of the given options, the compound that is essentially covalent in nature is BeCl2. Beryllium chloride (BeCl2) is a linear molecule in which the two chlorine atoms share their electrons with the beryllium atom. The electronegativity difference between beryllium and chlorine is small, which means that the sharing of electrons is almost equal. This results in a high degree of covalent character in the Be-Cl bond, making BeCl2 an essentially covalent compound.
On the other hand, CaCl2, SrCl2, and MgCl2 are ionic compounds. In these compounds, the electronegativity difference between the metal and the halogen is large, resulting in the transfer of electrons from the metal to the halogen. As a result, these compounds have a high degree of ionic character.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BeCl2 is an essentially covalent compound, while CaCl2, SrCl2, and MgCl2 are ionic compounds. The nature of a compound is determined by the type of bond formed between atoms, which is in turn determined by the electronegativity difference between the atoms.
Compounds are of two types based on their nature: covalent and ionic. Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, whereas ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The type of bond formed between atoms in a compound determines its nature.
Essentially covalent compound
An essentially covalent compound is a compound that has a high degree of covalent character. In other words, the sharing of electrons between atoms is so strong that the compound behaves as if it were a purely covalent compound. Essentially covalent compounds usually have low melting and boiling points, and they are poor conductors of electricity.
BeCl2 as an essentially covalent compound
Out of the given options, the compound that is essentially covalent in nature is BeCl2. Beryllium chloride (BeCl2) is a linear molecule in which the two chlorine atoms share their electrons with the beryllium atom. The electronegativity difference between beryllium and chlorine is small, which means that the sharing of electrons is almost equal. This results in a high degree of covalent character in the Be-Cl bond, making BeCl2 an essentially covalent compound.
On the other hand, CaCl2, SrCl2, and MgCl2 are ionic compounds. In these compounds, the electronegativity difference between the metal and the halogen is large, resulting in the transfer of electrons from the metal to the halogen. As a result, these compounds have a high degree of ionic character.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BeCl2 is an essentially covalent compound, while CaCl2, SrCl2, and MgCl2 are ionic compounds. The nature of a compound is determined by the type of bond formed between atoms, which is in turn determined by the electronegativity difference between the atoms.
Which one is not a feature of asexual reproduction?- a)It can occur with or without gamete formation
- b)New organisms inherit all of its chromosomes from one parent
- c)New individuals are formed even from the vegetative/somatic cells
- d)It can occur only through unspecialised parts of parent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a feature of asexual reproduction?
a)
It can occur with or without gamete formation
b)
New organisms inherit all of its chromosomes from one parent
c)
New individuals are formed even from the vegetative/somatic cells
d)
It can occur only through unspecialised parts of parent
|
|
Srestha Ahuja answered |
Features of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves only one parent. Here are some of the features of asexual reproduction:
- It can occur with or without gamete formation: Asexual reproduction can occur with or without the formation of gametes (sex cells).
- New organisms inherit all of its chromosomes from one parent: In asexual reproduction, the offspring inherit all of their chromosomes from a single parent.
- New individuals are formed even from the vegetative/somatic cells: Asexual reproduction can occur through the use of specialized reproductive structures, such as buds, or from the vegetative or somatic cells of the parent.
- It can occur only through unspecialized parts of parent: This statement is false. Asexual reproduction can occur through the use of specialized reproductive structures, such as buds, or from the vegetative or somatic cells of the parent.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves only one parent. Here are some of the features of asexual reproduction:
- It can occur with or without gamete formation: Asexual reproduction can occur with or without the formation of gametes (sex cells).
- New organisms inherit all of its chromosomes from one parent: In asexual reproduction, the offspring inherit all of their chromosomes from a single parent.
- New individuals are formed even from the vegetative/somatic cells: Asexual reproduction can occur through the use of specialized reproductive structures, such as buds, or from the vegetative or somatic cells of the parent.
- It can occur only through unspecialized parts of parent: This statement is false. Asexual reproduction can occur through the use of specialized reproductive structures, such as buds, or from the vegetative or somatic cells of the parent.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Select the correct sequence w.r.t. sexual reproduction.- a)Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy ⟶ Embryogenesis ⟶ Zygote
- b)Zygote ⟶ Embryogenesis ⟶ Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy
- c)Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy ⟶ Zygote Embryogenesis
- d)Syngamy ⟶ Zygote ⟶ Gametogeneis ⟶ Embryogenesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct sequence w.r.t. sexual reproduction.
a)
Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy ⟶ Embryogenesis ⟶ Zygote
b)
Zygote ⟶ Embryogenesis ⟶ Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy
c)
Gametogenesis ⟶ Syngamy ⟶ Zygote Embryogenesis
d)
Syngamy ⟶ Zygote ⟶ Gametogeneis ⟶ Embryogenesis
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Development of embryo from the diploid zygote is known as embryogenesis.
A spring of force constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other. The force constant of the longer piece will be- a)1.5k
- b)3k
- c)2k
- d)2/3 k
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A spring of force constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other. The force constant of the longer piece will be
a)
1.5k
b)
3k
c)
2k
d)
2/3 k
|
|
Sounak Shah answered |
Explanation:
When a spring is cut into two pieces, the force constant of the longer piece will be different from the force constant of the shorter piece. Let's denote the force constant of the original spring as k, and the lengths of the two pieces as L1 and L2, where L2 is double the length of L1.
Using Hooke's Law:
Hooke's Law states that the force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
F = -kx
Where F is the force applied, k is the force constant, and x is the displacement.
Relation between force constants and lengths:
The force constant of a spring is inversely proportional to its length. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
k ∝ 1/L
Where k is the force constant and L is the length of the spring.
Relation between lengths and force constants:
If we consider the original spring with force constant k and length L, and then cut it into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other, we can establish the following relations:
L2 = 2L1
k2 ∝ 1/L2 (Force constant of longer piece)
k1 ∝ 1/L1 (Force constant of shorter piece)
Using the relation between lengths:
From the given information, we know that L2 = 2L1. Substituting this into the relation for force constants, we get:
k2 ∝ 1/(2L1)
Comparing force constants:
We can compare the force constants of the longer and shorter pieces by taking their ratio:
k2/k1 = (1/(2L1))/(1/L1) = (1/(2L1))*(L1/1) = 1/2
Therefore, the force constant of the longer piece is half of the force constant of the shorter piece.
Conclusion:
From the above comparison, we can see that the force constant of the longer piece is half of the force constant of the shorter piece. Therefore, the correct answer is option A: 1.5k.
When a spring is cut into two pieces, the force constant of the longer piece will be different from the force constant of the shorter piece. Let's denote the force constant of the original spring as k, and the lengths of the two pieces as L1 and L2, where L2 is double the length of L1.
Using Hooke's Law:
Hooke's Law states that the force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
F = -kx
Where F is the force applied, k is the force constant, and x is the displacement.
Relation between force constants and lengths:
The force constant of a spring is inversely proportional to its length. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
k ∝ 1/L
Where k is the force constant and L is the length of the spring.
Relation between lengths and force constants:
If we consider the original spring with force constant k and length L, and then cut it into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other, we can establish the following relations:
L2 = 2L1
k2 ∝ 1/L2 (Force constant of longer piece)
k1 ∝ 1/L1 (Force constant of shorter piece)
Using the relation between lengths:
From the given information, we know that L2 = 2L1. Substituting this into the relation for force constants, we get:
k2 ∝ 1/(2L1)
Comparing force constants:
We can compare the force constants of the longer and shorter pieces by taking their ratio:
k2/k1 = (1/(2L1))/(1/L1) = (1/(2L1))*(L1/1) = 1/2
Therefore, the force constant of the longer piece is half of the force constant of the shorter piece.
Conclusion:
From the above comparison, we can see that the force constant of the longer piece is half of the force constant of the shorter piece. Therefore, the correct answer is option A: 1.5k.
In a ccp structure, if 2/3 rd face-centred atoms are removed, then the percentage of occupied space in unit cell will be- a)60%
- b)2.2%
- c)47.5 %
- d)37%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a ccp structure, if 2/3 rd face-centred atoms are removed, then the percentage of occupied space in unit cell will be
a)
60%
b)
2.2%
c)
47.5 %
d)
37%
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
In CCP (FCC) lattice,
1 unit cell contain

Atoms removed from face centre
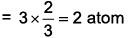
Since atoms become half so occupied space will become half that is
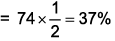
If power dissipated in the 9 Ω resistor in the circuit shown is 36 W, the potential difference across the 2 Ω resistor is
- a)4 V
- b)8 V
- c)2 V
- d)10 V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If power dissipated in the 9 Ω resistor in the circuit shown is 36 W, the potential difference across the 2 Ω resistor is

a)
4 V
b)
8 V
c)
2 V
d)
10 V
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
We have,
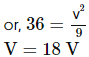
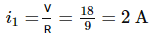
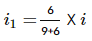
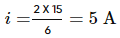
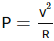
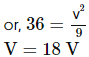
Current passing through the 9 Ω resistor is
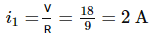
The 9 Ω and 6 Ω resistors are in parallel, therefore
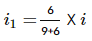
where i is the current delivered by the battery.
Therefore,
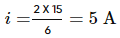
Thus, the potential difference across the 2 Ω resistor is
V = iRV = iR = 5 × 2 = 5 × 2 = 10 V
Which of the following classes is incorrectly matched with its general characters?- a)Cyclostomata: Lack jaws and paired fins and body is covered with placoid scales.
- b)Osteichthyes: Four pairs of gills are covered with an operculum and skin is covered with cycloid scales.
- c)Reptilia: Tympanum represents ear and fertilization is internal.
- d)Aves: Endoskeleton is fully ossified and long bones are hollow with air cavities called as pneumatic bones.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following classes is incorrectly matched with its general characters?
a)
Cyclostomata: Lack jaws and paired fins and body is covered with placoid scales.
b)
Osteichthyes: Four pairs of gills are covered with an operculum and skin is covered with cycloid scales.
c)
Reptilia: Tympanum represents ear and fertilization is internal.
d)
Aves: Endoskeleton is fully ossified and long bones are hollow with air cavities called as pneumatic bones.
|
|
Nishanth Chawla answered |
Incorrectly matched Class and General Characters
Class: Cyclostomata
Incorrect General Characters:
- Lack jaws and paired fins
- Body is covered with placoid scales
Correct General Characters:
- Lack jaws and paired fins
- Body is covered with a slimy skin without scales
Explanation:
Cyclostomata are jawless fish that include lampreys and hagfish. They have a circular mouth with sharp teeth and a tongue covered in tiny, sharp projections. They also lack paired fins and have a slimy skin without scales. The incorrect general characters listed in option A actually describe the cartilaginous fish, which include sharks and rays. These fish have jaws and paired fins, and their skin is covered with placoid scales. Therefore, option A is the incorrectly matched class and general characters.
Class: Cyclostomata
Incorrect General Characters:
- Lack jaws and paired fins
- Body is covered with placoid scales
Correct General Characters:
- Lack jaws and paired fins
- Body is covered with a slimy skin without scales
Explanation:
Cyclostomata are jawless fish that include lampreys and hagfish. They have a circular mouth with sharp teeth and a tongue covered in tiny, sharp projections. They also lack paired fins and have a slimy skin without scales. The incorrect general characters listed in option A actually describe the cartilaginous fish, which include sharks and rays. These fish have jaws and paired fins, and their skin is covered with placoid scales. Therefore, option A is the incorrectly matched class and general characters.
Which of the following secondary metabolites belong to toxin category?
- a)Codeine
- b)Concanavalin-A
- c)Anthocyanin
- d)Abrin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following secondary metabolites belong to toxin category?
a)
Codeine
b)
Concanavalin-A
c)
Anthocyanin
d)
Abrin
|
|
Naina Choudhary answered |
Toxic Secondary Metabolites
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds produced by plants that are not directly involved in the growth, development, or reproduction of the plant. Many of these compounds have important functions in the ecosystem, including defense against herbivores, attraction of pollinators, and inhibition of competing plants.
Some secondary metabolites have toxic properties and can cause harm to humans and animals if ingested or even touched. One such example of a toxic secondary metabolite is abrin.
Abrin
Abrin is a toxic protein found in the seeds of the Abrus precatorius plant, also known as the rosary pea. The seeds of this plant are often used in jewelry and other decorative items, but can be deadly if ingested.
Abrin works by inhibiting protein synthesis, which can lead to cell death and organ failure. Symptoms of abrin poisoning can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and seizures, and can be fatal in high doses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, abrin is an example of a toxic secondary metabolite produced by plants. While many secondary metabolites have important ecological functions, some can pose a risk to human and animal health. It is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with exposure to these compounds and to take appropriate precautions.
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds produced by plants that are not directly involved in the growth, development, or reproduction of the plant. Many of these compounds have important functions in the ecosystem, including defense against herbivores, attraction of pollinators, and inhibition of competing plants.
Some secondary metabolites have toxic properties and can cause harm to humans and animals if ingested or even touched. One such example of a toxic secondary metabolite is abrin.
Abrin
Abrin is a toxic protein found in the seeds of the Abrus precatorius plant, also known as the rosary pea. The seeds of this plant are often used in jewelry and other decorative items, but can be deadly if ingested.
Abrin works by inhibiting protein synthesis, which can lead to cell death and organ failure. Symptoms of abrin poisoning can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and seizures, and can be fatal in high doses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, abrin is an example of a toxic secondary metabolite produced by plants. While many secondary metabolites have important ecological functions, some can pose a risk to human and animal health. It is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with exposure to these compounds and to take appropriate precautions.
In which of the following defects density of crystal remain same?- a)Schottky defect
- b)Impurity defect
- c)Frenkel defect
- d)F-centre defect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following defects density of crystal remain same?
a)
Schottky defect
b)
Impurity defect
c)
Frenkel defect
d)
F-centre defect
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In Frenkel defect density of the crystal remains unchanged.
Nodes of Ranvier in myelinated neurons of PNS- a)Possess neurilemma
- b)Lack neurilemma
- c)Lack axolemma
- d)Possess myelin sheath
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nodes of Ranvier in myelinated neurons of PNS
a)
Possess neurilemma
b)
Lack neurilemma
c)
Lack axolemma
d)
Possess myelin sheath
|
|
Nitya Shah answered |
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). These nodes play a crucial role in the conduction of nerve impulses along the axon.
Nodes of Ranvier possess neurilemma.
- Neurilemma: The neurilemma is the outermost layer of the myelin sheath that surrounds the axon. It is formed by the Schwann cells in the PNS. The presence of the neurilemma at the nodes of Ranvier allows for rapid and efficient conduction of nerve impulses.
- Function of the Neurilemma: The neurilemma plays a vital role in the regeneration of damaged or injured axons in the PNS. It provides a pathway for the regrowth of axons and facilitates the repair process.
- Importance of Nodes of Ranvier: The nodes of Ranvier are crucial for the saltatory conduction of nerve impulses along the axon. Saltatory conduction is a process in which the nerve impulses jump from one node to the next, allowing for faster and more efficient transmission of the signal. The presence of the nodes of Ranvier allows for the depolarization and repolarization of the axon membrane, which facilitates the conduction of the nerve impulse.
- Role in Nerve Impulse Conduction: The myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing the leakage of ions and increasing the speed of conduction. However, for efficient transmission of the nerve impulse, the depolarization and repolarization of the axon membrane need to occur at regular intervals. This is achieved at the nodes of Ranvier, where the axon is exposed. The depolarization occurs at one node, and the nerve impulse jumps to the next node, where repolarization occurs. This process continues along the axon, resulting in the rapid and efficient conduction of the nerve impulse.
In conclusion, nodes of Ranvier possess neurilemma, which is important for the saltatory conduction of nerve impulses along the myelinated neurons in the PNS.
Nodes of Ranvier possess neurilemma.
- Neurilemma: The neurilemma is the outermost layer of the myelin sheath that surrounds the axon. It is formed by the Schwann cells in the PNS. The presence of the neurilemma at the nodes of Ranvier allows for rapid and efficient conduction of nerve impulses.
- Function of the Neurilemma: The neurilemma plays a vital role in the regeneration of damaged or injured axons in the PNS. It provides a pathway for the regrowth of axons and facilitates the repair process.
- Importance of Nodes of Ranvier: The nodes of Ranvier are crucial for the saltatory conduction of nerve impulses along the axon. Saltatory conduction is a process in which the nerve impulses jump from one node to the next, allowing for faster and more efficient transmission of the signal. The presence of the nodes of Ranvier allows for the depolarization and repolarization of the axon membrane, which facilitates the conduction of the nerve impulse.
- Role in Nerve Impulse Conduction: The myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing the leakage of ions and increasing the speed of conduction. However, for efficient transmission of the nerve impulse, the depolarization and repolarization of the axon membrane need to occur at regular intervals. This is achieved at the nodes of Ranvier, where the axon is exposed. The depolarization occurs at one node, and the nerve impulse jumps to the next node, where repolarization occurs. This process continues along the axon, resulting in the rapid and efficient conduction of the nerve impulse.
In conclusion, nodes of Ranvier possess neurilemma, which is important for the saltatory conduction of nerve impulses along the myelinated neurons in the PNS.
Given below are two statements:I. In Lucas test, primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their reactivity with conc. HCl+ZnCl2, known as Lucas Reagent.II.Primary alcohols are most reactive and immediately produce turbidity at room temperature on reaction with Lucas Reagent.In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- a)I is incorrect but II is correct
- b)Both I and II correct
- c)Both I and II are incorrect
- d)I is correct but II is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements:
I. In Lucas test, primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their reactivity with conc. HCl+ZnCl2, known as Lucas Reagent.
II.Primary alcohols are most reactive and immediately produce turbidity at room temperature on reaction with Lucas Reagent.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
a)
I is incorrect but II is correct
b)
Both I and II correct
c)
Both I and II are incorrect
d)
I is correct but II is incorrect
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
In the Lucas test, primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their reactivity with conc. HCl+ZnCl2, known as Lucas Reagent.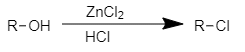
Tertiary alcohol gives immediate white turbidity with Lucas reagent, secondary alcohol gives white turbidity in 5 minutes, and primary alcohol does not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature.
The general reaction is as follows:
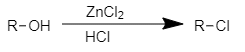
Hence, Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect.
Acidic pH in stomach, saliva in mouth and tears from the eyes are parts of- a)Physical barriers of innate immunity
- b)Physiological barriers of innate immunity
- c)Cytokine barriers of innate immunity
- d)Humoral/fluid mediated specific immunity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acidic pH in stomach, saliva in mouth and tears from the eyes are parts of
a)
Physical barriers of innate immunity
b)
Physiological barriers of innate immunity
c)
Cytokine barriers of innate immunity
d)
Humoral/fluid mediated specific immunity
|
|
Meera Dey answered |
Physiological barriers of innate immunity
Physiological barriers of innate immunity are the natural defense mechanisms that are present in the body to protect against pathogens and prevent infections. These barriers are always present and provide a continuous line of defense against invading microorganisms.
There are several physiological barriers that play a crucial role in innate immunity, and three of them are the acidic pH in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, and tears from the eyes.
Acidic pH in the stomach
- The stomach has an extremely low pH due to the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl) secreted by the stomach lining.
- The acidic environment in the stomach serves as a barrier against ingested pathogens.
- Most microorganisms cannot survive in the highly acidic environment of the stomach, preventing them from causing infections.
Saliva in the mouth
- Saliva contains various antimicrobial substances, including lysozyme, lactoferrin, and antibodies.
- Lysozyme is an enzyme that can break down the cell walls of certain bacteria, preventing their growth and replication.
- Lactoferrin binds to iron, which is essential for bacterial growth, making it unavailable for bacteria to use.
- Antibodies present in saliva can neutralize pathogens and prevent their entry into the body.
Tears from the eyes
- Tears contain lysozyme, lactoferrin, and antibodies, similar to saliva.
- These components help to protect the eyes from infections by preventing the growth and survival of microorganisms on the surface of the eye.
These physiological barriers act as the first line of defense against pathogens and help in preventing infections. They provide a hostile environment for microorganisms, making it difficult for them to survive and cause harm to the body. These barriers work together with other components of the immune system to provide effective protection against pathogens.
Physiological barriers of innate immunity are the natural defense mechanisms that are present in the body to protect against pathogens and prevent infections. These barriers are always present and provide a continuous line of defense against invading microorganisms.
There are several physiological barriers that play a crucial role in innate immunity, and three of them are the acidic pH in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, and tears from the eyes.
Acidic pH in the stomach
- The stomach has an extremely low pH due to the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl) secreted by the stomach lining.
- The acidic environment in the stomach serves as a barrier against ingested pathogens.
- Most microorganisms cannot survive in the highly acidic environment of the stomach, preventing them from causing infections.
Saliva in the mouth
- Saliva contains various antimicrobial substances, including lysozyme, lactoferrin, and antibodies.
- Lysozyme is an enzyme that can break down the cell walls of certain bacteria, preventing their growth and replication.
- Lactoferrin binds to iron, which is essential for bacterial growth, making it unavailable for bacteria to use.
- Antibodies present in saliva can neutralize pathogens and prevent their entry into the body.
Tears from the eyes
- Tears contain lysozyme, lactoferrin, and antibodies, similar to saliva.
- These components help to protect the eyes from infections by preventing the growth and survival of microorganisms on the surface of the eye.
These physiological barriers act as the first line of defense against pathogens and help in preventing infections. They provide a hostile environment for microorganisms, making it difficult for them to survive and cause harm to the body. These barriers work together with other components of the immune system to provide effective protection against pathogens.
Select the incorrect statementsA. Indian agriculture accounts for approximately 62 percent of India’s GDP.B. During the period 1960 and 2000, wheat and rice production increased from 11 million tonnes to 89.5 million tonnesC. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1D. Saccharum officinarum was originally grown in North India having high sugar content and yield- a)A and C
- b)B, C and D
- c)Only D
- d)A, B and D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statements
A. Indian agriculture accounts for approximately 62 percent of India’s GDP.
B. During the period 1960 and 2000, wheat and rice production increased from 11 million tonnes to 89.5 million tonnes
C. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1
D. Saccharum officinarum was originally grown in North India having high sugar content and yield
a)
A and C
b)
B, C and D
c)
Only D
d)
A, B and D
|
|
Moumita Chauhan answered |
Incorrect Statements:
A. Indian agriculture accounts for approximately 62 percent of India’s GDP.
This statement is incorrect. According to the latest data, agriculture contributes around 17-18 percent to India's GDP, not 62 percent.
B. During the period 1960 and 2000, wheat and rice production increased from 11 million tonnes to 89.5 million tonnes.
This statement is correct. During the period mentioned, there was a significant increase in wheat and rice production in India. The Green Revolution, which included the adoption of high-yielding varieties, improved irrigation, and increased use of fertilizers, played a crucial role in this increase.
C. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1.
This statement is correct. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were indeed derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1. IR-8, also known as "Miracle Rice," was developed by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and played a significant role in increasing rice production. Taichung Native-1 was another important variety used in the development of semi-dwarf varieties.
D. Saccharum officinarum was originally grown in North India having high sugar content and yield.
This statement is incorrect. Saccharum officinarum, commonly known as sugarcane, is not originally grown in North India. It is believed to have originated in New Guinea and spread to Southeast Asia and India. It is mainly cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of North India, but it is not exclusive to that region. Sugarcane is known for its high sugar content and yield.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) A, B, and D as all the statements are incorrect.
A. Indian agriculture accounts for approximately 62 percent of India’s GDP.
This statement is incorrect. According to the latest data, agriculture contributes around 17-18 percent to India's GDP, not 62 percent.
B. During the period 1960 and 2000, wheat and rice production increased from 11 million tonnes to 89.5 million tonnes.
This statement is correct. During the period mentioned, there was a significant increase in wheat and rice production in India. The Green Revolution, which included the adoption of high-yielding varieties, improved irrigation, and increased use of fertilizers, played a crucial role in this increase.
C. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1.
This statement is correct. Semi-dwarf rice varieties were indeed derived from IR-8 and Taichung Native-1. IR-8, also known as "Miracle Rice," was developed by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and played a significant role in increasing rice production. Taichung Native-1 was another important variety used in the development of semi-dwarf varieties.
D. Saccharum officinarum was originally grown in North India having high sugar content and yield.
This statement is incorrect. Saccharum officinarum, commonly known as sugarcane, is not originally grown in North India. It is believed to have originated in New Guinea and spread to Southeast Asia and India. It is mainly cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of North India, but it is not exclusive to that region. Sugarcane is known for its high sugar content and yield.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) A, B, and D as all the statements are incorrect.
The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination ϕ is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough. A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower half is- a)tan ϕ
- b)2 tan ϕ
- c)2 cos ϕ
- d)2 sin ϕ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination ϕ is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough. A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower half is
a)
tan ϕ
b)
2 tan ϕ
c)
2 cos ϕ
d)
2 sin ϕ
|
|
Sahil Goyal answered |
Analysis:
To understand why the correct answer is option 'B', let's analyze the motion of the body on the inclined plane.
1. Motion on the Upper Half:
Since the upper half of the inclined plane is perfectly smooth, there is no friction acting on the body. Therefore, the body will slide down the incline without any hindrance. Let's denote the acceleration of the body on the upper half as 'a'.
2. Motion on the Lower Half:
On the lower half of the inclined plane, the surface is rough, and there is friction acting on the body. Let's denote the coefficient of friction as 'μ'. The body will experience a frictional force in the opposite direction to its motion.
3. Equations of Motion:
To determine the condition for the body to come to rest at the bottom, we can use the equations of motion.
On the upper half:
- Distance traveled, d₁ = h/2
- Initial velocity, u = 0
- Final velocity, v = ?
- Acceleration, a = ?
Using the equation v² = u² + 2as, we can find the acceleration on the upper half:
v² = 0 + 2a(h/2)
v² = ah
On the lower half:
- Distance traveled, d₂ = h/2
- Initial velocity, u = ?
- Final velocity, v = 0
- Acceleration, a = ?
Since the body comes to rest at the bottom, we can use the equation v² = u² + 2as to find the acceleration on the lower half:
0 = u² + 2a(h/2)
u² = -ah
4. Condition for Rest:
For the body to come to rest at the bottom, the velocity on the lower half should be zero. Therefore, we can equate the final velocity on the upper half to the initial velocity on the lower half:
v² = u²
Substituting the values of v² and u² from the equations of motion:
ah = -ah
2ah = 0
ah = 0
5. Coefficient of Friction:
The frictional force acting on the lower half of the inclined plane is given by f = μN, where N is the normal force. The normal force N is equal to the weight of the body, which is mg.
Since the body is not accelerating on the lower half (ah = 0), the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, the frictional force must be equal to the component of the weight along the incline.
Using trigonometry, we can write:
mg sin ϕ = μmg cos ϕ
sin ϕ = μ cos ϕ
μ = tan ϕ
The coefficient of friction μ is equal to tan ϕ.
6. Conclusion:
From the above analysis, we can conclude that the coefficient of friction for the lower half of the inclined plane is equal to tan ϕ. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - 2 tan ϕ.
To understand why the correct answer is option 'B', let's analyze the motion of the body on the inclined plane.
1. Motion on the Upper Half:
Since the upper half of the inclined plane is perfectly smooth, there is no friction acting on the body. Therefore, the body will slide down the incline without any hindrance. Let's denote the acceleration of the body on the upper half as 'a'.
2. Motion on the Lower Half:
On the lower half of the inclined plane, the surface is rough, and there is friction acting on the body. Let's denote the coefficient of friction as 'μ'. The body will experience a frictional force in the opposite direction to its motion.
3. Equations of Motion:
To determine the condition for the body to come to rest at the bottom, we can use the equations of motion.
On the upper half:
- Distance traveled, d₁ = h/2
- Initial velocity, u = 0
- Final velocity, v = ?
- Acceleration, a = ?
Using the equation v² = u² + 2as, we can find the acceleration on the upper half:
v² = 0 + 2a(h/2)
v² = ah
On the lower half:
- Distance traveled, d₂ = h/2
- Initial velocity, u = ?
- Final velocity, v = 0
- Acceleration, a = ?
Since the body comes to rest at the bottom, we can use the equation v² = u² + 2as to find the acceleration on the lower half:
0 = u² + 2a(h/2)
u² = -ah
4. Condition for Rest:
For the body to come to rest at the bottom, the velocity on the lower half should be zero. Therefore, we can equate the final velocity on the upper half to the initial velocity on the lower half:
v² = u²
Substituting the values of v² and u² from the equations of motion:
ah = -ah
2ah = 0
ah = 0
5. Coefficient of Friction:
The frictional force acting on the lower half of the inclined plane is given by f = μN, where N is the normal force. The normal force N is equal to the weight of the body, which is mg.
Since the body is not accelerating on the lower half (ah = 0), the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, the frictional force must be equal to the component of the weight along the incline.
Using trigonometry, we can write:
mg sin ϕ = μmg cos ϕ
sin ϕ = μ cos ϕ
μ = tan ϕ
The coefficient of friction μ is equal to tan ϕ.
6. Conclusion:
From the above analysis, we can conclude that the coefficient of friction for the lower half of the inclined plane is equal to tan ϕ. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - 2 tan ϕ.
The unit of permittivity of free space is- a)A2 N-1 m-2
- b)C2N-1m-1
- c)C2 N m-1
- d)F m-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit of permittivity of free space is
a)
A2 N-1 m-2
b)
C2N-1m-1
c)
C2 N m-1
d)
F m-1
|
|
Pranjal Malik answered |
Explanation:
Permittivity of free space is defined as the measure of the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field.
The SI unit of permittivity of free space is Farad per meter (F/m).
In other words, the permittivity of free space is the ratio of the electric flux density to the electric field intensity in a vacuum.
The formula for permittivity of free space is given by:
ε0 = 1/(μ0c^2)
where ε0 is the permittivity of free space, μ0 is the permeability of free space, and c is the speed of light in vacuum.
The value of ε0 is approximately 8.85 x 10^-12 F/m.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, which states that the unit of permittivity of free space is F/m.
In summary:
- The permittivity of free space is the measure of the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field.
- The SI unit of permittivity of free space is Farad per meter (F/m).
- The formula for permittivity of free space is ε0 = 1/(μ0c^2).
- The value of ε0 is approximately 8.85 x 10^-12 F/m.
Permittivity of free space is defined as the measure of the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field.
The SI unit of permittivity of free space is Farad per meter (F/m).
In other words, the permittivity of free space is the ratio of the electric flux density to the electric field intensity in a vacuum.
The formula for permittivity of free space is given by:
ε0 = 1/(μ0c^2)
where ε0 is the permittivity of free space, μ0 is the permeability of free space, and c is the speed of light in vacuum.
The value of ε0 is approximately 8.85 x 10^-12 F/m.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, which states that the unit of permittivity of free space is F/m.
In summary:
- The permittivity of free space is the measure of the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field.
- The SI unit of permittivity of free space is Farad per meter (F/m).
- The formula for permittivity of free space is ε0 = 1/(μ0c^2).
- The value of ε0 is approximately 8.85 x 10^-12 F/m.
The bioactive molecule used in detergent formulation as dirt buster is- a)Cyclosporin-A
- b)Streptokinase
- c)Pectinase
- d)Lipase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The bioactive molecule used in detergent formulation as dirt buster is
a)
Cyclosporin-A
b)
Streptokinase
c)
Pectinase
d)
Lipase
|
|
Samridhi Gupta answered |
The bioactive molecule used in detergent formulation as dirt buster is Lipase.
Lipase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the breakdown of fats or lipids. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. This makes it an essential component in detergent formulations as it helps to remove grease and oil stains from fabrics and surfaces.
Why is Lipase used in detergent formulation?
Lipase is chosen for detergent formulation due to its ability to break down lipid-based stains, making it an effective dirt buster. Here are the reasons why lipase is preferred:
1. Breaks down fatty stains: Lipase targets and breaks down fatty substances, such as oils, grease, and other lipid-based stains. These stains are commonly found on clothes, dishes, and various surfaces.
2. Enhances cleaning efficiency: By specifically targeting and breaking down lipids, lipase enhances the cleaning efficiency of detergents. It helps to remove stubborn stains and ensures a thorough clean.
3. Effective at low temperatures: Lipase is active at a wide range of temperatures, including lower temperatures. This is important for energy-saving purposes as it allows detergents to be effective even in cold water washes.
4. Compatible with other enzymes: Lipase can work synergistically with other enzymes commonly used in detergents, such as proteases and amylases. This combination allows for the removal of a wide range of stains, including protein-based and starch-based stains.
5. Environmentally friendly: Lipase is biodegradable and environmentally friendly. It does not persist in the environment and does not contribute to pollution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lipase is a bioactive molecule used in detergent formulations as a dirt buster. Its ability to break down lipid-based stains, enhance cleaning efficiency, work at low temperatures, and be compatible with other enzymes makes it an effective and environmentally friendly choice for detergent manufacturers.
Lipase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the breakdown of fats or lipids. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. This makes it an essential component in detergent formulations as it helps to remove grease and oil stains from fabrics and surfaces.
Why is Lipase used in detergent formulation?
Lipase is chosen for detergent formulation due to its ability to break down lipid-based stains, making it an effective dirt buster. Here are the reasons why lipase is preferred:
1. Breaks down fatty stains: Lipase targets and breaks down fatty substances, such as oils, grease, and other lipid-based stains. These stains are commonly found on clothes, dishes, and various surfaces.
2. Enhances cleaning efficiency: By specifically targeting and breaking down lipids, lipase enhances the cleaning efficiency of detergents. It helps to remove stubborn stains and ensures a thorough clean.
3. Effective at low temperatures: Lipase is active at a wide range of temperatures, including lower temperatures. This is important for energy-saving purposes as it allows detergents to be effective even in cold water washes.
4. Compatible with other enzymes: Lipase can work synergistically with other enzymes commonly used in detergents, such as proteases and amylases. This combination allows for the removal of a wide range of stains, including protein-based and starch-based stains.
5. Environmentally friendly: Lipase is biodegradable and environmentally friendly. It does not persist in the environment and does not contribute to pollution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lipase is a bioactive molecule used in detergent formulations as a dirt buster. Its ability to break down lipid-based stains, enhance cleaning efficiency, work at low temperatures, and be compatible with other enzymes makes it an effective and environmentally friendly choice for detergent manufacturers.
A substance absorbs an amount of heat Q1 in going from one state to another and releases an amount of heat Q2 in coming back from the second state to the first state. How much work is done by the substance?- a)Q1 / Q2
- b)Q1 - Q2
- c)Q2 / Q1
- d)Q1 + Q2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A substance absorbs an amount of heat Q1 in going from one state to another and releases an amount of heat Q2 in coming back from the second state to the first state. How much work is done by the substance?
a)
Q1 / Q2
b)
Q1 - Q2
c)
Q2 / Q1
d)
Q1 + Q2
|
|
Upasana Sharma answered |
Explanation:
When a substance absorbs heat Q1, it gains internal energy and undergoes a change in state. This change in state could be a phase change or a chemical reaction.
When the substance comes back to its initial state, it releases heat Q2. This heat release could be due to the reverse reaction or the reverse phase change.
During these processes, work is done by the substance. This work could be due to the expansion or compression of the substance.
The work done by the substance is given by the difference between the heat absorbed and the heat released.
Mathematically, work done = Q1 - Q2
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
When a substance absorbs heat Q1, it gains internal energy and undergoes a change in state. This change in state could be a phase change or a chemical reaction.
When the substance comes back to its initial state, it releases heat Q2. This heat release could be due to the reverse reaction or the reverse phase change.
During these processes, work is done by the substance. This work could be due to the expansion or compression of the substance.
The work done by the substance is given by the difference between the heat absorbed and the heat released.
Mathematically, work done = Q1 - Q2
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Which one of the following statements is true?- a)All organ system level animals have a tube within tube plan
- b)All blind sac animals contain diploblastic conditions
- c)Animals having radial symmetry contain blindsac body plan
- d)All chordates are vertebrates but all vertebrates are not chordates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is true?
a)
All organ system level animals have a tube within tube plan
b)
All blind sac animals contain diploblastic conditions
c)
Animals having radial symmetry contain blindsac body plan
d)
All chordates are vertebrates but all vertebrates are not chordates
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
All organ system level animals have a tube within a tube plan involving two tubes or openings. This plan calls for two openings: one for food to enter the body (mouth), one for wastes to leave the body (anus). Aschelminthes are the first organisms to show this type of body plan.
Aniline is less basic than cyclohexylamine because of which of the following reasons?- a)−I effect of NH2.
- b)+R effect of NH2.
- c)−R effect of NH2.
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Aniline is less basic than cyclohexylamine because of which of the following reasons?
a)
−I effect of NH2.
b)
+R effect of NH2.
c)
−R effect of NH2.
d)
None of these.
|
|
Kajal Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
+R effect of NH2:
- Aniline has a benzene ring with an NH2 group attached to it, which exhibits a +R effect due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- This +R effect disperses the electron density throughout the benzene ring, making the nitrogen less available for protonation and hence reducing the basicity of aniline.
- In contrast, cyclohexylamine does not have such an electron-donating group attached to the amino group, leading to higher basicity compared to aniline.
Therefore, the reason why aniline is less basic than cyclohexylamine is due to the +R effect of the NH2 group in aniline, which reduces its basicity.
+R effect of NH2:
- Aniline has a benzene ring with an NH2 group attached to it, which exhibits a +R effect due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- This +R effect disperses the electron density throughout the benzene ring, making the nitrogen less available for protonation and hence reducing the basicity of aniline.
- In contrast, cyclohexylamine does not have such an electron-donating group attached to the amino group, leading to higher basicity compared to aniline.
Therefore, the reason why aniline is less basic than cyclohexylamine is due to the +R effect of the NH2 group in aniline, which reduces its basicity.
Which of the following is not a pre-fertilisation event?- a)Gametogenesis
- b)Embryogenesis
- c)Gamete Transfer
- d)Pollen-pistil interaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a pre-fertilisation event?
a)
Gametogenesis
b)
Embryogenesis
c)
Gamete Transfer
d)
Pollen-pistil interaction
|
|
Upasana Sharma answered |
**The correct answer is option B: Embryogenesis**
**Explanation:**
**Pre-fertilization events** refer to the series of processes that occur before the fusion of male and female gametes during sexual reproduction in plants. These events are essential for the successful fertilization and subsequent development of the embryo.
Let's discuss each of the given options and why option B is not a pre-fertilization event:
a) **Gametogenesis**:
- Gametogenesis is the process of formation and development of male and female gametes (sperm and egg cells) in plants.
- In plants, male gametes are produced in the anther through the process of microsporogenesis, which includes the formation of microspore mother cells and their subsequent division to produce microspores.
- Female gametes are produced in the ovule through the process of megasporogenesis, which involves the formation of megaspore mother cells and their subsequent division to produce megaspores.
- Gametogenesis is a crucial pre-fertilization event as it leads to the formation of mature and functional gametes.
b) **Embryogenesis**:
- Embryogenesis is the process of development and formation of an embryo from the fertilized egg (zygote).
- It occurs after fertilization and involves the division and differentiation of cells to form the embryonic structures.
- Therefore, embryogenesis is a post-fertilization event and not a pre-fertilization event. This is why option B is the correct answer.
c) **Gamete Transfer**:
- Gamete transfer refers to the transfer of male gametes (pollen grains) from the anther to the female reproductive organ (pistil).
- In plants, this transfer can occur through various means, such as wind, water, insects, or other pollinators.
- Gamete transfer is an essential pre-fertilization event as it brings the male gametes in close proximity to the female reproductive organ for potential fertilization.
d) **Pollen-pistil interaction**:
- Pollen-pistil interaction refers to the physical and biochemical interactions that occur between the pollen grains and the pistil (female reproductive organ).
- These interactions are important for successful pollen germination, pollen tube growth, and eventual fertilization.
- Pollen-pistil interaction is a crucial pre-fertilization event as it allows for the recognition and acceptance of compatible pollen grains by the pistil.
In summary, the correct answer is option B: Embryogenesis, as it is a post-fertilization event and not a pre-fertilization event.
**Explanation:**
**Pre-fertilization events** refer to the series of processes that occur before the fusion of male and female gametes during sexual reproduction in plants. These events are essential for the successful fertilization and subsequent development of the embryo.
Let's discuss each of the given options and why option B is not a pre-fertilization event:
a) **Gametogenesis**:
- Gametogenesis is the process of formation and development of male and female gametes (sperm and egg cells) in plants.
- In plants, male gametes are produced in the anther through the process of microsporogenesis, which includes the formation of microspore mother cells and their subsequent division to produce microspores.
- Female gametes are produced in the ovule through the process of megasporogenesis, which involves the formation of megaspore mother cells and their subsequent division to produce megaspores.
- Gametogenesis is a crucial pre-fertilization event as it leads to the formation of mature and functional gametes.
b) **Embryogenesis**:
- Embryogenesis is the process of development and formation of an embryo from the fertilized egg (zygote).
- It occurs after fertilization and involves the division and differentiation of cells to form the embryonic structures.
- Therefore, embryogenesis is a post-fertilization event and not a pre-fertilization event. This is why option B is the correct answer.
c) **Gamete Transfer**:
- Gamete transfer refers to the transfer of male gametes (pollen grains) from the anther to the female reproductive organ (pistil).
- In plants, this transfer can occur through various means, such as wind, water, insects, or other pollinators.
- Gamete transfer is an essential pre-fertilization event as it brings the male gametes in close proximity to the female reproductive organ for potential fertilization.
d) **Pollen-pistil interaction**:
- Pollen-pistil interaction refers to the physical and biochemical interactions that occur between the pollen grains and the pistil (female reproductive organ).
- These interactions are important for successful pollen germination, pollen tube growth, and eventual fertilization.
- Pollen-pistil interaction is a crucial pre-fertilization event as it allows for the recognition and acceptance of compatible pollen grains by the pistil.
In summary, the correct answer is option B: Embryogenesis, as it is a post-fertilization event and not a pre-fertilization event.
At a certain place on earth, the true angle of dip is 60°, if the dip circle is oriented at an angle of 45º with the magnetic meridian, then the apparent angle of dip shown by the dip circle will be- a)tan-1(√6)
- b)45°
- c)tan-1(2)
- d)tan-1(√2)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At a certain place on earth, the true angle of dip is 60°, if the dip circle is oriented at an angle of 45º with the magnetic meridian, then the apparent angle of dip shown by the dip circle will be
a)
tan-1(√6)
b)
45°
c)
tan-1(2)
d)
tan-1(√2)
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |

A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in certain region. If an electron is projected in the region such that its velocity is pointed along direction of fields, then the electron:- a)Will turn towards left of direction of motion
- b)Will turn towards right of direction of motion
- c)Speed will decrease
- d)Speed will increase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in certain region. If an electron is projected in the region such that its velocity is pointed along direction of fields, then the electron:
a)
Will turn towards left of direction of motion
b)
Will turn towards right of direction of motion
c)
Speed will decrease
d)
Speed will increase
|
|
Anshika Roy answered |
Explanation:
When an electron is projected into a region where there is a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field along the same direction, it experiences both the electric and magnetic forces simultaneously. The direction of the electric force is given by the equation F = qE, where F is the force experienced by the electron, q is the charge of the electron, and E is the electric field. The direction of the magnetic force is given by the equation F = qvB, where v is the velocity of the electron and B is the magnetic field.
Forces acting on the electron:
The electric force and the magnetic force act in the same direction on the electron. This means that the net force on the electron is the sum of these two forces. Since the electron is projected with a velocity along the direction of the fields, there is no initial force acting on the electron perpendicular to its velocity. Therefore, the only forces acting on the electron are the electric and magnetic forces.
Effect of the electric force:
The electric force acts in the same direction as the velocity of the electron. This means that the electric force does not change the magnitude or direction of the electron's velocity. Hence, the speed of the electron remains unchanged.
Effect of the magnetic force:
The magnetic force acts perpendicular to both the velocity of the electron and the magnetic field. Since the magnetic force is perpendicular to the velocity of the electron, it causes the electron to move in a circular path. This circular motion is due to the magnetic force acting as a centripetal force. According to the equation F = mv^2/r, where m is the mass of the electron and r is the radius of the circular path, the magnetic force is given by F = qvB = mv^2/r. From this equation, we can find that r = mv/(qB). Since the velocity of the electron remains constant, the radius of the circular path is inversely proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
Conclusion:
When an electron is projected into a region with a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field along the same direction, the electron moves in a circular path due to the magnetic force acting as a centripetal force. The electric force does not change the magnitude or direction of the electron's velocity. Therefore, the speed of the electron remains constant.
When an electron is projected into a region where there is a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field along the same direction, it experiences both the electric and magnetic forces simultaneously. The direction of the electric force is given by the equation F = qE, where F is the force experienced by the electron, q is the charge of the electron, and E is the electric field. The direction of the magnetic force is given by the equation F = qvB, where v is the velocity of the electron and B is the magnetic field.
Forces acting on the electron:
The electric force and the magnetic force act in the same direction on the electron. This means that the net force on the electron is the sum of these two forces. Since the electron is projected with a velocity along the direction of the fields, there is no initial force acting on the electron perpendicular to its velocity. Therefore, the only forces acting on the electron are the electric and magnetic forces.
Effect of the electric force:
The electric force acts in the same direction as the velocity of the electron. This means that the electric force does not change the magnitude or direction of the electron's velocity. Hence, the speed of the electron remains unchanged.
Effect of the magnetic force:
The magnetic force acts perpendicular to both the velocity of the electron and the magnetic field. Since the magnetic force is perpendicular to the velocity of the electron, it causes the electron to move in a circular path. This circular motion is due to the magnetic force acting as a centripetal force. According to the equation F = mv^2/r, where m is the mass of the electron and r is the radius of the circular path, the magnetic force is given by F = qvB = mv^2/r. From this equation, we can find that r = mv/(qB). Since the velocity of the electron remains constant, the radius of the circular path is inversely proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
Conclusion:
When an electron is projected into a region with a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field along the same direction, the electron moves in a circular path due to the magnetic force acting as a centripetal force. The electric force does not change the magnitude or direction of the electron's velocity. Therefore, the speed of the electron remains constant.
Chapter doubts & questions for NEET Practice Tests (Old NCERT) - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of NEET Practice Tests (Old NCERT) - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup