All Exams >
JEE >
Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Work, Energy and Power for JEE Exam
For what angle between Force and Displacement will the work done be positive?- a)

- b)
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For what angle between Force and Displacement will the work done be positive?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- If a force acting on a body has a component in the opposite direction of displacement, the work done is negative.
- So when a body slides against a rough horizontal surface, its displacement is opposite to that of the force of friction. The work done by the friction is negative.
A 1.0 kg block collides with a horizontal weightless spring of force constant 2.75 Nm−1 as shown in figure. The block compresses the spring 4.0 m from the rest position. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and horizontal surface is 0.25, the speed of the block at the instant of collision is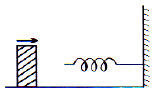
- a)0.4 ms−1
- b)4 ms−1
- c)0.8 ms−1
- d)8 ms −1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A 1.0 kg block collides with a horizontal weightless spring of force constant 2.75 Nm−1 as shown in figure. The block compresses the spring 4.0 m from the rest position. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and horizontal surface is 0.25, the speed of the block at the instant of collision is
a)
0.4 ms−1
b)
4 ms−1
c)
0.8 ms−1
d)
8 ms −1

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
Work done on m=change in kinetic energy
⇒ work done by friction and PE energy in spring= Δk.E
⇒ μn(x)+1/2kx2=1/2mv2
⇒ 0.25 x 10 x 4 + 1/2 x 275/100 x 16 = 1/2 x (1) v2
⇒10+22=1/2v2
⇒ 32x2=v2
⇒ 64=v2
⇒ v=8m/s
⇒ work done by friction and PE energy in spring= Δk.E
⇒ μn(x)+1/2kx2=1/2mv2
⇒ 0.25 x 10 x 4 + 1/2 x 275/100 x 16 = 1/2 x (1) v2
⇒10+22=1/2v2
⇒ 32x2=v2
⇒ 64=v2
⇒ v=8m/s
Work done by gravitational force on a man, in lifting a bucket out of the well by rope tied to the bucket is- a)negative
- b)positive
- c)zero
- d)infinity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by gravitational force on a man, in lifting a bucket out of the well by rope tied to the bucket is
a)
negative
b)
positive
c)
zero
d)
infinity
|
|
Om Desai answered |
When the man pulls the bucket outside the well the gravitational potential of the man + bucket system increases and hence the work done by the gravitational force is negative.
An engine generates a power of 10 kW. In how much time will it raise a mass of 200 kg through a height of 40m.- a)4 sec
- b)10 sec
- c)5 sec
- d)8 sec
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An engine generates a power of 10 kW. In how much time will it raise a mass of 200 kg through a height of 40m.
a)
4 sec
b)
10 sec
c)
5 sec
d)
8 sec
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Power = work done / time
work = force x distance
so power = (force x distance) / time
time = (force x distance) / power
= (2000 N x 40m) / 10000W = 8 seconds
A particle is dropped from a height h. A constant horizontal velocity is given to the particle.
Taking g to be constant every where, kinetic energy E of the particle with respect to time t is correctly shown in- a)
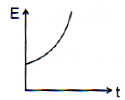
- b)
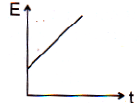
- c)
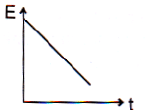
- d)
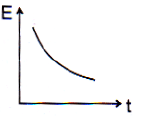
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is dropped from a height h. A constant horizontal velocity is given to the particle.
Taking g to be constant every where, kinetic energy E of the particle with respect to time t is correctly shown in
Taking g to be constant every where, kinetic energy E of the particle with respect to time t is correctly shown in
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
As particle is projected with some velocity therefore its initial kinetic energy will not be zero. As it moves downward under gravity then its velocity increases with time K.E. μ v2 μ t2 (As υ ∝ t) So the graph between kinetic energy and time will be parabolic in nature.
A body dropped from height H reaches the ground with a speed of 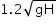
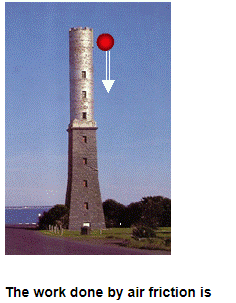
- a)mgh
- b)-0.28mgH
- c)2gh
- d)0.5gh
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body dropped from height H reaches the ground with a speed of 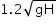
a)
mgh
b)
-0.28mgH
c)
2gh
d)
0.5gh
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The forces acting on the body are the force of gravity and the air friction. By work energy theorem, the total work done on the body is
W=1/2m(1.2√gH)2−0=0.72mgH
The work done by the force of gravity is mgH.
. Hence, the work done by the air friction is,
=0.72mgH-mgH
=00.28mgH.
W=1/2m(1.2√gH)2−0=0.72mgH
The work done by the force of gravity is mgH.
. Hence, the work done by the air friction is,
=0.72mgH-mgH
=00.28mgH.
Three blocks A, B and C are kept as shown in figure. The coefficient of friction between A and B is 0.2, B and C is 0.1, C and ground is 0.0. The mass of A, B and C are 3 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg respectively. A is given a horizontal velocity 10 m/s. A, B and C always remain in contact i.e. lies as in figure. The total work done by friction will be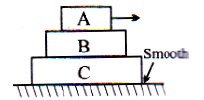
- a)– 75 J
- b)75 J
- c)– 150 J
- d)– 100 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three blocks A, B and C are kept as shown in figure. The coefficient of friction between A and B is 0.2, B and C is 0.1, C and ground is 0.0. The mass of A, B and C are 3 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg respectively. A is given a horizontal velocity 10 m/s. A, B and C always remain in contact i.e. lies as in figure. The total work done by friction will be
a)
– 75 J
b)
75 J
c)
– 150 J
d)
– 100 J
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The block A is given 10m/s velocity
Initial momentum of the system = 3 x 10 = 30
As no external force is applied the linear momentum of the system: 30=6xv
v=5 m/s
The final mass will be taken 6 kg as it is given that finally, all the blocks are moving together as a system.
Initial momentum of the system = 3 x 10 = 30
As no external force is applied the linear momentum of the system: 30=6xv
v=5 m/s
The final mass will be taken 6 kg as it is given that finally, all the blocks are moving together as a system.
By the conversation of energy
(1/2) x 3 x 102 + frictional work done = (1/2) x 6 x 52
⇒ Frictional work done = -75J
(1/2) x 3 x 102 + frictional work done = (1/2) x 6 x 52
⇒ Frictional work done = -75J
What is the dimension of k/m where k is the force constant and m is the mass of the oscillating object?- a)[T2]
- b)[T1]
- c)[T-1]
- d)[T-2]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the dimension of k/m where k is the force constant and m is the mass of the oscillating object?
a)
[T2]
b)
[T1]
c)
[T-1]
d)
[T-2]
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
F=k x (compression in string).
X=L.
a=LT-2.
F=ma.
ma= k L.
LT-2/L=k/m.
T-2=k/m.
X=L.
a=LT-2.
F=ma.
ma= k L.
LT-2/L=k/m.
T-2=k/m.
A person 'A' pushes a body of 5 kg placed on a rough surface of co-efficient of friction 0.3 by a distance of 4 m in 15 seconds. Another person 'B' pushes the body of 7 kg on same surface by a distance of 3 m in the same time. Who has more energy and power?- a)A
- b)B
- c)Both A and B have developed equal power but B has more energy
- d)Both A and B have developed equal power but A has more energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person 'A' pushes a body of 5 kg placed on a rough surface of co-efficient of friction 0.3 by a distance of 4 m in 15 seconds. Another person 'B' pushes the body of 7 kg on same surface by a distance of 3 m in the same time. Who has more energy and power?
a)
A
b)
B
c)
Both A and B have developed equal power but B has more energy
d)
Both A and B have developed equal power but A has more energy
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
For person A,
Mass of body, m1 = 5kg
Coefficient of friction, μ =0.3
So, The force of friction,
F1= μm1g=0.3 X 5 X 10=15N
Displacement, S1=4m
Therefore,
Work done, W1=15X4=60J
Time taken, t1=15sec
So, Power, P1=60/15=4W
For Person B
Mass of body, m2=7kg
Coefficient of friction, μ =0.3
So, The force of friction,
F1= μm2g=0.3 X 7 X 10=21N
Displacement, S2=3m
Therefore,
Work done, W2=21X3=63J
Time taken, t2=15sec
So, Power, P3=63/15=4.2W
Mass of body, m1 = 5kg
Coefficient of friction, μ =0.3
So, The force of friction,
F1= μm1g=0.3 X 5 X 10=15N
Displacement, S1=4m
Therefore,
Work done, W1=15X4=60J
Time taken, t1=15sec
So, Power, P1=60/15=4W
For Person B
Mass of body, m2=7kg
Coefficient of friction, μ =0.3
So, The force of friction,
F1= μm2g=0.3 X 7 X 10=21N
Displacement, S2=3m
Therefore,
Work done, W2=21X3=63J
Time taken, t2=15sec
So, Power, P3=63/15=4.2W
So person B has more energy and power.
A block weighing 10 N travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to a rough horizontal surface (figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of 0.20 with the block. If the block starts slipping on the track from a point 1.0 m above the horizontal surface, the distance it will moves on the rough surface is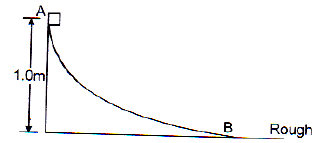
- a)5.0 m
- b)10.0 m
- c)15.0 m
- d)20.0 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block weighing 10 N travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to a rough horizontal surface (figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of 0.20 with the block. If the block starts slipping on the track from a point 1.0 m above the horizontal surface, the distance it will moves on the rough surface is
a)
5.0 m
b)
10.0 m
c)
15.0 m
d)
20.0 m
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Let the velocity at point B be v.
By conservation of energy, mgh = (1/2 ) mv2 ⇒ v = √(2gh)
Now deceleration due to friction is a = μg = 0.2 g
So stopping distance, s = v2/(2a) = (2gh) / (0.4g) = 5 h = 5 × 1 = 5m
Now deceleration due to friction is a = μg = 0.2 g
So stopping distance, s = v2/(2a) = (2gh) / (0.4g) = 5 h = 5 × 1 = 5m
A man A of mass 80 kg runs up a staircase in 12 seconds. Another man of mass 60 kg runs up the same staircase in 11 seconds. The ratio of powers of A and B is :
- a)11:12
- b)9:11
- c)12:11
- d)11:9
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man A of mass 80 kg runs up a staircase in 12 seconds. Another man of mass 60 kg runs up the same staircase in 11 seconds. The ratio of powers of A and B is :
a)
11:12
b)
9:11
c)
12:11
d)
11:9
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
According to question, 60 kg man runs up a staircase in 12 sec.
m₁ = 80 kg
t₁ = 12 sec
=> A 50 kg man runs up the same staircase in 11 sec:
m₂ = 60 kg
t₂ = 11 sec
=> Rate of work done is equals to power.
∴ P = E/ t and E = mgh
∴ P₁ = m₁gh / t₁
P₂ = m₂gh/ t₂
=> The ratio of Power or Rate of work done is:
P₁/P₂ = m₁gh / t₁ / m₂gh/ t₂
= m₁ * t₂ / m₂ * t₁
= 80x11/60x12
= 11 : 9
Thus, the ratio of rate of doing their work is 11 : 9.
An electric motor creates a tension of 4500 N in a hoisting cable and reels it in at the rate of 2 m/s. What is the power of the electric motor?
- a)225W
- b)15kW
- c)9kW
- d)900 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric motor creates a tension of 4500 N in a hoisting cable and reels it in at the rate of 2 m/s. What is the power of the electric motor?
a)
225W
b)
15kW
c)
9kW
d)
900 W
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
F=4500N
v=2ms−1
The power of motor is given by
P=F.v
P=4500×2
P=9000W=9kW
v=2ms−1
The power of motor is given by
P=F.v
P=4500×2
P=9000W=9kW
Time rate at which work is done by a force is- a)Power
- b)Torque
- c)Centrifugal Force
- d)Acceleration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Time rate at which work is done by a force is
a)
Power
b)
Torque
c)
Centrifugal Force
d)
Acceleration
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
We know that Work done, W = F.s
where F is force and s is displacement due to that force.
Thus rate of work done is:
where F is force and s is displacement due to that force.
Thus rate of work done is:
dW/dt = d(F.s)/dt
So as F is constant we get,
dW/dt = F.d(s)/dt = F.v = P (Power)
dW/dt = F.d(s)/dt = F.v = P (Power)
There are two bodies X and Y with equal kinetic energy but different masses m and 4m respectively. The ratio of their linear momentum is-- a)1:2
- b)4:1
- c)1:√2
- d)1:4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two bodies X and Y with equal kinetic energy but different masses m and 4m respectively. The ratio of their linear momentum is-
a)
1:2
b)
4:1
c)
1:√2
d)
1:4
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
X and Y have equal kinetic energy but their masses are m and 4m respectively.
► 1/2 m1v12 = 1/2 m2v22
► mv12 = 4m * v22
► v1 : v2 = 2 : 1
Hence the ratio of their linear momentum is:
m1v1 : m2v2 = m * 2v : 4m * v = 1 : 2
► 1/2 m1v12 = 1/2 m2v22
► mv12 = 4m * v22
► v1 : v2 = 2 : 1
Hence the ratio of their linear momentum is:
m1v1 : m2v2 = m * 2v : 4m * v = 1 : 2
By how much does kinetic energy increase if the momentum is increased by 20%?- a)55 %
- b)20 %
- c)44 %
- d)60 %
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
By how much does kinetic energy increase if the momentum is increased by 20%?
a)
55 %
b)
20 %
c)
44 %
d)
60 %
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The kinetic energy is given by:
KE= p2/2m
So, ΔKE = 2pΔp / 2m = pΔp / m
ΔKE / KE = (pΔp/m) * (2m/p2) = 2Δp / p
Since the momentum p increases by 20%, so the final momentum becomes 1.2p.
Hence, KEfinal = (1.2p)2 / 2m = 1.44p2 / 2m = 1.44KE
So, % change in KE = 44%
ΔKE / KE = (pΔp/m) * (2m/p2) = 2Δp / p
Since the momentum p increases by 20%, so the final momentum becomes 1.2p.
Hence, KEfinal = (1.2p)2 / 2m = 1.44p2 / 2m = 1.44KE
So, % change in KE = 44%
You are in a lift moving from the 3rd floor to the 12th floor, having a height difference of H = 40 m. Your mass is M = 80 kg and the acceleration due to gravity is g = 10 m/s2. If the elevator moves at a constant speed without stopping, what is the total work performed by all of the forces together (the net force) acting on you?- a)Mgh
- b)-Mgh
- c)0
- d)Mg
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
You are in a lift moving from the 3rd floor to the 12th floor, having a height difference of H = 40 m. Your mass is M = 80 kg and the acceleration due to gravity is g = 10 m/s2. If the elevator moves at a constant speed without stopping, what is the total work performed by all of the forces together (the net force) acting on you?
a)
Mgh
b)
-Mgh
c)
0
d)
Mg
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
As the final velocity after the action of all forces is 0, therefore the person has 0 net acceleration.
And, as we know that
Fnet = m.anet
Therefore, the net force is 0 and hence, the net work done is also 0.
Output of a truck is 4500 J and its efficiency is 50%, the input energy provided to the truck is- a)5000 J
- b)900 J
- c)9000 J
- d)500 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Output of a truck is 4500 J and its efficiency is 50%, the input energy provided to the truck is
a)
5000 J
b)
900 J
c)
9000 J
d)
500 J
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
► η = work output / heat input
► η = 50% = 50/100 = 1/2
► 1/2 = 4500 / Heat input
► Heat input = 9000 J
► η = 50% = 50/100 = 1/2
► 1/2 = 4500 / Heat input
► Heat input = 9000 J
A wheel is at rest. Its angular velocity increases uniformly and becomes 80 radian per second after 5 second. The total angular displacement is :- a)800 Red
- b)400 Red
- c)200 Red
- d)100 Red
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A wheel is at rest. Its angular velocity increases uniformly and becomes 80 radian per second after 5 second. The total angular displacement is :
a)
800 Red
b)
400 Red
c)
200 Red
d)
100 Red
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
As stated
if the angular velocity increases uniformly . The angular acceleration must be constant.
Hence the formula
s= ut+ 0.5 a t^2
Where.
u= initial angular velocity
a= angular acceleration (i.e = 80/5=16 rad/s^2)
S= angular displacement
t= time taken
Now.
s= 0 + 0.5 X 16*5*5 = 200
Hence angar displacement = 200 radians
A body moves under a force such that momentum of the body at any instant 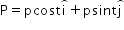 . What is the rate of work done by the force?
. What is the rate of work done by the force?- a)
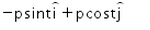
- b)

- c)
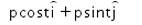
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body moves under a force such that momentum of the body at any instant 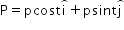 . What is the rate of work done by the force?
. What is the rate of work done by the force?
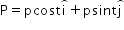 . What is the rate of work done by the force?
. What is the rate of work done by the force?a)
b)
c)
d)
zero
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
P = p Cos(t) i + p Sin(t) j
dP/dt = -p Sin(t) j + p Cos(t) i
Work done, W = P2/2m
Rate of work done = d/dt(P2/2m)
= 2P/2m x dP/dt
= P/m x dP/dt
= -p2.Sin(t).Cos(t) + p2.Sin(t).Cos(t)
=> Rate of work done = 0
Calculate the power developed when the force of 10 N is exerted on a body moving with velocity of 3.65 m/s.- a)36.5W
- b)3.65W
- c)365W
- d)0.365W
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the power developed when the force of 10 N is exerted on a body moving with velocity of 3.65 m/s.
a)
36.5W
b)
3.65W
c)
365W
d)
0.365W
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Power =F.V
i.e, Power = force x velocity.
here, force (f)= 10N
and velocity (v) = 3.65 m/s
so, Power = f x v,
i.e, 10 x 3.65 = 36.5 w.
i.e, Power = force x velocity.
here, force (f)= 10N
and velocity (v) = 3.65 m/s
so, Power = f x v,
i.e, 10 x 3.65 = 36.5 w.
An elastic spring of force constant k is compressed by an amount x. Then its potential energy will be- a)kx
- b)-kx
- c)
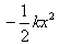
- d)
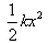
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An elastic spring of force constant k is compressed by an amount x. Then its potential energy will be
a)
kx
b)
-kx
c)
d)
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
F= kx
Now as we know
f.ds = potential energy
differentiate
potential energy = kx .ds
k is a constant .... and diff of x .ds is = x^2 / 2
so here potential energy will be = 1/2 k x^2
How much work is done by a man weighing 80 kgf in raising a stone of weight 20 kgf to the top of a building of height 40 m? (g = 9.8 m/s2)- a)30,900 J
- b)29,678 J
- c)39,200 J
- d)25,000 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How much work is done by a man weighing 80 kgf in raising a stone of weight 20 kgf to the top of a building of height 40 m? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
a)
30,900 J
b)
29,678 J
c)
39,200 J
d)
25,000 J

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Total mass=80+20=100
w=mgh(where m=100, g=9.8, h=40m)
w=100×9.8×40
w=39200J
work done by man weighing 80 kg raising a stone of 20kgf to the top of building of Height is 40m is 39,200J
w=mgh(where m=100, g=9.8, h=40m)
w=100×9.8×40
w=39200J
work done by man weighing 80 kg raising a stone of 20kgf to the top of building of Height is 40m is 39,200J
How should the force applied on a body be varied with velocity to keep the power of force constant?- a)Force should be inversely proportional to the square root of the velocity of the body
- b)Force should be inversely proportional to the velocity of the body
- c)Force should be directly proportional to the velocity of the body
- d)Force should not be varied. It should remain constant with the velocity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How should the force applied on a body be varied with velocity to keep the power of force constant?
a)
Force should be inversely proportional to the square root of the velocity of the body
b)
Force should be inversely proportional to the velocity of the body
c)
Force should be directly proportional to the velocity of the body
d)
Force should not be varied. It should remain constant with the velocity
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
We know that power (P) = force (F) x velocity (v).
Since the body is moving with acceleration,v changes and as a result of that P also changes,F being constant.
For P to be constant, F v = constant or F ∝ 1/v i.e
Force should be inversely proportional to the velocity of the body.
Thus,as v increases, F should decrease to keep P constant.
In the given figure, what is the work done by the spring force?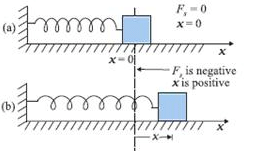
- a)
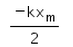
- b)
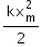
- c)
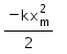
- d)
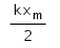
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure, what is the work done by the spring force?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
We know that for a spring with spring constant k, work done by the spring when a compression or expansion is done of some length say x is ½ kx2
Also as the work done is in the opposite direction to that of force applied, we get the sign of the force to be negative.
Also as the work done is in the opposite direction to that of force applied, we get the sign of the force to be negative.
A machine gun fires 60 bullets per minute, with a velocity of 700 m/s. If each bullet has a mass of 50g, find the power developed by the gun.
- a)1225 W
- b)12250 W
- c)122.5 W
- d)122 W
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A machine gun fires 60 bullets per minute, with a velocity of 700 m/s. If each bullet has a mass of 50g, find the power developed by the gun.
a)
1225 W
b)
12250 W
c)
122.5 W
d)
122 W
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Each bullet will have KE = 1/2 * 0.05 * 700 * 700 = 12250 J
So for 60 bullets the energy given by machine in 60 second = 60 x 12250 J
Hence power developed = Energy / time =60 x12250/60 =12250W
Or power = 12.250 kW.
So for 60 bullets the energy given by machine in 60 second = 60 x 12250 J
Hence power developed = Energy / time =60 x12250/60 =12250W
Or power = 12.250 kW.
A wedge of mass M is fitted with a spring of stiffness ‘k’ is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. A rod of mass m is kept on the wedge as shown in the figure. System is in equilibrium.
Assuming that all surfaces are smooth, the potential energy stored in the spring is: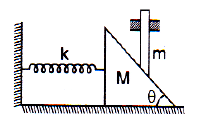
- a)
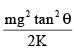
- b)
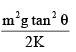
- c)
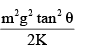
- d)
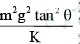
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A wedge of mass M is fitted with a spring of stiffness ‘k’ is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. A rod of mass m is kept on the wedge as shown in the figure. System is in equilibrium.
Assuming that all surfaces are smooth, the potential energy stored in the spring is:
Assuming that all surfaces are smooth, the potential energy stored in the spring is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
N sinθ = kx
N cosθ = mg
We get the value of x,
x = (mg tanθ) / k
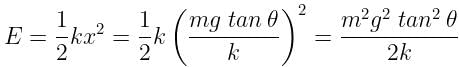
N cosθ = mg
We get the value of x,
x = (mg tanθ) / k
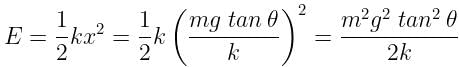
A vehicle of 50 quintal climbs up a hill of 10 m. The potential energy gained by it is (take g = 10 m/s2)- a)5 J
- b)5000 J
- c)500 J
- d)5 x 105 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A vehicle of 50 quintal climbs up a hill of 10 m. The potential energy gained by it is (take g = 10 m/s2)
a)
5 J
b)
5000 J
c)
500 J
d)
5 x 105 J
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
mass = 50 x 100 = 5000 kg, g = 10 m/s2, h = 10 m
Potential energy gained = mgh = 5000 x 10 x 10 = 5 x 105 J
Potential energy gained = mgh = 5000 x 10 x 10 = 5 x 105 J
Which of the following is not conserved in inelastic collision?- a)momentum
- b)kinetic energy
- c)both momentum and kinetic energy
- d)neither momentum nor kinetic energ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not conserved in inelastic collision?
a)
momentum
b)
kinetic energy
c)
both momentum and kinetic energy
d)
neither momentum nor kinetic energ
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
In an inelastic collision, the force of reformation is not equal to the force of deformation and thus some amount of energy is lost. But still as no external force acts upon the system momentum is still conserved.
In an elastic collision in one dimension if a body A collides against the body B of equal mass at rest, then the body A will- a)moves with the same velocity but in opposite direction
- b)move with twice its initial velocity
- c)moves with the same velocity in the same direction
- d)come to rest.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an elastic collision in one dimension if a body A collides against the body B of equal mass at rest, then the body A will
a)
moves with the same velocity but in opposite direction
b)
move with twice its initial velocity
c)
moves with the same velocity in the same direction
d)
come to rest.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Since collision is elastic and mass is same then after velocity exchange A body will stop and B will start moving with A's velocity in the same direction.
Which of the following is not a unit of energy?- a)newton meter
- b)electron volt
- c)joule/meter
- d)kilowatt hour
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
a)
newton meter
b)
electron volt
c)
joule/meter
d)
kilowatt hour

|
Gargey Dudhe answered |
C is correct option because energy The joule ( symbol: J) is a derived unit of energy in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy transferred to (or work done on) an object when a force of one newton acts on that object in the direction of its motion through a distance of one metre (1 newton metreor N⋅m). pls upvote and follow me.
Which of the following statement is not related to conservative force?- a)Work done in closed path is zero
- b)Work done is recoverable
- c)Path independent
- d)Path dependent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not related to conservative force?
a)
Work done in closed path is zero
b)
Work done is recoverable
c)
Path independent
d)
Path dependent
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
A force is said to be conservative if the work done by or against the force on a body is independent of path followed by the body and depends only on initial and final positions.
Work done by or against the conservative force in moving a particle along a closed path is zero.
Work done by or against the conservative force in moving a particle along a closed path is zero.
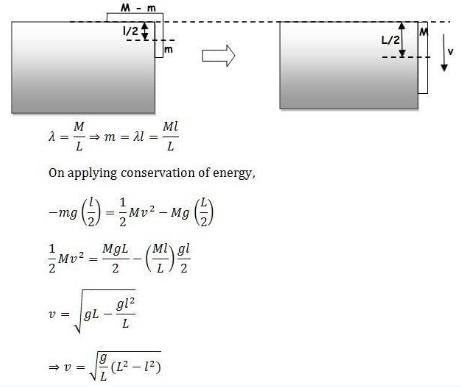
A uniform chain has a mass M and length L. It is placed on a frictionless table with length l0 hanging over the edge. The chain begins to slide down. The speed V with which the chain slides away from the edge is given by- a)
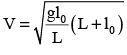
- b)
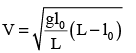
- c)
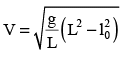
- d)
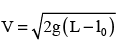
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniform chain has a mass M and length L. It is placed on a frictionless table with length l0 hanging over the edge. The chain begins to slide down. The speed V with which the chain slides away from the edge is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Since the given chain is uniform we can find the mass of the hanging part of the chain if we define some quantity lambda as mass per unit length and then multiplying it with the length of the hanging part of the chain.
- Also, while applying the energy conservation equation for extended bodies (like chain, etc) we need to consider the energies (both kinetic and potential) of the center of mass only. We will consider the dotted line as a reference line while applying energy equation.
No work is done by a force on an object if- a)The force is always perpendicular to its velocity
- b)The force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
- c)The object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object.
- d)The object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
No work is done by a force on an object if
a)
The force is always perpendicular to its velocity
b)
The force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
c)
The object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object.
d)
The object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Work done = f.ds
So on perpendicular application for product becomes zero so no work is done
So on perpendicular application for product becomes zero so no work is done
When does the potential energy of a spring increase?- a)only when spring is stretched
- b)only when spring is compressed
- c)when spring is neither stretched nor compressed
- d)when spring is compressed or stretched
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When does the potential energy of a spring increase?
a)
only when spring is stretched
b)
only when spring is compressed
c)
when spring is neither stretched nor compressed
d)
when spring is compressed or stretched
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Potential energy of a spring is proportional to the square of the difference of the springs length and its original length, hence whether it is compressed or stretched the potential the potential energy will eventually increase only.
When a ball is allowed to fall from a height of 20 m, 40% of its energy is lost due to impact. After one impact the ball will go up to a height of- a)12 m
- b)15 m
- c)8 m
- d)10 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a ball is allowed to fall from a height of 20 m, 40% of its energy is lost due to impact. After one impact the ball will go up to a height of
a)
12 m
b)
15 m
c)
8 m
d)
10 m
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Before the impact the KE was ½ x m x (2g x 20) = 20mg
And let say v be the velocity after impact and for height h, v2= 2gh
Thus KE = ½ mv2 = ½m2gh = ⅗ x 20mg
Thus we get mgh = 12mg
thus h = 12 m
And let say v be the velocity after impact and for height h, v2= 2gh
Thus KE = ½ mv2 = ½m2gh = ⅗ x 20mg
Thus we get mgh = 12mg
thus h = 12 m
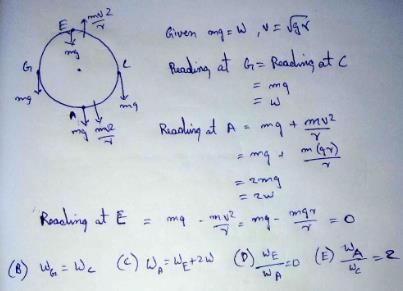
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage at the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speedv = 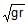 . The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
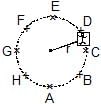
- a)The reading of his weight on the machine is the same at all positions
- b)The weight reading at A is greater than the weight reading at E by 2 w.
- c)The weight reading at G = w
- d)The ratio of the weight reading at E to that at A=0
- e)The ratio of the weight reading at A to that at C=2
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D,E'. Can you explain this answer?
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage at the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speed
v = 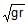 . The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct

a)
The reading of his weight on the machine is the same at all positions
b)
The weight reading at A is greater than the weight reading at E by 2 w.
c)
The weight reading at G = w
d)
The ratio of the weight reading at E to that at A=0
e)
The ratio of the weight reading at A to that at C=2

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is 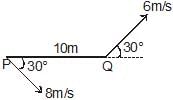
- a)Zero
- b)0.1 rad/sec
- c)0.4 rad/sec
- d)0.7 rad sec
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is
a)
Zero
b)
0.1 rad/sec
c)
0.4 rad/sec
d)
0.7 rad sec
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
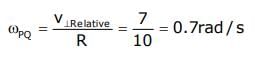
The potential energy of a body at height h is mgh. Then its kinetic energy just before hitting the ground is- a)mgh
- b)
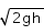
- c)mv2
- d)
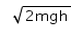
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy of a body at height h is mgh. Then its kinetic energy just before hitting the ground is
a)
mgh
b)
c)
mv2
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
From the law of conservation of mechanical energy, the potential energy of a body at height h is converted into kinetic energy when it falls down. So, the magnitude of kinetic energy just before hitting the ground is equal to the potential energy at height h which is mgh.
Frictional force is an example of- a)ectrostatic force
- b)Non conservative force
- c)conservative force
- d)nuclear force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Frictional force is an example of
a)
ectrostatic force
b)
Non conservative force
c)
conservative force
d)
nuclear force
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. This friction is applied tangentially to the surfaces in contact. Thus the main thing is that the forces on both of the surfaces act tangential to each other.
When conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body:- a)increases
- b)decreases
- c)remains unaltered
- d)there is no relationship between force and potential energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body:
a)
increases
b)
decreases
c)
remains unaltered
d)
there is no relationship between force and potential energy
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
We have a relation between potential energy and work done: 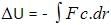
The negative sign just shows the inverse relation between potential energy and work done by conservative force.
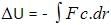
The negative sign just shows the inverse relation between potential energy and work done by conservative force.
A bomb of mass 4 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 3 kg and 1 kg. The smaller mass goes at a speed of 90 m/s. The total energy imparted to two fragments is.- a)2.4 kj
- b)5.4 kj
- c)5.9 kJ
- d)3.8 kJ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bomb of mass 4 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 3 kg and 1 kg. The smaller mass goes at a speed of 90 m/s. The total energy imparted to two fragments is.
a)
2.4 kj
b)
5.4 kj
c)
5.9 kJ
d)
3.8 kJ
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
By conservation of momentum we get the speed of the bigger part let say, v = 1 x90 / 3
Hence we get v = 30
Thus the total KE of the system after collision is ½ (3 X 900 + 1 X 8100)
Thus KE = ½ (10800) = 5400
Now if we apply WET to the system, as no external force has acted upon it, we get
W = ΔKE
= 5400 - 0
= 5.4 kJ
Hence we get v = 30
Thus the total KE of the system after collision is ½ (3 X 900 + 1 X 8100)
Thus KE = ½ (10800) = 5400
Now if we apply WET to the system, as no external force has acted upon it, we get
W = ΔKE
= 5400 - 0
= 5.4 kJ
Select the odd one out- a)Viscous force
- b)Frictional force
- c)Electrostatic force
- d)Air-resistance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the odd one out
a)
Viscous force
b)
Frictional force
c)
Electrostatic force
d)
Air-resistance
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The correct answer is muscular force because all these forces are non-contact forces and muscular force is a contact force.
A rigid body of mass m is moving in a circle of radius r with a constant speed v. The force on the body is 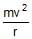 and is directed towards the centre. What is the work done by this force in moving the body over half the cirumference of the circle.
and is directed towards the centre. What is the work done by this force in moving the body over half the cirumference of the circle.- a)
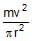
- b) Zero
- c)
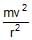
- d)
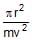
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A rigid body of mass m is moving in a circle of radius r with a constant speed v. The force on the body is 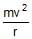 and is directed towards the centre. What is the work done by this force in moving the body over half the cirumference of the circle.
and is directed towards the centre. What is the work done by this force in moving the body over half the cirumference of the circle.
a)
b)
Zero
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
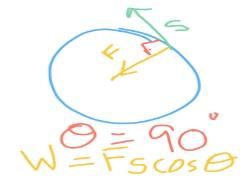
Force = mv2/r ( towards the centre )
displacement = 2r
Work done = FScosѲ
here ,
= mv2/r × s × cos 90
= 0 answer.
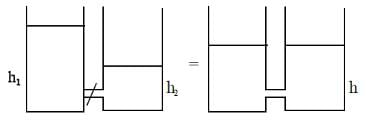
Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area 16 cm2 contain water up to heights 100 cm and 150 cm, respectively. The vessels are interconnected so that the water levels in them become equal. The work done by the force of gravity during the process is: [Take density of water = 103 kg/m3 and g = 10 ms-2]
- a)0.25 J
- b)12 J
- c)8 J
- d)1 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area 16 cm2 contain water up to heights 100 cm and 150 cm, respectively. The vessels are interconnected so that the water levels in them become equal. The work done by the force of gravity during the process is: [Take density of water = 103 kg/m3 and g = 10 ms-2]
a)
0.25 J
b)
12 J
c)
8 J
d)
1 J
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
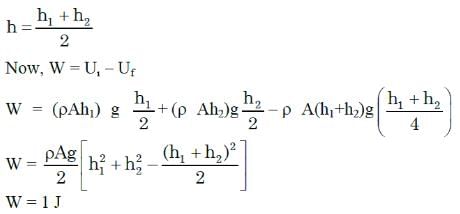
Which of the following statements is false:- a)kinetic energy is positiv
- b)potential energy is positive
- c)kinetic energy is negative
- d)potential energy is negative
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false:
a)
kinetic energy is positiv
b)
potential energy is positive
c)
kinetic energy is negative
d)
potential energy is negative

|
Aiims answered |
K.E never negative as velocity negative then its square becomes it positive.
From a waterfall, water is falling at the rate of 100 kg/s on the blades of a turbine. If the height of fall is 100 m, the power delivered to the turbine is- a)100kW
- b)100W
- c)1kW
- d)10kW
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
From a waterfall, water is falling at the rate of 100 kg/s on the blades of a turbine. If the height of fall is 100 m, the power delivered to the turbine is
a)
100kW
b)
100W
c)
1kW
d)
10kW
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Power = work done / time taken
or P = mgh / t
P = (m/t) gh = 100 x 10 x 100 = 100 kW
Chapter doubts & questions for Work, Energy and Power - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Work, Energy and Power - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup