All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Plant Kingdom for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?- a) Parenchyma
- b) Sclerenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Epithelial tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Sclerenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Epithelial tissue

|
Nandita Saha answered |
Sclerenchyma → cells are the permanent tissues present in the plants. They provide hardness and stiffness to the plant and are composed of dead cells.
From which of the following part of a plant opium is obtained?- a)Dried leaves
- b)Dried latex
- c)Roots
- d)Stem bark
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From which of the following part of a plant opium is obtained?
a)
Dried leaves
b)
Dried latex
c)
Roots
d)
Stem bark

|
Nishanth Jain answered |
Opium is the dried latex obtained from the opium poppy
Meristematic tissues are found in- a) only stems of the plants
- b)both roots and stems
- c)in all growing tips of the plant body
- d)only roots of the plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Meristematic tissues are found in
a)
only stems of the plants
b)
both roots and stems
c)
in all growing tips of the plant body
d)
only roots of the plants

|
Debanshi Sarkar answered |
A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place. Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of a plant and are responsible for growth
Various functions like photosynthesis, storage, excretion performed by _________.- a) Sclerenchyma
- b) parenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Aerenchyma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Various functions like photosynthesis, storage, excretion performed by _________.
a)
Sclerenchyma
b)
parenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Aerenchyma

|
Dhruba Saini answered |
Parenchyma forms the bulk of plant ground tissue, where they may be specialised to function in photosynthesis, storage, or transport.
Cavity or lumen is narrow in- a) Sclerenchyma
- b) Parenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Tracheids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cavity or lumen is narrow in
a)
Sclerenchyma
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Tracheids

|
Dipika Gupta answered |
Lumen are cavities present inside the cell,cells of sclerenchyma tissue have narrow lumen because sclerenchyma are strongly lignified which lead to compressing the cell and thus only narrow cavity is left
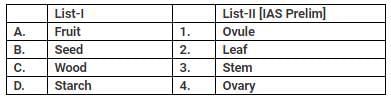
- a)A-2; B-1; C-3; D- 4
- b) A-4; B-1; C-3; D-2
- c) A-2; B-3; C-1; D-4
- d) A-4; B-3; C-1; D-2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

a)
A-2; B-1; C-3; D- 4
b)
A-4; B-1; C-3; D-2
c)
A-2; B-3; C-1; D-4
d)
A-4; B-3; C-1; D-2
|
|
Sharad Chavan answered |
1. fruits is made up of ovary
2. seed is made up of ovule
3. wood is made up of stem
4. starch is present in leaf
so the correct answer is B.
2. seed is made up of ovule
3. wood is made up of stem
4. starch is present in leaf
so the correct answer is B.
Which tissue does lack blood supply and heals slowly?- a) nervous
- b) muscle
- c) cartilage
- d) bone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which tissue does lack blood supply and heals slowly?
a)
nervous
b)
muscle
c)
cartilage
d)
bone

|
Debanshi Sarkar answered |
Cartilage heals slowly because it has no blood supply
Nucleated part of nerve cell is called- a) axon
- b) dendrites
- c) cyton
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleated part of nerve cell is called
a)
axon
b)
dendrites
c)
cyton
d)
None of the above

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
Axon is the long, thin hair like part arising from the cell body of the neuron.
Dendrites are short, branched parts arising from cell body or cyton. Dendrites are many in number.
Cyton is a part of neuron containing the nucleus. It is also called cell body. Therefore, option C is correct.
Dendrites are short, branched parts arising from cell body or cyton. Dendrites are many in number.
Cyton is a part of neuron containing the nucleus. It is also called cell body. Therefore, option C is correct.
Main function of lenticel is- a) transpiration
- b) guttation
- c) gaseous exchange
- d) both [a] & [c]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticel is
a)
transpiration
b)
guttation
c)
gaseous exchange
d)
both [a] & [c]

|
Shreya Desai answered |
The lenticels functions as a pore, providing a pathway for the direct exchange of gasesbetween the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gases.The lenticels help in the gaseous exchange between the atmosphere and the internal tissue of the stem. The lenticels also helps in transpiration called as the lenticular transpiration.Lenticels are a portions of periderm with numerous intercellular spaces and loosely organized cells
The most stable measure of central tendency is- a)mean
- b)median
- c)mode
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable measure of central tendency is
a)
mean
b)
median
c)
mode
d)
none of these
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Range is not a measure of central tendency at all. It is an absolute measure of Dispersion that is explained by the difference between the maximum and the minimum values in a series. Now, a comparison between the stability amongst Mean, Median and Mode depends on the nature of the distribution that you're working with. Let's say your data has a lot of outliers, in such a case mean will not serve the purpose well as a measure of CT, Median would be more appropriate. Remember that Mean is affected by extreme values while Median is not. Mode is more appropriate when you're more concerned about the frequency of occurences. For example if you wanted to know what size of shoes should a shoe seller keep more in stock compared to the other sizes.
Cloves, used as a spice, are derived from which of the following plant parts? - a) Seeds
- b) Fruits
- c) Flower buds
- d) Young leaves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cloves, used as a spice, are derived from which of the following plant parts?
a)
Seeds
b)
Fruits
c)
Flower buds
d)
Young leaves

|
Janhavi Bajaj answered |
Cloves are the rich, brown, dried, unopened flower buds of Syzygium aromaticum, an evergreen tree in the myrtle family. The name comes from the French "clou" meaning nail. Cloves come from Madagascar, Indonesia and Sri Lanka. Cloves are used in spice cookies and cakes.
Which plant kingdom can survive both on land and in water?- a)Tracheophyta
- b)Pteridophyta
- c)Thallophyta
- d)Bryophyta
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant kingdom can survive both on land and in water?
a)
Tracheophyta
b)
Pteridophyta
c)
Thallophyta
d)
Bryophyta

|
Nidhi Pillai answered |
The sperm of bryophyte (antherozoids) are flagellate and need water to swim to the eggs. In other words, as these plants need water for reproduction unlike other plants, they are called as amphibians. Amphibians are those organisms which live on both land and in water.
Presence of vessel in the wood is- a)A primitive character
- b)An advanced character
- c)A vestigeal character
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Presence of vessel in the wood is
a)
A primitive character
b)
An advanced character
c)
A vestigeal character
d)
None of the above

|
Nandita Saha answered |
Vessels are usually present in angiosperms while in other lower plants they are not present.
Total number of ATP consume during Kreb's cycle is- a) 0
- b) 1
- c) 2
- d) 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of ATP consume during Kreb's cycle is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Saranya Basak answered |
The Krebs cycle produces two molecules of ATP for every molecule of glucose. The Krebs cycle also produces eight molecules of NADH and two molecules of FADH2 per molecule of glucose.
The equilibrium constant in a reversible chemical reaction at a given temperature- a)depends on the initial concentration of the reactants
- b)depends on the concentration of one of the products at equilibrium
- c)does not depend on the initial concentrations of reactants
- d)is not characteristic of the reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant in a reversible chemical reaction at a given temperature
a)
depends on the initial concentration of the reactants
b)
depends on the concentration of one of the products at equilibrium
c)
does not depend on the initial concentrations of reactants
d)
is not characteristic of the reaction
|
|
Swati Khanna answered |
The correct option is C.
The equilibrium constant in a reversible reaction at a given temperature. Solution : Equilibrium constant is independent of original concentration of reactant.
The equilibrium constant in a reversible reaction at a given temperature. Solution : Equilibrium constant is independent of original concentration of reactant.
Which one of the following plant nutrients is not supplemented in the soil for growing legumes?- a)Nitrogen
- b)Potassium
- c)Phosphorus
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following plant nutrients is not supplemented in the soil for growing legumes?
a)
Nitrogen
b)
Potassium
c)
Phosphorus
d)
None of these

|
Avantika Mukherjee answered |
- Growing legume cover crops is one of the most important tools for increasing soil fertility in an organic garden.
- The bacteria take gaseous nitrogen from the air in the soil and feed this nitrogen to the legumes; in exchange the plant provides carbohydrates to the bacteria.
- The bacteria take gaseous nitrogen from the air in the soil and feed this nitrogen to the legumes; in exchange the plant provides carbohydrates to the bacteria.
What is the advantage of micropropagation by plant tissue culture?- a)It produces genetically diverse plants.
- b)It requires a large amount of space.
- c)It can produce virus-free clones.
- d)It is limited to dicot plants.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It produces genetically diverse plants.
b)
It requires a large amount of space.
c)
It can produce virus-free clones.
d)
It is limited to dicot plants.
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
Micropropagation by plant tissue culture has the advantage of producing virus-free clones by raising callus from shoot apex. This technique is useful for obtaining disease-free plants.
The phenomenon in which seeds germinate and seedlings grow while still attached to their mother plant before dropping down to establish themselves or be transported elsewhere, is most commonly found in which among the following plants?- a)Allium cepa
- b)Rhizophora
- c)Solanum tuberosum
- d)Solanum melongena
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomenon in which seeds germinate and seedlings grow while still attached to their mother plant before dropping down to establish themselves or be transported elsewhere, is most commonly found in which among the following plants?
a)
Allium cepa
b)
Rhizophora
c)
Solanum tuberosum
d)
Solanum melongena

|
Samarth Gupta answered |
Allium cepa is onion. Solanum tuberosum is potato, Solanum melongena is Brinjal. The phenomenon given in this question is shown by Mangrove Plants and is known as Vivipary and Rhizophora belongs to that category.
Fungi are plants that lack:- a)Oxygen
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Chlorophyll
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fungi are plants that lack:
a)
Oxygen
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Chlorophyll
d)
None of these
|
|
Preethi Chauhan answered |
Fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, which is a key characteristic of plants. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells that is responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into energy through the process of photosynthesis. Fungi, on the other hand, obtain their nutrients by absorbing organic matter from their environment, such as decaying plant and animal material.
Here is a detailed explanation of why fungi are not plants:
1. Absence of Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is essential for plants to carry out photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and are incapable of performing photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their energy by breaking down organic matter through the secretion of enzymes and absorbing the resulting nutrients.
2. Mode of Nutrition:
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on external sources for nutrients. They are decomposers, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. In contrast, plants are autotrophic organisms that can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis.
3. Cell Wall Composition:
The cell walls of fungi are primarily composed of chitin, a tough and flexible polysaccharide. In contrast, the cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. This difference in cell wall composition is another distinguishing feature between fungi and plants.
4. Reproduction:
Fungi have a unique mode of reproduction that sets them apart from plants. While plants reproduce through seeds or spores produced within flowers or cones, fungi reproduce through the production of spores, which are released into the environment to establish new fungal colonies.
5. Taxonomic Classification:
Fungi belong to the kingdom Fungi, which is distinct from the kingdom Plantae. The kingdom Fungi includes diverse organisms such as mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and lichens. This taxonomic classification further emphasizes the biological differences between fungi and plants.
In conclusion, fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, have a different mode of nutrition, possess cell walls made of chitin, reproduce differently, and are classified in a separate kingdom. These characteristics differentiate fungi from plants and highlight their unique biological features.
Here is a detailed explanation of why fungi are not plants:
1. Absence of Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is essential for plants to carry out photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and are incapable of performing photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their energy by breaking down organic matter through the secretion of enzymes and absorbing the resulting nutrients.
2. Mode of Nutrition:
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on external sources for nutrients. They are decomposers, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. In contrast, plants are autotrophic organisms that can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis.
3. Cell Wall Composition:
The cell walls of fungi are primarily composed of chitin, a tough and flexible polysaccharide. In contrast, the cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. This difference in cell wall composition is another distinguishing feature between fungi and plants.
4. Reproduction:
Fungi have a unique mode of reproduction that sets them apart from plants. While plants reproduce through seeds or spores produced within flowers or cones, fungi reproduce through the production of spores, which are released into the environment to establish new fungal colonies.
5. Taxonomic Classification:
Fungi belong to the kingdom Fungi, which is distinct from the kingdom Plantae. The kingdom Fungi includes diverse organisms such as mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and lichens. This taxonomic classification further emphasizes the biological differences between fungi and plants.
In conclusion, fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, have a different mode of nutrition, possess cell walls made of chitin, reproduce differently, and are classified in a separate kingdom. These characteristics differentiate fungi from plants and highlight their unique biological features.
A tissue is a group of cells which are- a)similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
- b)dissimilar in origin, form and function.
- c)dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
- d)similar in origin, form and function.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A tissue is a group of cells which are
a)
similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
b)
dissimilar in origin, form and function.
c)
dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
d)
similar in origin, form and function.
|
|
Akansha Chourse answered |
A tissue is a group of cells which are similar in origin,form and function
What are the four whorls typically found in a flower?- a)Sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
- b)Leaves, stems, roots, fruits
- c)Calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium
- d)Xylem, phloem, cortex, pith
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
b)
Leaves, stems, roots, fruits
c)
Calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium
d)
Xylem, phloem, cortex, pith

|
Capstone Ias Learning answered |
Flowers typically have four whorls: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. These whorls together make up the floral structure and are involved in the reproductive process.
Which plant group includes naked seeded plants with vascular tissues and is often considered a fossil group?- a)Bryophyta
- b)Gymnosperms
- c)Pteridophyta
- d)Angiosperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bryophyta
b)
Gymnosperms
c)
Pteridophyta
d)
Angiosperms

|
Capstone Ias Learning answered |
Gymnosperms are a group of plants that produce naked seeds (seeds not enclosed in a fruit) and have well-developed vascular tissues. Gymnosperms are often considered a "fossil group" because they have ancient origins and include plants like conifers that have been around for a long time. The term "gymnosperm" means "naked seed," referring to the fact that the seeds are exposed on the surface of cone scales or other structures.
Which method of artificial vegetative propagation involves the use of an individual bud with adjacent bark?- a)Cutting
- b)Budding
- c)Grafting
- d)Micropropagation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Cutting
b)
Budding
c)
Grafting
d)
Micropropagation

|
Ias Masters answered |
Budding is a method of artificial vegetative propagation that involves the use of an individual bud with adjacent bark from one plant and inserting it into a cut made in the stock of another plant.
The dead element present in the phloem is- a) companion cells
- b) phloem fibres
- c) phloem parenchyma
- d) sieve tube
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The dead element present in the phloem is
a)
companion cells
b)
phloem fibres
c)
phloem parenchyma
d)
sieve tube

|
Athul Saini answered |
Phloem fibres are thick walled, elongated spindle shaped dead cells which possess narrow lumen. They provides mechanical support to the tissue. Phloem parenchyma are thin walled-living cells of parenchyma. They have two functions, storage and lateral food conduction
Cork is formed from- a) phellogen
- b) vascular cambium
- c) phloem
- d) xylem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cork is formed from
a)
phellogen
b)
vascular cambium
c)
phloem
d)
xylem

|
Akanksha Ahuja answered |
The meristematic cell layer which is responsible for the development of the periderm is called phelloge. It produces cells both in and outwards. Cells which grow inwards will be phelloderm, and cells which develop outwards will be phellem or cork
A plant that has seeds but no flowers and fruits?- a)Bryophyte
- b)Gymnosperms
- c)Mosses
- d)Pteridophyte
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant that has seeds but no flowers and fruits?
a)
Bryophyte
b)
Gymnosperms
c)
Mosses
d)
Pteridophyte

|
Saanvi Iyer answered |
Gymnosperms evolved to have seeds but do not have flowers. Examples of gymnosperms include the Redwood, Fir, and Cypress trees. Gymnos means "naked" in Greek; the seeds of gymnosperms are naked, not protected by flowers. Flowering plants, or angiosperms, evolved to have vascular tissue, seeds, and flowers.
A yellow dust appears on the fingers, whenever we touch the middle of a flower. These tiny yellow grains are one of the most precious substances in nature because they contain the secret of plant life. What is this dust called?- a)Pollen
- b)Sperm
- c)Spore
- d)Sporocyst
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A yellow dust appears on the fingers, whenever we touch the middle of a flower. These tiny yellow grains are one of the most precious substances in nature because they contain the secret of plant life. What is this dust called?
a)
Pollen
b)
Sperm
c)
Spore
d)
Sporocyst

|
Aashna Singh answered |
The yellow powder is called pollen and the stick that holds it is known as stamen.
What is the main difference between bacteria and viruses?- a)Bacteria have a nucleus, while viruses do not.
- b)Bacteria are larger than viruses.
- c)Bacteria can reproduce on their own, while viruses require a host.
- d)Bacteria are always harmful, while viruses can be beneficial.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bacteria have a nucleus, while viruses do not.
b)
Bacteria are larger than viruses.
c)
Bacteria can reproduce on their own, while viruses require a host.
d)
Bacteria are always harmful, while viruses can be beneficial.
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
Main difference between bacteria and viruses:
Reproduction:
- Bacteria can reproduce on their own through a process called binary fission. They can replicate their DNA and divide into two daughter cells.
- On the other hand, viruses cannot reproduce independently. They require a host cell to replicate themselves. Viruses inject their genetic material into a host cell and hijack the cellular machinery to produce more virus particles.
Structure:
- Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms, which means they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They have a relatively simple cellular structure with a cell wall, cell membrane, and genetic material floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Viruses, on the other hand, are much smaller and simpler than bacteria. They are not considered living organisms as they lack cellular structure. Viruses consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses may also have an outer envelope derived from the host cell.
Size:
- Bacteria are generally larger than viruses. Bacterial cells can vary in size, ranging from a few micrometers to hundreds of micrometers in length.
- In contrast, viruses are much smaller, usually ranging from 20 to 300 nanometers in size. They are significantly smaller than most bacterial cells and can only be seen under an electron microscope.
Impact on Health:
- Bacteria can have both positive and negative impacts on health. While some bacteria are harmful and cause diseases, many bacteria are beneficial and play essential roles in various natural processes and even in our bodies, such as aiding digestion and synthesizing vitamins.
- Viruses, on the other hand, are generally associated with causing diseases. They can infect various organisms, including humans, animals, and plants, and cause illnesses ranging from common colds to more severe conditions like influenza, HIV, and COVID-19.
Conclusion:
The main difference between bacteria and viruses lies in their ability to reproduce. Bacteria can reproduce independently through binary fission, while viruses require a host cell to replicate. Additionally, bacteria are larger and have a more complex cellular structure compared to viruses. While bacteria can have both positive and negative impacts on health, viruses are generally associated with causing diseases.
Reproduction:
- Bacteria can reproduce on their own through a process called binary fission. They can replicate their DNA and divide into two daughter cells.
- On the other hand, viruses cannot reproduce independently. They require a host cell to replicate themselves. Viruses inject their genetic material into a host cell and hijack the cellular machinery to produce more virus particles.
Structure:
- Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms, which means they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They have a relatively simple cellular structure with a cell wall, cell membrane, and genetic material floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Viruses, on the other hand, are much smaller and simpler than bacteria. They are not considered living organisms as they lack cellular structure. Viruses consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses may also have an outer envelope derived from the host cell.
Size:
- Bacteria are generally larger than viruses. Bacterial cells can vary in size, ranging from a few micrometers to hundreds of micrometers in length.
- In contrast, viruses are much smaller, usually ranging from 20 to 300 nanometers in size. They are significantly smaller than most bacterial cells and can only be seen under an electron microscope.
Impact on Health:
- Bacteria can have both positive and negative impacts on health. While some bacteria are harmful and cause diseases, many bacteria are beneficial and play essential roles in various natural processes and even in our bodies, such as aiding digestion and synthesizing vitamins.
- Viruses, on the other hand, are generally associated with causing diseases. They can infect various organisms, including humans, animals, and plants, and cause illnesses ranging from common colds to more severe conditions like influenza, HIV, and COVID-19.
Conclusion:
The main difference between bacteria and viruses lies in their ability to reproduce. Bacteria can reproduce independently through binary fission, while viruses require a host cell to replicate. Additionally, bacteria are larger and have a more complex cellular structure compared to viruses. While bacteria can have both positive and negative impacts on health, viruses are generally associated with causing diseases.
What is the term for the response of plants to the timing of light and darkness?- a)Respiration
- b)Photoperiodism
- c)Vernalization
- d)Budding
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Respiration
b)
Photoperiodism
c)
Vernalization
d)
Budding

|
Valor Academy answered |
Photoperiodism refers to the response of plants to the timing of light and darkness, which influences flowering and other developmental processes.
What is the primary function of roots in plants?- a)Absorption of sunlight
- b)Anchoring the plant and absorbing water and minerals
- c)Storage of food
- d)Transport of nutrients to leaves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Absorption of sunlight
b)
Anchoring the plant and absorbing water and minerals
c)
Storage of food
d)
Transport of nutrients to leaves
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
Primary Function of Roots in Plants: Anchoring the Plant and Absorbing Water and Minerals
Roots are an essential part of the plant structure and play a crucial role in its overall growth and survival. While they may not be as visible as leaves or flowers, roots serve several important functions that are vital for the plant's well-being. The primary function of roots in plants is to anchor the plant securely in the ground and to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Let's delve into the details of these functions:
1. Anchoring the Plant:
Roots provide stability and support to the plant by anchoring it firmly in the ground. This is particularly important for tall and large plants that need a strong foundation to withstand winds, heavy rainfall, and other environmental factors. The root system forms an underground network that helps to keep the plant upright and prevents it from toppling over. Without proper anchorage, plants would be vulnerable to physical damage and would struggle to grow and survive.
2. Absorbing Water and Minerals:
One of the most crucial roles of roots is to absorb water and essential minerals from the soil. The root system consists of numerous tiny root hairs that greatly increase the surface area for absorption. These root hairs have a thin cell wall, which allows for efficient uptake of water and minerals through a process called osmosis. The root hairs also have a close association with mycorrhizal fungi, which further enhance nutrient absorption.
Water is vital for the plant's survival as it is involved in various physiological processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient transportation, and maintaining turgidity. Roots absorb water from the soil and transport it upwards to the stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant through the xylem tissue.
Similarly, minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and various micronutrients are essential for the plant's growth and development. Roots absorb these minerals from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant through the phloem tissue. These minerals are used in various biochemical reactions and are crucial for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and other important compounds.
In summary, the primary function of roots in plants is to anchor the plant securely in the ground and to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Without a well-developed root system, plants would be unable to survive and grow efficiently. Therefore, roots are fundamental to the overall health and productivity of plants.
Roots are an essential part of the plant structure and play a crucial role in its overall growth and survival. While they may not be as visible as leaves or flowers, roots serve several important functions that are vital for the plant's well-being. The primary function of roots in plants is to anchor the plant securely in the ground and to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Let's delve into the details of these functions:
1. Anchoring the Plant:
Roots provide stability and support to the plant by anchoring it firmly in the ground. This is particularly important for tall and large plants that need a strong foundation to withstand winds, heavy rainfall, and other environmental factors. The root system forms an underground network that helps to keep the plant upright and prevents it from toppling over. Without proper anchorage, plants would be vulnerable to physical damage and would struggle to grow and survive.
2. Absorbing Water and Minerals:
One of the most crucial roles of roots is to absorb water and essential minerals from the soil. The root system consists of numerous tiny root hairs that greatly increase the surface area for absorption. These root hairs have a thin cell wall, which allows for efficient uptake of water and minerals through a process called osmosis. The root hairs also have a close association with mycorrhizal fungi, which further enhance nutrient absorption.
Water is vital for the plant's survival as it is involved in various physiological processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient transportation, and maintaining turgidity. Roots absorb water from the soil and transport it upwards to the stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant through the xylem tissue.
Similarly, minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and various micronutrients are essential for the plant's growth and development. Roots absorb these minerals from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant through the phloem tissue. These minerals are used in various biochemical reactions and are crucial for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and other important compounds.
In summary, the primary function of roots in plants is to anchor the plant securely in the ground and to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Without a well-developed root system, plants would be unable to survive and grow efficiently. Therefore, roots are fundamental to the overall health and productivity of plants.
What is the term for the loss of excess water in the form of vapor through the aerial parts of a plant?- a)Respiration
- b)Photosynthesis
- c)Guttation
- d)Transpiration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Respiration
b)
Photosynthesis
c)
Guttation
d)
Transpiration
|
|
Jaideep Roy answered |
Transpiration
Transpiration is the process by which excess water in the form of vapor is lost through the aerial parts of a plant, mainly through the stomata on the leaves. This process is crucial for plants as it helps in cooling the plant, transporting nutrients and minerals, and maintaining turgidity in the cells.
Significance of Transpiration
- **Cooling mechanism**: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant by releasing excess heat during the process of water vaporization.
- **Nutrient transport**: Water and minerals absorbed by the roots are transported to different parts of the plant through the process of transpiration.
- **Maintaining turgidity**: Transpiration helps in maintaining turgidity in the plant cells, which is essential for plant structure and growth.
Mechanism of Transpiration
- **Stomata**: Tiny openings on the surface of leaves through which water vapor escapes.
- **Guard cells**: Surround the stomata and regulate their opening and closing to control transpiration.
- **Root pressure and cohesion-tension theory**: Water is absorbed by roots and transported to leaves, where it evaporates through stomata due to differences in water potential.
Factors affecting Transpiration
- **Environmental conditions**: Temperature, humidity, wind speed, and light intensity influence the rate of transpiration.
- **Plant factors**: Number and distribution of stomata, leaf surface area, and plant species affect transpiration rates.
Conclusion
Transpiration is a vital process for plants as it helps in maintaining water balance, nutrient transport, and overall plant health. Understanding the mechanisms and factors influencing transpiration is crucial for effective plant growth and development.
Transpiration is the process by which excess water in the form of vapor is lost through the aerial parts of a plant, mainly through the stomata on the leaves. This process is crucial for plants as it helps in cooling the plant, transporting nutrients and minerals, and maintaining turgidity in the cells.
Significance of Transpiration
- **Cooling mechanism**: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant by releasing excess heat during the process of water vaporization.
- **Nutrient transport**: Water and minerals absorbed by the roots are transported to different parts of the plant through the process of transpiration.
- **Maintaining turgidity**: Transpiration helps in maintaining turgidity in the plant cells, which is essential for plant structure and growth.
Mechanism of Transpiration
- **Stomata**: Tiny openings on the surface of leaves through which water vapor escapes.
- **Guard cells**: Surround the stomata and regulate their opening and closing to control transpiration.
- **Root pressure and cohesion-tension theory**: Water is absorbed by roots and transported to leaves, where it evaporates through stomata due to differences in water potential.
Factors affecting Transpiration
- **Environmental conditions**: Temperature, humidity, wind speed, and light intensity influence the rate of transpiration.
- **Plant factors**: Number and distribution of stomata, leaf surface area, and plant species affect transpiration rates.
Conclusion
Transpiration is a vital process for plants as it helps in maintaining water balance, nutrient transport, and overall plant health. Understanding the mechanisms and factors influencing transpiration is crucial for effective plant growth and development.
What is the primary advantage of transpiration in plants?- a)Removal of excess water
- b)Reduction of mineral absorption
- c)Inhibition of photosynthesis
- d)Increased carbon dioxide concentration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Removal of excess water
b)
Reduction of mineral absorption
c)
Inhibition of photosynthesis
d)
Increased carbon dioxide concentration
|
|
Jaideep Roy answered |
The primary advantage of transpiration in plants is the removal of excess water.
- Regulation of water balance: Transpiration helps plants maintain a proper water balance by allowing them to release excess water. This process is crucial for preventing waterlogging and ensuring that the plant does not become overly hydrated.
- Cooling mechanism: Transpiration also serves as a cooling mechanism for plants. As water evaporates from the leaves, it takes away heat energy, which helps regulate the plant's temperature and prevent overheating.
- Nutrient uptake: Transpiration creates a negative pressure in the plant, which helps in the uptake of water and essential nutrients from the soil. This process is essential for the plant's growth and overall health.
- Transport of minerals: Transpiration facilitates the movement of minerals and nutrients through the plant's vascular system. As water evaporates from the leaves, it creates a pull that helps transport minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
In conclusion, transpiration plays a vital role in the overall health and functioning of plants by regulating water balance, facilitating nutrient uptake, and serving as a cooling mechanism. It is a crucial process that helps plants thrive in their environment.
- Regulation of water balance: Transpiration helps plants maintain a proper water balance by allowing them to release excess water. This process is crucial for preventing waterlogging and ensuring that the plant does not become overly hydrated.
- Cooling mechanism: Transpiration also serves as a cooling mechanism for plants. As water evaporates from the leaves, it takes away heat energy, which helps regulate the plant's temperature and prevent overheating.
- Nutrient uptake: Transpiration creates a negative pressure in the plant, which helps in the uptake of water and essential nutrients from the soil. This process is essential for the plant's growth and overall health.
- Transport of minerals: Transpiration facilitates the movement of minerals and nutrients through the plant's vascular system. As water evaporates from the leaves, it creates a pull that helps transport minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
In conclusion, transpiration plays a vital role in the overall health and functioning of plants by regulating water balance, facilitating nutrient uptake, and serving as a cooling mechanism. It is a crucial process that helps plants thrive in their environment.
Root hairs develop from- a) region of maturation
- b) region of elongation
- c) region of meristematic activity
- d) root cap
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Root hairs develop from
a)
region of maturation
b)
region of elongation
c)
region of meristematic activity
d)
root cap

|
Gargi Saha answered |
Root hairs develop from the region of maturation or the region of differentiation.
If a,b,c are any three vectors, the statement is true- a)ax(bxc)=(axb)xc
- b)axb=bxa
- c)a.(bxc)=a.b+a.c
- d)a.(b-c)=a.b-a.c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a,b,c are any three vectors, the statement is true
a)
ax(bxc)=(axb)xc
b)
axb=bxa
c)
a.(bxc)=a.b+a.c
d)
a.(b-c)=a.b-a.c
|
|
Partho Sen answered |
D is the correct option.a.(b-c)=a.b-a.c is correct if a,b,c are any three vectors.
Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by- a)SN1 mechanism
- b)SN2 mechanism
- c)SN1 and SN2 mechanism
- d)Neither SN1 nor SN2 mechanism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by
a)
SN1 mechanism
b)
SN2 mechanism
c)
SN1 and SN2 mechanism
d)
Neither SN1 nor SN2 mechanism
|
|
Sreemoyee Gupta answered |
Secondary, primary allylic and primary benzylic halides may react predominantly either by SN1 or SN2 mechanism or by both the mechanisms without much preference, depending upon the nature of the nuclephile and the solvent.
Roots develop from parts of the plant other than radicle are called- a) tap roots
- b) fibrous roots
- c) adventitious roots
- d) nodular roots
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Roots develop from parts of the plant other than radicle are called
a)
tap roots
b)
fibrous roots
c)
adventitious roots
d)
nodular roots

|
Nishanth Jain answered |
Adventitious roots are the type of roots that are grown from different parts of plants such as stem, leaf and tubers etc.
These are used in vegetative propagation.
These are mostly grown on root tubers and the apex of these tubers contains numerous adventitious roots which grow into new plants.
Read more on Brainly.in - https://brainly.in/question/147876#readmore
The Indian Pipe Plant or Monotrapa can be best placed in which among the following groups?- a)Parasite
- b)Saprophyte
- c) Insectivorous
- d)Lithophyte
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Indian Pipe Plant or Monotrapa can be best placed in which among the following groups?
a)
Parasite
b)
Saprophyte
c)
Insectivorous
d)
Lithophyte
|
|
Simran Menon answered |
The Indian Pipe Plant or Monotropa
The Indian Pipe Plant, also known as Monotropa, belongs to the group of saprophytes. Saprophytes are plants that obtain their nutrients by decomposing dead organic matter. Let's understand why Monotropa is classified as a saprophyte.
Saprophytes
Saprophytes are unique plants that do not have chlorophyll and therefore cannot perform photosynthesis. Instead, they rely on obtaining nutrients from decaying organic matter, such as dead plants, animal remains, or fecal matter. These plants play a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down organic material and recycling nutrients.
Characteristics of Monotropa
Monotropa, commonly known as the Indian Pipe Plant, is a fascinating parasitic plant that belongs to the saprophyte group. Some key characteristics of Monotropa are as follows:
1. Lack of chlorophyll: Monotropa does not possess chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color in plants. This absence of chlorophyll makes it unable to carry out photosynthesis and produce its own food.
2. Dependence on mycorrhizal fungi: Monotropa forms a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi are present in the soil and help in absorbing nutrients from decaying organic matter. The fungi provide essential nutrients to Monotropa, while the plant provides carbohydrates to the fungi.
3. White or pale coloration: Due to the absence of chlorophyll, Monotropa appears pale or white in color. It has a waxy texture, giving it a ghostly appearance.
4. Habitat and distribution: Monotropa is commonly found in moist, shady areas of forests. It grows on the forest floor, often in association with certain tree species. It is found in various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Indian Pipe Plant or Monotropa is classified as a saprophyte. It lacks chlorophyll and relies on mycorrhizal fungi to obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter. Understanding the classification of plants helps us appreciate the diversity of the plant kingdom and their unique adaptations for survival.
The Indian Pipe Plant, also known as Monotropa, belongs to the group of saprophytes. Saprophytes are plants that obtain their nutrients by decomposing dead organic matter. Let's understand why Monotropa is classified as a saprophyte.
Saprophytes
Saprophytes are unique plants that do not have chlorophyll and therefore cannot perform photosynthesis. Instead, they rely on obtaining nutrients from decaying organic matter, such as dead plants, animal remains, or fecal matter. These plants play a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down organic material and recycling nutrients.
Characteristics of Monotropa
Monotropa, commonly known as the Indian Pipe Plant, is a fascinating parasitic plant that belongs to the saprophyte group. Some key characteristics of Monotropa are as follows:
1. Lack of chlorophyll: Monotropa does not possess chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color in plants. This absence of chlorophyll makes it unable to carry out photosynthesis and produce its own food.
2. Dependence on mycorrhizal fungi: Monotropa forms a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi are present in the soil and help in absorbing nutrients from decaying organic matter. The fungi provide essential nutrients to Monotropa, while the plant provides carbohydrates to the fungi.
3. White or pale coloration: Due to the absence of chlorophyll, Monotropa appears pale or white in color. It has a waxy texture, giving it a ghostly appearance.
4. Habitat and distribution: Monotropa is commonly found in moist, shady areas of forests. It grows on the forest floor, often in association with certain tree species. It is found in various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Indian Pipe Plant or Monotropa is classified as a saprophyte. It lacks chlorophyll and relies on mycorrhizal fungi to obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter. Understanding the classification of plants helps us appreciate the diversity of the plant kingdom and their unique adaptations for survival.
Which type of respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen?- a)Aerobic respiration
- b)Anaerobic respiration
- c)Glycolysis
- d)Catabolic respiration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Aerobic respiration
b)
Anaerobic respiration
c)
Glycolysis
d)
Catabolic respiration

|
Valor Academy answered |
Respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration. In this process, incomplete oxidation of organic compounds takes place, leading to the production of products like ethanol or lactic acid.
What is the metamorphosed part of the shoot meant for plant reproduction?- a)Stipule
- b)Petiole
- c)Pulvinus
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Stipule
b)
Petiole
c)
Pulvinus
d)
Flower
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
Flower: The Reproductive Part of a Plant
The metamorphosed part of the shoot that is meant for plant reproduction is the flower. Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms, which are a group of plants that produce seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are the most diverse and abundant group of plants on Earth, and their flowers play a crucial role in their reproductive process.
Structure and Function of a Flower
A flower is composed of several different parts, each with its specific function in the reproductive process. These parts include:
1. Petals: Petals are the colorful, leaf-like structures that surround the reproductive organs of the flower. They are responsible for attracting pollinators, such as insects or birds, to facilitate pollination.
2. Sepals: Sepals are the small, usually green, leaf-like structures that protect the developing flower bud. They are located at the base of the flower and enclose it before it blooms.
3. Stamens: Stamens are the male reproductive organs of the flower. They consist of two main parts: the filament and the anther. The filament is a thin stalk that supports the anther, which contains pollen grains. Pollen is the male gamete that is necessary for fertilization.
4. Carpels: Carpels are the female reproductive organs of the flower. They are composed of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky structure at the top of the carpel that receives pollen. The style is a long tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary contains the ovules, which are the female gametes that develop into seeds after fertilization.
5. Receptacle: The receptacle is the base of the flower where all the other parts are attached. It provides support and protection for the reproductive organs.
Plant Reproduction
The flower plays a crucial role in plant reproduction by facilitating the process of pollination and fertilization. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel. This can happen through various means, including wind, water, or the assistance of pollinators.
Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates and grows a pollen tube down through the style, eventually reaching the ovary. The male gametes inside the pollen grain travel down the pollen tube and fertilize the ovules inside the ovary. This process leads to the formation of seeds.
After fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. The seeds can then germinate and grow into new plants, continuing the life cycle.
In conclusion, the metamorphosed part of the shoot that is meant for plant reproduction is the flower. Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms and consist of various parts, including petals, sepals, stamens, carpels, and the receptacle. The flower plays a crucial role in facilitating pollination, fertilization, and the formation of seeds, which are essential for plant reproduction and the continuation of the plant life cycle.
The metamorphosed part of the shoot that is meant for plant reproduction is the flower. Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms, which are a group of plants that produce seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are the most diverse and abundant group of plants on Earth, and their flowers play a crucial role in their reproductive process.
Structure and Function of a Flower
A flower is composed of several different parts, each with its specific function in the reproductive process. These parts include:
1. Petals: Petals are the colorful, leaf-like structures that surround the reproductive organs of the flower. They are responsible for attracting pollinators, such as insects or birds, to facilitate pollination.
2. Sepals: Sepals are the small, usually green, leaf-like structures that protect the developing flower bud. They are located at the base of the flower and enclose it before it blooms.
3. Stamens: Stamens are the male reproductive organs of the flower. They consist of two main parts: the filament and the anther. The filament is a thin stalk that supports the anther, which contains pollen grains. Pollen is the male gamete that is necessary for fertilization.
4. Carpels: Carpels are the female reproductive organs of the flower. They are composed of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky structure at the top of the carpel that receives pollen. The style is a long tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary contains the ovules, which are the female gametes that develop into seeds after fertilization.
5. Receptacle: The receptacle is the base of the flower where all the other parts are attached. It provides support and protection for the reproductive organs.
Plant Reproduction
The flower plays a crucial role in plant reproduction by facilitating the process of pollination and fertilization. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel. This can happen through various means, including wind, water, or the assistance of pollinators.
Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates and grows a pollen tube down through the style, eventually reaching the ovary. The male gametes inside the pollen grain travel down the pollen tube and fertilize the ovules inside the ovary. This process leads to the formation of seeds.
After fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. The seeds can then germinate and grow into new plants, continuing the life cycle.
In conclusion, the metamorphosed part of the shoot that is meant for plant reproduction is the flower. Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms and consist of various parts, including petals, sepals, stamens, carpels, and the receptacle. The flower plays a crucial role in facilitating pollination, fertilization, and the formation of seeds, which are essential for plant reproduction and the continuation of the plant life cycle.
What is the function of stipules in a plant leaf?- a)Aiding in photosynthesis
- b)Protecting against herbivores
- c)Attaching the leaf to the stem
- d)Supporting water conservation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Aiding in photosynthesis
b)
Protecting against herbivores
c)
Attaching the leaf to the stem
d)
Supporting water conservation
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
B. Protecting against herbivores
Stipules are small, leaf-like structures that are typically found at the base of a leaf where it attaches to the stem. They can vary in size, shape, and color, depending on the plant species. Stipules serve several functions in plants, including protection against herbivores.
1. Protection against herbivores:
Stipules can have various adaptations that help protect the plant from being eaten by herbivores. Some stipules are modified into sharp spines or thorns, which can deter animals from feeding on the plant. These structures act as physical barriers, making it more difficult for herbivores to access the leaves or other parts of the plant. The presence of stipules can also signal the presence of chemical defenses in the plant, such as toxins or unpleasant tastes, further deterring herbivores.
2. Aiding in photosynthesis:
While stipules primarily serve a protective function, some stipules may also contribute to photosynthesis. Stipules that are green and contain chlorophyll can carry out photosynthesis, helping the plant produce energy from sunlight. However, this function is not as common or significant as protection against herbivores.
3. Attaching the leaf to the stem:
Stipules play a role in attaching the leaf to the stem. They provide support and stability, preventing the leaf from falling off or being easily detached from the plant. Stipules can act as a bridge between the leaf and the stem, ensuring a secure connection.
4. Supporting water conservation:
In some plants, stipules may have adaptations that aid in water conservation. For example, certain stipules can be modified into small, scale-like structures that cover the leaf bud during dormancy or periods of water scarcity. These modified stipules help reduce water loss through evaporation and protect the delicate leaf bud from desiccation.
In conclusion, while stipules can have multiple functions, the primary function of stipules in a plant leaf is to protect against herbivores. They can also aid in photosynthesis, attach the leaf to the stem, and support water conservation in certain plant species.
Stipules are small, leaf-like structures that are typically found at the base of a leaf where it attaches to the stem. They can vary in size, shape, and color, depending on the plant species. Stipules serve several functions in plants, including protection against herbivores.
1. Protection against herbivores:
Stipules can have various adaptations that help protect the plant from being eaten by herbivores. Some stipules are modified into sharp spines or thorns, which can deter animals from feeding on the plant. These structures act as physical barriers, making it more difficult for herbivores to access the leaves or other parts of the plant. The presence of stipules can also signal the presence of chemical defenses in the plant, such as toxins or unpleasant tastes, further deterring herbivores.
2. Aiding in photosynthesis:
While stipules primarily serve a protective function, some stipules may also contribute to photosynthesis. Stipules that are green and contain chlorophyll can carry out photosynthesis, helping the plant produce energy from sunlight. However, this function is not as common or significant as protection against herbivores.
3. Attaching the leaf to the stem:
Stipules play a role in attaching the leaf to the stem. They provide support and stability, preventing the leaf from falling off or being easily detached from the plant. Stipules can act as a bridge between the leaf and the stem, ensuring a secure connection.
4. Supporting water conservation:
In some plants, stipules may have adaptations that aid in water conservation. For example, certain stipules can be modified into small, scale-like structures that cover the leaf bud during dormancy or periods of water scarcity. These modified stipules help reduce water loss through evaporation and protect the delicate leaf bud from desiccation.
In conclusion, while stipules can have multiple functions, the primary function of stipules in a plant leaf is to protect against herbivores. They can also aid in photosynthesis, attach the leaf to the stem, and support water conservation in certain plant species.
What is the primary function of the ovary in a flower's gynoecium?- a)To trap pollen
- b)To develop into a fruit
- c)To contain the stigma
- d)To produce endosperm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To trap pollen
b)
To develop into a fruit
c)
To contain the stigma
d)
To produce endosperm
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
The primary function of the ovary in a flower's gynoecium is to develop into a fruit.
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of a flower, consisting of one or more carpels. Each carpel consists of three major parts - the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky surface at the top of the carpel that receives pollen, the style is a slender tube connecting the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary is the enlarged basal portion that contains the ovules.
The ovary plays a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants. It is responsible for the development and maturation of the ovules, which are the structures that contain the female gametes or eggs. After pollination occurs, the pollen grains land on the stigma and germinate, forming pollen tubes that grow down through the style and into the ovary. The ovules are then fertilized by the male gametes contained within the pollen tubes, resulting in the formation of seeds.
Once fertilization occurs, the ovary begins to develop into a fruit. The ovary wall thickens and undergoes various changes, such as the formation of additional tissues, to protect and nourish the developing seeds. The ovary may also undergo changes in color, texture, and size, depending on the specific type of fruit. This process is known as fruit development or fruit ripening.
The fruit serves several important functions for the plant. Firstly, it protects the seeds from external damage and provides a suitable environment for their development. It also aids in seed dispersal by attracting animals or wind, which help to spread the seeds away from the parent plant. Additionally, the fruit may contain substances that attract animals to consume it, thereby facilitating seed dispersal through their excretion.
In conclusion, the primary function of the ovary in a flower's gynoecium is to develop into a fruit. This process ensures the protection, development, and dispersal of the seeds, contributing to the reproductive success of flowering plants.
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of a flower, consisting of one or more carpels. Each carpel consists of three major parts - the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky surface at the top of the carpel that receives pollen, the style is a slender tube connecting the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary is the enlarged basal portion that contains the ovules.
The ovary plays a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants. It is responsible for the development and maturation of the ovules, which are the structures that contain the female gametes or eggs. After pollination occurs, the pollen grains land on the stigma and germinate, forming pollen tubes that grow down through the style and into the ovary. The ovules are then fertilized by the male gametes contained within the pollen tubes, resulting in the formation of seeds.
Once fertilization occurs, the ovary begins to develop into a fruit. The ovary wall thickens and undergoes various changes, such as the formation of additional tissues, to protect and nourish the developing seeds. The ovary may also undergo changes in color, texture, and size, depending on the specific type of fruit. This process is known as fruit development or fruit ripening.
The fruit serves several important functions for the plant. Firstly, it protects the seeds from external damage and provides a suitable environment for their development. It also aids in seed dispersal by attracting animals or wind, which help to spread the seeds away from the parent plant. Additionally, the fruit may contain substances that attract animals to consume it, thereby facilitating seed dispersal through their excretion.
In conclusion, the primary function of the ovary in a flower's gynoecium is to develop into a fruit. This process ensures the protection, development, and dispersal of the seeds, contributing to the reproductive success of flowering plants.
The chief function of vessels in the plant body is- a) to translocate food material
- b) to conduct water and mineral salts
- c) to support living cells
- d) all above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The chief function of vessels in the plant body is
a)
to translocate food material
b)
to conduct water and mineral salts
c)
to support living cells
d)
all above

|
Dipika Gupta answered |
Xylem, plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support.
Which one of the following process releases a carbon dioxide molecule?- a) Glycolysis
- b) Lactic acid fermentation
- c) Alcohol fermentation
- d) Hydrolysis of glycogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following process releases a carbon dioxide molecule?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Lactic acid fermentation
c)
Alcohol fermentation
d)
Hydrolysis of glycogen

|
Shreya Mishra answered |
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose and other six-carbon sugars (also, disaccharides of six-carbon sugars, e.g. sucrose or lactose) are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate.
What is the name for the uppermost part of the gynoecium that serves as a device to trap pollen?- a)Ovary
- b)Stigma
- c)Style
- d)Endocarp
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Ovary
b)
Stigma
c)
Style
d)
Endocarp
|
|
Pallavi Kulkarni answered |
Stigma: The Uppermost Part of the Gynoecium that Traps Pollen
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', Stigma. The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium, which is the female reproductive part of a flower. It plays a crucial role in the process of pollination, specifically in the capture and recognition of pollen.
Explanation:
1. Structure of the Gynoecium:
The gynoecium is the collective term for all the female reproductive organs of a flower. It is made up of three main parts:
- Ovary: The ovary is the enlarged basal part of the gynoecium. It contains one or more ovules, which are responsible for the development of seeds after fertilization.
- Style: The style is a slender, elongated structure that connects the ovary to the stigma. It provides support and allows the pollen tube to grow during fertilization.
- Stigma: The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium. It is located at the top of the style and serves as a landing platform for pollen during pollination.
2. Function of the Stigma:
The stigma plays a crucial role in the pollination process. Its main functions include:
- Pollen Capture: The stigma is designed to capture pollen grains from visiting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, or birds. It is often sticky or covered in specialized cells called papillae, which help trap the pollen grains.
- Pollen Recognition: After capturing the pollen, the stigma plays a role in recognizing and accepting compatible pollen. It has specific receptors that can detect and differentiate between pollen grains of different species or individuals.
- Pollen Germination: Once the pollen has been recognized as compatible, it germinates on the stigma. The pollen grain forms a pollen tube, which grows down through the style towards the ovary. This tube serves as the conduit for the male gametes to reach the ovules for fertilization.
Conclusion:
The stigma, as the uppermost part of the gynoecium, is responsible for capturing and recognizing pollen during the process of pollination. Its sticky or specialized surface helps trap pollen grains, and it also plays a role in determining the compatibility of the pollen. The stigma is a vital component of the female reproductive system in flowers, ensuring successful fertilization and seed development.
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', Stigma. The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium, which is the female reproductive part of a flower. It plays a crucial role in the process of pollination, specifically in the capture and recognition of pollen.
Explanation:
1. Structure of the Gynoecium:
The gynoecium is the collective term for all the female reproductive organs of a flower. It is made up of three main parts:
- Ovary: The ovary is the enlarged basal part of the gynoecium. It contains one or more ovules, which are responsible for the development of seeds after fertilization.
- Style: The style is a slender, elongated structure that connects the ovary to the stigma. It provides support and allows the pollen tube to grow during fertilization.
- Stigma: The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium. It is located at the top of the style and serves as a landing platform for pollen during pollination.
2. Function of the Stigma:
The stigma plays a crucial role in the pollination process. Its main functions include:
- Pollen Capture: The stigma is designed to capture pollen grains from visiting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, or birds. It is often sticky or covered in specialized cells called papillae, which help trap the pollen grains.
- Pollen Recognition: After capturing the pollen, the stigma plays a role in recognizing and accepting compatible pollen. It has specific receptors that can detect and differentiate between pollen grains of different species or individuals.
- Pollen Germination: Once the pollen has been recognized as compatible, it germinates on the stigma. The pollen grain forms a pollen tube, which grows down through the style towards the ovary. This tube serves as the conduit for the male gametes to reach the ovules for fertilization.
Conclusion:
The stigma, as the uppermost part of the gynoecium, is responsible for capturing and recognizing pollen during the process of pollination. Its sticky or specialized surface helps trap pollen grains, and it also plays a role in determining the compatibility of the pollen. The stigma is a vital component of the female reproductive system in flowers, ensuring successful fertilization and seed development.
Lignin is the important constituent in the cell wall of- a) phloem
- b) parenchyma
- c) xylem
- d) cambium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lignin is the important constituent in the cell wall of
a)
phloem
b)
parenchyma
c)
xylem
d)
cambium

|
Aashna Patel answered |
Lignin is a constituent of the cell walls of almost all dry land plant cell walls.
The structure of white phosphorus is- a)Square planar
- b)Pyramidal
- c)Tetrahedral
- d)Trigonal planar
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure of white phosphorus is
a)
Square planar
b)
Pyramidal
c)
Tetrahedral
d)
Trigonal planar
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
C is the correct option.The structure of white phosphorus is tetrahedral.
White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus or simply tetraphosphorus (P4) exists as molecules made up of four atoms in a tetrahedral structure. The tetrahedral arrangement results in ring strain and instability. The molecule is described as consisting of six single P–P bonds.
White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus or simply tetraphosphorus (P4) exists as molecules made up of four atoms in a tetrahedral structure. The tetrahedral arrangement results in ring strain and instability. The molecule is described as consisting of six single P–P bonds.
Chapter doubts & questions for Plant Kingdom - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Plant Kingdom - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams
129 videos|571 docs|225 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup


 .
.