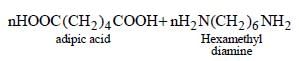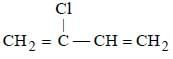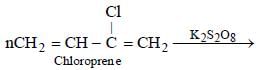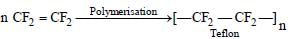All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Polymers for NEET Exam
PVC is a type of:- a)Homopolymers
- b)Synthetic polymer
- c)Natural rubber
- d)Addition polymer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PVC is a type of:
a)
Homopolymers
b)
Synthetic polymer
c)
Natural rubber
d)
Addition polymer
|
|
Priyanshu Intelligent answered |
Polyvinyl chloride colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). ... PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
Name the monomer of nylon-6:- a)hexamethylene
- b)ethylene glycol
- c)Caprolactum
- d)Ethene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the monomer of nylon-6:
a)
hexamethylene
b)
ethylene glycol
c)
Caprolactum
d)
Ethene
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Nylon 6 is synthesized by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. Caprolactam has 6 carbons, hence Nylon 6.
Nylon 6 is synthesized by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. Caprolactam has 6 carbons, hence Nylon 6.
Which intermolecular force is present in Nylon 6,6?- a)Copolymers
- b)Hydrogen bonding
- c)Dipole-dipole interaction
- d)van der Waals forces
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which intermolecular force is present in Nylon 6,6?
a)
Copolymers
b)
Hydrogen bonding
c)
Dipole-dipole interaction
d)
van der Waals forces
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Van der Waals forces include attraction and repulsions between atoms, molecules, and surfaces.
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Dipole-dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule.
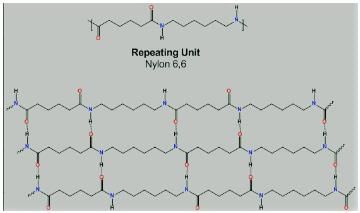
From the picture of Nylon-6,6, we can see there is hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
Though hydrogen bonds are also one type of dipole-dipole attraction, here, a more appropriate answer will be - The intermolecular forces present in nylon-6,6 are hydrogen bonding.
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Dipole-dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule.

From the picture of Nylon-6,6, we can see there is hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
Though hydrogen bonds are also one type of dipole-dipole attraction, here, a more appropriate answer will be - The intermolecular forces present in nylon-6,6 are hydrogen bonding.
Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers?
- a)3-hydroxybutyric acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
- b)Ethylene glycol + phthalic acid
- c)Glycine + aminocaproic acid
- d)Caprolactam
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers?
a)
3-hydroxybutyric acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
b)
Ethylene glycol + phthalic acid
c)
Glycine + aminocaproic acid
d)
Caprolactam
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Poly-β−hydroxybutyrate co-β− valerate (PHBV). It is obtained by the copolymerization of 3−hydroxybutyric acid and 3−hydroxypentanoic acid. PHBV is used in specially packaging orthopedic devices and in controlled release of drugs. PHBV undergoes bacterial degradation in the environment.
Nylon−2−. It is an alternating polyamide copolymer of glycine (H2N−CH2−COOH) and aminocaproic acid [NH2(CH2)5COOH] and is biodegradable.
Nylon−2−. It is an alternating polyamide copolymer of glycine (H2N−CH2−COOH) and aminocaproic acid [NH2(CH2)5COOH] and is biodegradable.
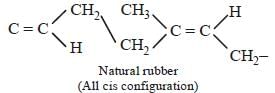
Natural rubber is a polymer of
[1999]
a)butadieneb)2-methylbutadienec)Hexa-1, 3-diened)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Natural rubber, also called India rubber or caoutchouc, as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds, plus water. ... Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the rubber tree or others.
The correct name of the polymer below is: 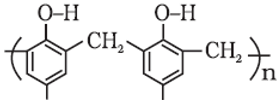
- a)Dacron
- b)Novolac
- c)Melamine polymer
- d)Bakelite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct name of the polymer below is:
a)
Dacron
b)
Novolac
c)
Melamine polymer
d)
Bakelite

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Novolac
-> Linear structure formed as a product of condensation reaction between phenol and formaldehyde with excess of phenol.
-> It is used in paints
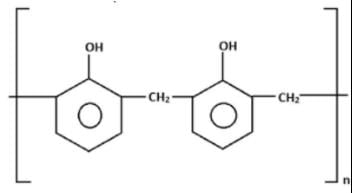
Novolac
-> Linear structure formed as a product of condensation reaction between phenol and formaldehyde with excess of phenol.
-> It is used in paints

Which polymerisation occurs among the molecules containing double bonds?- a)Condensation polymerization
- b)Natural polymer
- c)Synthetic polymer
- d)Addition polymer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which polymerisation occurs among the molecules containing double bonds?
a)
Condensation polymerization
b)
Natural polymer
c)
Synthetic polymer
d)
Addition polymer
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Addition polymerization takes place when the monomer molecule contains double carbon bonds, as in alkenes, or triple carbon bonds, as in alkynes. In this lesson we will consider alkene monomers.
Vitamin B12 contains [2003]- a)Ca(II)
- b)Fe(II)
- c)Co(III)
- d)Zn(II)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vitamin B12 contains [2003]
a)
Ca(II)
b)
Fe(II)
c)
Co(III)
d)
Zn(II)

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Vit B12 also called Cyanocobaltamine, is antipernicious
anaemia vitamin. It is
C63H84O14N14PCo.
anaemia vitamin. It is
C63H84O14N14PCo.
Which one of the following is not a condensation polymer?- a)Dacron
- b)Neoprene
- c)Melamine
- d)Glyptal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a condensation polymer?
a)
Dacron
b)
Neoprene
c)
Melamine
d)
Glyptal
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
Condensation Polymers and Neoprene
Condensation polymers are formed by the condensation reaction between two or more different monomers. The reaction results in the formation of a polymer and a small molecule, such as water or alcohol. Some common examples of condensation polymers include Dacron, melamine, and glyptal.
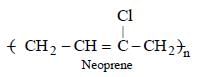
Neoprene, on the other hand, is not a condensation polymer. It is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. This polymerization reaction does not involve the elimination of any small molecules, and therefore, it is not a condensation reaction.
Explanation:
Condensation Polymers
Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction between two or more different monomers. In this reaction, the monomers condense together, eliminating a small molecule such as water or alcohol. The resulting polymer is made up of repeating units of the monomers that have reacted together.
Some common examples of condensation polymers include:
- Dacron: This is a polyester that is formed by the condensation reaction between terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. It is used in the manufacture of fabrics and plastic bottles.
- Melamine: This is a thermosetting plastic that is formed by the condensation reaction between melamine and formaldehyde. It is used in the manufacture of dinnerware, electrical components, and laminates.
- Glyptal: This is a thermosetting plastic that is formed by the condensation reaction between glycerol and phthalic anhydride. It is used as an insulating varnish for electrical equipment.
Neoprene
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. This polymerization reaction does not involve the elimination of any small molecules, and therefore, it is not a condensation reaction.
Neoprene is used in a variety of applications, including wetsuits, gloves, gaskets, and orthopedic braces. It is known for its excellent resistance to water, oil, and chemicals, as well as its ability to maintain its flexibility over a wide range of temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, neoprene is not a condensation polymer. It is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. Condensation polymers are formed by the condensation reaction between two or more different monomers, resulting in the elimination of a small molecule. Some common examples of condensation polymers include Dacron, melamine, and glyptal.
Condensation polymers are formed by the condensation reaction between two or more different monomers. The reaction results in the formation of a polymer and a small molecule, such as water or alcohol. Some common examples of condensation polymers include Dacron, melamine, and glyptal.
Neoprene, on the other hand, is not a condensation polymer. It is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. This polymerization reaction does not involve the elimination of any small molecules, and therefore, it is not a condensation reaction.
Explanation:
Condensation Polymers
Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction between two or more different monomers. In this reaction, the monomers condense together, eliminating a small molecule such as water or alcohol. The resulting polymer is made up of repeating units of the monomers that have reacted together.
Some common examples of condensation polymers include:
- Dacron: This is a polyester that is formed by the condensation reaction between terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. It is used in the manufacture of fabrics and plastic bottles.
- Melamine: This is a thermosetting plastic that is formed by the condensation reaction between melamine and formaldehyde. It is used in the manufacture of dinnerware, electrical components, and laminates.
- Glyptal: This is a thermosetting plastic that is formed by the condensation reaction between glycerol and phthalic anhydride. It is used as an insulating varnish for electrical equipment.
Neoprene
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. This polymerization reaction does not involve the elimination of any small molecules, and therefore, it is not a condensation reaction.
Neoprene is used in a variety of applications, including wetsuits, gloves, gaskets, and orthopedic braces. It is known for its excellent resistance to water, oil, and chemicals, as well as its ability to maintain its flexibility over a wide range of temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, neoprene is not a condensation polymer. It is a synthetic rubber that is formed by the polymerization of chloroprene. Condensation polymers are formed by the condensation reaction between two or more different monomers, resulting in the elimination of a small molecule. Some common examples of condensation polymers include Dacron, melamine, and glyptal.
Which of the following is not correctly matched?[2001]- a)
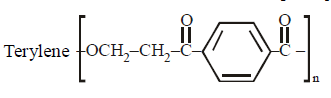
- b)
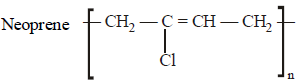
- c)
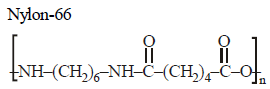
- d)
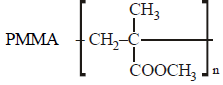
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
[2001]
a)
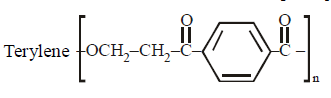
b)
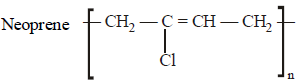
c)
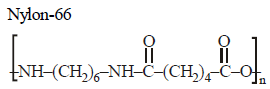
d)
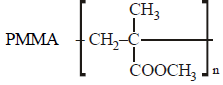

|
Swara Desai answered |
Terylene is prepared by condensing
dimethylterephthalate and ethylene glycol
in presence of a weak base, (calcium
acetate). Methanol is eliminated during
condensation.
dimethylterephthalate and ethylene glycol
in presence of a weak base, (calcium
acetate). Methanol is eliminated during
condensation.
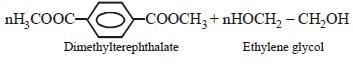
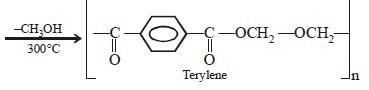
A condensation polymer among the following is:
- a) Teflon
- b) Dacron
- c) Polystyrene
- d) PVC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A condensation polymer among the following is:
a)
Teflonb)
Dacronc)
Polystyrened)
PVC|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Decron is a condensation polymer. It is formed by the condensation of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
Nylon is an example of : [NEET 2013]- a)Polysaccharide
- b)Polyamide
- c)Polythene
- d)Polyester
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nylon is an example of : [NEET 2013]
a)
Polysaccharide
b)
Polyamide
c)
Polythene
d)
Polyester

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Nylon is a synthetic polyamide polymer.
Polyacrylonitrile is an example of:- a)Addition polymer
- b)Condensation polymer
- c)Natural polymer
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Polyacrylonitrile is an example of:
a)
Addition polymer
b)
Condensation polymer
c)
Natural polymer
d)
None of the above
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Polyacrylonitrile is an example of addition polymer. The addition polymerisation of acrylonitrile in presence of a peroxide catalyst leads to the formation of polyacrylonitrile.
The polymers which are prepared in the laboratories are called:- a)Branched Polymer
- b)Homopolymer
- c)Co-polymer
- d)Synthetic Polymer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The polymers which are prepared in the laboratories are called:
a)
Branched Polymer
b)
Homopolymer
c)
Co-polymer
d)
Synthetic Polymer
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Synthetic Polymers. Polymers are large molecules composed of repeated chemical units. The smallest repeating unit is called a mer. The term polymer is derived from the Greek words poly and mers meaning "many parts."
A synthetic polymer which resembles natural rubber is:- a)Nylon
- b)Glyptal
- c)Neoprene
- d)Chloroprene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A synthetic polymer which resembles natural rubber is:
a)
Nylon
b)
Glyptal
c)
Neoprene
d)
Chloroprene

|
Innocy answered |
Neoprene.... it's monomer is isopropene.... given in ncert
PAN is prepared from:- a)Vinylacetylene
- b)Butadiene and Styrene
- c)Styrene
- d)Acrylonitrile
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PAN is prepared from:
a)
Vinylacetylene
b)
Butadiene and Styrene
c)
Styrene
d)
Acrylonitrile
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Polyacrylonitrile. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), a synthetic resin prepared by the polymerization of acrylonitrile.Most polyacrylonitrile is produced as acrylic and modacrylic fibre, a common substitute for wool in clothing and home furnishings.
The weakest inter-particle forces are present in:- a)Thermosetting polymers
- b)Fibres
- c)Thermoplastic polymers
- d)Elastomers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The weakest inter-particle forces are present in:
a)
Thermosetting polymers
b)
Fibres
c)
Thermoplastic polymers
d)
Elastomers
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The weakest interparticle forces are present in thermoplastic polymers hence they possess low softening temperature.
Condensation polymerisation of ethylene glycol and terepthalic acid gives:- a)Glyptal
- b)Buna-S
- c)PVC
- d)Terylene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Condensation polymerisation of ethylene glycol and terepthalic acid gives:
a)
Glyptal
b)
Buna-S
c)
PVC
d)
Terylene
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is option D
Terylene or Dacron is obtained by the condensation polymerisation of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
It is an example of polyester. The balanced equation is as shown.
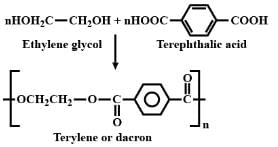
Terylene or Dacron is obtained by the condensation polymerisation of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
It is an example of polyester. The balanced equation is as shown.

Which one of the following statement is not true? [2008]- a)In vulcanization the formation of sulphurbridges between different chains makerubber harder and stronger.
- b)Natural rubber has the trans -configurationat every double bond
- c)Buna-S is a copolymer of butadiene andstyrene
- d)Natural rubber is a 1, 4 - polymer of isoprene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is not true? [2008]
a)
In vulcanization the formation of sulphurbridges between different chains makerubber harder and stronger.
b)
Natural rubber has the trans -configurationat every double bond
c)
Buna-S is a copolymer of butadiene andstyrene
d)
Natural rubber is a 1, 4 - polymer of isoprene

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
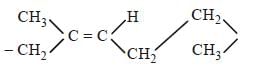
All statements except (b) are correct
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Bakelite is used for making
- A:
laminated sheets
- B:
electrical switches
- C:
water pipes.
- D:
paints
The answer is b.
Bakelite is used for making
laminated sheets
electrical switches
water pipes.
paints

|
Anjana Sen answered |
Bakelite is used in making electrical switches.
Isoprene is the monomer of:- a)Bakelite
- b)PVC
- c)Teflon
- d)Natural rubber
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Isoprene is the monomer of:
a)
Bakelite
b)
PVC
c)
Teflon
d)
Natural rubber
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Natural rubber is from the monomer isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene). Since isoprene has two double bonds, it still retains one of them after the polymerization reaction. Natural rubber has the cis configuration for the methyl groups.
Polymers that are found in nature are called:- a)Homopolymers
- b)Natural polymers
- c)Addition polymer
- d)Synthetic polymer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Polymers that are found in nature are called:
a)
Homopolymers
b)
Natural polymers
c)
Addition polymer
d)
Synthetic polymer
|
|
Sankar Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
Natural polymers are the polymers that are found in nature. They are also known as biopolymers. These are macromolecules that are formed by the combination of same or different monomers. Natural polymers are widely found in living organisms and are responsible for various biological processes. Some examples of natural polymers are proteins, nucleic acids, cellulose, chitin, and natural rubber. Here are some characteristics of natural polymers:
- Natural polymers are biodegradable and environment-friendly.
- They have a complex structure and are often used for specific functions.
- Natural polymers have a wide range of properties, such as strength, elasticity, and flexibility.
- They are often used in medical applications.
Examples of Natural Polymers:
- Proteins: Proteins are long chains of amino acids that are found in living organisms. They are responsible for various biological processes such as the formation of enzymes, hormones, and antibodies.
- Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. They are responsible for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
- Cellulose: Cellulose is a polymer that is found in the cell walls of plants. It provides structural support to the plant cell.
- Chitin: Chitin is a polymer that is found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans. It provides structural support and protection to these organisms.
- Natural Rubber: Natural rubber is a polymer that is obtained from the sap of the rubber tree. It is used in the production of various rubber products.
Advantages of Natural Polymers:
- Biodegradable and environmentally friendly
- Ability to undergo complex chemical reactions
- Non-toxic and safe for medical applications
- High strength and durability
Disadvantages of Natural Polymers:
- Limited availability and high cost of production
- Variable properties due to natural variability
- Vulnerable to degradation by microorganisms and enzymes
- Limited ability to be modified for specific applications
Natural polymers are the polymers that are found in nature. They are also known as biopolymers. These are macromolecules that are formed by the combination of same or different monomers. Natural polymers are widely found in living organisms and are responsible for various biological processes. Some examples of natural polymers are proteins, nucleic acids, cellulose, chitin, and natural rubber. Here are some characteristics of natural polymers:
- Natural polymers are biodegradable and environment-friendly.
- They have a complex structure and are often used for specific functions.
- Natural polymers have a wide range of properties, such as strength, elasticity, and flexibility.
- They are often used in medical applications.
Examples of Natural Polymers:
- Proteins: Proteins are long chains of amino acids that are found in living organisms. They are responsible for various biological processes such as the formation of enzymes, hormones, and antibodies.
- Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. They are responsible for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
- Cellulose: Cellulose is a polymer that is found in the cell walls of plants. It provides structural support to the plant cell.
- Chitin: Chitin is a polymer that is found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans. It provides structural support and protection to these organisms.
- Natural Rubber: Natural rubber is a polymer that is obtained from the sap of the rubber tree. It is used in the production of various rubber products.
Advantages of Natural Polymers:
- Biodegradable and environmentally friendly
- Ability to undergo complex chemical reactions
- Non-toxic and safe for medical applications
- High strength and durability
Disadvantages of Natural Polymers:
- Limited availability and high cost of production
- Variable properties due to natural variability
- Vulnerable to degradation by microorganisms and enzymes
- Limited ability to be modified for specific applications
Cotton is an example of:- a)Synthetic polymer
- b)Natural fibre
- c)Condensation polymerization
- d)Addition polymer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cotton is an example of:
a)
Synthetic polymer
b)
Natural fibre
c)
Condensation polymerization
d)
Addition polymer
|
|
Subhankar Choudhary answered |
Answer:
Natural Fibre:
Cotton is a natural fibre that is obtained from the cotton plant's seed pod. It is composed of cellulose, which is a naturally occurring polymer. Natural fibres are obtained from plants and animals and do not require any chemical or industrial processing.
Synthetic Polymer:
Synthetic polymers are man-made polymers that are produced by chemical methods. These polymers are not found in nature and are made from petrochemicals. Examples of synthetic polymers include nylon, polyester, and PVC.
Condensation Polymerization:
Condensation polymerization is a process in which small molecules combine to form larger molecules, releasing a byproduct in the process. This process is used to produce many natural and synthetic polymers. Examples of condensation polymers include nylon and polyester.
Addition Polymer:
Addition polymerization is a process in which monomers combine to form a polymer without the release of any byproducts. This process is used to produce many synthetic polymers. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene and polypropylene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' as cotton is a natural fibre obtained from the cotton plant's seed pod.
Natural Fibre:
Cotton is a natural fibre that is obtained from the cotton plant's seed pod. It is composed of cellulose, which is a naturally occurring polymer. Natural fibres are obtained from plants and animals and do not require any chemical or industrial processing.
Synthetic Polymer:
Synthetic polymers are man-made polymers that are produced by chemical methods. These polymers are not found in nature and are made from petrochemicals. Examples of synthetic polymers include nylon, polyester, and PVC.
Condensation Polymerization:
Condensation polymerization is a process in which small molecules combine to form larger molecules, releasing a byproduct in the process. This process is used to produce many natural and synthetic polymers. Examples of condensation polymers include nylon and polyester.
Addition Polymer:
Addition polymerization is a process in which monomers combine to form a polymer without the release of any byproducts. This process is used to produce many synthetic polymers. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene and polypropylene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' as cotton is a natural fibre obtained from the cotton plant's seed pod.
In elastomer, intermolecular forces are [1995]- a)strong
- b)weak
- c)nil
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In elastomer, intermolecular forces are [1995]
a)
strong
b)
weak
c)
nil
d)
none of these

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Elastomers are the polymers having very
weak intermolecular forces of attraction
between the polymer chain. The weak forces
permit the polymer to be streched.
weak intermolecular forces of attraction
between the polymer chain. The weak forces
permit the polymer to be streched.
Which of the following statements is not true about low density polythene?- a)Tough
- b)Hard
- c)Poor conductor of electricity
- d)Highly branched structure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true about low density polythene?
a)
Tough
b)
Hard
c)
Poor conductor of electricity
d)
Highly branched structure
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Low density polythene : It is obtained by the polymerisation of ethene under high presure of 1000-2000 atm. at a temp. of 350 K to 570 K in the pressure of traces of dioxygen or a peroxide initiator (cont). Low density polythene is chemically inert and poor conductor of electricity. It is used for manufacture squeeze bottles. toys and flexible pipes.
Which one of the following is not a condensation polymer?- a)Dacron
- b)Neoprene
- c)Melamine
- d)Glyptal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a condensation polymer?
a)
Dacron
b)
Neoprene
c)
Melamine
d)
Glyptal

|
Sonali answered |
Condensation polymer is formed by the condensation reaction.where molecules join together and loss some small molecules as by-products such as water.so , among these four option neoprene does not formed through condensation process.
Which of the following statements is false?[2012]- a)Artificial silk is derived from cellulose.
- b)Nylon-66 is an example of elastomer.
- c)The repeat unit in natural rubber is isoprene.
- d)Both starch and cellulose are polymers ofglucose.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false?[2012]
a)
Artificial silk is derived from cellulose.
b)
Nylon-66 is an example of elastomer.
c)
The repeat unit in natural rubber is isoprene.
d)
Both starch and cellulose are polymers ofglucose.

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Nylon-66 is an example of first synthetic
fibres produced from the simple molecules.
It is prepared by condensation polymerisation
of adipic acid and haxamethylene
diamine.
fibres produced from the simple molecules.
It is prepared by condensation polymerisation
of adipic acid and haxamethylene
diamine.
Cellulose acetate is a:- a)Plasticiser
- b)Natural polymer
- c)Semi-synthetic polymer
- d)Synthetic polymer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellulose acetate is a:
a)
Plasticiser
b)
Natural polymer
c)
Semi-synthetic polymer
d)
Synthetic polymer
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
A semi synthetic polymer is a polymer made by chemically treating a natural polymer. ... For example, cellulose acetate is a thermoplastic polymer that is produced from cellulose, a natural polymer, rather than through polymerization reaction of a monomer.
Bakelite is prepared by the reaction between [1995]- a)urea and formaldehyde
- b)ethylene glycol
- c)phenol and formaldehyde
- d)tetramethylene glycol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bakelite is prepared by the reaction between [1995]
a)
urea and formaldehyde
b)
ethylene glycol
c)
phenol and formaldehyde
d)
tetramethylene glycol
|
|
Sounak Mukherjee answered |
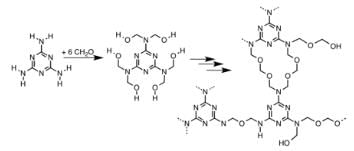
Bakelite is a type of thermosetting plastic which is prepared by the reaction between Phenol and Formaldehyde.
Explanation:
- Bakelite was the first synthetic plastic which was invented by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in 1907.
- It is formed by the reaction between Phenol (C6H5OH) and Formaldehyde (HCHO) in the presence of a catalyst like hydrochloric acid or zinc chloride.
- This reaction is called Condensation Polymerization or Step-Growth Polymerization as it involves the combination of smaller molecules to form a larger molecule with the elimination of a small molecule like water or methanol.
- The reaction proceeds as follows:
Phenol + Formaldehyde → Bakelite + Water
- The Bakelite formed is a hard and durable plastic which can withstand high temperatures, pressures, and electrical insulations.
- It is widely used for making electrical switches, handles, knobs, and other household items.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is C- Phenol and Formaldehyde.
Explanation:
- Bakelite was the first synthetic plastic which was invented by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in 1907.
- It is formed by the reaction between Phenol (C6H5OH) and Formaldehyde (HCHO) in the presence of a catalyst like hydrochloric acid or zinc chloride.
- This reaction is called Condensation Polymerization or Step-Growth Polymerization as it involves the combination of smaller molecules to form a larger molecule with the elimination of a small molecule like water or methanol.
- The reaction proceeds as follows:
Phenol + Formaldehyde → Bakelite + Water
- The Bakelite formed is a hard and durable plastic which can withstand high temperatures, pressures, and electrical insulations.
- It is widely used for making electrical switches, handles, knobs, and other household items.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is C- Phenol and Formaldehyde.
Vulcanisation is used in processing of:- a)Rubber
- b)Polythene
- c)Bakelite
- d)Liquid fuels
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vulcanisation is used in processing of:
a)
Rubber
b)
Polythene
c)
Bakelite
d)
Liquid fuels
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The correct answer is option A
Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur, accelerator and activator at 140–160°C. The process involves the formation of cross-links between long rubber molecules so as to achieve improved elasticity, resilience, tensile strength, viscosity, hardness and weather resistance.
Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur, accelerator and activator at 140–160°C. The process involves the formation of cross-links between long rubber molecules so as to achieve improved elasticity, resilience, tensile strength, viscosity, hardness and weather resistance.
Which is the monomer of Neoprene in the following ? [NEET 2013]- a)
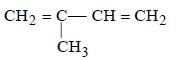
- b)
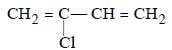
- c)CH2 = CH — C ≡ CH
- d)CH2 = CH — CH = CH2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the monomer of Neoprene in the following ? [NEET 2013]
a)
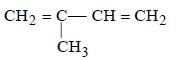
b)
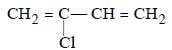
c)
CH2 = CH — C ≡ CH
d)
CH2 = CH — CH = CH2

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
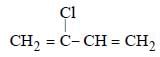 (chloroprene) is
(chloroprene) isthe monomer of neoprene.
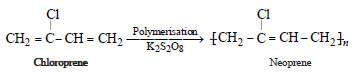
One of the statements below is not true for the classification of polymers can be classified on the basis of their- a)resistance to different agents
- b)mode of polymerisation
- c)structure of the polymers
- d)unique mechanical properties
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the statements below is not true for the classification of polymers can be classified on the basis of their
a)
resistance to different agents
b)
mode of polymerisation
c)
structure of the polymers
d)
unique mechanical properties
|
|
Snehal Iyer answered |
Classification of Polymers
Polymers are classified based on several factors, which are discussed below:
Mode of Polymerisation
Polymers can be classified based on their mode of polymerisation, which is the process of forming a polymer chain from monomers. The two types of polymerisation are:
- Addition polymerisation: In this process, monomers are added to each other to form a polymer chain. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene and polystyrene.
- Condensation polymerisation: In this process, monomers react with each other and eliminate a small molecule, such as water, to form a polymer chain. Examples of condensation polymers include nylon and polyester.
Structure of Polymers
Polymers can be classified based on their structure, which is the arrangement of monomer units in a polymer chain. The three types of polymer structures are:
- Linear polymers: In this structure, monomer units are arranged in a straight line. Examples of linear polymers include polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Branched polymers: In this structure, monomer units are arranged in a branched pattern. Examples of branched polymers include low-density polyethylene and amylopectin.
- Cross-linked polymers: In this structure, polymer chains are linked together to form a three-dimensional network. Examples of cross-linked polymers include vulcanized rubber and epoxy resins.
Unique Mechanical Properties
Polymers can also be classified based on their unique mechanical properties, such as:
- Elastomers: These polymers have the ability to return to their original shape after being stretched or deformed. Examples of elastomers include natural rubber and silicone rubber.
- Thermoplastics: These polymers can be melted and re-molded multiple times without losing their properties. Examples of thermoplastics include polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Thermosets: These polymers cannot be re-molded once they have been set. Examples of thermosets include epoxy resins and melamine formaldehyde.
Resistance to Different Agents
The statement that polymers can be classified based on their resistance to different agents is not true. While some polymers may exhibit better resistance to certain agents, such as acids or solvents, this is not a primary factor in their classification.
Polymers are classified based on several factors, which are discussed below:
Mode of Polymerisation
Polymers can be classified based on their mode of polymerisation, which is the process of forming a polymer chain from monomers. The two types of polymerisation are:
- Addition polymerisation: In this process, monomers are added to each other to form a polymer chain. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene and polystyrene.
- Condensation polymerisation: In this process, monomers react with each other and eliminate a small molecule, such as water, to form a polymer chain. Examples of condensation polymers include nylon and polyester.
Structure of Polymers
Polymers can be classified based on their structure, which is the arrangement of monomer units in a polymer chain. The three types of polymer structures are:
- Linear polymers: In this structure, monomer units are arranged in a straight line. Examples of linear polymers include polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Branched polymers: In this structure, monomer units are arranged in a branched pattern. Examples of branched polymers include low-density polyethylene and amylopectin.
- Cross-linked polymers: In this structure, polymer chains are linked together to form a three-dimensional network. Examples of cross-linked polymers include vulcanized rubber and epoxy resins.
Unique Mechanical Properties
Polymers can also be classified based on their unique mechanical properties, such as:
- Elastomers: These polymers have the ability to return to their original shape after being stretched or deformed. Examples of elastomers include natural rubber and silicone rubber.
- Thermoplastics: These polymers can be melted and re-molded multiple times without losing their properties. Examples of thermoplastics include polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Thermosets: These polymers cannot be re-molded once they have been set. Examples of thermosets include epoxy resins and melamine formaldehyde.
Resistance to Different Agents
The statement that polymers can be classified based on their resistance to different agents is not true. While some polymers may exhibit better resistance to certain agents, such as acids or solvents, this is not a primary factor in their classification.
Polymers having ester linkage are called:- a)Homopolymers
- b)Addition polymer
- c)Polyesters
- d)Synthetic rubber
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Polymers having ester linkage are called:
a)
Homopolymers
b)
Addition polymer
c)
Polyesters
d)
Synthetic rubber

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
A water molecule is removed as the ester linkage is formed. Because the monomers above are all joined by ester linkages, the polymer chain is a polyester.
Polythene is not one of the following?- a)Branched chain polymers
- b)Semi – synthetic polymer
- c)Linear polymer
- d)Synthetic polymer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Polythene is not one of the following?
a)
Branched chain polymers
b)
Semi – synthetic polymer
c)
Linear polymer
d)
Synthetic polymer

|
Pragati Choudhury answered |
Polymer is not semi synthetic. It is synthetic.
Which one of the following is used to make "nonstick"cook-wares ? [1997]- a)Polystyrene
- b)Polyethylene terephthalate
- c)Polytetrafluoroethylene
- d)Polyvinyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is used to make "nonstick"cook-wares ? [1997]
a)
Polystyrene
b)
Polyethylene terephthalate
c)
Polytetrafluoroethylene
d)
Polyvinyl chloride

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
We know that polytetrafluoroethylene or
teflon is a tough material, resistance to heat
and bad conductor of electricity. Therefore
it is used for coating the cookware to make
them non-sticky.
teflon is a tough material, resistance to heat
and bad conductor of electricity. Therefore
it is used for coating the cookware to make
them non-sticky.
One of the following rubbers is used in making oil seals, tank lining, etc.- a)Buna – S
- b)Neoprene
- c)Buna – N
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following rubbers is used in making oil seals, tank lining, etc.
a)
Buna – S
b)
Neoprene
c)
Buna – N
d)
None of these

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
Buna N is used in making oil seals , tank linings.
Painting material among the following is- a)Glyptal
- b)Polypropene
- c)Polyvinyl chloride
- d)Polystyrene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Painting material among the following is
a)
Glyptal
b)
Polypropene
c)
Polyvinyl chloride
d)
Polystyrene
|
|
Puja Gupta answered |
Painting Material: Glyptal
Glyptal is a type of paint material that is commonly used for various painting applications. It is a synthetic resin that is known for its durability and resistance to chemicals. Glyptal is widely used in industrial settings, particularly for coating metal surfaces to protect them from corrosion and wear.
Properties of Glyptal:
1. Chemical Resistance: Glyptal exhibits excellent resistance to various chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids. This property makes it suitable for applications where the painted surface may come into contact with corrosive substances.
2. Adhesion: Glyptal forms a strong bond with the painted surface, ensuring good adhesion. This property allows it to provide long-lasting protection to the painted material.
3. Durability: Glyptal is known for its durability and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. It can resist extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
4. Electrical Insulation: Glyptal has excellent electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for coating electrical components and insulating wire connections. It helps prevent electrical leakage and improves the overall performance and safety of the painted objects.
Applications of Glyptal:
1. Industrial Coatings: Glyptal is commonly used in industries for coating metal surfaces, such as machinery, equipment, and structures. It provides a protective layer that prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of the painted materials.
2. Electrical Industry: Glyptal is widely used in the electrical industry for coating electrical components, such as transformers, capacitors, and motors. Its electrical insulation properties help prevent electrical leakage and ensure safe operation.
3. Automotive Industry: Glyptal is used in the automotive industry for painting engine components, such as cylinder heads and engine blocks. It provides protection against heat, oil, and other chemicals commonly found in engines.
4. Marine Industry: Glyptal is also used in the marine industry for coating metal surfaces exposed to saltwater and harsh marine environments. It helps prevent corrosion and extends the life of marine equipment and structures.
In conclusion, Glyptal is a versatile painting material that offers excellent chemical resistance, adhesion, durability, and electrical insulation properties. It is commonly used in industries, electrical applications, automotive components, and marine equipment.
Glyptal is a type of paint material that is commonly used for various painting applications. It is a synthetic resin that is known for its durability and resistance to chemicals. Glyptal is widely used in industrial settings, particularly for coating metal surfaces to protect them from corrosion and wear.
Properties of Glyptal:
1. Chemical Resistance: Glyptal exhibits excellent resistance to various chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids. This property makes it suitable for applications where the painted surface may come into contact with corrosive substances.
2. Adhesion: Glyptal forms a strong bond with the painted surface, ensuring good adhesion. This property allows it to provide long-lasting protection to the painted material.
3. Durability: Glyptal is known for its durability and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. It can resist extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
4. Electrical Insulation: Glyptal has excellent electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for coating electrical components and insulating wire connections. It helps prevent electrical leakage and improves the overall performance and safety of the painted objects.
Applications of Glyptal:
1. Industrial Coatings: Glyptal is commonly used in industries for coating metal surfaces, such as machinery, equipment, and structures. It provides a protective layer that prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of the painted materials.
2. Electrical Industry: Glyptal is widely used in the electrical industry for coating electrical components, such as transformers, capacitors, and motors. Its electrical insulation properties help prevent electrical leakage and ensure safe operation.
3. Automotive Industry: Glyptal is used in the automotive industry for painting engine components, such as cylinder heads and engine blocks. It provides protection against heat, oil, and other chemicals commonly found in engines.
4. Marine Industry: Glyptal is also used in the marine industry for coating metal surfaces exposed to saltwater and harsh marine environments. It helps prevent corrosion and extends the life of marine equipment and structures.
In conclusion, Glyptal is a versatile painting material that offers excellent chemical resistance, adhesion, durability, and electrical insulation properties. It is commonly used in industries, electrical applications, automotive components, and marine equipment.
Buna-S is a copolymer of:- a)Butadiene and styrene
- b)Adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine
- c)Urea and styrene
- d)Chloroprene and Butadiene
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Buna-S is a copolymer of:
a)
Butadiene and styrene
b)
Adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine
c)
Urea and styrene
d)
Chloroprene and Butadiene

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) describe families of synthetic rubbers derived from styrene and butadiene (the version developed by Goodyear is called Neolite). These materials have good abrasion resistance and good aging stability when protected by additives.
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?- a)Tertiary butyl chloride
- b)Isohexane
- c)Neohexane
- d)Neopentane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?
a)
Tertiary butyl chloride
b)
Isohexane
c)
Neohexane
d)
Neopentane

|
Nisha Banerjee answered |
Since we are getting monosubstituted alkyl halide so it is neopentane.
The monomer of the polymer; [2005]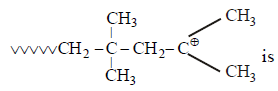
- a)
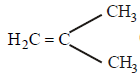
- b)CH3CH=CHCH3
- c)CH3CH = CH2
- d)(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The monomer of the polymer; [2005]
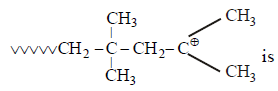
a)
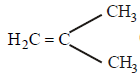
b)
CH3CH=CHCH3
c)
CH3CH = CH2
d)
(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2

|
Mahi Shah answered |
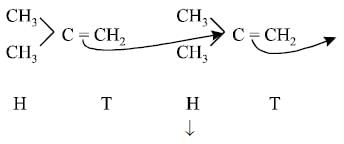
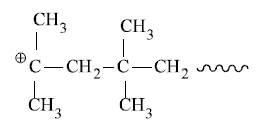
Addition of monomers follows isoprene rule
Nylon – 2 – Nylon – 6 is- a)biodegradable polymer
- b)copolymer
- c)homopolymer
- d)condensation polymer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nylon – 2 – Nylon – 6 is
a)
biodegradable polymer
b)
copolymer
c)
homopolymer
d)
condensation polymer

|
Rashi Bose answered |
They both are biodegradable polymer.
For macromolecules to form, one more of the following criteria are essential- a)by joining of repeating structural units on a large scale
- b)the molecules in C are linked to each other by covalent bonds
- c)The repeating structural units are derived from some simple and reactive molecules
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For macromolecules to form, one more of the following criteria are essential
a)
by joining of repeating structural units on a large scale
b)
the molecules in C are linked to each other by covalent bonds
c)
The repeating structural units are derived from some simple and reactive molecules
d)
All of these
|
|
Anuj Unni answered |
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of repeating units known as monomers. They are essential to life as they form the building blocks of all living organisms. For macromolecules to form, one or more of the following criteria are essential:
By Joining of Repeating Structural Units on a Large Scale:
- Macromolecules are formed by joining repeating structural units on a large scale. This process is known as polymerization.
- In polymerization, monomers are linked together through covalent bonds to form a polymer.
- This process can occur through different types of reactions, such as condensation polymerization and addition polymerization.
The Molecules in C are Linked to Each Other by Covalent Bonds:
- Covalent bonds are essential for macromolecules to form.
- Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that involve the sharing of electrons.
- Macromolecules are formed when monomers are linked together by covalent bonds.
The Repeating Structural Units are Derived from Some Simple and Reactive Molecules:
- Macromolecules are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers.
- Monomers are small molecules that can react together to form larger molecules.
- The repeating units in macromolecules are derived from these monomers.
All of These:
- All of the above criteria are essential for macromolecules to form.
- Macromolecules are formed by joining repeating structural units on a large scale through covalent bonds.
- The repeating units are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers.
- Without any of these criteria, macromolecules would not exist.
In conclusion, macromolecules are essential to life, and their formation requires the joining of repeating structural units on a large scale through covalent bonds. The repeating units are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers. All of these criteria are essential for macromolecules to form.
By Joining of Repeating Structural Units on a Large Scale:
- Macromolecules are formed by joining repeating structural units on a large scale. This process is known as polymerization.
- In polymerization, monomers are linked together through covalent bonds to form a polymer.
- This process can occur through different types of reactions, such as condensation polymerization and addition polymerization.
The Molecules in C are Linked to Each Other by Covalent Bonds:
- Covalent bonds are essential for macromolecules to form.
- Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that involve the sharing of electrons.
- Macromolecules are formed when monomers are linked together by covalent bonds.
The Repeating Structural Units are Derived from Some Simple and Reactive Molecules:
- Macromolecules are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers.
- Monomers are small molecules that can react together to form larger molecules.
- The repeating units in macromolecules are derived from these monomers.
All of These:
- All of the above criteria are essential for macromolecules to form.
- Macromolecules are formed by joining repeating structural units on a large scale through covalent bonds.
- The repeating units are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers.
- Without any of these criteria, macromolecules would not exist.
In conclusion, macromolecules are essential to life, and their formation requires the joining of repeating structural units on a large scale through covalent bonds. The repeating units are derived from simple and reactive molecules known as monomers. All of these criteria are essential for macromolecules to form.
Rubber tree is found in- a)India
- b)Russia
- c)Mauritius
- d)Japan
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rubber tree is found in
a)
India
b)
Russia
c)
Mauritius
d)
Japan

|
Chirag Banerjee answered |
Rubber tree is found in India.
Formation of Buna – S, involves polymerization of- a)Styrene
- b)Polypropylene
- c)1, 3 – Butadiene and Styrene
- d)1, 3 – Butadiene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of Buna – S, involves polymerization of
a)
Styrene
b)
Polypropylene
c)
1, 3 – Butadiene and Styrene
d)
1, 3 – Butadiene

|
Om Kumar answered |
Buna S involves the polymerization of 1, 3 butadiene and styrene.
Which polymers occur naturally in nature- a)Proteins and buno
- b)Starch and nylon
- c)Proteins and PVC
- d)Starch and cellulose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which polymers occur naturally in nature
a)
Proteins and buno
b)
Starch and nylon
c)
Proteins and PVC
d)
Starch and cellulose
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
Starch and cellulose are two very similar polymers. In fact, they are both made from the same monomer, glucose, and have the same glucose-based repeat units.Examples of synthetic polymers include nylon, polyethylene, polyester, Teflon, and epoxy. Natural polymers occur in nature and can be extracted. They are often water-based. Examples of naturally occurring polymers are silk, wool, DNA, cellulose and proteins.
Chapter doubts & questions for Polymers - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Polymers - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup