All questions of Motion for Class 9 Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The displacement covered by a seconds’ hand of radius r in a clock after one revolution is:- A:360 degree
- B:zero
- C:3r
- D:2r
The answer is b.

|
Piyush Srivastava answered |
What is the average velocity of a car that moved 60 km in 3 hours?
- a)60 km/h
- b)20 km/h
- c)30 km/h
- d)10 km/h
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Kamakshi Singh answered |
To calculate the average velocity of a car that moved 60 km in 3 hours, we need to use the formula:
Average Velocity = Total Distance/Total Time
Substituting the given values in the formula, we get:
Average Velocity = 60 km/3 hours
Simplifying this expression, we get:
Average Velocity = 20 km/h
Therefore, the average velocity of the car is 20 km/h.
Explanation
The average velocity of an object is the total distance covered by the object divided by the total time taken to cover that distance. In this case, the car covered a distance of 60 km in a time of 3 hours. Dividing the total distance by the total time gives us the average velocity of the car, which is 20 km/h.
Conclusion
The average velocity of a car that moved 60 km in 3 hours is 20 km/h. It is important to remember that velocity is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. In this case, since no direction is given, we assume that the car travelled in a straight line.
The SI unit for speed is- a)km/hour
- b)m/s
- c)cm/min
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shubham Unni answered |
The SI unit for speed is meter per second (m/s).
Explanation
Speed is defined as the distance traveled by an object in a given time. It is a scalar quantity and is measured in units of distance per time. The SI unit of distance is meter (m) and the SI unit of time is second (s). Therefore, the SI unit of speed is meter per second (m/s).
For example, if a car travels a distance of 100 meters in 10 seconds, its speed can be calculated as:
Speed = Distance/Time
= 100 meters/10 seconds
= 10 meters per second (m/s)
Therefore, the speed of the car is 10 m/s.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SI unit for speed is meter per second (m/s). It is important to use the correct units when measuring speed to ensure consistency and accuracy in calculations.
The SI unit for speed is- a)km/hour
- b)m/s
- c)cm/min
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prachi Rathore answered |
1 km/ h = ________ m/s
- a)3/50
- b)18/5
- c)50/3
- d)5/18
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Amrutha Mukherjee answered |
To convert km/h to m/s, we need to use the following conversion factor:
1 km/h = 1000 m/3600 s = 5/18 m/s
So, to convert 1 km/h to m/s, we simply multiply it by 5/18.
Solution
Given, 1 km/h = ?
We need to convert it to m/s.
1 km/h × 5/18 = 5/18 m/s
Therefore, the correct option is (d) 5/18.
Which of the following is a correct measure of velocity?
- a)30 s
- b)30 m/s
- c)30 South
- d)30 m/s, South
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
-
30 s: This is a measure of time, not velocity.
-
30 m/s: This is a measure of speed, not velocity, because it does not include a direction.
-
30 South: This describes a direction but lacks the magnitude (speed), so it is not a complete measure of velocity.
-
30 m/s, South: This provides both magnitude (30 m/s) and direction (South), making it a complete measure of velocity.
A car moved 60 km East and 90 km West. What is the distance?- a)30 km
- b)60 km
- c)90 km
- d)150 km
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Tanvi Chauhan answered |
To find the distance covered by the car, we need to calculate the net displacement.
Net displacement = Total distance covered in the East direction - Total distance covered in the West direction
Total distance covered in the East direction = 60 km
Total distance covered in the West direction = 90 km
Net displacement = 60 km - 90 km = -30 km (negative sign indicates that car moved in the opposite direction)
Distance covered by the car = Magnitude of net displacement = | -30 km | = 30 km
Therefore, the correct option is (a) 30 km.
How far will a car travel in 25 min at 12 m/s?
- a)24 km
- b)10 km
- c)18 km
- d)14 km
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Molik answered |
Distance is a __________ quantity- a)vector
- b)name of these
- c)can’t say
- d)scalar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Jatin Basu answered |
A body is said to be in non-uniform motion if it travels- a)Equal distance in unequal interval of time
- b)Equal distance in equal interval of time
- c)Unequal distance in unequal interval of time
- d)Unequal distance in equal interval of time
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:An ant moves from one corner of a hall to the diagonally opposite corner. If the dimension of the hall are 8 m x 6 m, the displacement of the ant is :
- A:
10 m
- B:
14 m
- C:
28m
- D:
2 m
The answer is a.
An ant moves from one corner of a hall to the diagonally opposite corner. If the dimension of the hall are 8 m x 6 m, the displacement of the ant is :
10 m
14 m
28m
2 m
|
|
Nilanjan Ghosh answered |
Dimensions of hall = 8 m x 6 m
To find:
Displacement of the ant
Solution:
We can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the displacement of the ant. According to the theorem, in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Let us consider the hall as a rectangle ABCD, where AB = 8 m and BC = 6 m. The ant moves from A to C, which is the diagonally opposite corner.
We can draw a right-angled triangle ACD, where AC is the hypotenuse, AD is one side (which is equal to AB), and CD is the other side (which is equal to BC).
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we have:
AC^2 = AD^2 + CD^2
Substituting the values, we get:
AC^2 = 8^2 + 6^2
AC^2 = 64 + 36
AC^2 = 100
AC = √100
AC = 10 m
Therefore, the displacement of the ant is 10 m.
Answer:
a) 10 m
Direction: The distance moved by a student at different intervals of time, while walking to school, is given in the table below.A distance time graph for the motion of the student is also shown. Study the table and the graph and choose correct options to answer any four questions given below:
 Q. What will be the speed if the body travels a distance of 15 metres in 10 seconds?
Q. What will be the speed if the body travels a distance of 15 metres in 10 seconds?- a)0.5 m/s
- b)1.5 m/s
- c)5 m/s
- d)10 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?


|
|
Piyush answered |
=15/10 = 1.5 m/s
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The speed at any instant of time is known as
- A:
velocity
- B:
given speed
- C:
average speed
- D:
instantaneous speed
The answer is d.
The speed at any instant of time is known as
velocity
given speed
average speed
instantaneous speed

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
On a velocity-time graph, a horizontal straight line corresponds to motion at- a)constant velocity
- b)zero velocity
- c)increasing velocity
- d)decreasing velocity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
An external influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest or uniform motion of body or its dimensions is called:- a)momentum
- b)force
- c)moment of force
- d)pressure
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
If a moving body comes to rest, then its acceleration is______.
- a)Positive
- b)Both of these depending upon the initial velocity
- c)Constant
- d)Negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Karthik Namboothiri answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:An athlete uniformly increases his speed from rest at the rate of 1 m/s2. The time taken to complete 200 m race is:
- A:
10 s
- B:
14 s
- C:
5 s
- D:
20 s
The answer is d.
An athlete uniformly increases his speed from rest at the rate of 1 m/s2. The time taken to complete 200 m race is:
10 s
14 s
5 s
20 s

|
Ashish Saha answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:An object travels 20 m in 5 sec and then another 40 m in 5 sec. What is the average speed of the object?
- A:
6 m/s
- B:
2 m/s
- C:
12 m/s
- D:
0 m/s
The answer is a.
An object travels 20 m in 5 sec and then another 40 m in 5 sec. What is the average speed of the object?
6 m/s
2 m/s
12 m/s
0 m/s

|
Learning Education answered |
Choose the correct option:- a)distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector , acceleration is a vector.
- b)distance is a vector, velocity is a scalar, acceleration is a vector.
- c)distance is a vector, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector.
- d)distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a scalar.
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
- Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion.
- Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity.
- Velocity is a vector quantity that refers to the speed of an object in a particular direction.
A boy throws a ball up and catches it when the ball falls back. In which part of the motion the ball is accelerating?- a)During downward motion
- b)When the ball comes to rest
- c)During upward motion
- d)When the boy catches the ball
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- When the ball moves upward, the force of gravitation is acting in the opposite direction of the ball that is why in that case acceleration is negative or in other words deceleration takes place.
- But when the ball is moving downwards the force of gravitation is in the same direction of the motion of the ball thus acceleration takes place in this case.
The ratio of C.G.S. to M.K.S. unit of acceleration is:- a)1:10
- b)1:1
- c)1:100
- d)10:1
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:If a person walked at 2 m/s for 12 s he/she would travel a distance of
- A:
24 m
- B:
6 m
- C:
4 m
- D:
none of the answers
The answer is a.
If a person walked at 2 m/s for 12 s he/she would travel a distance of
24 m
6 m
4 m
none of the answers

|
Piyush Srivastava answered |
Name the instrument used to measure instantaneous speed of a vehicle- a)multimeter
- b)ammeter
- c)speedometer
- d)accelerator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The area under the speed-time graph gives the ________.- a)velocity
- b)distance
- c)acceleration
- d)time
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
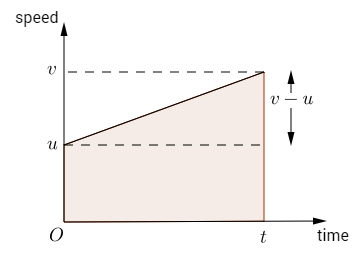
- When calculating the area under a speed-time graph, you are essentially finding the total distance traveled by an object over a certain period of time.
- This is because the area under a speed-time graph represents the total distance covered by an object as it moves at varying speeds.
- By finding the area under the curve on a speed-time graph, you can determine the total distance traveled by the object during that time interval.
A person sitting in the truck projected a ball vertically upwards. The ball- a)falls by the side of car
- b)falls back in his hand
- c)falls in front of the car.
- d)falls outside the car
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
180° plane angle is equal to- a)π/2 radian
- b)π radian
- c)2π radian
- d)none of these
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Find the average speed of a bicycle if it completes two round of a circular track of radius 140m twice in 5min 52 sec.- a)10m/s
- b)5m/s
- c)2m/s
- d)4m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
circumfarance
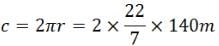
Time taken to cover the distance = t = 5 min 52 sec = 352 sec
Since it complete 2 rounds, therefor distance it travels is 2 times of circumference.
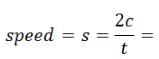
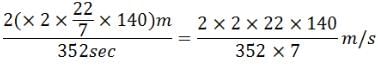
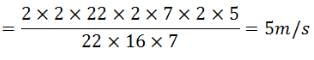
If car A is at 40 km/h and car B is at 10 km/h in the opposite direction, what is the velocity of the car A relative to the car B?
- a)40 km/h
- b)50 km/h.
- c)10 km/h
- d)30 km/h
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Hiral Datta answered |
In a distance-time graph, if the line is horizontal, then the object is:- a)Accelerating
- b)Speeding up
- c)At rest
- d)Slowing down
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Destroyed answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A man is moving with 36 kmph. The time of reaction is 0.9 seconds. On seeing an obstacle in the path, he applies brakes and decelerates at 5 m/s2, the total distance covered before he stops is:- A:19 m
- B:17 m
- C:16 m
- D:18 m
The answer is a.
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A man leaves his house at 7:30 a.m. for a morning walk, and returns back at 8:15 a.m. after covering 3 km. Is displacement in this time is:- A:2 km
- B:Zero
- C:8 km
- D:4 km
The answer is b.
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
The S.I. unit of acceleration is:- a) ms2
- b)ms
- c)ms-2
- d)m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shambhavi Singh answered |
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of:- a)Distance
- b)Velocity
- c)Speed
- d)Displacement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:‘A body can be at rest and in motion at the same time’ the above statement is
- A:
false
- B:
true
- C:
partially true
- D:
Partially false.
The answer is A.
‘A body can be at rest and in motion at the same time’ the above statement is
false
true
partially true
Partially false.

|
Prachi Rathore answered |
Equations of motion can be used for a body having- a)uniform motion
- b)non-uniform motion
- c)uniform acceleration
- d)non-uniform acceleration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
To describe the motion of an object we first specify a- a)The acceleration of the body
- b)Reference point
- c)The speed
- d)The direction of motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pritam Sen answered |
The motion of an object can be described in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. When we talk about the motion of an object, we need to have a reference point or a frame of reference. This reference point is used to determine the position of the object and its changes over time.
What is a reference point?
A reference point is a fixed point or object that is used to describe the motion of other objects. It is a point of comparison that helps us understand the motion of an object in relation to something else. For example, if we are describing the motion of a car on a road, we can use a nearby tree or a milestone as a reference point.
Why is the reference point important?
The reference point is important because it provides a basis for comparison. It allows us to determine the position, speed, and direction of an object with respect to something else. Without a reference point, we cannot accurately describe the motion of an object.
How is the reference point used?
The reference point is used to determine the position of the object at a given time. The position of an object is defined as its location in space relative to the reference point. By comparing the object's position at different times, we can determine its displacement (change in position) and calculate its velocity.
Example:
Let's consider a scenario where a person is walking along a straight road. In this case, the reference point could be a lamppost located at the beginning of the road. As the person walks, we can describe their motion relative to the lamppost.
- If the person walks away from the lamppost, we can say that their motion is in the positive direction.
- If the person walks towards the lamppost, we can say that their motion is in the negative direction.
By specifying the reference point, we can accurately describe the motion of the person in terms of their position, speed, and direction relative to the lamppost.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when describing the motion of an object, it is important to specify the reference point. The reference point provides a basis for comparison and helps us determine the position, speed, and direction of the object. Without a reference point, it would be difficult to accurately describe the motion of an object.
The area enclosed by velocity-time graph and the time axis will be equal to the magnitude of- a)displacement
- b)speed
- c)acceleration
- d)distance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ishaan Chauhan answered |
Derivation:
Conclusion:
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Motion" are available for CBSE Class 9 Science and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 9 ScienceQ A body moves in a uniform circular motion- a)it is moving with constant velocity.
- b)its acceleration is zero
- c)the body has an acceleration
- d)none of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pranjal Gupta answered |
**Uniform Circular Motion:**
Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object in a circle at a constant speed. In this motion, the object moves along the circumference of the circle with a constant speed, but its velocity is continuously changing due to the change in direction.
**Centripetal Acceleration:**
In uniform circular motion, there is a force acting towards the center of the circle called the centripetal force. This force is responsible for continuously changing the direction of the object's velocity. As a result, the object experiences an acceleration towards the center of the circle, known as the centripetal acceleration.
**Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion:**
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. Even though the object's speed remains constant in uniform circular motion, its velocity is changing because the direction is constantly changing. Therefore, there is a change in velocity, and consequently, there is an acceleration.
**Direction of Acceleration:**
In uniform circular motion, the acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circle. This is because the centripetal force, which is responsible for the circular motion, acts towards the center. The acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity vector and points towards the center of the circle.
**Magnitude of Acceleration:**
The magnitude of the acceleration in uniform circular motion can be calculated using the formula:
a = v² / r
where a is the acceleration, v is the speed of the object, and r is the radius of the circle.
**Conclusion:**
Based on the above explanation, we can conclude that in uniform circular motion, the body has an acceleration. Therefore, option C is the correct answer. The acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle and its magnitude depends on the speed of the object and the radius of the circle.
The slope of the distance-time graph is:- a)Distance
- b)acceleration
- c)Speed
- d)Displacement
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
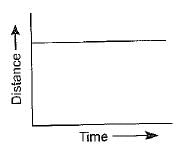
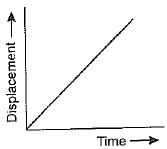
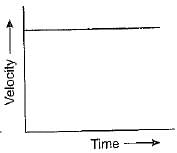
Which of the following graphs show that the body is at rest?- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
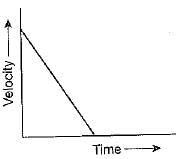
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?




|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
An ant moves from one corner of a hall to the diagonally opposite corner. If the dimension of the hall are 8 m x 6 m, the displacement of the ant is :- a)10 m
- b)14 m
- c)28m
- d)2 m
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Aniket Yadav answered |
Displacement = hypotenuse
Displacement = (82 +62)1/2 = 10 m
A body is moving with a velocity of 10m/s. If the motion is uniform, what will be the velocity after 10 second?- a)15m/s.
- b)5m/s
- c)10m/s
- d)20m/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
An ant moves from one corner of a hall to the diagonally opposite corner. If the dimension of the hall are 8 m x 6 m, the displacement of the ant is :- a)10 m
- b)14 m
- c)28m
- d)2 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Mainak Chawla answered |
To calculate the displacement of the ant, we need to use Pythagoras theorem.
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
So, the displacement of the ant will be the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle formed by the two sides of the hall.
Given,
Length of hall (l) = 8 m
Breadth of hall (b) = 6 m
Using Pythagoras theorem,
Displacement of ant = √(l² + b²)
= √(8² + 6²)
= √(64 + 36)
= √100
= 10 m
Therefore, the displacement of the ant is 10 m.
Hence, the correct option is (a) 10 m.
Odometer of automobiles records
- a)average speed
- b)instantaneous speed
- c)distance travelled
- d)acceleration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
- Odometer of automobiles records distance travelled.
- The primary function of an odometer in automobiles is to measure and display the total distance the vehicle has traveled since it was first put into use.
- This distance is usually displayed in kilometers or miles depending on the unit system used in the region.
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion - Physics for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Physics for Class 9
16 videos|69 docs|56 tests
|

Contact Support
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|












