All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Olympiad Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Natural Resources for Class 9 Exam
All the elements of life support system are- a)Inter connected
- b)Inter related
- c)Inter dependent
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All the elements of life support system are
a)
Inter connected
b)
Inter related
c)
Inter dependent
d)
All the above
|
|
Abhay Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
Life support system refers to the various components of the environment that support life on Earth. These components include air, water, soil, and sunlight. All these elements are interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated. Let's understand each of them in detail.
Interconnected:
All the elements of the life support system are interconnected. For example, air is required for breathing, which is made up of oxygen and carbon dioxide. These gases are produced by plants during photosynthesis, which requires sunlight and nutrients from the soil. Hence, plants are interconnected with air, sunlight, and soil.
Interrelated:
All the elements of the life support system are interrelated. For example, water is essential for the survival of living organisms. It is used for various purposes such as drinking, cooking, cleaning, and agriculture. However, access to clean water is dependent on the quality of the soil, which affects the water cycle. The water cycle is a process through which water evaporates from the surface, forms clouds, and falls back to the ground as precipitation. Hence, soil and water are interrelated.
Interdependent:
All the elements of the life support system are interdependent. For example, the quality of air is dependent on the quality of water and soil. Pollution of water and soil leads to the release of harmful chemicals into the air, which affects the health of living organisms. Similarly, the quality of soil is dependent on the quality of water and air. Hence, all the elements of the life support system are interdependent.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the elements of the life support system are interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated. Any disturbance in one element can affect the other elements, leading to a chain reaction. Therefore, it is essential to maintain the balance of the life support system to ensure the survival of living organisms.
Life support system refers to the various components of the environment that support life on Earth. These components include air, water, soil, and sunlight. All these elements are interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated. Let's understand each of them in detail.
Interconnected:
All the elements of the life support system are interconnected. For example, air is required for breathing, which is made up of oxygen and carbon dioxide. These gases are produced by plants during photosynthesis, which requires sunlight and nutrients from the soil. Hence, plants are interconnected with air, sunlight, and soil.
Interrelated:
All the elements of the life support system are interrelated. For example, water is essential for the survival of living organisms. It is used for various purposes such as drinking, cooking, cleaning, and agriculture. However, access to clean water is dependent on the quality of the soil, which affects the water cycle. The water cycle is a process through which water evaporates from the surface, forms clouds, and falls back to the ground as precipitation. Hence, soil and water are interrelated.
Interdependent:
All the elements of the life support system are interdependent. For example, the quality of air is dependent on the quality of water and soil. Pollution of water and soil leads to the release of harmful chemicals into the air, which affects the health of living organisms. Similarly, the quality of soil is dependent on the quality of water and air. Hence, all the elements of the life support system are interdependent.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the elements of the life support system are interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated. Any disturbance in one element can affect the other elements, leading to a chain reaction. Therefore, it is essential to maintain the balance of the life support system to ensure the survival of living organisms.
Sanctuaries are established to ______- a)Entrap animals
- b)Protect animals
- c)Rear animals for milk
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sanctuaries are established to ______
a)
Entrap animals
b)
Protect animals
c)
Rear animals for milk
d)
None of the above
|
|
Manasi Srinivasan answered |
Introduction:
Sanctuaries are established to provide a safe and protected environment for animals. These specially designated areas aim to conserve and protect various species of wildlife.
Explanation:
1. Protection of Animals:
The primary purpose of establishing sanctuaries is to protect animals. These areas are carefully chosen to provide a suitable habitat and ensure the safety of the animals residing within them. Sanctuaries offer a sanctuary for wildlife, protecting them from threats such as hunting, poaching, habitat destruction, and human interference.
2. Conservation of Biodiversity:
Sanctuaries are crucial for the conservation of biodiversity. By protecting various species of animals, sanctuaries help maintain the ecological balance. They provide a safe space for wildlife to thrive and contribute to the overall health of ecosystems. By preserving different species, sanctuaries also help in preserving genetic diversity, which is essential for the long-term survival of species.
3. Research and Education:
Sanctuaries often serve as research and education centers. Scientists and researchers study the behavior, habitat requirements, and ecological roles of different species within sanctuaries. This research helps in understanding the needs of animals and developing effective conservation strategies. Sanctuaries also provide opportunities for educational visits, allowing people to learn about wildlife and the importance of conservation.
4. Habitat Restoration:
Some sanctuaries focus on habitat restoration. They work towards creating and maintaining suitable habitats for endangered or threatened species. These areas may involve reforestation, wetland restoration, or other habitat rehabilitation activities. By restoring habitats, sanctuaries aim to provide a sustainable ecosystem for animals to thrive.
5. Ecotourism and Economic Benefits:
Sanctuaries can also contribute to local economies through ecotourism. Visitors who come to admire the wildlife and natural beauty of these areas provide economic opportunities for local communities. Revenue generated from tourism can be used for the maintenance and further development of the sanctuaries.
Conclusion:
Sanctuaries are established with the primary objective of protecting animals. They play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity, conducting research, educating the public, restoring habitats, and providing economic benefits through ecotourism. By fulfilling these functions, sanctuaries contribute to the overall well-being of wildlife and the environment.
Sanctuaries are established to provide a safe and protected environment for animals. These specially designated areas aim to conserve and protect various species of wildlife.
Explanation:
1. Protection of Animals:
The primary purpose of establishing sanctuaries is to protect animals. These areas are carefully chosen to provide a suitable habitat and ensure the safety of the animals residing within them. Sanctuaries offer a sanctuary for wildlife, protecting them from threats such as hunting, poaching, habitat destruction, and human interference.
2. Conservation of Biodiversity:
Sanctuaries are crucial for the conservation of biodiversity. By protecting various species of animals, sanctuaries help maintain the ecological balance. They provide a safe space for wildlife to thrive and contribute to the overall health of ecosystems. By preserving different species, sanctuaries also help in preserving genetic diversity, which is essential for the long-term survival of species.
3. Research and Education:
Sanctuaries often serve as research and education centers. Scientists and researchers study the behavior, habitat requirements, and ecological roles of different species within sanctuaries. This research helps in understanding the needs of animals and developing effective conservation strategies. Sanctuaries also provide opportunities for educational visits, allowing people to learn about wildlife and the importance of conservation.
4. Habitat Restoration:
Some sanctuaries focus on habitat restoration. They work towards creating and maintaining suitable habitats for endangered or threatened species. These areas may involve reforestation, wetland restoration, or other habitat rehabilitation activities. By restoring habitats, sanctuaries aim to provide a sustainable ecosystem for animals to thrive.
5. Ecotourism and Economic Benefits:
Sanctuaries can also contribute to local economies through ecotourism. Visitors who come to admire the wildlife and natural beauty of these areas provide economic opportunities for local communities. Revenue generated from tourism can be used for the maintenance and further development of the sanctuaries.
Conclusion:
Sanctuaries are established with the primary objective of protecting animals. They play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity, conducting research, educating the public, restoring habitats, and providing economic benefits through ecotourism. By fulfilling these functions, sanctuaries contribute to the overall well-being of wildlife and the environment.
Which of the following soil is the best for plant growth?- a)Sandy soil
- b)Loamy soil
- c)Gravel
- d)Clay
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following soil is the best for plant growth?
a)
Sandy soil
b)
Loamy soil
c)
Gravel
d)
Clay
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Loamy soil is the best soil for the proper growth of the plants.
Which step is not involved in the carbon cycle?- a)Respiration
- b)Transpiration
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)Burning of fossil fuels.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which step is not involved in the carbon cycle?
a)
Respiration
b)
Transpiration
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Burning of fossil fuels.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Carbon-cycle is a process in which the carbon is circulated, transformed between living things and the environment. The burning of fossil fuels and respiration expels carbon dioxide in the environment which is fixed by the process of photosynthesis.
Transpiration is a process in which the moisture is carried from roots to the leaves and then evaporation occurs from the pores present on the underside of the leaves.
Air is a mixture of- a)Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon monoxide, water vapours
- b)Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapours
- c)Nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, carbon monoioxide
- d)Nitrogen, oxygen, methane, carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Air is a mixture of
a)
Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon monoxide, water vapours
b)
Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapours
c)
Nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, carbon monoioxide
d)
Nitrogen, oxygen, methane, carbon dioxide
|
|
Chirag Menon answered |
< b="" />Air is a mixture of< />
Air is a mixture of several gases, and the composition of air can vary slightly depending on the location and environmental factors. However, the major components of air are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
< b="" />Option B: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor< />
The correct answer is Option B, which states that air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Let's understand the role of each component in the air.
1. < b="" />Nitrogen< />:
- Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, making up around 78% of the total volume of air.
- It is a colorless and odorless gas that is essential for the growth and development of plants.
- Nitrogen is also used in various industrial processes, such as in the production of ammonia for fertilizers and in the manufacturing of electronics.
2. < b="" />Oxygen< />:
- Oxygen is the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere, accounting for approximately 21% of the air.
- It is a colorless and odorless gas that is vital for the survival of most living organisms, including humans.
- Oxygen is necessary for cellular respiration, the process by which organisms convert food into energy.
- It is also used in various industrial applications, such as in the production of steel and in medical treatments.
3. < b="" />Carbon Dioxide< />:
- Carbon dioxide is present in the air in relatively small quantities, usually around 0.04%.
- It is a greenhouse gas that plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system.
- Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere through natural processes like respiration and volcanic activity, as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels.
- It is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and is an essential component of the carbon cycle.
4. < b="" />Water Vapor< />:
- Water vapor is the gaseous form of water and is present in the air in varying amounts.
- It is an important component of the Earth's water cycle, where water evaporates from the surface, condenses into clouds, and eventually falls back to the ground as precipitation.
- Water vapor plays a crucial role in weather patterns and helps regulate the Earth's temperature.
In conclusion, air is a mixture of several gases, with nitrogen and oxygen being the main components. Carbon dioxide and water vapor are present in smaller amounts but still play significant roles in the Earth's atmosphere and climate system.
Air is a mixture of several gases, and the composition of air can vary slightly depending on the location and environmental factors. However, the major components of air are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
< b="" />Option B: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor< />
The correct answer is Option B, which states that air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Let's understand the role of each component in the air.
1. < b="" />Nitrogen< />:
- Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, making up around 78% of the total volume of air.
- It is a colorless and odorless gas that is essential for the growth and development of plants.
- Nitrogen is also used in various industrial processes, such as in the production of ammonia for fertilizers and in the manufacturing of electronics.
2. < b="" />Oxygen< />:
- Oxygen is the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere, accounting for approximately 21% of the air.
- It is a colorless and odorless gas that is vital for the survival of most living organisms, including humans.
- Oxygen is necessary for cellular respiration, the process by which organisms convert food into energy.
- It is also used in various industrial applications, such as in the production of steel and in medical treatments.
3. < b="" />Carbon Dioxide< />:
- Carbon dioxide is present in the air in relatively small quantities, usually around 0.04%.
- It is a greenhouse gas that plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system.
- Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere through natural processes like respiration and volcanic activity, as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels.
- It is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and is an essential component of the carbon cycle.
4. < b="" />Water Vapor< />:
- Water vapor is the gaseous form of water and is present in the air in varying amounts.
- It is an important component of the Earth's water cycle, where water evaporates from the surface, condenses into clouds, and eventually falls back to the ground as precipitation.
- Water vapor plays a crucial role in weather patterns and helps regulate the Earth's temperature.
In conclusion, air is a mixture of several gases, with nitrogen and oxygen being the main components. Carbon dioxide and water vapor are present in smaller amounts but still play significant roles in the Earth's atmosphere and climate system.
Photochemical smog is formed by- a)CO
- b)SO2
- c)NO2
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Photochemical smog is formed by
a)
CO
b)
SO2
c)
NO2
d)
CO2
|
|
Amrita Kapoor answered |
Photochemical smog is formed by NO2.
Explanation:
Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution that is formed through the interaction of sunlight with certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It is primarily composed of a mixture of nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other reactive gases. The formation of photochemical smog involves a complex series of chemical reactions.
Key Points:
1. Formation of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):
- Nitrogen oxides are formed through the combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes.
- The primary nitrogen oxide responsible for the formation of photochemical smog is nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
2. Role of Sunlight:
- Sunlight plays a crucial role in the formation of photochemical smog.
- When sunlight interacts with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), it leads to the splitting of the molecule into nitric oxide (NO) and an oxygen atom (O).
- The oxygen atom then reacts with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3), which is a key component of photochemical smog.
3. Formation of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted from various sources, including vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and solvents.
- VOCs such as hydrocarbons are released into the atmosphere and undergo reactions in the presence of sunlight.
- These reactions result in the formation of secondary pollutants like peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and aldehydes, which contribute to the formation of photochemical smog.
4. Chemical Reactions:
- The formation of photochemical smog involves a complex series of chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and other reactive gases.
- These reactions produce a range of pollutants, including ozone, peroxyacetyl nitrate, and formaldehyde, which contribute to the characteristic brownish haze and unpleasant odor associated with photochemical smog.
In conclusion, photochemical smog is primarily formed by the interaction of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) with sunlight, leading to the production of ozone and other reactive gases. It is important to reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds to mitigate the formation of photochemical smog and improve air quality.
Explanation:
Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution that is formed through the interaction of sunlight with certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It is primarily composed of a mixture of nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other reactive gases. The formation of photochemical smog involves a complex series of chemical reactions.
Key Points:
1. Formation of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):
- Nitrogen oxides are formed through the combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes.
- The primary nitrogen oxide responsible for the formation of photochemical smog is nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
2. Role of Sunlight:
- Sunlight plays a crucial role in the formation of photochemical smog.
- When sunlight interacts with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), it leads to the splitting of the molecule into nitric oxide (NO) and an oxygen atom (O).
- The oxygen atom then reacts with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3), which is a key component of photochemical smog.
3. Formation of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted from various sources, including vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and solvents.
- VOCs such as hydrocarbons are released into the atmosphere and undergo reactions in the presence of sunlight.
- These reactions result in the formation of secondary pollutants like peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and aldehydes, which contribute to the formation of photochemical smog.
4. Chemical Reactions:
- The formation of photochemical smog involves a complex series of chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and other reactive gases.
- These reactions produce a range of pollutants, including ozone, peroxyacetyl nitrate, and formaldehyde, which contribute to the characteristic brownish haze and unpleasant odor associated with photochemical smog.
In conclusion, photochemical smog is primarily formed by the interaction of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) with sunlight, leading to the production of ozone and other reactive gases. It is important to reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds to mitigate the formation of photochemical smog and improve air quality.
Choose the correct sequencein atmosphere → organic carbon in plants- a)CO2 in atmosphere → decomposers → organic carbon in animals → organic carbon in plants
- b)Organic carbon in animals → decomposers → CO2
- c)CO2 in atmosphere → organic carbon in plants → organic carbon in animals → inorganic carbon in soil
- d)Inorganic carbonates in water →organic carbon in plants → organic carbon in animals → scavengers.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct sequence
in atmosphere → organic carbon in plants
a)
CO2 in atmosphere → decomposers → organic carbon in animals → organic carbon in plants
b)
Organic carbon in animals → decomposers → CO2
c)
CO2 in atmosphere → organic carbon in plants → organic carbon in animals → inorganic carbon in soil
d)
Inorganic carbonates in water →organic carbon in plants → organic carbon in animals → scavengers.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Nutrient cycles circulate matter through the biosphere. The nutrients regularly alternate between living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components. Hence the nutrient cycles are also called as biogeochemical cycles. The important nutrient cycles are water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, mineral cycle. In the carbon cycle, atmospheric carbon is fixed into organic compounds like carbohydrates by green plants during the process of photosynthesis. The organic compounds are consumed by heterotrophic organisms like animals.
The two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere are- a)Water and oxygen
- b)Water and ozone
- c)Water and carbon dioxide
- d)Ozone and oxygen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere are
a)
Water and oxygen
b)
Water and ozone
c)
Water and carbon dioxide
d)
Ozone and oxygen
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere are
Oxygen, O2
Ozone, O3 is found upper layer of the atmosphere.
Biogas generation is mainly based on the principle of- a)Degradation
- b)Purification
- c)Fermentation
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Biogas generation is mainly based on the principle of
a)
Degradation
b)
Purification
c)
Fermentation
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Biogas generation is mainly based on the principle of biodegradation. Biogas is a type of gas which is produced from the decomposition of any biodegradable waste by various bacteria. It results the formation of methane.
One of the following factors does not lead to soil formation in nature- a)Sun
- b)Polythene bags
- c)Water
- d)Wind
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following factors does not lead to soil formation in nature
a)
Sun
b)
Polythene bags
c)
Water
d)
Wind
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Polythene bags are not involved in soil formation. However, plastic bags are threat to environment, because these bags are non-degradable, i.e., do not decay and thus, do not lead to soil formation.
Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere mainly by- a)Burning of fossil fuel
- b)Photosynthesis
- c)Respiration
- d)Fungi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere mainly by
a)
Burning of fossil fuel
b)
Photosynthesis
c)
Respiration
d)
Fungi
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Photosynthesis is the process in which autotrophs such as green plants use carbon dioxide and water in presence of sunlight to synthesize nutrients such carbohydrates in the form of glucose and release oxygen. Hence oxygen is returned to the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
In nitrogen cycle which bacteria are responsible for nitrification- a)Rhizobium
- b)Clostridium
- c)Nitrosomonas
- d)Nitrosomonas and nitrobacter
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In nitrogen cycle which bacteria are responsible for nitrification
a)
Rhizobium
b)
Clostridium
c)
Nitrosomonas
d)
Nitrosomonas and nitrobacter
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
In nitrogen cycle Nitrosomonas & Nitrobacter bacteria are responsible for nitrification) During nitrification, the nitrogenous wastes from dead plants and animals are converted into ammonia by the action of bacteria such as Bacillus ramosus, Clostridium spp. etc.
The microbes which carry out biological nitrogen fixation are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers. for eg: Rhizobium and Azotobacter.
The species of certain plants and animals which are present within certain region or area is called- a)Phytoplankton
- b)Biota
- c)Kingdom
- d)Zooplankton
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The species of certain plants and animals which are present within certain region or area is called
a)
Phytoplankton
b)
Biota
c)
Kingdom
d)
Zooplankton
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora, and for fungi, it is funga. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as biota.
Major component of the atmosphere on venus and mars planet is- a)Carbon dioxide
- b)Water vapours
- c)Oxygen
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Major component of the atmosphere on venus and mars planet is
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Water vapours
c)
Oxygen
d)
Nitrogen
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Carbon dioxide is an important gaseous component of the environment. It is fixed by the green plants by the process of photosynthesis. It is released during expiration by the process of respiration. Venus is twin planet to earth as it has atmosphere. It is the hottest planet as its is made up of 97% carbon dioxide. Mars is also a planet which has atmosphere made up of 95.5% carbon dioxide.
One of the following processes is not a step involved in water-cycle operating in nature- a)Precipitation
- b)Transpiration
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following processes is not a step involved in water-cycle operating in nature
a)
Precipitation
b)
Transpiration
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
None of these
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Photosynthesis is the process in plants where sunlight, carbon dioxide and water are converted to organic compounds, starch, energy and oxygen. This is not involved in the water cycle and hence, it is the correct option.
__________ is the major raw material for biogas- a)Cow dung
- b)Mud
- c)Grass
- d)Plant leaves
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
__________ is the major raw material for biogas
a)
Cow dung
b)
Mud
c)
Grass
d)
Plant leaves
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Cattle dung has been recognized as the chief raw material for bio-gas plants, other materials like night-soil, poultry litter and agricultural wastes can also be used.
Nif genes occur in- a)Aspergillus
- b)Penicillium
- c)Rhizobium
- d)Streptococcus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nif genes occur in
a)
Aspergillus
b)
Penicillium
c)
Rhizobium
d)
Streptococcus
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Nif genes (Nitrogen fixing gene) are present in the soil bacterium Rhizobium which symbiotically fixes atmospheric nitrogen in the roots of leguminous plants.
Which of the following soil is transported by air?- a)Alluvial
- b)Glacial
- c)Eolian
- d)Elluvial
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following soil is transported by air?
a)
Alluvial
b)
Glacial
c)
Eolian
d)
Elluvial
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Transported soils are brought from other places under the influence of gravity (Colluvial), running water (Alluvial), wind (Eolian) and glaciers (Glacial soil).
‘Ozone - hole’ means- a)Thining of the ozone layer
- b)A large sized hole in the ozone layer
- c)Small holes scattered in the ozone layer
- d)Thickening of ozone in the ozone layer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Ozone - hole’ means
a)
Thining of the ozone layer
b)
A large sized hole in the ozone layer
c)
Small holes scattered in the ozone layer
d)
Thickening of ozone in the ozone layer
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Ozone layer is a region of concentration of ozone molecule. O3 (O2 +O) in the earth's atmosphere. The layer lies in the stratosphere at an altitude of 18-50 kms. The ozone layer naturally Shields earth's life from the harmful effect of the Sun's ultraviolet radiations. A severe depletion of ozone (ozone hole) in a region of the ozone layer was found particularly over Antarctica. The depletion is caused by chlorofluorocarbons and by other compounds like CCI4,CF4 etc. So, the correct answer is 'Thinning of the ozone layer'.
Low visibility during cold weather is due to- a)Formation of fossil fuel
- b)Lack of adequate power supply
- c)Unburnt carbon particles or hydrocarbons suspended in air
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Low visibility during cold weather is due to
a)
Formation of fossil fuel
b)
Lack of adequate power supply
c)
Unburnt carbon particles or hydrocarbons suspended in air
d)
None of these
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
During winter, the water droplets condense in the air and lower visibility by forming fog. The dust particles also stick around the droplets thus lowering the visibility further. This phenomenon results in the formation of smog (smoke + fog) which lowers the visibility during cold weather seasons.
Growth of lichens on barren rocks is followed by the growth of- a)Moss
- b)Algae
- c)Ferns
- d)Gymnosperms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Growth of lichens on barren rocks is followed by the growth of
a)
Moss
b)
Algae
c)
Ferns
d)
Gymnosperms
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The process of community development over time, which involves species in one stage being replaced by other species, is called ecological succession. It is divided as primary succession and secondary succession. An area is initially colonized by certain early-successional species such as Lichens, they are often the first organism to colonize an area that will undergo primary succession. Once new soil has formed in an area it gives way over time to mild-successional species, such as mosses and grasses, which in turn give way much later to late-successional species.
Biosphere occurs- a)In atmosphere and hydrosphere
- b)In lithosphere
- c)In lithosphere and hydrosphere
- d)At place of interaction of lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biosphere occurs
a)
In atmosphere and hydrosphere
b)
In lithosphere
c)
In lithosphere and hydrosphere
d)
At place of interaction of lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Environment consist of mainly four components- atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere.
Atmosphere consists of air and gas molecules. Lithosphere is the mantle of rocks constituting the earths crust. It is the solid component of the earth, which includes soil, earth, rocks and mountains etc. Hydrosphere consists of water bodies found on, under and over the surface of a planet. And biosphere is formed by the living organisms and it is the sum of all ecosystem.
Oxygen is harmful for- a)Ferns
- b)Chara
- c)Mango tree
- d)Nitrogen fixing bacteria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen is harmful for
a)
Ferns
b)
Chara
c)
Mango tree
d)
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Oxygen degrades nitrogenases easily. Therefore, in the presence of oxygen, several bacteria avoid producing the enzyme.: Oxygen is this harmful for Nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
In the atmosphere, the layer above the troposphere is- a)Exosphere
- b)Mesosphere
- c)Stratosphere
- d)Thermosphere
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the atmosphere, the layer above the troposphere is
a)
Exosphere
b)
Mesosphere
c)
Stratosphere
d)
Thermosphere
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The stratosphere starts just above the troposphere and extends to 50 kilometers (31 miles) high. The ozone layer, which absorbs and scatters the solar ultraviolet radiation, is in this layer.
Signs of eutrophication of water bodies include- a)Fluorosis
- b)Algal bloom
- c)Reduced oxygen
- d)Rapid decomposition of organic matter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Signs of eutrophication of water bodies include
a)
Fluorosis
b)
Algal bloom
c)
Reduced oxygen
d)
Rapid decomposition of organic matter
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Eutrophication is characterized by excessive plant and algal growth due to the increased availability of one or more limiting growth factors needed for photosynthesis (Schindler 2006), such as sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrient fertilizers.
SPM includes- a)Dust
- b)Flyash
- c)Soot and smoke
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
SPM includes
a)
Dust
b)
Flyash
c)
Soot and smoke
d)
All the above
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)are finely divided matter particles that cause aur pollution. They may be dispersed into air by combustion or industrial processes. Dust, soot and smoke, flyash are all Suspended Particulate Matter.
Marked temperature changes in aquatic environment can affect.- a)Availability of nutrients
- b)More growth of aquatic plants
- c)Process of digestion in animals
- d)Breeding of animals
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Marked temperature changes in aquatic environment can affect.
a)
Availability of nutrients
b)
More growth of aquatic plants
c)
Process of digestion in animals
d)
Breeding of animals
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Marked temperature changes in aquatic environment can affect more breeding and the growth of aquatic plants, as the aquatic organisms and plants were highly dependent on the temperature factor.
Which one is inexhaustible resource?- a)Soil
- b)Solar radiation
- c)Fossil fuels
- d)Minerals
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is inexhaustible resource?
a)
Soil
b)
Solar radiation
c)
Fossil fuels
d)
Minerals
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Solar radiation is an inexhaustible and renewable source of energy. Soil, Fossil fuels and Minerals, all are exhaustible and their replenishment becomes impossible or very difficult.
The term used to identify the living components of the environment is- a)Topographic
- b)Ecosystem
- c)biotic
- d)Abiotic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term used to identify the living components of the environment is
a)
Topographic
b)
Ecosystem
c)
biotic
d)
Abiotic
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The living organisms in the environment like plants and animals including human beings are called biotic components.
The death of the last individual of a species is called- a)Clad
- b)Extinction
- c)Neither (a) nor (b)
- d)Species diversity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The death of the last individual of a species is called
a)
Clad
b)
Extinction
c)
Neither (a) nor (b)
d)
Species diversity
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point.
Match the column A with column B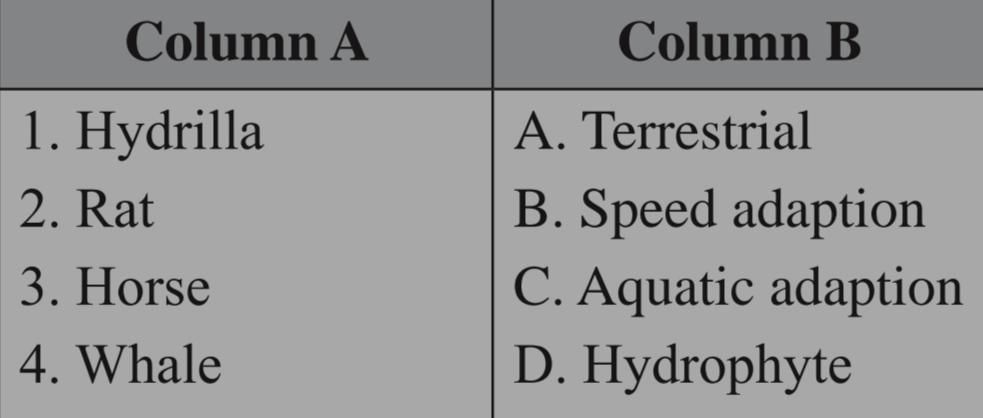
- a)1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – B, 4 – C
- b)1 – B, 2 – A, 3 – D, 4 – C
- c)1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – C, 4 –B
- d)1 – D, 2 – C, 3 – A, 4 – B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the column A with column B

a)
1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – B, 4 – C
b)
1 – B, 2 – A, 3 – D, 4 – C
c)
1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – C, 4 –B
d)
1 – D, 2 – C, 3 – A, 4 – B
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Hydrophytes are aquatic plants that live in water and are evolutionarily suited to thrive in aquatic environments. Hydrilla, also called water thyme is a submerged hydrophyte, which is a troublesome aquatic weed at many places.
In their natural habitats rats are primarily nocturnal—the brown rat is a prominent exception, being active day and night in both urban and rural environments. All rats are terrestrial, and many are also arboreal.
Horses have good vascularization, meaning there are lots of blood vessels going to large muscles. This allows for both explosive power and endurance power. All of these things combine to make horses run at a high speed.
To help them adapt to the ocean, whales developed echolocation, thick layers of blubber, modified lungs, better hearing, and larger arteries, among other things, to ensure their survival and prosperity.
Red Data Book provides a list of- a)Disease resistant animals
- b)Advanced plants
- c)Rare endangered or endemic species
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Red Data Book provides a list of
a)
Disease resistant animals
b)
Advanced plants
c)
Rare endangered or endemic species
d)
None of the above
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The Red data book is the state document established for documenting rare and endangered species of animals, plants and fungi. This book provides central information for studies and monitoring programmes on rare and endangered species and their habits.
Rain fall patterns depend on- a)The underground water table
- b)The prevailing season in an area
- c)The number of water bodies in an area
- d)The density pattern of human population in an area
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain fall patterns depend on
a)
The underground water table
b)
The prevailing season in an area
c)
The number of water bodies in an area
d)
The density pattern of human population in an area
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Rainfall pattern will depend on number of water bodies in an area, as there will be large water bodies, (ocean, river) the rate of evaporation would be high, which will help to cause rain in the area.
An increase in carbon dioxide contents in the atmosphere would not cause:- a)Increase in photosynthesis in plants
- b)Global warming
- c)Abundance of desert plants
- d)More heat to be retained by the environment
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An increase in carbon dioxide contents in the atmosphere would not cause:
a)
Increase in photosynthesis in plants
b)
Global warming
c)
Abundance of desert plants
d)
More heat to be retained by the environment
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Earth surface re-emits heat, obtained from the sun, in the form of infrared radiation but part of this does not escape into space as atmospheric gases (e.g., carbon dioxide, methane, etc.) absorb a major fraction of it. The molecules of these gases radiate heat energy, and a major part of which again comes to Earths surface, thus heating it up once again. This cycle is repeated many times.
The gases carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons and nitrous oxide are commonly known as greenhouse gases because they are responsible for the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect leads to global warming. Carbon dioxide is also one of the substrates used in the photosynthesis process. An increase in carbon dioxide concentration will increase the rate of photosynthesis. An increase in deserts is called desertification. Desertification will lead to the spread of desert plants. Several factors like a decrease in rainfall, atmospheric pollution, deforestation etc. are responsible for the spread of deserts but desertification is not directly linked to increasing carbon dioxide concentration.
Ozone layer is getting depleted because of- a)Excessive deforestation
- b)Excessive use of automobiles
- c)Excessive formation of industrial units
- d)Excessive use of man made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozone layer is getting depleted because of
a)
Excessive deforestation
b)
Excessive use of automobiles
c)
Excessive formation of industrial units
d)
Excessive use of man made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Excessive use of man-made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine. The ozone layer is getting depleted because of the excessive use of man-made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine.
If there were no atmosphere around the earth, the temperature of the earth will- a)Be unaffected
- b)Increase
- c)Go on decreasing
- d)Increase during day and decrease during night
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If there were no atmosphere around the earth, the temperature of the earth will
a)
Be unaffected
b)
Increase
c)
Go on decreasing
d)
Increase during day and decrease during night
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
If there were no atmosphere around the earth, the temperature of the earth will increase during day and decrease during night. In the absence of atmosphere around the earth, it will be like a moon. There would be no life, no winds, no rains, no fires, no protection against harmful solar radiations. Due to absence of atmosphere around the moon, the temperature ranges from -190° C to 110° C. Air is a bad conductor of heat. The atmosphere has an average temperature of the earth almost steady during the day and night. It prevents sudden increase in temperature during the day time. Also, it decreases the rate of escape of heat during night time.
Thus, the correct answer is 'Increase during day and decrease during night.'
Green plants in an ecosystem are called- a)Producers
- b)Consumers
- c)Decomposers
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Green plants in an ecosystem are called
a)
Producers
b)
Consumers
c)
Decomposers
d)
All of the above
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
In the ecosystem, producers are those organisms which are capable of preparing their own food. Green plants are called producers as they manufacture their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
The conversion of NO3 to N2 is called- a)Nitrification
- b)Denitrification
- c)Ammonifiction
- d)Nitrogen fixation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The conversion of NO3 to N2 is called
a)
Nitrification
b)
Denitrification
c)
Ammonifiction
d)
Nitrogen fixation
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
De-Nitrification: Nitrogen in its nitrate form (NO3–) is converted back into atmospheric nitrogen gas (N2) by bacterial species such as Pseudomonas and Clostridium, usually in anaerobic conditions.
Cloud formation takes place in which part of atmosphere- a)Troposphere
- b)Ozonosphere
- c)Stratosphere
- d)Thermosphere
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cloud formation takes place in which part of atmosphere
a)
Troposphere
b)
Ozonosphere
c)
Stratosphere
d)
Thermosphere
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
There are 5 layers of atmosphere present around the earth. They include Troposphere, Stratosphere, mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere. Out of all these, the closest to the surface of the earth is troposphere. Formation of clouds takes place at this layer.
What is the range of temperature of the surface of moon?- a)– 180°C to 100°C
- b)– 170°C to 100°C
- c)– 170°C to 120°C
- d)– 190°C to 110°C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the range of temperature of the surface of moon?
a)
– 180°C to 100°C
b)
– 170°C to 100°C
c)
– 170°C to 120°C
d)
– 190°C to 110°C
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The moon is about the same distance from the Sun than the Earth is. Despite that, on the surface of the moon, with no atmosphere, the temperature ranges from –190° C to 110° C.
Nitromonas bacteria convert- a)Nitrite to nitrate
- b)Ammonia into nitrate
- c)Ammonia into nitrite
- d)Nitrite into ammonia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitromonas bacteria convert
a)
Nitrite to nitrate
b)
Ammonia into nitrate
c)
Ammonia into nitrite
d)
Nitrite into ammonia
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The nitrification process requires the mediation of two distinct groups: bacteria that convert ammonia to nitrites (Nitrosomonas, Nitrosospira, Nitrosococcus, and Nitrosolobus) and bacteria that convert nitrites (toxic to plants) to nitrates (Nitrobacter, Nitrospina, and Nitrococcus).
What would happen, if all land and water present in the environment is converted to ozone?- a)We will be protected more
- b)Ozone is not stable, hence it will be toxic
- c)It will become poisonous and kill living forms
- d)It will help harmful sun radiations to reach earth and damage many life forms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What would happen, if all land and water present in the environment is converted to ozone?
a)
We will be protected more
b)
Ozone is not stable, hence it will be toxic
c)
It will become poisonous and kill living forms
d)
It will help harmful sun radiations to reach earth and damage many life forms
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Ozone is triatomic `[O_(3)]` allotrope (occurrence of one element in more than one form) of oxygen. It is a blue gas with purgent odour and is highly poisonous to the living system. It is present in stratosphere region of atmosphere however, it does not exists in the lower atmosphere region called troposphere, hence does not show any fatal effect on life form. It its value in the atmosphere increases the appreciable amount, it may becomes fatal, i.e., becomes poisonous and will kill all the living forms.
In a natural ecosystem, decomposers include- a)Parasitic algae
- b)Bacteria and fungi
- c)Macroscopic animals
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a natural ecosystem, decomposers include
a)
Parasitic algae
b)
Bacteria and fungi
c)
Macroscopic animals
d)
All the above
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
In a natural ecosystem, decomposers include only bacteria and fungi.
Major source of mineral in soil is the- a)Plants
- b)Animals
- c)Bacteria
- d)Parent - rock from which soil is formed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Major source of mineral in soil is the
a)
Plants
b)
Animals
c)
Bacteria
d)
Parent - rock from which soil is formed
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The soil minerals and organic matter can be replenished with help of decomposers. Hence, the correct answer is option D i.e., the major source of the minerals in the soil is parent rock from which soil is formed.
Percentage of total water found as freshwater is- a)32%
- b)2.5%
- c)16%
- d)46%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of total water found as freshwater is
a)
32%
b)
2.5%
c)
16%
d)
46%
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Only 2.5% of total water present on the surface of the earth is present as freshwater which can be used for drinking and is potable. Rest of it is present in the form of seawater which is not salt-free and cannot be used for drinking. So, freshwater should be used very judiciously and used for drinking.
Chapter doubts & questions for Natural Resources - Science Olympiad Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Natural Resources - Science Olympiad Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Olympiad Class 9
28 videos|115 docs|52 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









