All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Olympiad Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life for Class 9 Exam
Unicellular organisms take in oxygen and pass out carbon dioxide through- a)Active transport
- b)endosmosis
- c)Exosmosis
- d)Diffusion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Unicellular organisms take in oxygen and pass out carbon dioxide through
a)
Active transport
b)
endosmosis
c)
Exosmosis
d)
Diffusion
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
In unicellular organisms like Amoeba, gaseous exchange takes place through the process of diffusion.
Amoeba acquires its food through a process termed as- a)Exocytosis
- b)Endocytosis
- c)Plasmolysis
- d)Exocytosis and endocytosis both
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amoeba acquires its food through a process termed as
a)
Exocytosis
b)
Endocytosis
c)
Plasmolysis
d)
Exocytosis and endocytosis both
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Endocytosis is the process of engulfing food particles from the exterior medium with the help of cell membrane. In this process a food vacuole enclosing the food is formed by extending the pseudopodia and encircling it.
Example, Amoeba
So, the correct answer is 'Endocytosis'
Select odd one outsubstances dissolved in it- a)Membranes are made of organic molecules such as proteins and lipids
- b)The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the amount of
- c)Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane
- d)Plasma membrane contain chitin sugar in plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select odd one out
substances dissolved in it
a)
Membranes are made of organic molecules such as proteins and lipids
b)
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the amount of
c)
Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane
d)
Plasma membrane contain chitin sugar in plants
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Each cell is bounded by an extremely delicate, thin elastic living membrane, called the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is made up of two layers of lipid (fat) molecules with protein molecules which is sandwitched between the lipid layer. The structure of plasma membrane can be observed under an electron microscope only. It is a selectively permeable membrane which allows the flow of only some substances into the cell and out of the cell. Viruses do not have any membranes.
Photosynthetic pigments are located in- a)Grana
- b)Stroma
- c)Outer membrane of chloroplast
- d)Inner membrane of chloroplast
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthetic pigments are located in
a)
Grana
b)
Stroma
c)
Outer membrane of chloroplast
d)
Inner membrane of chloroplast

|
Pallabi Choudhury answered |
Photosynthetic pigments are located in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
Photosynthetic pigments are molecules found in the chloroplasts of plant cells that are responsible for capturing light energy and initiating the process of photosynthesis. They absorb light at specific wavelengths and transfer this energy to other molecules involved in the photosynthetic process.
Chloroplast Structure:
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in the cells of green plants and algae. They are the sites of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy. Chloroplasts have a complex structure that consists of several compartments and membranes.
Thylakoid Membranes:
The thylakoid membranes are located within the chloroplasts and contain the photosynthetic pigments. These membranes are arranged in stacks called grana. The grana are connected by intergranal lamellae, which are flattened regions of thylakoid membranes.
Stroma:
The stroma is the fluid-filled space that surrounds the thylakoid membranes. It contains various enzymes and molecules necessary for the dark reactions of photosynthesis. The stroma also contains DNA, ribosomes, and other components necessary for protein synthesis.
Role of Photosynthetic Pigments:
The photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll and carotenoids, are embedded within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. These pigments absorb light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the thylakoid membranes, initiating the process of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis. It absorbs light in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color. There are several types of chlorophyll, including chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
Carotenoids:
Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb light in the blue and green regions of the spectrum. They help to broaden the range of light that can be absorbed by the chloroplasts, thereby increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. Carotenoids also protect the chlorophyll molecules from damage caused by excessive light energy.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, photosynthetic pigments are located in the stroma of the chloroplasts. These pigments are embedded within the thylakoid membranes, which are organized into grana. The pigments capture light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the thylakoid membranes, initiating the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthetic pigments are molecules found in the chloroplasts of plant cells that are responsible for capturing light energy and initiating the process of photosynthesis. They absorb light at specific wavelengths and transfer this energy to other molecules involved in the photosynthetic process.
Chloroplast Structure:
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in the cells of green plants and algae. They are the sites of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy. Chloroplasts have a complex structure that consists of several compartments and membranes.
Thylakoid Membranes:
The thylakoid membranes are located within the chloroplasts and contain the photosynthetic pigments. These membranes are arranged in stacks called grana. The grana are connected by intergranal lamellae, which are flattened regions of thylakoid membranes.
Stroma:
The stroma is the fluid-filled space that surrounds the thylakoid membranes. It contains various enzymes and molecules necessary for the dark reactions of photosynthesis. The stroma also contains DNA, ribosomes, and other components necessary for protein synthesis.
Role of Photosynthetic Pigments:
The photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll and carotenoids, are embedded within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. These pigments absorb light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the thylakoid membranes, initiating the process of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis. It absorbs light in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color. There are several types of chlorophyll, including chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
Carotenoids:
Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb light in the blue and green regions of the spectrum. They help to broaden the range of light that can be absorbed by the chloroplasts, thereby increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. Carotenoids also protect the chlorophyll molecules from damage caused by excessive light energy.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, photosynthetic pigments are located in the stroma of the chloroplasts. These pigments are embedded within the thylakoid membranes, which are organized into grana. The pigments capture light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the thylakoid membranes, initiating the process of photosynthesis.
Colourless plastids are known as- a)Leucoplast
- b)Chromoplast
- c)Chloroplast
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Colourless plastids are known as
a)
Leucoplast
b)
Chromoplast
c)
Chloroplast
d)
None of the above
|
|
Akanksha Choudhury answered |
Colourless plastids are known as Leucoplasts
Leucoplasts are a type of plastid that are colorless and lack pigments. They are primarily involved in the storage of starch, lipids, proteins, and other macromolecules. Leucoplasts are found in non-photosynthetic tissues of plants, such as roots, tubers, and seeds.
Types of Leucoplasts:
There are three main types of leucoplasts, each with a specific function:
1. Amyloplasts:
Amyloplasts, also known as starch grains, store starch in plants. They are commonly found in storage organs such as roots, tubers, and seeds. Amyloplasts are responsible for converting excess sugars into starch, which can be stored and used as an energy source for the plant.
2. Proteinoplasts:
Proteinoplasts, as the name suggests, are involved in the synthesis and storage of proteins. They are found in seeds, fruits, and other protein-rich tissues. Proteinoplasts play a crucial role in the development and germination of seeds, as well as in the accumulation of proteins during fruit ripening.
3. Elaioplasts:
Elaioplasts are responsible for the synthesis and storage of lipids, particularly oils and fats. They are found in oil-rich tissues such as seeds, fruits, and some roots. Elaioplasts are involved in lipid metabolism and can store large amounts of oils for energy reserves.
Function of Leucoplasts:
Leucoplasts are essential for the growth, development, and survival of plants. They perform various functions, including:
1. Storage: Leucoplasts store essential macromolecules such as starch, proteins, and lipids, which can be utilized by the plant during times of growth or energy requirement.
2. Synthesis: Some leucoplasts, such as proteinoplasts and elaioplasts, are involved in the synthesis of proteins and lipids, respectively. These synthesized molecules are crucial for the growth and development of the plant.
3. Conversion: Leucoplasts can convert excess sugars into starch, which is then stored for future use. This helps regulate sugar levels in the plant and provides an energy reserve.
4. Germination and Fruit Ripening: Leucoplasts, particularly proteinoplasts, play a vital role in the germination of seeds and the accumulation of proteins during fruit ripening.
In conclusion, colourless plastids are known as leucoplasts. They are involved in the storage and synthesis of various macromolecules and play a crucial role in the growth and development of plants.
Leucoplasts are a type of plastid that are colorless and lack pigments. They are primarily involved in the storage of starch, lipids, proteins, and other macromolecules. Leucoplasts are found in non-photosynthetic tissues of plants, such as roots, tubers, and seeds.
Types of Leucoplasts:
There are three main types of leucoplasts, each with a specific function:
1. Amyloplasts:
Amyloplasts, also known as starch grains, store starch in plants. They are commonly found in storage organs such as roots, tubers, and seeds. Amyloplasts are responsible for converting excess sugars into starch, which can be stored and used as an energy source for the plant.
2. Proteinoplasts:
Proteinoplasts, as the name suggests, are involved in the synthesis and storage of proteins. They are found in seeds, fruits, and other protein-rich tissues. Proteinoplasts play a crucial role in the development and germination of seeds, as well as in the accumulation of proteins during fruit ripening.
3. Elaioplasts:
Elaioplasts are responsible for the synthesis and storage of lipids, particularly oils and fats. They are found in oil-rich tissues such as seeds, fruits, and some roots. Elaioplasts are involved in lipid metabolism and can store large amounts of oils for energy reserves.
Function of Leucoplasts:
Leucoplasts are essential for the growth, development, and survival of plants. They perform various functions, including:
1. Storage: Leucoplasts store essential macromolecules such as starch, proteins, and lipids, which can be utilized by the plant during times of growth or energy requirement.
2. Synthesis: Some leucoplasts, such as proteinoplasts and elaioplasts, are involved in the synthesis of proteins and lipids, respectively. These synthesized molecules are crucial for the growth and development of the plant.
3. Conversion: Leucoplasts can convert excess sugars into starch, which is then stored for future use. This helps regulate sugar levels in the plant and provides an energy reserve.
4. Germination and Fruit Ripening: Leucoplasts, particularly proteinoplasts, play a vital role in the germination of seeds and the accumulation of proteins during fruit ripening.
In conclusion, colourless plastids are known as leucoplasts. They are involved in the storage and synthesis of various macromolecules and play a crucial role in the growth and development of plants.
Find out the false statement- a)Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes
- b)Mitochondria is said to be the power house of the cell as ATP is generated in them
- c)Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm
- d)Nucleus, mitochondria and plastid have DNA, hence they are able to make their own structural proteins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the false statement
a)
Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes
b)
Mitochondria is said to be the power house of the cell as ATP is generated in them
c)
Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm
d)
Nucleus, mitochondria and plastid have DNA, hence they are able to make their own structural proteins
|
|
Sankar Kaur answered |
Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes
This statement is true. The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and is involved in the modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins and lipids. One of its important functions is the formation of lysosomes. Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. The Golgi apparatus plays a vital role in packaging these enzymes into lysosomes before they are transported to their respective destinations within the cell.
Mitochondria is said to be the powerhouse of the cell as ATP is generated in them
This statement is also true. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for generating most of the cell's energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is required for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules. Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration, a process that involves the breakdown of glucose and other molecules to produce ATP through a series of biochemical reactions.
Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm
This statement is false. The term "cytoplasm" and "protoplasm" are not interchangeable. Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like substance present inside the cell, which includes the cytosol and the organelles (except the nucleus). On the other hand, protoplasm refers to the entire living content of a cell, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Protoplasm is a more inclusive term that encompasses the entire cell content, while cytoplasm specifically refers to the cellular material outside the nucleus.
Nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids have DNA, hence they are able to make their own structural proteins
This statement is true. Nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids (such as chloroplasts) have their own DNA molecules. The nucleus contains the nuclear DNA, which carries the genetic information and controls the cell's activities. Mitochondria have their own mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which encodes some of the proteins required for mitochondrial function. Similarly, plastids (specifically chloroplasts in plant cells) have plastid DNA, which is involved in the synthesis of proteins required for photosynthesis. The presence of DNA in these organelles allows them to produce their own structural proteins, which are essential for their proper functioning.
This statement is true. The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and is involved in the modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins and lipids. One of its important functions is the formation of lysosomes. Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. The Golgi apparatus plays a vital role in packaging these enzymes into lysosomes before they are transported to their respective destinations within the cell.
Mitochondria is said to be the powerhouse of the cell as ATP is generated in them
This statement is also true. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for generating most of the cell's energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is required for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules. Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration, a process that involves the breakdown of glucose and other molecules to produce ATP through a series of biochemical reactions.
Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm
This statement is false. The term "cytoplasm" and "protoplasm" are not interchangeable. Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like substance present inside the cell, which includes the cytosol and the organelles (except the nucleus). On the other hand, protoplasm refers to the entire living content of a cell, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Protoplasm is a more inclusive term that encompasses the entire cell content, while cytoplasm specifically refers to the cellular material outside the nucleus.
Nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids have DNA, hence they are able to make their own structural proteins
This statement is true. Nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids (such as chloroplasts) have their own DNA molecules. The nucleus contains the nuclear DNA, which carries the genetic information and controls the cell's activities. Mitochondria have their own mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which encodes some of the proteins required for mitochondrial function. Similarly, plastids (specifically chloroplasts in plant cells) have plastid DNA, which is involved in the synthesis of proteins required for photosynthesis. The presence of DNA in these organelles allows them to produce their own structural proteins, which are essential for their proper functioning.
A cell placed in hypotonic solution bursts up: It is- a)Plant cell
- b)Fungal cell
- c)Bacterial cell
- d)Animal cell
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell placed in hypotonic solution bursts up: It is
a)
Plant cell
b)
Fungal cell
c)
Bacterial cell
d)
Animal cell
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The cells of plant, fungi and bacteria can withstand in hypotonic solution without bursting. This is because of cell wall. While animal cell bursts up in hypotonic solution because cell wall is not found.
Chlorophyll is present in- a)Cristae
- b)Thylakoid
- c)Stroma
- d)Matrix
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll is present in
a)
Cristae
b)
Thylakoid
c)
Stroma
d)
Matrix

|
Shreya Bajaj answered |
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants and algae that is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. It is responsible for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant.
Chlorophyll is primarily located in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, which are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells. The thylakoid membranes are flattened, disc-like structures within the chloroplasts that contain the pigments and protein complexes necessary for capturing light energy and carrying out the initial steps of photosynthesis.
Below are the different parts of a chloroplast where chlorophyll is present:
Thylakoid (Correct answer: B)
- The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll molecules embedded within them. These chlorophyll molecules are arranged in complexes called photosystems, which are responsible for capturing light energy and transferring it to other molecules involved in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll molecules absorb light primarily in the blue and red regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, reflecting green light and giving plants their characteristic green color. This is why chlorophyll is most abundant in the parts of plants that are exposed to sunlight, such as leaves.
Other parts of a chloroplast where chlorophyll is present include:
Stroma (Option C)
- The stroma is the fluid-filled space inside the chloroplast that surrounds the thylakoid membranes. It contains enzymes and other molecules involved in the later steps of photosynthesis, including the Calvin cycle.
Matrix (Option D)
- The matrix is a term commonly used to describe the inner compartment of mitochondria, which are organelles responsible for cellular respiration. Chlorophyll is not present in the matrix of mitochondria, as it is primarily involved in photosynthesis, not cellular respiration.
In conclusion, chlorophyll is primarily located in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, specifically in the photosystems within these membranes. While it is also present in the stroma of chloroplasts, it is not found in the matrix of mitochondria.
Chlorophyll is primarily located in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, which are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells. The thylakoid membranes are flattened, disc-like structures within the chloroplasts that contain the pigments and protein complexes necessary for capturing light energy and carrying out the initial steps of photosynthesis.
Below are the different parts of a chloroplast where chlorophyll is present:
Thylakoid (Correct answer: B)
- The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll molecules embedded within them. These chlorophyll molecules are arranged in complexes called photosystems, which are responsible for capturing light energy and transferring it to other molecules involved in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll molecules absorb light primarily in the blue and red regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, reflecting green light and giving plants their characteristic green color. This is why chlorophyll is most abundant in the parts of plants that are exposed to sunlight, such as leaves.
Other parts of a chloroplast where chlorophyll is present include:
Stroma (Option C)
- The stroma is the fluid-filled space inside the chloroplast that surrounds the thylakoid membranes. It contains enzymes and other molecules involved in the later steps of photosynthesis, including the Calvin cycle.
Matrix (Option D)
- The matrix is a term commonly used to describe the inner compartment of mitochondria, which are organelles responsible for cellular respiration. Chlorophyll is not present in the matrix of mitochondria, as it is primarily involved in photosynthesis, not cellular respiration.
In conclusion, chlorophyll is primarily located in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, specifically in the photosystems within these membranes. While it is also present in the stroma of chloroplasts, it is not found in the matrix of mitochondria.
Which of these is not related to endoplasmic reticulum?- a)It transport materials between various regions in cytoplasm
- b)It behaves as transport channel for proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm.
- c)It can be the site of energy generation.
- d)It can be the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not related to endoplasmic reticulum?
a)
It transport materials between various regions in cytoplasm
b)
It behaves as transport channel for proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm.
c)
It can be the site of energy generation.
d)
It can be the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
|
|
Kalyan Choudhury answered |
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It is a network of interconnected sacs and tubules that extends throughout the cytoplasm. The ER plays a crucial role in many cellular processes, including protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage. However, one of the options listed is not related to the functions of the ER, which is option C: "It can be the site of energy generation." Let's explore why this is the correct answer.
1. Transport of materials
- The ER is responsible for the transport of materials between various regions in the cytoplasm.
- It provides a pathway for the movement of proteins, lipids, and other molecules within the cell.
- This transport function is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring proper functioning of the cell.
2. Transport channel for proteins
- The ER acts as a transport channel for proteins between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- It is involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins, including their folding and modification.
- Proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasmic ribosomes and then transported into the ER for further processing and eventual delivery to their target destinations within or outside the cell.
3. Site for biochemical activities
- The ER can also serve as the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
- It is involved in the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids and cholesterol.
- The ER also plays a role in detoxification processes, such as the metabolism of drugs and other foreign substances.
4. Not the site of energy generation
- Option C, stating that the ER can be the site of energy generation, is incorrect.
- Energy generation primarily occurs in the mitochondria through cellular respiration, where ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced.
- While the ER is involved in various metabolic processes, it is not directly responsible for energy production.
In summary, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in the transport of materials, acts as a transport channel for proteins, and serves as a site for some biochemical activities of the cell. However, it is not the site of energy generation, which primarily occurs in the mitochondria. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It is a network of interconnected sacs and tubules that extends throughout the cytoplasm. The ER plays a crucial role in many cellular processes, including protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage. However, one of the options listed is not related to the functions of the ER, which is option C: "It can be the site of energy generation." Let's explore why this is the correct answer.
1. Transport of materials
- The ER is responsible for the transport of materials between various regions in the cytoplasm.
- It provides a pathway for the movement of proteins, lipids, and other molecules within the cell.
- This transport function is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring proper functioning of the cell.
2. Transport channel for proteins
- The ER acts as a transport channel for proteins between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- It is involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins, including their folding and modification.
- Proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasmic ribosomes and then transported into the ER for further processing and eventual delivery to their target destinations within or outside the cell.
3. Site for biochemical activities
- The ER can also serve as the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
- It is involved in the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids and cholesterol.
- The ER also plays a role in detoxification processes, such as the metabolism of drugs and other foreign substances.
4. Not the site of energy generation
- Option C, stating that the ER can be the site of energy generation, is incorrect.
- Energy generation primarily occurs in the mitochondria through cellular respiration, where ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced.
- While the ER is involved in various metabolic processes, it is not directly responsible for energy production.
In summary, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in the transport of materials, acts as a transport channel for proteins, and serves as a site for some biochemical activities of the cell. However, it is not the site of energy generation, which primarily occurs in the mitochondria. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Cell wall of which one of these is not made up cellulose?- a)Mango tree
- b)Hydrilla
- c)Bacteria
- d)Cactus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall of which one of these is not made up cellulose?
a)
Mango tree
b)
Hydrilla
c)
Bacteria
d)
Cactus
|
|
Bibek Chaudhary answered |
Cell wall of bacteria is not made up of cellulose.
Explanation:
The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane of plants, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. It provides structural support and protection to the cell. In plants, the cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose units bonded together.
Cell wall of Mango tree:
The cell wall of a mango tree is made up of cellulose. Cellulose is a major component of plant cell walls, providing strength and rigidity to the cells.
Cell wall of Hydrilla:
The cell wall of Hydrilla, which is an aquatic plant, is also made up of cellulose. Cellulose is essential for maintaining the shape and structure of plant cells.
Cell wall of Bacteria:
Unlike plants, the cell wall of bacteria is not made up of cellulose. Bacterial cell walls have a different composition, depending on the type of bacteria. Most bacteria have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of sugars and amino acids. This peptidoglycan layer provides strength and protection to the bacterial cell.
Cell wall of Cactus:
The cell wall of a cactus is made up of cellulose, just like other plant cell walls. Cellulose is important for maintaining the shape and structure of the cactus cells, especially in drought conditions.
Conclusion:
In summary, the cell wall of bacteria is not made up of cellulose. Instead, it is composed of peptidoglycan, a polymer that provides strength and protection to bacterial cells. The cell walls of plants, including mango trees, hydrilla, and cacti, are made up of cellulose, which provides structural support to these organisms.
Explanation:
The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane of plants, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. It provides structural support and protection to the cell. In plants, the cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose units bonded together.
Cell wall of Mango tree:
The cell wall of a mango tree is made up of cellulose. Cellulose is a major component of plant cell walls, providing strength and rigidity to the cells.
Cell wall of Hydrilla:
The cell wall of Hydrilla, which is an aquatic plant, is also made up of cellulose. Cellulose is essential for maintaining the shape and structure of plant cells.
Cell wall of Bacteria:
Unlike plants, the cell wall of bacteria is not made up of cellulose. Bacterial cell walls have a different composition, depending on the type of bacteria. Most bacteria have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of sugars and amino acids. This peptidoglycan layer provides strength and protection to the bacterial cell.
Cell wall of Cactus:
The cell wall of a cactus is made up of cellulose, just like other plant cell walls. Cellulose is important for maintaining the shape and structure of the cactus cells, especially in drought conditions.
Conclusion:
In summary, the cell wall of bacteria is not made up of cellulose. Instead, it is composed of peptidoglycan, a polymer that provides strength and protection to bacterial cells. The cell walls of plants, including mango trees, hydrilla, and cacti, are made up of cellulose, which provides structural support to these organisms.
Which of the following is covered by a single membrane?- a)Plastid
- b)Nucleus
- c)Mitochondria
- d)Vacuole
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is covered by a single membrane?
a)
Plastid
b)
Nucleus
c)
Mitochondria
d)
Vacuole
|
|
Advait Desai answered |
A vacuole is covered by a single membrane.
Explanation:
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, fungi, and some protists. It is essentially a storage space within the cell and can contain various substances such as water, nutrients, ions, and waste products. Vacuoles are responsible for maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells and are involved in processes like nutrient storage, detoxification, and cell expansion.
A vacuole is surrounded by a single membrane known as the tonoplast. The tonoplast is a specialized membrane that separates the contents of the vacuole from the cytoplasm of the cell. It is made up of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting the movement of others.
The presence of a single membrane distinguishes vacuoles from other organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids, which are all covered by double membranes.
- The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the genetic material. It is covered by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope, which consists of an outer membrane and an inner membrane with a space called the perinuclear space in between.
- Mitochondria are tiny structures responsible for energy production in the cell. They have a double membrane system consisting of an outer membrane and an inner membrane with folds known as cristae.
- Plastids are organelles found in plant cells and are responsible for various functions such as photosynthesis, storage of pigments, and synthesis of lipids. They also have a double membrane structure.
In summary, while organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids have double membranes, a vacuole is covered by a single membrane known as the tonoplast.
Explanation:
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, fungi, and some protists. It is essentially a storage space within the cell and can contain various substances such as water, nutrients, ions, and waste products. Vacuoles are responsible for maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells and are involved in processes like nutrient storage, detoxification, and cell expansion.
A vacuole is surrounded by a single membrane known as the tonoplast. The tonoplast is a specialized membrane that separates the contents of the vacuole from the cytoplasm of the cell. It is made up of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting the movement of others.
The presence of a single membrane distinguishes vacuoles from other organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids, which are all covered by double membranes.
- The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the genetic material. It is covered by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope, which consists of an outer membrane and an inner membrane with a space called the perinuclear space in between.
- Mitochondria are tiny structures responsible for energy production in the cell. They have a double membrane system consisting of an outer membrane and an inner membrane with folds known as cristae.
- Plastids are organelles found in plant cells and are responsible for various functions such as photosynthesis, storage of pigments, and synthesis of lipids. They also have a double membrane structure.
In summary, while organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids have double membranes, a vacuole is covered by a single membrane known as the tonoplast.
Which cell organelle plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell?- a)Lysosomes
- b)Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- c)Vacuoles
- d)Golgi apparatus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which cell organelle plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell?
a)
Lysosomes
b)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
c)
Vacuoles
d)
Golgi apparatus
|
|
Anuj Sen answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER).
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a cell organelle that plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell. It is a network of membrane-bound tubes and sacs that are involved in various cellular processes.
Key Points:
1. Structure of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes on its surface, which gives it a smooth appearance under a microscope.
- It is interconnected with the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), which has ribosomes on its surface.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in eukaryotic cells, including animal cells and plant cells.
2. Function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Detoxification: One of the primary functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is detoxifying harmful substances. It contains enzymes called cytochrome P450, which are responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying various toxins, drugs, and poisons.
- Lipid Synthesis: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of lipids, such as phospholipids, steroids, and triglycerides. It plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism and the production of hormones.
- Calcium Regulation: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also plays a role in calcium regulation within the cell. It stores and releases calcium ions, which are important for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction and cell signaling.
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: Some cells in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum are involved in glycogen metabolism and the regulation of blood sugar levels.
- Drug Metabolism: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the metabolism of drugs, including the modification and breakdown of various medications.
In conclusion, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a cell organelle that plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell. Its specialized enzymes and metabolic processes make it an essential component for the overall functioning and survival of the cell.
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a cell organelle that plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell. It is a network of membrane-bound tubes and sacs that are involved in various cellular processes.
Key Points:
1. Structure of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes on its surface, which gives it a smooth appearance under a microscope.
- It is interconnected with the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), which has ribosomes on its surface.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in eukaryotic cells, including animal cells and plant cells.
2. Function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Detoxification: One of the primary functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is detoxifying harmful substances. It contains enzymes called cytochrome P450, which are responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying various toxins, drugs, and poisons.
- Lipid Synthesis: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of lipids, such as phospholipids, steroids, and triglycerides. It plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism and the production of hormones.
- Calcium Regulation: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also plays a role in calcium regulation within the cell. It stores and releases calcium ions, which are important for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction and cell signaling.
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: Some cells in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum are involved in glycogen metabolism and the regulation of blood sugar levels.
- Drug Metabolism: The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the metabolism of drugs, including the modification and breakdown of various medications.
In conclusion, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a cell organelle that plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell. Its specialized enzymes and metabolic processes make it an essential component for the overall functioning and survival of the cell.
Which material is present in bulk in plasma membrane say 75%- a)Phospholipids
- b)Polysaccharides
- c)Cholesterol
- d)Protein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which material is present in bulk in plasma membrane say 75%
a)
Phospholipids
b)
Polysaccharides
c)
Cholesterol
d)
Protein
|
|
Mohit Chavan answered |
Understanding the Composition of Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is crucial for maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating communication between the cell and its environment. Its composition primarily includes phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and polysaccharides.
Key Composition
- Phospholipids (75%)
- Phospholipids are the predominant component of the plasma membrane, constituting about 75% of its mass.
- They form a bilayer structure, with hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads facing outward and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails facing inward.
- This arrangement creates a semi-permeable membrane that allows selective passage of substances in and out of the cell.
- Proteins
- Membrane proteins, which can be integral or peripheral, play various roles, including transport, signaling, and structural support.
- Though significant, proteins comprise a lesser percentage of the membrane compared to phospholipids.
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol molecules are interspersed within the phospholipid bilayer, contributing to membrane fluidity and stability.
- They prevent the fatty acid chains of the phospholipids from packing too closely, thus maintaining membrane flexibility.
- Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are usually found on the extracellular surface of the membrane, forming glycoproteins and glycolipids that aid in cell recognition and communication.
- However, they make up a much smaller portion compared to phospholipids.
Conclusion
In summary, phospholipids are the major constituents of the plasma membrane, comprising about 75% of its structure. This unique composition allows cells to maintain their shape, regulate material exchange, and communicate effectively with their surroundings.
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is crucial for maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating communication between the cell and its environment. Its composition primarily includes phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and polysaccharides.
Key Composition
- Phospholipids (75%)
- Phospholipids are the predominant component of the plasma membrane, constituting about 75% of its mass.
- They form a bilayer structure, with hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads facing outward and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails facing inward.
- This arrangement creates a semi-permeable membrane that allows selective passage of substances in and out of the cell.
- Proteins
- Membrane proteins, which can be integral or peripheral, play various roles, including transport, signaling, and structural support.
- Though significant, proteins comprise a lesser percentage of the membrane compared to phospholipids.
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol molecules are interspersed within the phospholipid bilayer, contributing to membrane fluidity and stability.
- They prevent the fatty acid chains of the phospholipids from packing too closely, thus maintaining membrane flexibility.
- Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are usually found on the extracellular surface of the membrane, forming glycoproteins and glycolipids that aid in cell recognition and communication.
- However, they make up a much smaller portion compared to phospholipids.
Conclusion
In summary, phospholipids are the major constituents of the plasma membrane, comprising about 75% of its structure. This unique composition allows cells to maintain their shape, regulate material exchange, and communicate effectively with their surroundings.
Which of the following has an irregular or variable shape?- a)Amoeba
- b)Euglena
- c)Acetabularia
- d)Paramecium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has an irregular or variable shape?
a)
Amoeba
b)
Euglena
c)
Acetabularia
d)
Paramecium
|
|
Srishti Sarkar answered |
Irregular or variable shape
Amoeba is the correct answer as it has an irregular or variable shape. Let's further understand why amoeba has an irregular shape.
Explanation
Amoeba is a unicellular organism belonging to the kingdom Protista. It is a microscopic organism that can be found in freshwater bodies such as ponds and lakes. Amoebas are known for their ability to change their shape constantly and have an irregular or variable shape. This is due to the absence of a fixed cell wall or a rigid skeleton.
Morphological features of Amoeba
Amoeba has a simple structure with the following morphological features:
1. Shape: Amoeba appears irregular in shape and does not have a fixed body form. It can change its shape by extending finger-like projections called pseudopodia.
2. Pseudopodia: Pseudopodia are temporary projections of the cytoplasm that help in locomotion and capturing food. Amoeba extends pseudopodia in various directions, allowing it to move and engulf its prey.
3. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm of amoeba is granular and contains various organelles such as nucleus, food vacuoles, and contractile vacuoles.
4. Nucleus: Amoeba has a single nucleus that controls the cellular activities.
5. Contractile vacuole: It helps in maintaining the water balance of the cell by expelling excess water from the cytoplasm.
Importance of irregular shape
The irregular shape of amoeba is essential for its survival and functioning. Here are a few reasons why the irregular shape is beneficial for amoeba:
1. Locomotion: Amoeba uses its pseudopodia to move in search of food or to escape from unfavorable conditions. The irregular shape allows it to change direction easily and navigate through its environment.
2. Feeding: Amoeba captures its prey by extending pseudopodia around it and forming a food vacuole. The irregular shape helps in engulfing and trapping the food efficiently.
3. Surface area to volume ratio: The irregular shape increases the surface area to volume ratio of amoeba, allowing for efficient exchange of gases and nutrients with the environment.
4. Adaptability: The irregular shape of amoeba allows it to adapt to various environmental conditions. It can change its shape to squeeze through narrow spaces or to avoid predators.
In conclusion, amoeba has an irregular or variable shape due to the absence of a fixed cell wall or skeleton. This shape enables amoeba to perform various functions such as locomotion, feeding, and adaptability, making it a successful and versatile organism.
Amoeba is the correct answer as it has an irregular or variable shape. Let's further understand why amoeba has an irregular shape.
Explanation
Amoeba is a unicellular organism belonging to the kingdom Protista. It is a microscopic organism that can be found in freshwater bodies such as ponds and lakes. Amoebas are known for their ability to change their shape constantly and have an irregular or variable shape. This is due to the absence of a fixed cell wall or a rigid skeleton.
Morphological features of Amoeba
Amoeba has a simple structure with the following morphological features:
1. Shape: Amoeba appears irregular in shape and does not have a fixed body form. It can change its shape by extending finger-like projections called pseudopodia.
2. Pseudopodia: Pseudopodia are temporary projections of the cytoplasm that help in locomotion and capturing food. Amoeba extends pseudopodia in various directions, allowing it to move and engulf its prey.
3. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm of amoeba is granular and contains various organelles such as nucleus, food vacuoles, and contractile vacuoles.
4. Nucleus: Amoeba has a single nucleus that controls the cellular activities.
5. Contractile vacuole: It helps in maintaining the water balance of the cell by expelling excess water from the cytoplasm.
Importance of irregular shape
The irregular shape of amoeba is essential for its survival and functioning. Here are a few reasons why the irregular shape is beneficial for amoeba:
1. Locomotion: Amoeba uses its pseudopodia to move in search of food or to escape from unfavorable conditions. The irregular shape allows it to change direction easily and navigate through its environment.
2. Feeding: Amoeba captures its prey by extending pseudopodia around it and forming a food vacuole. The irregular shape helps in engulfing and trapping the food efficiently.
3. Surface area to volume ratio: The irregular shape increases the surface area to volume ratio of amoeba, allowing for efficient exchange of gases and nutrients with the environment.
4. Adaptability: The irregular shape of amoeba allows it to adapt to various environmental conditions. It can change its shape to squeeze through narrow spaces or to avoid predators.
In conclusion, amoeba has an irregular or variable shape due to the absence of a fixed cell wall or skeleton. This shape enables amoeba to perform various functions such as locomotion, feeding, and adaptability, making it a successful and versatile organism.
Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as- a)Shrinkage of nucleoplasm
- b)Shrinkage of cytoplasm is hypertonic medium
- c)Break down (lysis) of plasma membrane in hypotonic medium
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as
a)
Shrinkage of nucleoplasm
b)
Shrinkage of cytoplasm is hypertonic medium
c)
Break down (lysis) of plasma membrane in hypotonic medium
d)
None of the above.

|
Debolina Iyer answered |
Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as shrinkage of cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium.
Plasmolysis is a phenomenon that occurs in plant cells when they are placed in a hypertonic solution. In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell. As a result, water from inside the cell moves out to the surrounding solution through osmosis. This loss of water causes the cytoplasm to shrink away from the cell wall, resulting in plasmolysis.
Explanation:
1. Hypertonic medium:
- Plasmolysis occurs in a hypertonic medium where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell.
- The hypertonic medium creates a concentration gradient that causes water to move out of the cell.
2. Shrinkage of cytoplasm:
- As water moves out of the cell, the cytoplasm loses water and shrinks away from the cell wall.
- This shrinkage of the cytoplasm is a characteristic feature of plasmolysis.
3. Cell wall:
- The cell wall remains intact during plasmolysis and does not shrink.
- This is because the cell wall provides structural support and prevents the cell from collapsing completely.
4. Plasma membrane:
- The plasma membrane also contracts and pulls away from the cell wall as the cytoplasm shrinks.
- However, it does not break down (lysis) during plasmolysis in a hypertonic medium.
5. Reversibility:
- Plasmolysis is a reversible process. When a plasmolyzed cell is placed in a hypotonic medium (where the concentration of solutes is lower outside the cell), water moves back into the cell through osmosis, and the cell regains its turgidity.
In conclusion, plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as the shrinkage of the cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium. It occurs when water moves out of the cell, causing the cytoplasm to shrink away from the cell wall. The plasma membrane contracts but does not break down during plasmolysis. Plasmolysis is a reversible process and the cell can regain its turgidity when placed in a hypotonic medium.
Plasmolysis is a phenomenon that occurs in plant cells when they are placed in a hypertonic solution. In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell. As a result, water from inside the cell moves out to the surrounding solution through osmosis. This loss of water causes the cytoplasm to shrink away from the cell wall, resulting in plasmolysis.
Explanation:
1. Hypertonic medium:
- Plasmolysis occurs in a hypertonic medium where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell.
- The hypertonic medium creates a concentration gradient that causes water to move out of the cell.
2. Shrinkage of cytoplasm:
- As water moves out of the cell, the cytoplasm loses water and shrinks away from the cell wall.
- This shrinkage of the cytoplasm is a characteristic feature of plasmolysis.
3. Cell wall:
- The cell wall remains intact during plasmolysis and does not shrink.
- This is because the cell wall provides structural support and prevents the cell from collapsing completely.
4. Plasma membrane:
- The plasma membrane also contracts and pulls away from the cell wall as the cytoplasm shrinks.
- However, it does not break down (lysis) during plasmolysis in a hypertonic medium.
5. Reversibility:
- Plasmolysis is a reversible process. When a plasmolyzed cell is placed in a hypotonic medium (where the concentration of solutes is lower outside the cell), water moves back into the cell through osmosis, and the cell regains its turgidity.
In conclusion, plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as the shrinkage of the cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium. It occurs when water moves out of the cell, causing the cytoplasm to shrink away from the cell wall. The plasma membrane contracts but does not break down during plasmolysis. Plasmolysis is a reversible process and the cell can regain its turgidity when placed in a hypotonic medium.
Cytoplasm is- a)Unit mass of protoplasm
- b)Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane
- c)Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane and cell organelles
- d)Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane and nucleus.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cytoplasm is
a)
Unit mass of protoplasm
b)
Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane
c)
Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane and cell organelles
d)
Protoplasm excluding plasma membrane and nucleus.
|
|
Safiya Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
Definition of Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, excluding the nucleus and other organelles.
Components of Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm consists of cytosol, a gel-like substance where organelles are suspended, and various cytoplasmic inclusions like ribosomes, enzymes, and nutrients.
Exclusion of Plasma Membrane and Nucleus:
- When we refer to cytoplasm excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, we are essentially talking about the cytosol and cytoplasmic inclusions present within the cell.
- This definition helps in understanding the composition of the cell's internal environment, which is essential for various cellular processes like metabolism, protein synthesis, and transportation.
Significance of Understanding Cytoplasm:
- Understanding the composition and functions of cytoplasm is crucial for studying cell biology and cellular processes.
- It plays a vital role in maintaining the cell's shape, supporting organelles, and facilitating intracellular transport.
In conclusion, cytoplasm excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus refers to the cytosol and cytoplasmic inclusions present within the cell, which are essential for various cellular functions.
Definition of Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, excluding the nucleus and other organelles.
Components of Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm consists of cytosol, a gel-like substance where organelles are suspended, and various cytoplasmic inclusions like ribosomes, enzymes, and nutrients.
Exclusion of Plasma Membrane and Nucleus:
- When we refer to cytoplasm excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, we are essentially talking about the cytosol and cytoplasmic inclusions present within the cell.
- This definition helps in understanding the composition of the cell's internal environment, which is essential for various cellular processes like metabolism, protein synthesis, and transportation.
Significance of Understanding Cytoplasm:
- Understanding the composition and functions of cytoplasm is crucial for studying cell biology and cellular processes.
- It plays a vital role in maintaining the cell's shape, supporting organelles, and facilitating intracellular transport.
In conclusion, cytoplasm excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus refers to the cytosol and cytoplasmic inclusions present within the cell, which are essential for various cellular functions.
Solute concentration is higher in the external solution- a)Hypotonic
- b)Hypertonic
- c)Isotonic
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Solute concentration is higher in the external solution
a)
Hypotonic
b)
Hypertonic
c)
Isotonic
d)
None of these
|
|
Sameer Chaudhary answered |
Answer:
Hypertonic
Explanation:
When comparing the concentration of solute in the external solution, there are three possible scenarios: hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic.
- Hypotonic solution: In a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solute is lower in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is a higher concentration of water molecules in the external solution, which would cause water to move into the cell through osmosis. The net flow of water would be from the external solution into the cell, resulting in the cell swelling or even bursting.
- Hypertonic solution: In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solute is higher in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is a lower concentration of water molecules in the external solution, which would cause water to move out of the cell through osmosis. The net flow of water would be from the cell into the external solution, resulting in the cell shrinking or even shriveling.
- Isotonic solution: In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute is the same in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is an equal concentration of water molecules in both the external solution and the cell. In an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water into or out of the cell, and the cell remains in its normal state.
In the given question, the solute concentration is stated to be higher in the external solution. Therefore, the correct answer is hypertonic as the solute concentration is higher in the external solution compared to the internal solution.
Hypertonic
Explanation:
When comparing the concentration of solute in the external solution, there are three possible scenarios: hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic.
- Hypotonic solution: In a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solute is lower in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is a higher concentration of water molecules in the external solution, which would cause water to move into the cell through osmosis. The net flow of water would be from the external solution into the cell, resulting in the cell swelling or even bursting.
- Hypertonic solution: In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solute is higher in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is a lower concentration of water molecules in the external solution, which would cause water to move out of the cell through osmosis. The net flow of water would be from the cell into the external solution, resulting in the cell shrinking or even shriveling.
- Isotonic solution: In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute is the same in the external solution compared to the internal solution. This means that there is an equal concentration of water molecules in both the external solution and the cell. In an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water into or out of the cell, and the cell remains in its normal state.
In the given question, the solute concentration is stated to be higher in the external solution. Therefore, the correct answer is hypertonic as the solute concentration is higher in the external solution compared to the internal solution.
Which of the following is incorrect pair?- a)Lysosome – Recretory granules
- b)Mitochondria – Power house of the cell
- c)Chloroplast – Kitchen of the cell
- d)Nucleus – Brain of the cell.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect pair?
a)
Lysosome – Recretory granules
b)
Mitochondria – Power house of the cell
c)
Chloroplast – Kitchen of the cell
d)
Nucleus – Brain of the cell.

|
Prerna Chavan answered |
Incorrect Pair:
Lysosome – Recretory granules
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes. They are responsible for breaking down various molecules within the cell. On the other hand, secretory granules are vesicles that store and release various substances such as hormones or enzymes to the outside of the cell.
Correct Pair:
- Mitochondria – Power house of the cell
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell because they are responsible for generating most of the cell's energy through the process of cellular respiration.
- Chloroplast – Kitchen of the cell
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy-rich molecules.
- Nucleus – Brain of the cell
The nucleus is often referred to as the brain of the cell because it contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities.
In summary, the incorrect pair in the given options is lysosome – secretory granules.
Kitchen of the cell is- a)Endoplasmic reticulum
- b)Golgi apparatus
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Kitchen of the cell is
a)
Endoplasmic reticulum
b)
Golgi apparatus
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Chloroplast is a plastid that is involved in the synthesis of carbohydeates through photosynthesis and hence called as the kitchen of the cell.
Main difference between animal cell and plant cell is:- a)Growth
- b)Respiration
- c)Nutrition
- d)Movement
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main difference between animal cell and plant cell is:
a)
Growth
b)
Respiration
c)
Nutrition
d)
Movement
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The animal cell is heterotrophic, i.e., cannot synthesize their own food. They have to obtain food from other organisms.
Plant cells possess chloroplast using which they can synthesize their own food material, i.e., they are autotrophic. Therefore, their mode of nutrition differs.
Which one of the following is called the suicide bag of the cell?- a)Ribosomes
- b)Lysosomes
- c)Centrioles
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is called the suicide bag of the cell?
a)
Ribosomes
b)
Lysosomes
c)
Centrioles
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Lysosomes are called suicide bags because in the case of adversity they digest their own cell. They have hydrolytic enzymes that get activated at pH 4.8.
Which one of the following is absent in plant cell?- a)Mitochondria
- b)Centrioles
- c)Ribosomes
- d)Nucleus.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is absent in plant cell?
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Centrioles
c)
Ribosomes
d)
Nucleus.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Centrioles are the part of centrosome located near the nucleus in the animal cell and some lower plant cells. But in higher plants, it is absent. It is involved in the formation of spindle fibre during cell division.
Sheet of photosynthesis is- a)Chromoplast
- b)Leucoplast
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Omyloplast
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sheet of photosynthesis is
a)
Chromoplast
b)
Leucoplast
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Omyloplast
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The chloroplast is a type of plastid which produces green coloured pigment. The chloroplast is involved in carrying out photosynthesis. It gives a green colour to leaves.
Organelle without a cell membrane is- a)Chloroplast
- b)Nucleus
- c)Ribosome
- d)Mitochondrion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Organelle without a cell membrane is
a)
Chloroplast
b)
Nucleus
c)
Ribosome
d)
Mitochondrion
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Following are the cell organelles that are not bounded by the unit membrane
Ribosomes, Cytoskeletal structures, Centrioles, Basal bodies, Cilia and flagella.
Which one of the following is prokaryotic?- a)Blue-green algae
- b)Fungus
- c)Fly
- d)Plasmodium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is prokaryotic?
a)
Blue-green algae
b)
Fungus
c)
Fly
d)
Plasmodium
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells. These cells lack membrane-bound organelles and true nucleus. Prokaryotic organisms are unicellular organisms, which reproduce through binary fission e.g., bacteria, mycoplasma, and blue-green algae.
Who proposed the cell theory?- a)Watson and Crick
- b)Schleiden and Schwann
- c)Darwin and Wallace
- d)Mendel and Morgan
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who proposed the cell theory?
a)
Watson and Crick
b)
Schleiden and Schwann
c)
Darwin and Wallace
d)
Mendel and Morgan
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Cell theory was proposed by a German botanist, Matthias Schleiden, and English zoologist, Theodor Schwann in the year 1839. The cell theory states
• Cells are the building blocks of living organisms.
• All living organisms are composed of cells and a cell is the basic structural and functional unit
• All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Middle lamella is formed of- a)Calcium pectate
- b)Cellulose
- c)Lignin
- d)Hemicelluloses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Middle lamella is formed of
a)
Calcium pectate
b)
Cellulose
c)
Lignin
d)
Hemicelluloses
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The middle lamella is made up of calcium and magnesium pectates. In a mature plant cell, it is the outermost layer of the cell wall. In plants, the pectins form a unified and continuous layer between adjacent cells.
Nucleolus is a sheet of- a)RNA synthesis
- b)Enzyme synthesis
- c)Ribosome
- d)Protein synthesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleolus is a sheet of
a)
RNA synthesis
b)
Enzyme synthesis
c)
Ribosome
d)
Protein synthesis
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The nucleolus contains DNA, RNA and proteins. It is a ribosome factory. Cells from other species often have multiple nucleoli.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Root hairs of plants obsorve water from soil through:- a)Osmosis
- b)Imbibition
- c)Diffusion
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Root hairs of plants obsorve water from soil through:
a)
Osmosis
b)
Imbibition
c)
Diffusion
d)
All of these.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Osmosis is the process of the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of higher solvent concentration to the region of lower solvent concentration. Osmosis is of great importance in biological processes. As the soil has a higher concentration of water as compared to the root hair cells thus osmosis occurs.
Rough ER contains- a)Detoxification centres
- b)Ribosomes
- c)Lysosomes
- d)Carbohydrate synthesizing machinery.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rough ER contains
a)
Detoxification centres
b)
Ribosomes
c)
Lysosomes
d)
Carbohydrate synthesizing machinery.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum contains ribosomes attached to its surface for synthesizing proteins.
Bulk transport occurs through- a)Exocytosis
- b)Endocytosis
- c)Endoosmosis
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bulk transport occurs through
a)
Exocytosis
b)
Endocytosis
c)
Endoosmosis
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Bulk transport occurs through endocytosis and exocytosis. The process by which cell engulfs food is called endocytosis and ejects solid is called exocytosis.
Protein storing plastid is- a)Aleuroplast
- b)Elaioplast
- c)Omyloplast
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein storing plastid is
a)
Aleuroplast
b)
Elaioplast
c)
Omyloplast
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Protein storing plastids are called Aleuroplast.
The colourless plastid or leucoplast gets differentiated to form alueroplast or proteinoplast.
Its main function is to store proteins in plant cells.
So the correct answer is 'Aleuroplasts'.
The idea ‘omins cellula a cellula’ which means that all living cells arise from pre-existing cells, was given by- a)Purkinje
- b)Schleiden
- c)Rudolf Virchow
- d)Robert brown
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The idea ‘omins cellula a cellula’ which means that all living cells arise from pre-existing cells, was given by
a)
Purkinje
b)
Schleiden
c)
Rudolf Virchow
d)
Robert brown
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Rudolf Virchow modified the cell theory and gave the concept of 'omnis cellula e cellulae' - means new cells develop by division of the pre-existing cells. This is called theory of cell lineage or common ancestry.
So, the correct answer is 'Rudolf Virchow'.
Chromosomes are made up of- a)RNA
- b)DNA
- c)Protein
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Chromosomes are made up of
a)
RNA
b)
DNA
c)
Protein
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The chromosomes are made of tightly folded/packed DNA molecules. These DNA molecules are kept in a compact state with help of certain proteins, namely the nucleosome protein made of Histone octamers and the scaffold proteins. Hence, the chromosomes are made up of both DNA and proteins.
Genetic material of a eukaryotic cell is contained in- a)Nucleus
- b)Nucleoid
- c)Nucleolus
- d)Nucleoplasm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic material of a eukaryotic cell is contained in
a)
Nucleus
b)
Nucleoid
c)
Nucleolus
d)
Nucleoplasm
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The nucleus is bound with the double membrane in a eukaryotic cell in which most of the genetic material is present. The genetic material contains DNA and RNA.
Plasmolysis occurs due to- a)Exomosis
- b)Endosmosis
- c)Ssmosis
- d)Absorption.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmolysis occurs due to
a)
Exomosis
b)
Endosmosis
c)
Ssmosis
d)
Absorption.
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Exosmosis is a process in which the water molecules move from higher concentration region of the cell to the lower concentration region of surroundings through the cell membrane. Due to this, the cell shrinks. This happens when a cell is kept in hypertonic solution, i.e., a solution with higher solute concentration. Exosmosis is also termed as plasmolysis.
The in foldings in mitochondria are known as- a)Cristae
- b)Matrix
- c)Stroma
- d)Cisternal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The in foldings in mitochondria are known as
a)
Cristae
b)
Matrix
c)
Stroma
d)
Cisternal
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Cristae are folds in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that increases its surface area for chemical reactions to occur and gives the inner mitochondrial membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape. It is the site of aerobic cellular respiration and has important proteins attached on it, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes.
The answer is A) Cristae.
Lysosomes arise from- a)Nucleus
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Golgi apparatus
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lysosomes arise from
a)
Nucleus
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Golgi apparatus
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Lysosomes are formed by budding of the vesicles from Golgi bodies. It contains hydrolytic enzymes. The hydrolytic enzyme helps in the intracellular digestion. It helps in the removal of cell debris. They act as suicidal bags of the cell.
So, the correct answer is option C.
The term ‘cell’ was given by- a)Robert Brown
- b)Flemming
- c)Robert Hooke
- d)Leeuwen hoek
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘cell’ was given by
a)
Robert Brown
b)
Flemming
c)
Robert Hooke
d)
Leeuwen hoek
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
In the 1660s, Robert Hooke looked through a primitive microscope at a thinly cut piece of cork. He saw a series of walled boxes that reminded him of the tiny rooms, or cellula, occupied by monks. Medical historian Dr. Howard Markel discusses Hooke's coining of the word "cell."
The longest cell in the human body is- a)Muscle cell
- b)Nerve cell
- c)Kidney cell
- d)Liver cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The longest cell in the human body is
a)
Muscle cell
b)
Nerve cell
c)
Kidney cell
d)
Liver cell
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Neurons or nerve cells can be up to 3 feet long. A typical neuron has a cell morphology called soma, hair-like structures called dendrites, and an axon. Neurons are specialized in conveying knowledge throughout the body. The sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons are three types of neurons. Neurons have a membrane built to forward information to other cells.
A plant cell is placed in hypotonic solution will- a)Shrink
- b)Swell
- c)No change
- d)Exosmosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant cell is placed in hypotonic solution will
a)
Shrink
b)
Swell
c)
No change
d)
Exosmosis
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
When a cell is placed in the hypotonic medium, water will enter into the cell due to endosmosis and turgor pressure of cell will increase.
The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotes is also known as- a)Nucleus
- b)Nucleoid
- c)Nucleolus
- d)Nucleic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotes is also known as
a)
Nucleus
b)
Nucleoid
c)
Nucleolus
d)
Nucleic acid
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Prokaryotic cells are the primitive organism, which has a disorganized nucleus. It is devoid of any membrane-bounded organelles. The genetic material consists of chromatin threads without histones. Nucleoid is the region in a prokaryote, which contains all or most of the genetic material. The genetic material is in direct contact with the cytoplasm.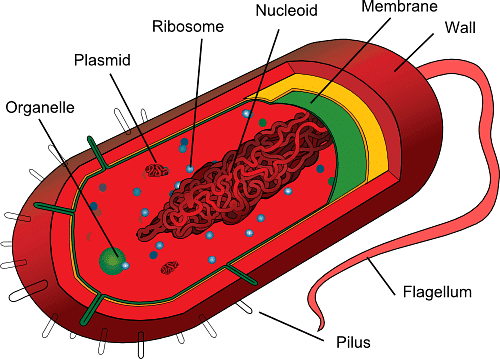
So, the correct answer is option B.

The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell- a)Mitochondria
- b)Plastids
- c)Ribosomes
- d)Lysosomes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Plastids
c)
Ribosomes
d)
Lysosomes
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two different types of cells. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
The ribosome is the only organelle that can be seen in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, though the types of ribosomes in the two types of cells vary.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Which one of the following is called the powerhouse of the cell?- a)Ribosomes
- b)Plastids
- c)Mitochondria
- d)Vacuoles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is called the powerhouse of the cell?
a)
Ribosomes
b)
Plastids
c)
Mitochondria
d)
Vacuoles
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) molecules. ATP is known as the energy currency of the cell. The body uses the energy stored in ATP for making new chemical compounds and for mechanical work.
Thus, the correct answer is 'Mitochondria'.
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by- a)Peroxisomes
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Golgi apparatus
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by
a)
Peroxisomes
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Golgi apparatus
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The endoplasmic reticulum is of two types on the basis of the presence of ribosomes. If the endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes are attached to them then it is called a rough endoplasmic reticulum and if there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum then it is called a smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum produces and transports protein and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum produces and transports lipid which provides a framework to the plasma membrane a known as membrane biogenesis.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Olympiad Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Olympiad Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Olympiad Class 9
28 videos|115 docs|52 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









