All Exams >
UPSC >
Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) >
All Questions
All questions of Environmental Issues for UPSC CSE Exam
Which one of the following diseases is caused by water pollution?- a)Conjunctivitis
- b)Respiratory infections
- c)Diarrhoea
- d)Bronchitis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following diseases is caused by water pollution?
a)
Conjunctivitis
b)
Respiratory infections
c)
Diarrhoea
d)
Bronchitis
|
|
Arka Sarkar answered |
**Water Pollution and Disease**
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, with harmful substances. These substances can come from various sources, including industrial waste, sewage, agricultural runoff, and chemical spills. Water pollution has detrimental effects on both the environment and human health. In the case of human health, water pollution can lead to the spread of various diseases.
**Diarrhea: A Waterborne Disease**
One of the diseases caused by water pollution is diarrhea. Diarrhea is characterized by the frequent passage of loose or watery stools. It is a common illness that affects people of all ages, particularly children under the age of five. Diarrhea is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in developing countries where access to clean and safe water is limited.
**How Water Pollution Causes Diarrhea**
Water pollution can contribute to the spread of diarrheal diseases in several ways:
1. **Contamination with Pathogens**: When water bodies become polluted with fecal matter, they can become reservoirs for disease-causing pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. These pathogens can enter the human body when contaminated water is ingested, leading to the development of diarrhea.
2. **Chemical Contaminants**: Water pollution can also introduce various chemical contaminants into water bodies. These contaminants may include heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. Exposure to these chemicals through contaminated water can irritate the digestive system and contribute to the development of diarrhea.
3. **Inadequate Sanitation**: Water pollution often occurs due to inadequate sanitation practices, such as the improper disposal of sewage and wastewater. When human waste is not properly treated or disposed of, it can contaminate water sources and increase the risk of diarrheal diseases.
**Prevention and Control**
Preventing water pollution is crucial in reducing the incidence of waterborne diseases like diarrhea. Some measures that can be taken to prevent water pollution and ensure access to clean and safe water include:
- **Proper Waste Management**: Implementing proper waste management systems, including the treatment and safe disposal of sewage and wastewater, can prevent the contamination of water bodies.
- **Improved Sanitation**: Providing access to adequate sanitation facilities, such as toilets and handwashing stations, can prevent the spread of diarrheal diseases.
- **Water Treatment**: Implementing effective water treatment methods, such as filtration, disinfection, and chlorination, can help remove pathogens and chemical contaminants from water sources.
- **Public Awareness and Education**: Promoting awareness and educating communities about the importance of clean water, proper sanitation, and hygiene practices can help prevent water pollution and reduce the incidence of waterborne diseases.
In conclusion, water pollution can contribute to the spread of various diseases, including diarrhea. It is essential to implement measures to prevent water pollution and ensure access to clean and safe water for the well-being of individuals and communities.
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, with harmful substances. These substances can come from various sources, including industrial waste, sewage, agricultural runoff, and chemical spills. Water pollution has detrimental effects on both the environment and human health. In the case of human health, water pollution can lead to the spread of various diseases.
**Diarrhea: A Waterborne Disease**
One of the diseases caused by water pollution is diarrhea. Diarrhea is characterized by the frequent passage of loose or watery stools. It is a common illness that affects people of all ages, particularly children under the age of five. Diarrhea is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in developing countries where access to clean and safe water is limited.
**How Water Pollution Causes Diarrhea**
Water pollution can contribute to the spread of diarrheal diseases in several ways:
1. **Contamination with Pathogens**: When water bodies become polluted with fecal matter, they can become reservoirs for disease-causing pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. These pathogens can enter the human body when contaminated water is ingested, leading to the development of diarrhea.
2. **Chemical Contaminants**: Water pollution can also introduce various chemical contaminants into water bodies. These contaminants may include heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. Exposure to these chemicals through contaminated water can irritate the digestive system and contribute to the development of diarrhea.
3. **Inadequate Sanitation**: Water pollution often occurs due to inadequate sanitation practices, such as the improper disposal of sewage and wastewater. When human waste is not properly treated or disposed of, it can contaminate water sources and increase the risk of diarrheal diseases.
**Prevention and Control**
Preventing water pollution is crucial in reducing the incidence of waterborne diseases like diarrhea. Some measures that can be taken to prevent water pollution and ensure access to clean and safe water include:
- **Proper Waste Management**: Implementing proper waste management systems, including the treatment and safe disposal of sewage and wastewater, can prevent the contamination of water bodies.
- **Improved Sanitation**: Providing access to adequate sanitation facilities, such as toilets and handwashing stations, can prevent the spread of diarrheal diseases.
- **Water Treatment**: Implementing effective water treatment methods, such as filtration, disinfection, and chlorination, can help remove pathogens and chemical contaminants from water sources.
- **Public Awareness and Education**: Promoting awareness and educating communities about the importance of clean water, proper sanitation, and hygiene practices can help prevent water pollution and reduce the incidence of waterborne diseases.
In conclusion, water pollution can contribute to the spread of various diseases, including diarrhea. It is essential to implement measures to prevent water pollution and ensure access to clean and safe water for the well-being of individuals and communities.
Ozone holes are more pronounced at the- a)Equator
- b)Tropic of Cancer
- c)Tropic of Capricorn
- d)Poles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozone holes are more pronounced at the
a)
Equator
b)
Tropic of Cancer
c)
Tropic of Capricorn
d)
Poles
|
|
Niti Basak answered |
Ozone Holes: More Pronounced at the Poles
Introduction:
Ozone holes are areas in the Earth's ozone layer where the concentration of ozone becomes significantly depleted. These ozone holes are caused by the release of certain chemicals, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which break down ozone molecules in the stratosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer allows more harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth's surface, posing risks to human health and the environment.
Explanation:
The ozone holes are more pronounced at the poles due to several factors:
1. Atmospheric conditions:
At the poles, the stratospheric conditions are more favorable for the formation of ozone holes. During winter, the polar regions experience a phenomenon called polar vortex, where a strong, stable, and cold air mass forms a swirling pattern. This vortex isolates the polar regions from the rest of the atmosphere, trapping the air and preventing it from mixing with air from lower latitudes. As a result, the polar regions experience extremely low temperatures, which contribute to the formation of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). PSCs provide the surface for chemical reactions that break down ozone molecules.
2. Presence of CFCs:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances released by human activities accumulate in the stratosphere. These substances can remain in the atmosphere for several decades, gradually drifting towards the poles due to atmospheric circulation patterns. As a result, the concentration of CFCs is higher at the poles compared to other latitudes. When exposed to UV radiation, CFCs release chlorine atoms that catalytically destroy ozone molecules.
3. Polar night:
During the polar winter, the polar regions experience an extended period of darkness known as polar night. The absence of sunlight during this period allows the formation of stable polar stratospheric clouds. These clouds provide a surface for chemical reactions involving CFCs and other ozone-depleting substances, leading to an accelerated depletion of ozone.
4. Stratospheric winds:
The polar regions are influenced by strong stratospheric winds, known as polar vortex winds, which circulate around the poles. These winds contribute to the isolation of the polar regions and prevent the mixing of air masses from lower latitudes, leading to the persistence of low temperatures and the accumulation of ozone-depleting substances.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ozone holes are more pronounced at the poles due to a combination of favorable atmospheric conditions, the presence of ozone-depleting substances, the occurrence of polar night, and the influence of polar vortex winds. These factors contribute to the localized depletion of ozone in the polar regions, making them more vulnerable to the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Introduction:
Ozone holes are areas in the Earth's ozone layer where the concentration of ozone becomes significantly depleted. These ozone holes are caused by the release of certain chemicals, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which break down ozone molecules in the stratosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer allows more harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth's surface, posing risks to human health and the environment.
Explanation:
The ozone holes are more pronounced at the poles due to several factors:
1. Atmospheric conditions:
At the poles, the stratospheric conditions are more favorable for the formation of ozone holes. During winter, the polar regions experience a phenomenon called polar vortex, where a strong, stable, and cold air mass forms a swirling pattern. This vortex isolates the polar regions from the rest of the atmosphere, trapping the air and preventing it from mixing with air from lower latitudes. As a result, the polar regions experience extremely low temperatures, which contribute to the formation of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). PSCs provide the surface for chemical reactions that break down ozone molecules.
2. Presence of CFCs:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances released by human activities accumulate in the stratosphere. These substances can remain in the atmosphere for several decades, gradually drifting towards the poles due to atmospheric circulation patterns. As a result, the concentration of CFCs is higher at the poles compared to other latitudes. When exposed to UV radiation, CFCs release chlorine atoms that catalytically destroy ozone molecules.
3. Polar night:
During the polar winter, the polar regions experience an extended period of darkness known as polar night. The absence of sunlight during this period allows the formation of stable polar stratospheric clouds. These clouds provide a surface for chemical reactions involving CFCs and other ozone-depleting substances, leading to an accelerated depletion of ozone.
4. Stratospheric winds:
The polar regions are influenced by strong stratospheric winds, known as polar vortex winds, which circulate around the poles. These winds contribute to the isolation of the polar regions and prevent the mixing of air masses from lower latitudes, leading to the persistence of low temperatures and the accumulation of ozone-depleting substances.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ozone holes are more pronounced at the poles due to a combination of favorable atmospheric conditions, the presence of ozone-depleting substances, the occurrence of polar night, and the influence of polar vortex winds. These factors contribute to the localized depletion of ozone in the polar regions, making them more vulnerable to the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Maximum ozone depletion has been observed in which of the following?- a)The North Pole
- b)The South Pole
- c)The Equator
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum ozone depletion has been observed in which of the following?
a)
The North Pole
b)
The South Pole
c)
The Equator
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Concept:
Ozone Layer:
- Ozone (O3) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. Ozone is a deadly poison.
- Ozone is found in the stratosphere layer of the atmosphere.
- However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings or can split the DNA.
- It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell.
- Ozone is an excellent oxidizing agent as it breaks down into oxygen gas and nascent oxygen. { O3 → O2 + [O] }
- It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope O2, breaking down in the lower atmosphere to O2 or di-oxygen
Its depletion:
- The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s.
- This decrease has been linked to synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
- The government bans those products which contain CFCs.
- Ozone is thermodynamically unstable and decomposes to molecular oxygen. Thus, a dynamic equilibrium exists between the production and decomposition of ozone molecules
Explanation:.
- In recent years, there have been reports of the depletion of this protective ozone layer because of the presence of certain chemicals in the stratosphere.
- The main reason for ozone layer depletion is believed to be the release of chlorofluorocarbon compounds (CFCs), also known as Freons.
- These compounds are non-reactive, non-flammable, non-toxic organic molecules and therefore used in refrigerators, air conditioners, in the production of plastic foam and by the electronic industry for cleaning computer parts etc.
- Once CFCs are released in the atmosphere, they mix with the normal atmospheric gases and eventually reach the stratosphere. Hence option 3 is correct.
- In the 1980s, for the first time, atmospheric scientists working in Antarctica reported about the depletion of the ozone layer commonly known as the ozone hole over the South Pole.
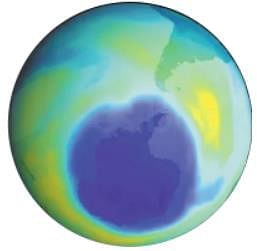
What is the meaning of denial of forest?- a)Neglect of the forest
- b)Afforestation
- c)Growing forests
- d)Forest destruction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the meaning of denial of forest?
a)
Neglect of the forest
b)
Afforestation
c)
Growing forests
d)
Forest destruction
|
|
Ishani Singh answered |
Meaning of Denial of Forest
Denial of forest refers to the act of destroying or degrading a forest, which leads to its disappearance or reduction in size. This can happen due to various reasons such as urbanization, deforestation for agricultural purposes, mining, logging, and industrialization. The consequences of this denial of forest are quite severe, and they can affect the environment, wildlife, and people in several ways.
Consequences of Denial of Forest
1. Loss of biodiversity: Forests are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. When forests are destroyed, many species lose their habitat, and their populations decline or become extinct.
2. Climate change: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to mitigate the effects of climate change. When forests are destroyed, this carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
3. Soil erosion: Forests help to prevent soil erosion by holding the soil together with their roots. When forests are destroyed, the soil becomes exposed to wind and water erosion, which can lead to land degradation and desertification.
4. Water cycle disruption: Forests play a vital role in the water cycle by absorbing rainwater and releasing it slowly into the soil and atmosphere. When forests are destroyed, this water cycle is disrupted, leading to reduced water availability, droughts, and floods.
5. Impact on indigenous people: Many indigenous people depend on forests for their livelihoods and cultural practices. When forests are destroyed, these people lose their way of life and can become displaced and marginalized.
Conclusion
Denial of forest has significant consequences for the environment, wildlife, and people. It is essential to take steps to prevent further forest destruction and promote afforestation and reforestation efforts. This can help to mitigate the effects of climate change, protect biodiversity, and preserve indigenous cultures and ways of life.
Denial of forest refers to the act of destroying or degrading a forest, which leads to its disappearance or reduction in size. This can happen due to various reasons such as urbanization, deforestation for agricultural purposes, mining, logging, and industrialization. The consequences of this denial of forest are quite severe, and they can affect the environment, wildlife, and people in several ways.
Consequences of Denial of Forest
1. Loss of biodiversity: Forests are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. When forests are destroyed, many species lose their habitat, and their populations decline or become extinct.
2. Climate change: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to mitigate the effects of climate change. When forests are destroyed, this carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
3. Soil erosion: Forests help to prevent soil erosion by holding the soil together with their roots. When forests are destroyed, the soil becomes exposed to wind and water erosion, which can lead to land degradation and desertification.
4. Water cycle disruption: Forests play a vital role in the water cycle by absorbing rainwater and releasing it slowly into the soil and atmosphere. When forests are destroyed, this water cycle is disrupted, leading to reduced water availability, droughts, and floods.
5. Impact on indigenous people: Many indigenous people depend on forests for their livelihoods and cultural practices. When forests are destroyed, these people lose their way of life and can become displaced and marginalized.
Conclusion
Denial of forest has significant consequences for the environment, wildlife, and people. It is essential to take steps to prevent further forest destruction and promote afforestation and reforestation efforts. This can help to mitigate the effects of climate change, protect biodiversity, and preserve indigenous cultures and ways of life.
In comparison to pure water, Boiling point of impure water- a)is same
- b)increases
- c)decreases
- d)first decreases then Increases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In comparison to pure water, Boiling point of impure water
a)
is same
b)
increases
c)
decreases
d)
first decreases then Increases
|
|
Meera Saha answered |
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure surrounding it. When a solute such as salt or sugar is added to water, it lowers the vapor pressure of the water, which means it takes longer for the water to boil. This phenomenon is known as boiling point elevation.
Explanation of the Answer
When impurities such as salt or sugar are added to pure water, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is because the presence of the solute lowers the vapor pressure of the solution, which means more heat is required to reach the boiling point. This is why we add salt to water when boiling pasta, as the higher boiling point allows the pasta to cook more evenly.
Therefore, in comparison to pure water, the boiling point of impure water increases. This is because the impurities in the water lower the vapor pressure, which means more heat is required to reach boiling point.
Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure surrounding it. When a solute such as salt or sugar is added to water, it lowers the vapor pressure of the water, which means it takes longer for the water to boil. This phenomenon is known as boiling point elevation.
Explanation of the Answer
When impurities such as salt or sugar are added to pure water, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is because the presence of the solute lowers the vapor pressure of the solution, which means more heat is required to reach the boiling point. This is why we add salt to water when boiling pasta, as the higher boiling point allows the pasta to cook more evenly.
Therefore, in comparison to pure water, the boiling point of impure water increases. This is because the impurities in the water lower the vapor pressure, which means more heat is required to reach boiling point.
Areas that are under the influence of DDT may observe a decline in the population of birds. This is due to the fact that- a)Birds stopped laying eggs altogether
- b)The eggs did not hatch
- c)Predation of the eggs increased
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Areas that are under the influence of DDT may observe a decline in the population of birds. This is due to the fact that
a)
Birds stopped laying eggs altogether
b)
The eggs did not hatch
c)
Predation of the eggs increased
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Niharika Roy answered |
DDT and Bird Population Decline
Introduction:
DDT or Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane is an insecticide that was widely used in the mid-20th century to control agricultural pests and diseases that spread through insects. It is a persistent organic pollutant that accumulates in the food chain, causing adverse effects on human and animal health. DDT was banned in most countries in the 1970s due to its harmful effects on the environment.
Effect of DDT on Bird Population:
DDT is known to cause a decline in the population of birds that feed on insects, such as eagles, falcons, and ospreys. This is due to the fact that DDT affects the reproductive system of birds, leading to a decline in their egg production and hatching rates.
Eggshell Thinning:
DDT causes the eggshells of birds to become thin, making them more susceptible to breakage. When birds lay their eggs, the shells are too thin to withstand the weight of the incubating parent, leading to the death of the embryo inside. This phenomenon is known as eggshell thinning, and it has been observed in several bird species, including Bald Eagles, Peregrine Falcons, and Brown Pelicans.
Decline in Hatching Rates:
Due to the thinning of eggshells, the hatching rates of birds that have been exposed to DDT decline significantly. This means that fewer chicks are born, leading to a decline in the overall population of the bird species.
Conclusion:
The decline in the population of birds due to DDT is a significant environmental issue. It is essential to limit the use of DDT and other persistent organic pollutants to protect the health and well-being of the ecosystem. The ban on DDT in most countries has helped to restore the populations of several bird species, but the effects of DDT are still felt in some areas where it was used extensively in the past.
Introduction:
DDT or Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane is an insecticide that was widely used in the mid-20th century to control agricultural pests and diseases that spread through insects. It is a persistent organic pollutant that accumulates in the food chain, causing adverse effects on human and animal health. DDT was banned in most countries in the 1970s due to its harmful effects on the environment.
Effect of DDT on Bird Population:
DDT is known to cause a decline in the population of birds that feed on insects, such as eagles, falcons, and ospreys. This is due to the fact that DDT affects the reproductive system of birds, leading to a decline in their egg production and hatching rates.
Eggshell Thinning:
DDT causes the eggshells of birds to become thin, making them more susceptible to breakage. When birds lay their eggs, the shells are too thin to withstand the weight of the incubating parent, leading to the death of the embryo inside. This phenomenon is known as eggshell thinning, and it has been observed in several bird species, including Bald Eagles, Peregrine Falcons, and Brown Pelicans.
Decline in Hatching Rates:
Due to the thinning of eggshells, the hatching rates of birds that have been exposed to DDT decline significantly. This means that fewer chicks are born, leading to a decline in the overall population of the bird species.
Conclusion:
The decline in the population of birds due to DDT is a significant environmental issue. It is essential to limit the use of DDT and other persistent organic pollutants to protect the health and well-being of the ecosystem. The ban on DDT in most countries has helped to restore the populations of several bird species, but the effects of DDT are still felt in some areas where it was used extensively in the past.
Oxygen demanding wastes- a)Decrease the oxygen level in water.
- b)Increase the oxygen level in water.
- c)Do not change the oxygen level in water.
- d)Increase the temperature of water.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen demanding wastes
a)
Decrease the oxygen level in water.
b)
Increase the oxygen level in water.
c)
Do not change the oxygen level in water.
d)
Increase the temperature of water.
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
- Oxygen demanding wastes are organic compounds, such as sewage and agricultural runoff, which decompose through microbial action in water.
- The process of microbial decomposition requires oxygen, and as a result, these wastes decrease the oxygen level in the water.
- If the oxygen level drops below a certain level, aquatic organisms can die due to suffocation, which leads to a condition called hypoxia.
- This can also cause a decrease in biodiversity and ecological productivity in water bodies.
- Therefore, it is important to reduce the discharge of oxygen-demanding wastes into water bodies to maintain the ecological balance.
Non-point sources of water pollution are:A. from specific location
B. diffuse
C. episodic
D. identifiable
E. difficult to monitorChoose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)B, C and E only
- b)A, B and C only
- c)B, C and D only
- d)C, D and E only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Non-point sources of water pollution are:
A. from specific location
B. diffuse
C. episodic
D. identifiable
E. difficult to monitor
B. diffuse
C. episodic
D. identifiable
E. difficult to monitor
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
B, C and E only
b)
A, B and C only
c)
B, C and D only
d)
C, D and E only
|
|
Debanshi Desai answered |
Non-point sources of water pollution refer to sources that are diffuse and difficult to pinpoint to a specific location. Let's understand this in detail.
Definition of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
Non-point sources of water pollution refer to pollution that comes from various sources and is not discharged from a specific location, such as a factory or sewage treatment plant. Examples of non-point sources of pollution include agricultural runoff, stormwater runoff, and residential runoff.
Characteristics of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
The characteristics of non-point sources of water pollution are as follows:
- Diffuse: Non-point sources of pollution come from various sources, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the pollution.
- Episodic: Non-point sources of pollution occur at different times and are not constant.
- Difficult to monitor: Non-point sources of pollution are difficult to monitor as they are not discharged from a specific location.
Examples of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
Some examples of non-point sources of water pollution are:
- Agricultural runoff: Pesticides and fertilizers used in agriculture can wash into nearby water bodies, causing water pollution.
- Stormwater runoff: When it rains, water runs off surfaces such as roads, parking lots, and rooftops, picking up pollutants such as oil, grease, and metals before entering the water system.
- Residential runoff: Residential areas can contribute to water pollution through activities such as lawn care, car washing, and improper disposal of household chemicals.
Conclusion
Non-point sources of water pollution are a significant environmental concern as they can have a cumulative impact on water quality. It is essential to understand the characteristics and sources of non-point sources of pollution to implement effective pollution control measures.
Definition of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
Non-point sources of water pollution refer to pollution that comes from various sources and is not discharged from a specific location, such as a factory or sewage treatment plant. Examples of non-point sources of pollution include agricultural runoff, stormwater runoff, and residential runoff.
Characteristics of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
The characteristics of non-point sources of water pollution are as follows:
- Diffuse: Non-point sources of pollution come from various sources, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the pollution.
- Episodic: Non-point sources of pollution occur at different times and are not constant.
- Difficult to monitor: Non-point sources of pollution are difficult to monitor as they are not discharged from a specific location.
Examples of Non-Point Sources of Water Pollution
Some examples of non-point sources of water pollution are:
- Agricultural runoff: Pesticides and fertilizers used in agriculture can wash into nearby water bodies, causing water pollution.
- Stormwater runoff: When it rains, water runs off surfaces such as roads, parking lots, and rooftops, picking up pollutants such as oil, grease, and metals before entering the water system.
- Residential runoff: Residential areas can contribute to water pollution through activities such as lawn care, car washing, and improper disposal of household chemicals.
Conclusion
Non-point sources of water pollution are a significant environmental concern as they can have a cumulative impact on water quality. It is essential to understand the characteristics and sources of non-point sources of pollution to implement effective pollution control measures.
Identify the correct sequence of continents in decreasing order of their yearly carbon dioxide emissions, at presentA. Africa
B. Asia
C. Europe
D. North AmericaChoose the correct answer from the option given below- a)B, D, A, C
- b)B, D, C, A
- c)D, B, C, A
- d)D, C, B, A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct sequence of continents in decreasing order of their yearly carbon dioxide emissions, at present
A. Africa
B. Asia
C. Europe
D. North America
B. Asia
C. Europe
D. North America
Choose the correct answer from the option given below
a)
B, D, A, C
b)
B, D, C, A
c)
D, B, C, A
d)
D, C, B, A
|
|
Lakshmi Singh answered |
Explanation:
The correct sequence of continents in decreasing order of their yearly carbon dioxide emissions at present is as follows:
B. Asia
Asia is the continent with the highest carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for approximately 50% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Asia are energy production, transportation, and industry.
D. North America
North America is the second-largest emitter of carbon dioxide, accounting for approximately 20% of the world's total emissions. The United States and Canada are the main sources of emissions in North America, with the energy and transportation sectors being the largest contributors.
C. Europe
Europe is the third-largest emitter of carbon dioxide, accounting for approximately 10% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Europe are energy production, transportation, and industry.
A. Africa
Africa is the continent with the lowest carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for approximately 4% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Africa are energy production and transportation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B: B, D, C, A.
The correct sequence of continents in decreasing order of their yearly carbon dioxide emissions at present is as follows:
B. Asia
Asia is the continent with the highest carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for approximately 50% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Asia are energy production, transportation, and industry.
D. North America
North America is the second-largest emitter of carbon dioxide, accounting for approximately 20% of the world's total emissions. The United States and Canada are the main sources of emissions in North America, with the energy and transportation sectors being the largest contributors.
C. Europe
Europe is the third-largest emitter of carbon dioxide, accounting for approximately 10% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Europe are energy production, transportation, and industry.
A. Africa
Africa is the continent with the lowest carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for approximately 4% of the world's total emissions. The main sources of emissions in Africa are energy production and transportation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B: B, D, C, A.
Day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is- a)75 dB
- b)65 dB
- c)55 dB
- d)50 dB
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is
a)
75 dB
b)
65 dB
c)
55 dB
d)
50 dB
|
|
Ankit Chakraborty answered |
Residential Areas Noise Standards in India
Introduction: Noise pollution is a major problem in Indian cities, especially in residential areas. It can lead to several health issues such as hearing loss, sleep disturbance, hypertension, and stress. In order to control noise pollution, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has prescribed noise standards for different areas, including residential areas.
Day Time Noise Standards: The day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is 55 dB. This means that the noise level during the day should not exceed 55 decibels.
Night Time Noise Standards: The night time noise standard for residential areas is lower than the day time standard. It is set at 45 dB. This is because people need a peaceful environment to sleep at night.
Impact of Noise Pollution on Health: Noise pollution can have several negative impacts on health. Some of the most common health problems caused by noise pollution include:
- Hearing Loss
- Hypertension
- Stress
- Sleep Disturbance
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Measures to Control Noise Pollution: There are several measures that can be taken to control noise pollution in residential areas. Some of these measures include:
- Use of Noise Barriers: Noise barriers can be installed along busy roads to reduce the amount of noise that enters residential areas.
- Planting Trees: Trees can help reduce noise levels by absorbing sound waves.
- Regulation of Traffic: Traffic regulation can help reduce noise pollution in residential areas. This can be done by imposing speed limits, restricting the use of horns, and enforcing noise emission standards for vehicles.
- Use of Low-Noise Equipment: The use of low-noise equipment such as lawn mowers, generators, and construction equipment can help reduce noise pollution in residential areas.
Conclusion: Noise pollution is a major problem in Indian cities, especially in residential areas. The day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is 55 dB. In order to control noise pollution, it is important to take measures such as using noise barriers, planting trees, regulating traffic, and using low-noise equipment.
Introduction: Noise pollution is a major problem in Indian cities, especially in residential areas. It can lead to several health issues such as hearing loss, sleep disturbance, hypertension, and stress. In order to control noise pollution, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has prescribed noise standards for different areas, including residential areas.
Day Time Noise Standards: The day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is 55 dB. This means that the noise level during the day should not exceed 55 decibels.
Night Time Noise Standards: The night time noise standard for residential areas is lower than the day time standard. It is set at 45 dB. This is because people need a peaceful environment to sleep at night.
Impact of Noise Pollution on Health: Noise pollution can have several negative impacts on health. Some of the most common health problems caused by noise pollution include:
- Hearing Loss
- Hypertension
- Stress
- Sleep Disturbance
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Measures to Control Noise Pollution: There are several measures that can be taken to control noise pollution in residential areas. Some of these measures include:
- Use of Noise Barriers: Noise barriers can be installed along busy roads to reduce the amount of noise that enters residential areas.
- Planting Trees: Trees can help reduce noise levels by absorbing sound waves.
- Regulation of Traffic: Traffic regulation can help reduce noise pollution in residential areas. This can be done by imposing speed limits, restricting the use of horns, and enforcing noise emission standards for vehicles.
- Use of Low-Noise Equipment: The use of low-noise equipment such as lawn mowers, generators, and construction equipment can help reduce noise pollution in residential areas.
Conclusion: Noise pollution is a major problem in Indian cities, especially in residential areas. The day time noise standard prescribed for residential areas in India is 55 dB. In order to control noise pollution, it is important to take measures such as using noise barriers, planting trees, regulating traffic, and using low-noise equipment.
Smog is:- a)Ozone and smoke
- b)Vehicular pollutant
- c)Fog and smoke
- d)Fog and ozone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Smog is:
a)
Ozone and smoke
b)
Vehicular pollutant
c)
Fog and smoke
d)
Fog and ozone
|
|
Lekshmi Basak answered |
Explanation:
Smog is a type of air pollution that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment. It is a mixture of fog and smoke, sometimes with added pollutants such as ozone.
What is smog composed of?
Smog is composed of various pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, ozone, and particulate matter. These pollutants are released by sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels.
Types of smog:
There are two types of smog, namely, classical smog and photochemical smog. Classical smog is caused by the burning of fossil fuels and is common in cities with a lot of traffic, while photochemical smog is caused by the reaction of sunlight with pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds.
Effects of smog:
Smog can have a number of harmful effects on human health, including respiratory problems such as asthma and bronchitis. It can also irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and can even cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea. In addition to its effects on human health, smog can also have a number of negative environmental effects, including acid rain, damage to crops and forests, and harm to wildlife.
Prevention of smog:
To prevent smog, it is important to reduce the amount of pollutants released into the air. This can be done by using cleaner forms of energy, such as wind and solar power, and by reducing the use of fossil fuels. It is also important to reduce vehicle emissions by using public transportation, carpooling, or walking or biking instead of driving alone.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, smog is a type of air pollution that is composed of fog and smoke, sometimes with added pollutants such as ozone. It can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, and it is important to take steps to reduce its impact by reducing the amount of pollutants released into the air.
Smog is a type of air pollution that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment. It is a mixture of fog and smoke, sometimes with added pollutants such as ozone.
What is smog composed of?
Smog is composed of various pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, ozone, and particulate matter. These pollutants are released by sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels.
Types of smog:
There are two types of smog, namely, classical smog and photochemical smog. Classical smog is caused by the burning of fossil fuels and is common in cities with a lot of traffic, while photochemical smog is caused by the reaction of sunlight with pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds.
Effects of smog:
Smog can have a number of harmful effects on human health, including respiratory problems such as asthma and bronchitis. It can also irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and can even cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea. In addition to its effects on human health, smog can also have a number of negative environmental effects, including acid rain, damage to crops and forests, and harm to wildlife.
Prevention of smog:
To prevent smog, it is important to reduce the amount of pollutants released into the air. This can be done by using cleaner forms of energy, such as wind and solar power, and by reducing the use of fossil fuels. It is also important to reduce vehicle emissions by using public transportation, carpooling, or walking or biking instead of driving alone.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, smog is a type of air pollution that is composed of fog and smoke, sometimes with added pollutants such as ozone. It can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, and it is important to take steps to reduce its impact by reducing the amount of pollutants released into the air.
Which of the following is NOT a water pollutant?- a)Chromium
- b)Silt
- c)Glacier
- d)Arsenic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a water pollutant?
a)
Chromium
b)
Silt
c)
Glacier
d)
Arsenic
|
|
Meghana Sharma answered |
Water Pollution: Explanation and Examples
Introduction:
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies like lakes, rivers, oceans, groundwater, and aquifers. It occurs when pollutants are discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment or when natural processes are unable to remove them.
Examples of Water Pollutants:
There are various types of water pollutants, such as chemicals, microorganisms, plastics, and sediments. Some of the common examples of water pollutants are as follows:
- Chromium: It is a heavy metal that is used in industrial processes like electroplating, tanning, and dyeing. Chromium can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and cancer.
- Silt: It is a type of sediment that is generated due to soil erosion caused by deforestation, construction activities, and agricultural practices. Silt can clog the waterways and reduce the oxygen levels, which can harm aquatic life.
- Glacier: It is not a water pollutant, but a natural feature formed by snow accumulation over several years. Glaciers are a source of freshwater, and their melting can contribute to the rise in sea levels.
- Arsenic: It is a toxic element that is found naturally in some groundwater sources. Arsenic can cause skin lesions, cancer, and other health problems.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, water pollution is a serious environmental problem that can have severe consequences for human health and the ecosystem. It is important to take measures to reduce water pollution by implementing proper waste management practices, using eco-friendly products, and promoting sustainable development.
Introduction:
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies like lakes, rivers, oceans, groundwater, and aquifers. It occurs when pollutants are discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment or when natural processes are unable to remove them.
Examples of Water Pollutants:
There are various types of water pollutants, such as chemicals, microorganisms, plastics, and sediments. Some of the common examples of water pollutants are as follows:
- Chromium: It is a heavy metal that is used in industrial processes like electroplating, tanning, and dyeing. Chromium can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and cancer.
- Silt: It is a type of sediment that is generated due to soil erosion caused by deforestation, construction activities, and agricultural practices. Silt can clog the waterways and reduce the oxygen levels, which can harm aquatic life.
- Glacier: It is not a water pollutant, but a natural feature formed by snow accumulation over several years. Glaciers are a source of freshwater, and their melting can contribute to the rise in sea levels.
- Arsenic: It is a toxic element that is found naturally in some groundwater sources. Arsenic can cause skin lesions, cancer, and other health problems.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, water pollution is a serious environmental problem that can have severe consequences for human health and the ecosystem. It is important to take measures to reduce water pollution by implementing proper waste management practices, using eco-friendly products, and promoting sustainable development.
In mined regions, ecological balance can be achieved by:- a)Developing a vegetational cover
- b)Preventing overgrazing
- c)Introducing agriculture
- d)Preventing soil erosion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In mined regions, ecological balance can be achieved by:
a)
Developing a vegetational cover
b)
Preventing overgrazing
c)
Introducing agriculture
d)
Preventing soil erosion
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
Ecological balance
- A number of the world's ecosystems have undergone significant degradation leading to a negative impact on biodiversity and livelihood.
- One such ecosystem that has depleted over the years is the mined habitats.
- Since the mineral-rich areas are also rich in forest resources. However continuous mining activities tend to change the ecological equilibrium.
- Restoration of the ecological equilibrium of the mined areas can be achieved by understanding the ecology, plant succession, and soil types of the place and revegetation of the spoils. Hence, option 1 is correct.
- Ecological equilibrium refers to a state of equilibrium between all living and non-living organisms in the environment.
- Mining sites are constantly subjected to mining activities, and as a result, the natural balance of the area is disrupted.
- The development of a plant cover in such an area will aid in the recovery or of the soil.
- The land is not intended for farming.
- There is no grazing in this location.
- It is possible to avoid soil erosion, but this does not guarantee that the soil will be totally restored.
- For the time being, vegetation cover and regular revegetation work will rebalance the ecology of the mined region.
Noise pollution is measured in -- a)Ohm
- b)Decibel
- c)Joule
- d)Ampere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Noise pollution is measured in -
a)
Ohm
b)
Decibel
c)
Joule
d)
Ampere
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Noise pollution is measured in Decibel.
- The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to measure sound level.
- It is also widely used in electronics, signals and communication.
- In ordinary usage, specification of the intensity of a sound implies a comparison of the intensity of the sound with that of a sound just perceptible to the human ear.
- In simple terms, the dB is the ratio between two power levels expressed in logarithmic terms with relation to some reference level.
- For example, if given two known power levels, P2 and P1, the relative value of P2 with respect to P1 in dB is given by:
- dB = 10 log 10 (P2/P1)
- Noise levels below 35–40 dB are usually necessary for a good night’s sleep.
- A busy office may be about 60 dB while the noise level on a footpath beside a busy road might be approximately 75 dB.
- A departing jumbo jet may result in 120 dB being recorded along the runway.
- Ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, transmitting a current of one ampere when subjected to a potential difference of one volt.
- Joule, unit of work or energy in the International System of Units (SI); it is equal to the work done by a force of one newton acting through one metre.
- Ampere is a unit of electric current equal to a flow of one coulomb per second.
Which of the following is NOT a "greenhouse gas" (GHG)?- a)Oxygen
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Water vapour
- d)Methane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a "greenhouse gas" (GHG)?
a)
Oxygen
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Water vapour
d)
Methane
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. Oxygen
- A Greenhouse gas (GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range.
- Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases and oxygen is not a GHG. Hence option 1 is correct.
- Some other gases such as surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap infrared radiation.
- Kyoto Protocol
- Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement that aimed to reduce Carbon dioxide emissions and the presence of Greenhouse Gases (GHG) in the atmosphere.
- It was adopted in Kyoto, Japan on 11th December 1997. and became international law on 16 February 2005.
Chapter doubts & questions for Environmental Issues - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Environmental Issues - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.
Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
1209 videos|2197 docs|849 tests
|
Related UPSC CSE Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









