All Exams >
SSC CGL >
General Intelligence and Reasoning for SSC CGL >
All Questions
All questions of Puzzles for SSC CGL Exam
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
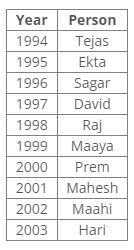
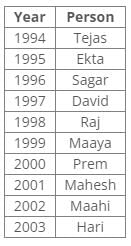
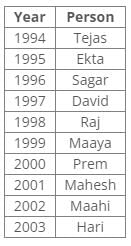
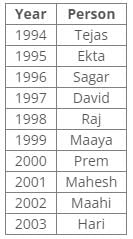
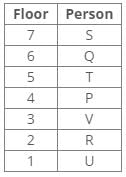
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.Q. Who among the following was born in 2002?- a)Hari
- b)Prem
- c)Maahi
- d)Maaya
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Q. Who among the following was born in 2002?
a)
Hari
b)
Prem
c)
Maahi
d)
Maaya

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
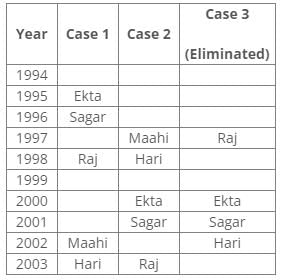
From the following common explanation, we get that Maahi was born in 2002.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:

References:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
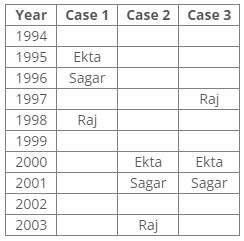
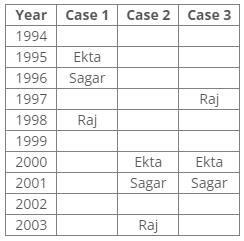
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
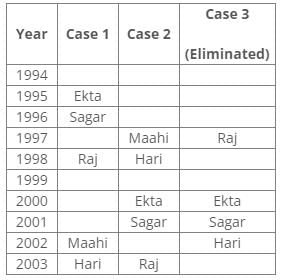
According to the given conditions, Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Thus case 3 is not valid.
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
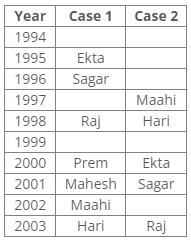
According to the given conditions, three people were between Prem and Sagar. Thus case 2 is not valid.
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
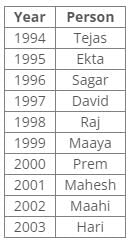
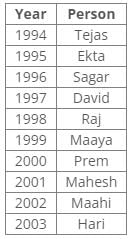
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Which of the following lives on the bottommost and the topmost floors respectively?- a)U, Q
- b)S, R
- c)R, U
- d)U, S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Which of the following lives on the bottommost and the topmost floors respectively?
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Which of the following lives on the bottommost and the topmost floors respectively?
a)
U, Q
b)
S, R
c)
R, U
d)
U, S
|
|
Pranab Goyal answered |
Analysis:
- T lives above V and P lives below T but above V, so the order is V-P-T.
- U does not live on an even-numbered floor, so U must be on an odd-numbered floor.
- V lives on the third floor, so the order is V-P-T-?-?-?-U.
- Exactly three persons live between Q and R, who lives below Q. So, the order is V-P-T-R-Q-?-?-U.
- Q lives immediately below S, so the order is V-P-T-R-Q-S-?-U.
Solution:
- The bottommost floor is an odd-numbered floor, and U is the only person who lives on an odd-numbered floor. So, U lives on the bottommost floor.
- The topmost floor is the seventh floor, and S is the only person left to be placed. So, S lives on the topmost floor.
Therefore, the persons who live on the bottommost and the topmost floors are U and S respectively.
- T lives above V and P lives below T but above V, so the order is V-P-T.
- U does not live on an even-numbered floor, so U must be on an odd-numbered floor.
- V lives on the third floor, so the order is V-P-T-?-?-?-U.
- Exactly three persons live between Q and R, who lives below Q. So, the order is V-P-T-R-Q-?-?-U.
- Q lives immediately below S, so the order is V-P-T-R-Q-S-?-U.
Solution:
- The bottommost floor is an odd-numbered floor, and U is the only person who lives on an odd-numbered floor. So, U lives on the bottommost floor.
- The topmost floor is the seventh floor, and S is the only person left to be placed. So, S lives on the topmost floor.
Therefore, the persons who live on the bottommost and the topmost floors are U and S respectively.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.Q. Which of the following box is placed 5th position from the bottom?- a)V
- b)Y
- c)W
- d)X
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Q. Which of the following box is placed 5th position from the bottom?
a)
V
b)
Y
c)
W
d)
X

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get box Y is placed 5th position from the bottom.
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
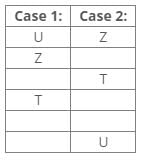
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
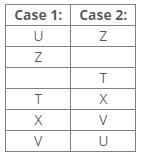
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.Q. Which of the following statements is definitely true?- a)R is heavier than Q
- b)P is the second heaviest
- c) Q is heavier than P
- d)M is heavier than O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Q. Which of the following statements is definitely true?
a)
R is heavier than Q
b)
P is the second heaviest
c)
Q is heavier than P
d)
M is heavier than O

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
Solution:
Based on the information provided:
- O weighs 70kg and is lighter than two people.
- P is lighter than O but not the lightest.
- Q weighs 55kg and is lighter than P.
- R is lighter than Q.
- N is lighter than M.
From this, we can deduce the following:
- The two people heavier than O must be M and someone else.
- P must weigh more than Q but less than O, indicating P is heavier than 55kg but less than 70kg.
- Since R is lighter than Q, R weighs less than 55kg.
- This implies that M must be heavier than O.
Thus, the only statement that is definitely true is that M is heavier than O.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
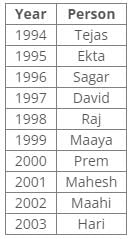
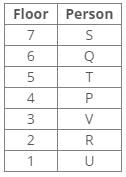
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.Q. Who is the youngest person?- a)Maaya
- b)Maahi
- c)Mahesh
- d)Hari
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Q. Who is the youngest person?
a)
Maaya
b)
Maahi
c)
Mahesh
d)
Hari

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get that Hari is youngest person.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:
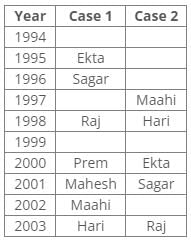
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:

References:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
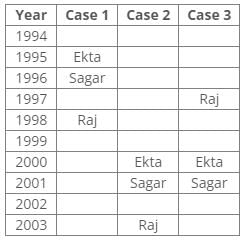
References:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
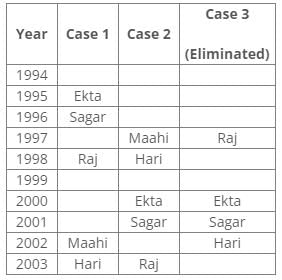
According to the given conditions, Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Thus case 3 is not valid.
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
According to the given conditions, three people were between Prem and Sagar. Thus case 2 is not valid.
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
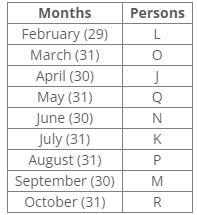
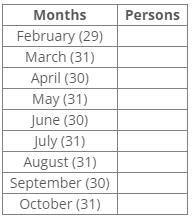
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Which of the following is the eldest person?- a)O
- b)R
- c)L
- d)M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Which of the following is the eldest person?
Q. Which of the following is the eldest person?
a)
O
b)
R
c)
L
d)
M

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
From the above reference, we can conclude that L is the eldest person.
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:

References:
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:
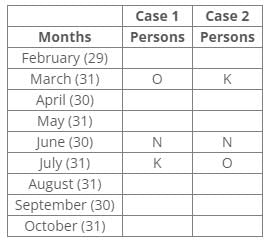
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:

References:
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:
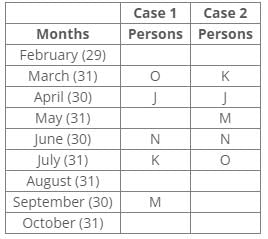
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:

References:
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:
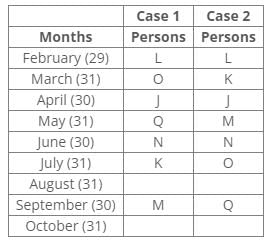
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:

References:
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:
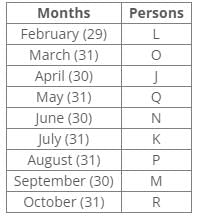
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who among the following one lives on the bottommost floor?- a)N
- b)Q
- c)I
- d)H
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who among the following one lives on the bottommost floor?
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who among the following one lives on the bottommost floor?
a)
N
b)
Q
c)
I
d)
H

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we can conclude that “H” lives on the bottommost floor.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
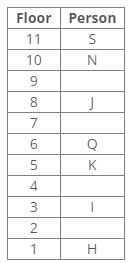
Common Explanation:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
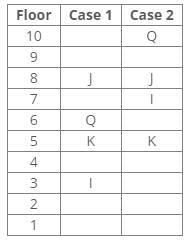
References:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
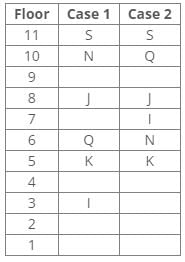
References:
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:
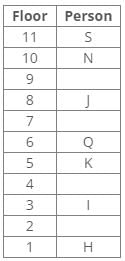
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:

Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.Q. Who among the following scored the lowest runs in the match?- a)F
- b)E
- c)B
- d)C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Q. Who among the following scored the lowest runs in the match?
a)
F
b)
E
c)
B
d)
C

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “E scored lowest runs in the match”.
Hence option B is correct.
Final arrangement:
Hence option B is correct.
Final arrangement:
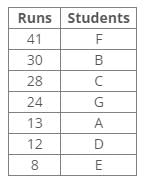
Common explanation:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by S?- a)Science
- b)Botany
- c)Geography
- d)Chemistry
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by S?
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by S?
a)
Science
b)
Botany
c)
Geography
d)
Chemistry

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
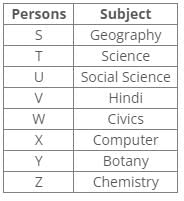
From the following common explanation, we get “S” has chosen Geography.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Common Explanation:
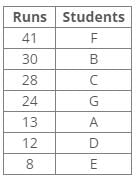
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.

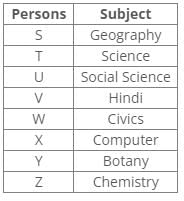
References:
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the first friend she visited?- a)Reena
- b)Aditi
- c)Aruna
- d)Esha
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the first friend she visited?
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the first friend she visited?
a)
Reena
b)
Aditi
c)
Aruna
d)
Esha

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
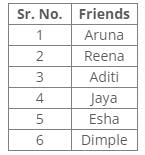
From the following common explanation, we get “Aruna” was the first friend she visited.
Hence, Option C is correct
References:
She visited two friends after Jaya.
Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena.
She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Hence, Option C is correct
References:
She visited two friends after Jaya.
Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena.
She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
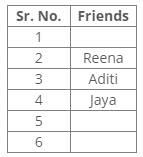
References:
She visited three between Esha and Aruna.
Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement final arrangement:
She visited three between Esha and Aruna.
Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement final arrangement:
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Civics?- a)Y
- b)W
- c)T
- d)U
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Civics?
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Civics?
a)
Y
b)
W
c)
T
d)
U

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get “W” has chosen Civics.
Hence, Option B is correct.
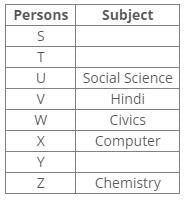
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.
Hence, Option B is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.

References:
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
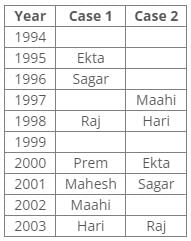
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.Q. In which year was Mahesh born?- a)1994
- b)1997
- c)1998
- d)2001
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Q. In which year was Mahesh born?
a)
1994
b)
1997
c)
1998
d)
2001

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get Mahesh was born in 2001.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:

References:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
According to the given conditions, Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Thus case 3 is not valid.
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
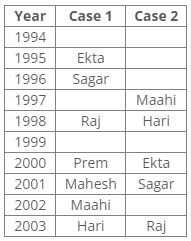
According to the given conditions, three people were between Prem and Sagar. Thus case 2 is not valid.
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
Seven persons are arranged according to their weight in descending order from left to right. The weight of S is 1/5th of L. The one who is 4th heaviest is of 35kg. Only two persons heavier than W. Q is just heavier to B, who is not the lightest among all. G is heavier to M, who is heavier than the 4th lightest person among all. S is lighter to Q, who is not 35kg.
If M is 45kg heavier to 5 then what is the possible weight of W ?- a)70 Kg
- b)48 Kg
- c)54 Kg
- d)50 Kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Seven persons are arranged according to their weight in descending order from left to right. The weight of S is 1/5th of L. The one who is 4th heaviest is of 35kg. Only two persons heavier than W. Q is just heavier to B, who is not the lightest among all. G is heavier to M, who is heavier than the 4th lightest person among all. S is lighter to Q, who is not 35kg.
If M is 45kg heavier to 5 then what is the possible weight of W ?
If M is 45kg heavier to 5 then what is the possible weight of W ?
a)
70 Kg
b)
48 Kg
c)
54 Kg
d)
50 Kg

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
To determine the possible weight of W, consider the following points:
- The 4th heaviest person weighs 35kg.
- There are only two persons heavier than W.
- B is not the lightest, and Q is just heavier than B.
- G is heavier than M, and M is heavier than the 4th lightest person.
- S weighs 1/5th of L and is lighter than Q.
- If M is 45kg heavier than a weight of 5kg, M weighs 50kg.
Given these details, we can deduce the possible weights:
- If W is heavier than two persons, W must be lighter than the 3rd heaviest person.
- Since M weighs 50kg and is heavier than the 4th heaviest at 35kg, W must be less than 50kg.
Therefore, the possible weight of W is:
- 48kg (as the best feasible option that satisfies all conditions).
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment in Ranchi?- a)C
- b)B
- c)E
- d)A
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment in Ranchi?
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment in Ranchi?
a)
C
b)
B
c)
E
d)
A

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “A has an appointment in Ranchi”.
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
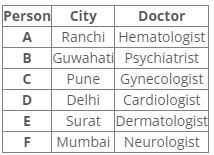
Common explanation:
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
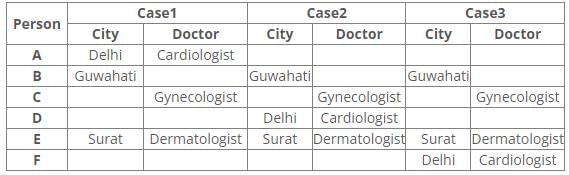
References:
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.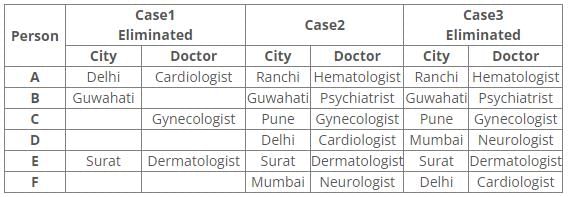
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.

Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.Q. Find the odd one out.- a)Ekta
- b)Prem
- c)Sagar
- d)Raj
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Q. Find the odd one out.
a)
Ekta
b)
Prem
c)
Sagar
d)
Raj

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get except Ekta all were born in even years.
Hence, Option A is correct.
Hence, Option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:

References:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
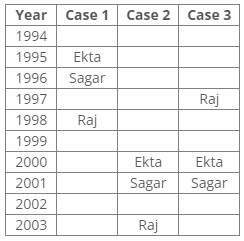
References:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
According to the given conditions, Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Thus case 3 is not valid.
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
According to the given conditions, three people were between Prem and Sagar. Thus case 2 is not valid.
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
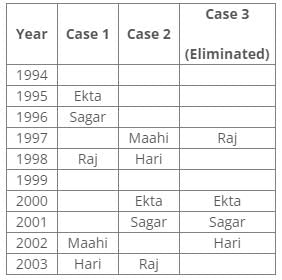
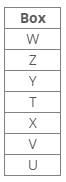
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.Q. Find the odd one out?- a)Box W
- b)Box U
- c)Box T
- d)Box X
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Q. Find the odd one out?
a)
Box W
b)
Box U
c)
Box T
d)
Box X

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get except box T, all are placed at odd position from both top and bottom.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
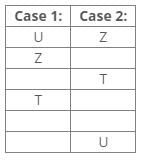
Common Explanation:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
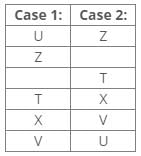
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
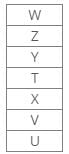
Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
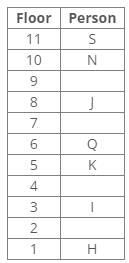
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who lives on 8th floor?- a)H
- b)Q
- c)J
- d)N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who lives on 8th floor?
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. Who lives on 8th floor?
a)
H
b)
Q
c)
J
d)
N

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we can conclude that “J” lives on 8th floor.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
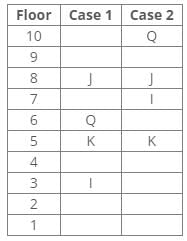
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
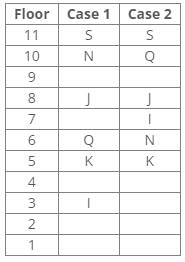
References:
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:
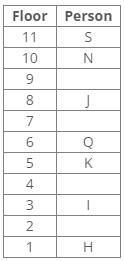
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which of the following statement is true?- a)V has chosen Science
- b)W has Chosen Chemistry
- c)Hindi was chosen by V
- d)Computer was chosen by T
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which of the following statement is true?
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which of the following statement is true?
a)
V has chosen Science
b)
W has Chosen Chemistry
c)
Hindi was chosen by V
d)
Computer was chosen by T

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get Hindi was chosen by “V”.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.
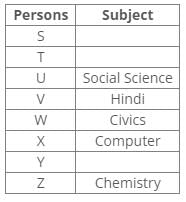
Hence, Option C is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.

References:
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.
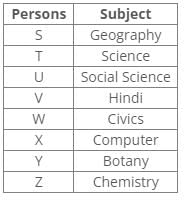
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.

Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.Q. Who among the following scored 28 runs in the match?- a)F
- b)G
- c)E
- d)C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Q. Who among the following scored 28 runs in the match?
a)
F
b)
G
c)
E
d)
C

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “C scored 28 runs in the match”.
Hence option D is correct.
Final arrangement:
Hence option D is correct.
Final arrangement:
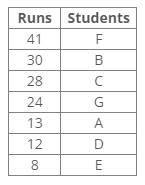
Common explanation:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
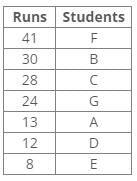
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.Q. How many boxes are placed below box T?- a)None
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Q. How many boxes are placed below box T?
a)
None
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get three boxes are placed below box T.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
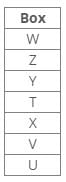
Common Explanation:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
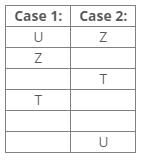
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
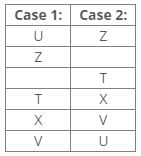
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
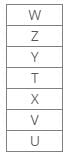
Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Who lives just below P?- a)U
- b)R
- c)T
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Who lives just below P?
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. Who lives just below P?
a)
U
b)
R
c)
T
d)
None of these

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get “V” lives just below P.
Hence, Option D is correct.
References:
V lives on the third floor.
Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q lives immediately below S.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Hence, Option D is correct.
References:
V lives on the third floor.
Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q lives immediately below S.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
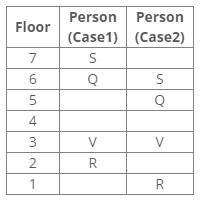
References:
T lives above V.
U does not live on an even-numbered floor.
P lives below T but above V.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 is not valid as if put U on 7th floor we cannot arrange the conditions P lives below T but above V and T lives above V.
So, the final arrangement:
T lives above V.
U does not live on an even-numbered floor.
P lives below T but above V.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 is not valid as if put U on 7th floor we cannot arrange the conditions P lives below T but above V and T lives above V.
So, the final arrangement:
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.Q. How many runs are scored by D in the match?- a)13
- b)24
- c)8
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Q. How many runs are scored by D in the match?
a)
13
b)
24
c)
8
d)
None of these

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “D scored 12 runs in the match”.
Hence option D is correct.
Final arrangement:
Hence option D is correct.
Final arrangement:
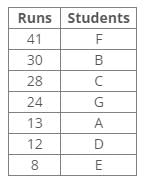
Common explanation:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. F has an appointment with ________ in ________.- a)Neurologist, Mumbai
- b)Neurologist, Surat
- c)Cardiologist, Ranchi
- d)Psychiatrist, Mumbai
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. F has an appointment with ________ in ________.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. F has an appointment with ________ in ________.
a)
Neurologist, Mumbai
b)
Neurologist, Surat
c)
Cardiologist, Ranchi
d)
Psychiatrist, Mumbai

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai”.
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:
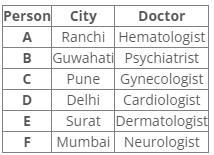
Common explanation:
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
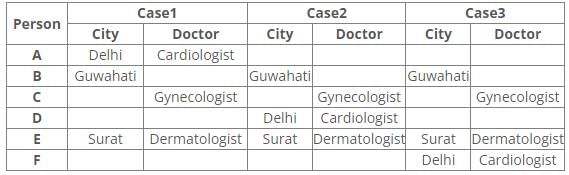
References:
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.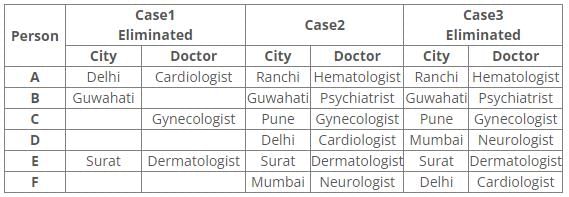
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.

Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live between S and Q?- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Five
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live between S and Q?
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live between S and Q?
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Five
d)
None of these

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
From the following common explanation, we can conclude that four persons live between S and Q.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Common Explanation:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
References:
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:
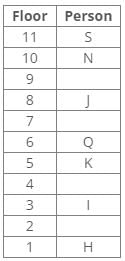
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:

Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way thus formed a group. Which of the following is not the part of the group?- a)M
- b)Q
- c)P
- d)K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way thus formed a group. Which of the following is not the part of the group?
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way thus formed a group. Which of the following is not the part of the group?
a)
M
b)
Q
c)
P
d)
K

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the common explanation, we can conclude that all the persons in the given option are born in the month having 31 days except M.
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:
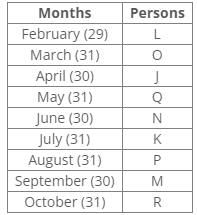
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:

References:
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:
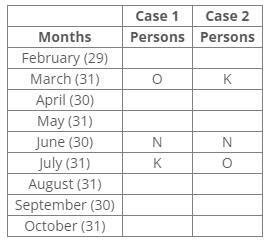
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:

References:
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:
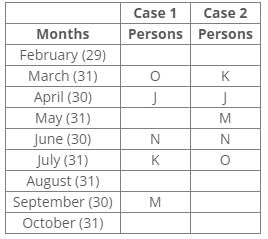
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:

References:
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:
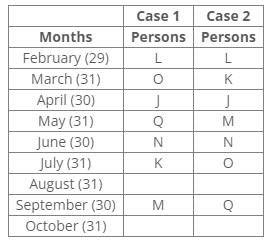
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:

References:
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:
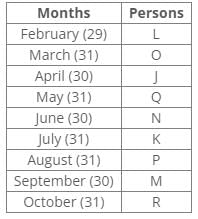
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live below the person who lives three floors below J?- a)8
- b)7
- c)6
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live below the person who lives three floors below J?
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live below the person who lives three floors below J?
a)
8
b)
7
c)
6
d)
4

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
From the following common explanation, we can conclude that four persons live below K, who lives three floors below J.
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
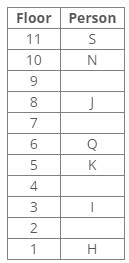
Common Explanation:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
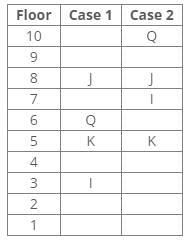
References:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
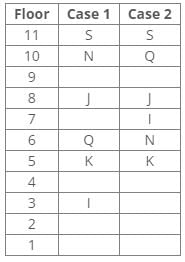
References:
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:
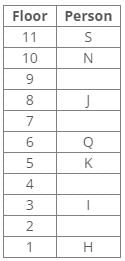
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:

Among P, Q, R, S and T each having a different height. Q is shorter than only T and S is shorter than P and R. Who among them is the shortest?- a)R
- b)S
- c)P
- d)Data inadequate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among P, Q, R, S and T each having a different height. Q is shorter than only T and S is shorter than P and R. Who among them is the shortest?
a)
R
b)
S
c)
P
d)
Data inadequate

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
Q is shorter than only T.
S is shorter than P and R.
T > Q > R/P > R/P > S
Hence, option B is correct.
S is shorter than P and R.
T > Q > R/P > R/P > S
Hence, option B is correct.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. In which city Psychiatrist is?- a)Pune
- b)Delhi
- c)Guwahati
- d)Mumbai
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. In which city Psychiatrist is?
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. In which city Psychiatrist is?
a)
Pune
b)
Delhi
c)
Guwahati
d)
Mumbai

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “Psychiatrist is in Guwahati”.
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
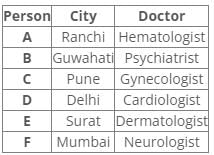
Common explanation:
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
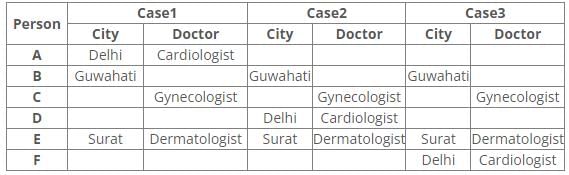
References:
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.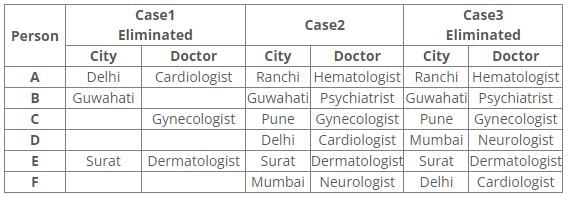
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.

Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Which of the following statement is false?- a)Q was born in the month having 31 days
- b)P born immediate after K
- c)R is the youngest person
- d)One person born before K
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Which of the following statement is false?
Q. Which of the following statement is false?
a)
Q was born in the month having 31 days
b)
P born immediate after K
c)
R is the youngest person
d)
One person born before K

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the common explanation, we can conclude that one person born before K is false.
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:

References:
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:
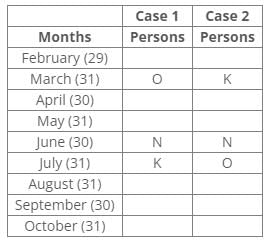
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:

References:
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:
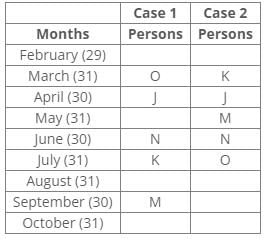
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:

References:
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:
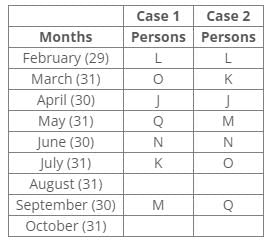
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:

References:
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:
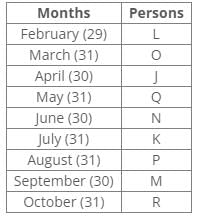
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Choose the incorrect pair.- a)C - Pune
- b)E - Guwahati
- c)Delhi - Cardiologist
- d)Neurologist - Mumbai
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Choose the incorrect pair.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Choose the incorrect pair.
a)
C - Pune
b)
E - Guwahati
c)
Delhi - Cardiologist
d)
Neurologist - Mumbai

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “E – Guwahati is the incorrect pair”.
Hence, option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
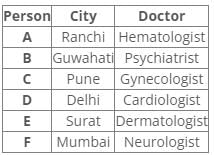
Common explanation:
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
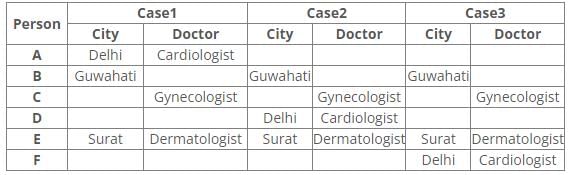
References:
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.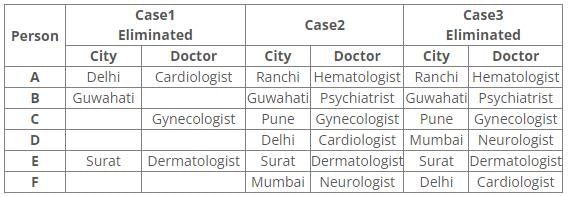
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.

Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Botany?- a)T
- b)U
- c)X
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Botany?
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Who has chosen Botany?
a)
T
b)
U
c)
X
d)
None of these

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get “Y” has chosen Botany.
Hence, Option E is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.
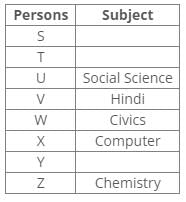
Hence, Option E is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.

References:
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.
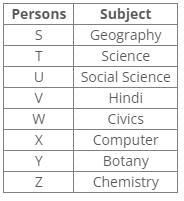
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by T?- a)Hindi
- b)Botany
- c)Chemistry
- d)Science
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by T?
There are eight persons – S to Z, appearing for the state-level exam. Each one has chosen a different optional subject from among, Hindi, Science, Geography, Social Science, Computer, Civics, Botany and Chemistry but not necessarily in the same order.
T has chosen either Science or Botany. V has chosen either Hindi or Science. Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography. X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry. U has chosen Social Science and W has chosen either Civics or Hindi. V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
Q. Which subject is chosen by T?
a)
Hindi
b)
Botany
c)
Chemistry
d)
Science

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get “T” has chosen Science.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Common Explanation:
References:
X has chosen Computer and Z has chosen Chemistry.
U has chosen Social Science
V has chosen either Hindi or Science.
V has chosen neither Civics nor Science.
W has chosen either Civics or Hindi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
V has chosen Hindi.
W has chosen Civics.

References:
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.
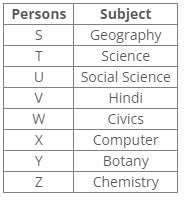
T has chosen either Science or Botany.
Y has not chosen Civics, Science and Geography.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Y must have chosen Botany and T must have chosen Science. So S must have chosen Geography.

Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Who was born in April?- a)Q
- b)J
- c)K
- d)O
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. Who was born in April?
Q. Who was born in April?
a)
Q
b)
J
c)
K
d)
O

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the above reference, we can conclude that J was born in April.
Hence, option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:

References:
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:
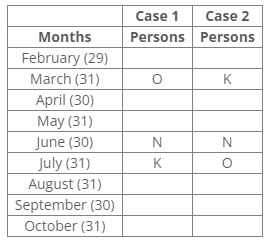
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:

References:
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:
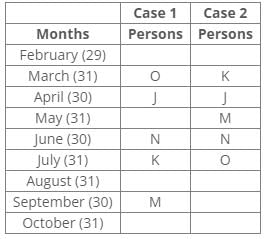
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:

References:
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:
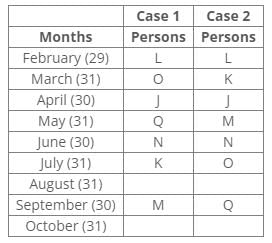
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:

References:
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:
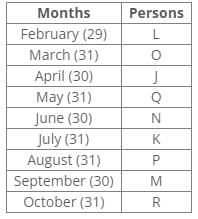
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the last friend she visited?- a)Reena
- b)Aditi
- c)Esha
- d)Dimple
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the last friend she visited?
Radha visited each of her friends viz. Aditi, Aruna, Dimple, Esha, Jaya and Reena in a day, each of her friends was visited at a different time. She visited three between Esha and Aruna. Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena. She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena. She visited two friends after Jaya. Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Q. Who among the following was the last friend she visited?
a)
Reena
b)
Aditi
c)
Esha
d)
Dimple

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get “Dimple” was the last friend she visited.
Hence, Option D is correct.
References:
She visited two friends after Jaya.
Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena.
She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
Hence, Option D is correct.
References:
She visited two friends after Jaya.
Only one friend was visited between Jaya and Reena.
She visited Aditi immediately after she visited Reena.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
References:
She visited three between Esha and Aruna.
Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement final arrangement:
She visited three between Esha and Aruna.
Aruna was visited before Jaya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement final arrangement:
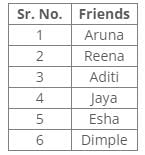
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. How many persons are elder than Q?- a)3
- b)2
- c)4
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. No one was born after October and none of them was born in January. Only one person was born in one month. For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
P was born before R. The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L. Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days. The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N. The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M. J was born in the month having 30 days, but not in September. The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q. L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Q. How many persons are elder than Q?
Q. How many persons are elder than Q?
a)
3
b)
2
c)
4
d)
1

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
From the common explanation, we can conclude that 3 persons are elder than Q.
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:
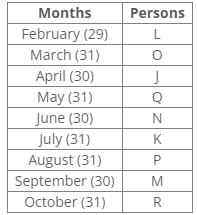
Hence, option A is correct.
Final Arrangement:

Common Explanation:
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
References:
Nine people J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R were born on the 13th of nine different months of the year 2000 but not necessarily in the same order.
No one was born after October and none of them was born in January.
Only one person was born in one month.
For all calculations of ages use 2022 as the current year.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:
From the above references, we can conclude the following:

References:
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:
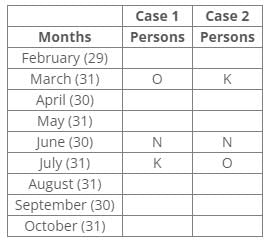
Three persons were born between O and K, where both were born in a month having 31 days.
The number of persons born before N is the same as the number of persons born after N.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can conclude the following cases:

References:
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:
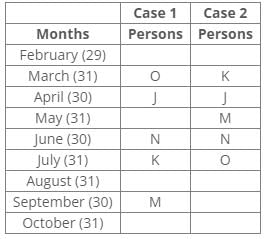
The number of persons born between O and N is the same as the number of persons born between N and M.
J was born in the month of having 30 days, but not in September.
Inferences:

References:
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:
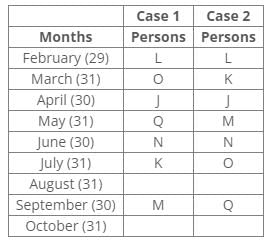
The number of persons born after K is the same as the number of persons born before Q.
L was born in the month having days less than 31.
Inferences:

References:
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:
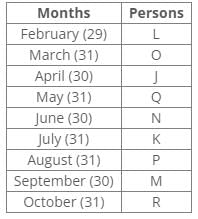
P was born before R.
The number of persons born between P and Q is the same as the number of persons born between Q and L.
Inferences:
From the above references, we can eliminate case 2.
Hence, the final arrangement is as follows:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live above N?- a)None
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live above N?
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live above N?
a)
None
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we can conclude that only one person lives above N.
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
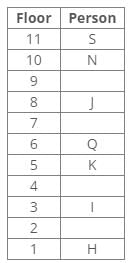
Common Explanation:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
K lives on the 5th floor.
J lives three floors above K.
One person lives between Q and J.
Q lives three floors above I.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
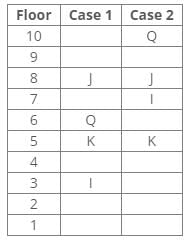
References:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
One person lives between J and N.
The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S.
S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor.
Inferences:
From the above references we get the following arrangement:
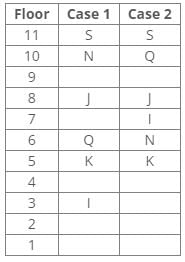
References:
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:
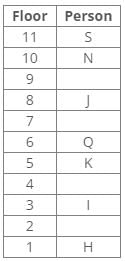
One person lives between I and H.
The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 gets eliminated because the number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S.
So, the final arrangement:

Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. How many persons live below Q?- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. How many persons live below Q?
P, Q, R, S, T, U and V live on different floors of a building, in which floors are numbered 1 to 7 from bottom to top.
T lives above V. U does not live on an even-numbered floor. P lives below T but above V. Q lives immediately below S. V lives on the third floor. Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q. How many persons live below Q?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the following common explanation, we get, only 5 persons live below Q.
Hence, Option C is correct.
References:
V lives on the third floor.
Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q lives immediately below S.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Hence, Option C is correct.
References:
V lives on the third floor.
Exactly three persons live between Q and R who lives below Q.
Q lives immediately below S.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
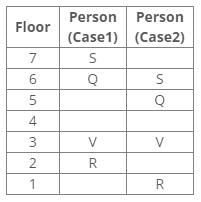
References:
T lives above V.
U does not live on an even-numbered floor.
P lives below T but above V.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 is not valid as if put U on 7th floor we cannot arrange the conditions P lives below T but above V and T lives above V.
So, the final arrangement:
T lives above V.
U does not live on an even-numbered floor.
P lives below T but above V.
Inferences:
From the above references, case 2 is not valid as if put U on 7th floor we cannot arrange the conditions P lives below T but above V and T lives above V.
So, the final arrangement:
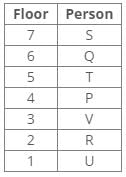
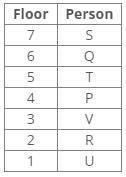
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.Q. If the average tank capacity of Cars T and G is 55 liters, then what could be the possible tank capacity of Car K?- a)75 liters
- b)40 liters
- c)50 liters
- d)45 liters
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Q. If the average tank capacity of Cars T and G is 55 liters, then what could be the possible tank capacity of Car K?
a)
75 liters
b)
40 liters
c)
50 liters
d)
45 liters

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
T + G = 55 * 2 = 110 liters
65 + G = 110
G = 45 liters
So, the possible tank capacity of Car K is 40 liters (45 > K > 35)
Hence, Option E is correct.
Final Arrangement:
65 + G = 110
G = 45 liters
So, the possible tank capacity of Car K is 40 liters (45 > K > 35)
Hence, Option E is correct.
Final Arrangement:
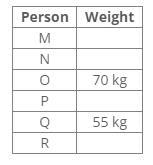
Common Explanation:
References:
P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O.
P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O.
R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M.
Inferences:
O weighs 70kg and only two people are heavier than O so O is 3rd heaviest person.
P, who is heavier than Q, is lighter than O and R is lighter than Q. So, P is 4th heaviest, Q is 5th heaviest and R is the lightest person. N is lighter than M, so M is the heaviest and N is 2nd heaviest person.
Thus we get:
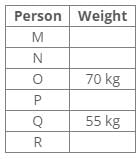
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.Q. How many boxes are placed between box Y and box U?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Q. How many boxes are placed between box Y and box U?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get three boxes placed between box Y and box U.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
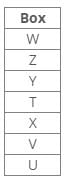
Common Explanation:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
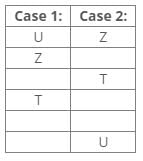
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
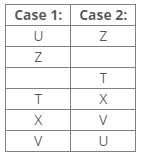
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.Q.How many players scored less runs than A?- a)Two
- b)One
- c)Four
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Q.How many players scored less runs than A?
a)
Two
b)
One
c)
Four
d)
Three

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “Two players scored less runs than A”.
Hence option A is correct.
Final arrangement:
Hence option A is correct.
Final arrangement:
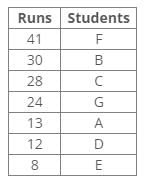
Common explanation:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
References:
1. Runs of B are more than 28.
2. F scored more runs than B.
3. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
4. The score of A is not a multiple of 4.
5. C scored 16 runs more than D.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following arrangement:
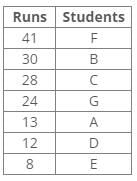
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.Q. If we arrange all the boxes according to the English alphabetical order from top to bottom then how many boxes remain in the same position?- a)None
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Seven boxes T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are kept one above the other in a stack. One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T. Box V is placed below box Z. Box X is placed just above box V. Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W. Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U. Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Q. If we arrange all the boxes according to the English alphabetical order from top to bottom then how many boxes remain in the same position?
a)
None
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
From the following common explanation, only one box ‘X’ remain in the same position after rearrangement.
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, Option B is correct.
Final Arrangement:
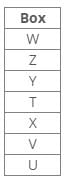
Common Explanation:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Two boxes are placed between boxes T and U.
One box is placed between boxes T and Z, which is placed above T.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
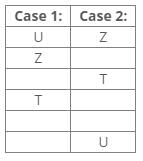
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Three boxes are placed between boxes V and Z.
Box V is placed below box Z.
Box X is placed just above box V.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
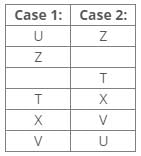
References:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
Three boxes are placed between boxes X and W.
Inferences:
From the above references, Case 1 is not valid we can place box W by using these references:
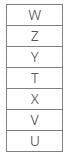
Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.Q. How many persons were born between Prem and Maaya?- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)One
- d)None of These
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003. Two people were born between Ekta and Raj. Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Four people were born between Hari and Raj. Sagar was born immediately after Ekta. Mahesh was born after Prem. David was born after Tejas but before Maya. Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5. Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Q. How many persons were born between Prem and Maaya?
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
One
d)
None of These

|
Ssc Cgl answered |
From the following common explanation, we get that no one sits between Prem and Maaya.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
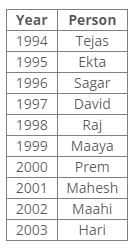
Common Explanation:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:
References:
Ten people were born in ten different years from 1994 to 2003.
Inferences:
So, we need to arrange as follows to accommodate the information stated in the reference:

References:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Ekta was born in a year which is a multiple of 5.
Two people were born between Ekta and Raj.
Sagar was born immediately after Ekta.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
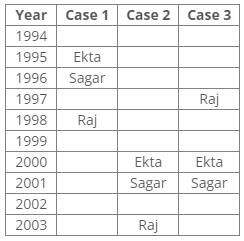
References:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
Four people were between Hari and Raj.
Maahi was born immediately before Hari.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
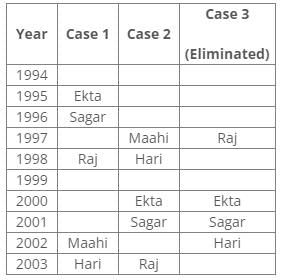
According to the given conditions, Maahi was born immediately before Hari. Thus case 3 is not valid.
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
References:
Three people were born between Prem and Sagar.
Mahesh was born after Prem.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the following cases:
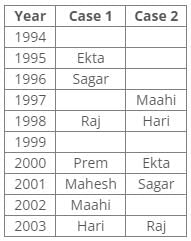
According to the given conditions, three people were between Prem and Sagar. Thus case 2 is not valid.
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
References:
David was born after Tejas but before Maya.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get the final arrangement:
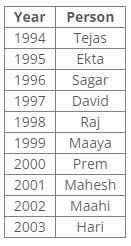
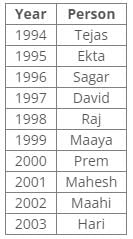
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment with Cardiologist?- a)E
- b)C
- c)D
- d)A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment with Cardiologist?
Six people A, B, C, D, E and F have an appointment with different doctors i.e. Neurologist, Cardiologist, Dermatologist, Hematologist, Gynecologist and Psychiatrist in different cities i.e. Pune, Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, Surat and Ranchi but not necessarily in the same order.
C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat. Dermatologist is in Surat. Cardiologist is in Delhi. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist. C has an appointment with Gynecologist. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai. B has appointment in Guwahati. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi. E has an appointment in Surat.
Q. Who has an appointment with Cardiologist?
a)
E
b)
C
c)
D
d)
A

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Following the common explanation, we get “D has an appointment with Cardiologist”.
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
Hence, option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
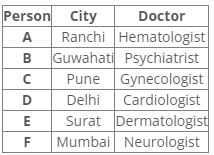
Common explanation:
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
References:
1. C has an appointment with Gynecologist.
2. Dermatologist is in Surat.
3. E has an appointment in Surat.
4. B has appointment in Guwahati.
5. Cardiologist is in Delhi.
Inferences:
From the above references, we get
From references 2 and 3, E has an appointment with Dermatologist in Surat.
From reference 5, we get three possible cases.
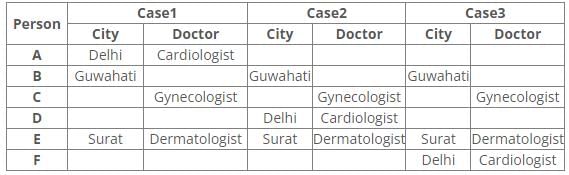
References:
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.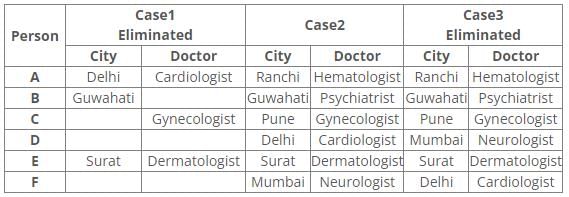
6. Neither D nor F has an appointment with Hematologist, who is in Ranchi.
7. Psychiatrist is not in Mumbai.
8. C is neither going to Mumbai nor Surat.
9. F has an appointment with either Neurologist or Psychiatrist.
Inferences:
From reference 6, case1 is eliminated.
In case2 and 3, A has an appointment with Hematologist in Ranchi.
From reference 7, B has an appointment with a Psychiatrist in Guwahati.
From reference 8, C has an appointment with Gynecologist in Pune.
From reference 9, in case2 F has an appointment with Neurologist in Mumbai.
Here case3 is eliminated.

Hence, Case 2 is the final arrangement.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.Q. Which of the following can be the weight of P?- a)44 kg
- b)48 kg
- c)50 kg
- d)60 kg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Q. Which of the following can be the weight of P?
a)
44 kg
b)
48 kg
c)
50 kg
d)
60 kg

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the common explanation, we get ’70 > P > 55, so weight of P is 60kg.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Final Arrangement:
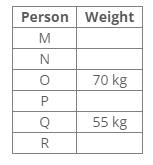
Common Explanation:
References:
References:
P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O.
P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O.
R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M.
Inferences:
O weighs 70kg and only two people are heavier than O so O is 3rd heaviest person.
P, who is heavier than Q, is lighter than O and R is lighter than Q. So, P is 4th heaviest, Q is 5th heaviest and R is the lightest person. N is lighter than M, so M is the heaviest and N is 2nd heaviest person.
Thus we get:
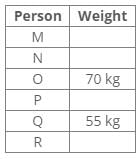
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.Q. How many people are lighter than N?- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Six people R, Q, P, O, N and M have different weights in kg. The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O. P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O. R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M. P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
Q. How many people are lighter than N?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5

|
EduRev SSC CGL answered |
From the common explanation, we get Only 4 people are lighter than N.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Final Arrangement:
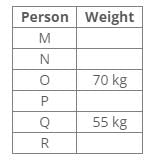
Common Explanation:
References:
P is heavier than Q, whose weight is 55kg.
The weight of O is 70kg and only two people are heavier than O.
P, who is not the lightest, is lighter than O.
R is lighter than Q and N is lighter than M.
Inferences:
O weighs 70kg and only two people are heavier than O so O is 3rd heaviest person.
P, who is heavier than Q, is lighter than O and R is lighter than Q. So, P is 4th heaviest, Q is 5th heaviest and R is the lightest person. N is lighter than M, so M is the heaviest and N is 2nd heaviest person.
Thus we get:
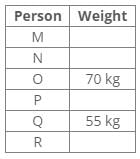
Chapter doubts & questions for Puzzles - General Intelligence and Reasoning for SSC CGL 2025 is part of SSC CGL exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the SSC CGL exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for SSC CGL 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Puzzles - General Intelligence and Reasoning for SSC CGL in English & Hindi are available as part of SSC CGL exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC CGL Exam by signing up for free.
General Intelligence and Reasoning for SSC CGL
201 videos|226 docs|197 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









