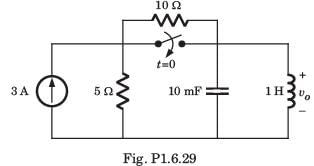
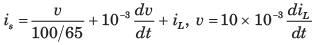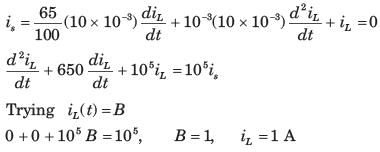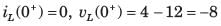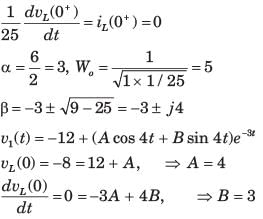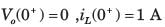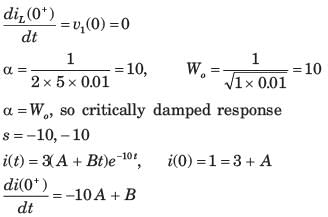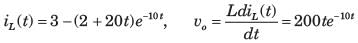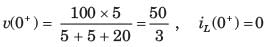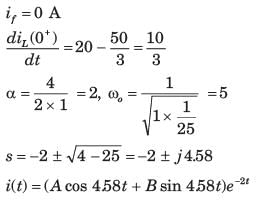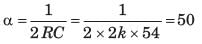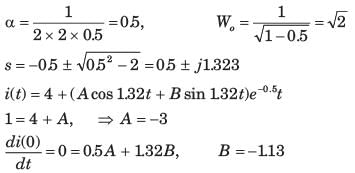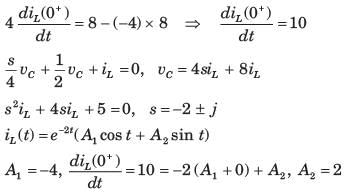All Exams >
Electrical Engineering (EE) >
RRB JE for Electrical Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of AC Fundamentals for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
What will be the period of the sinusoid, v(t) = 12 cos (50t + 30°)?- a)0.1257 s
- b)1.257 s
- c)12.57 s
- d)50 s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the period of the sinusoid, v(t) = 12 cos (50t + 30°)?
a)
0.1257 s
b)
1.257 s
c)
12.57 s
d)
50 s
|
|
Disha Das answered |
To determine the period of the sinusoid, we need to find the value of the coefficient of 't' in the argument of the cosine function.
In this case, the coefficient of 't' is 50. The period of a sinusoid is given by 2π divided by the coefficient of 't'. Therefore, the period is:
Period = 2π / 50
Simplifying this expression, we get:
Period = π / 25
In this case, the coefficient of 't' is 50. The period of a sinusoid is given by 2π divided by the coefficient of 't'. Therefore, the period is:
Period = 2π / 50
Simplifying this expression, we get:
Period = π / 25
In P (t) equation, if θ = 0, then P (t) =?- a)(VmIm/2)(1 + cosωt)
- b)(VmIm/2)(cosωt)
- c)(VmIm/2)(cos2ωt)
- d)(VmIm)(1+cos2ωt)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In P (t) equation, if θ = 0, then P (t) =?
a)
(VmIm/2)(1 + cosωt)
b)
(VmIm/2)(cosωt)
c)
(VmIm/2)(cos2ωt)
d)
(VmIm)(1+cos2ωt)
|
|
Vibhor Goyal answered |
In P (t) equation, if θ=0⁰, then P (t) =(VmIm/2)(1+cos2ωt). The power wave has a frequency twice that of the voltage or current. Here the average value of power is VmIm/2.
An AC voltage is given by v(t) = 5 + sin(2000πt), what is the time period and the dc component in v(t)?- a)0.05 ms, 0V
- b)1 ms, 0V
- c)0.05 ms, 5V
- d)1 ms, 5V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An AC voltage is given by v(t) = 5 + sin(2000πt), what is the time period and the dc component in v(t)?
a)
0.05 ms, 0V
b)
1 ms, 0V
c)
0.05 ms, 5V
d)
1 ms, 5V
|
|
Ayush Kumar answered |
The AC voltage given by v(t) = 5 sin(2000t) has an amplitude of 5 volts and a frequency of 2000 Hz. The time variable, t, represents time in seconds.
If the voltage and current in an A.C. circuit is 90° out of phase, then the power in the circuit will be -- a)Minimum
- b)Maximum
- c)Zero
- d)90 Watt
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the voltage and current in an A.C. circuit is 90° out of phase, then the power in the circuit will be -
a)
Minimum
b)
Maximum
c)
Zero
d)
90 Watt
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
The correct answer is 'option C'
Concept:
The power in an AC circuit is given by the expression
ϕP=VIcosϕ........(1)
here, ϕ is the angle between voltage and current.
Solution:
It is given to us that ϕ = 900
From eqn(1)
P = 0 Watts
At θ = π/2, positive portion is __________ negative portion in power cycle.- a)greater than
- b)less than
- c)equal to
- d)greater than or equal to
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At θ = π/2, positive portion is __________ negative portion in power cycle.
a)
greater than
b)
less than
c)
equal to
d)
greater than or equal to
|
|
Devansh Das answered |
Understanding Power Cycle at θ = π/2
The power cycle of an electrical system can be analyzed using the sine wave representation of alternating current (AC). At θ = π/2, we are at the maximum point of the sine wave.
Positive and Negative Portions of the Cycle
- The power cycle can be divided into two portions: positive and negative.
- The positive portion occurs when the sine function is above zero (from 0 to π) and the negative portion when it is below zero (from π to 2π).
Analysis at θ = π/2
- At this specific angle, the sine function reaches its peak value of +1.
- The positive portion of the power cycle represents the energy delivered to the load, while the negative portion indicates the energy returned to the source.
Equal Energy Distribution
- When analyzing the entire cycle from 0 to 2π, the areas under the curve for the positive and negative portions are equal.
- However, at the point θ = π/2, the instantaneous value of the sine wave (and thus the power) is at its maximum.
Conclusion
- Therefore, at θ = π/2, the positive portion is equal to the negative portion in terms of area under the curve over a complete cycle.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'C': the positive portion is equal to the negative portion in the context of power cycles.
In summary, while the instantaneous values differ at θ = π/2, when integrated over a full cycle, the positive and negative contributions balance each other out, leading to the conclusion that they are equal.
The power cycle of an electrical system can be analyzed using the sine wave representation of alternating current (AC). At θ = π/2, we are at the maximum point of the sine wave.
Positive and Negative Portions of the Cycle
- The power cycle can be divided into two portions: positive and negative.
- The positive portion occurs when the sine function is above zero (from 0 to π) and the negative portion when it is below zero (from π to 2π).
Analysis at θ = π/2
- At this specific angle, the sine function reaches its peak value of +1.
- The positive portion of the power cycle represents the energy delivered to the load, while the negative portion indicates the energy returned to the source.
Equal Energy Distribution
- When analyzing the entire cycle from 0 to 2π, the areas under the curve for the positive and negative portions are equal.
- However, at the point θ = π/2, the instantaneous value of the sine wave (and thus the power) is at its maximum.
Conclusion
- Therefore, at θ = π/2, the positive portion is equal to the negative portion in terms of area under the curve over a complete cycle.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'C': the positive portion is equal to the negative portion in the context of power cycles.
In summary, while the instantaneous values differ at θ = π/2, when integrated over a full cycle, the positive and negative contributions balance each other out, leading to the conclusion that they are equal.
The equation of instantaneous power is?- a)P (t) = (VmIm/2)(cos(2ωt + θ) + sinθ)
- b)P (t) = (VmIm/2)(sin(2ωt + θ) + cosθ)
- c)P (t) = (VmIm/2)(cos(2ωt + θ) + cosθ)
- d)P (t) = (VmIm/2)(sin(2ωt + θ) + sinθ)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of instantaneous power is?
a)
P (t) = (VmIm/2)(cos(2ωt + θ) + sinθ)
b)
P (t) = (VmIm/2)(sin(2ωt + θ) + cosθ)
c)
P (t) = (VmIm/2)(cos(2ωt + θ) + cosθ)
d)
P (t) = (VmIm/2)(sin(2ωt + θ) + sinθ)

|
EduRev GATE answered |
The equation of instantaneous power is P (t) = (VmIm/2)(cos(2ωt + θ) + cosθ). It consists of two parts. One is a fixed part and the other is time varying which has frequency twice that of the voltage or current wave forms.
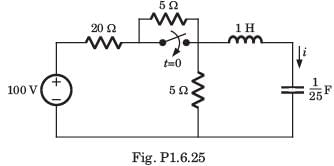
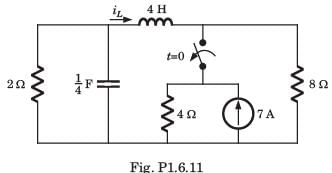
In the circuit shown, the current I flowing through the 50 Ω resistor will be zero if the value of capacitor C (in μF) is ______.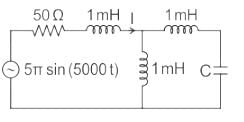
Correct answer is '20'. Can you explain this answer?
In the circuit shown, the current I flowing through the 50 Ω resistor will be zero if the value of capacitor C (in μF) is ______.


|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Concept:
Current through an open circuit or through a circuit with impedance tending to infinity is zero.
Calculation:
We are given a circuit shown below:
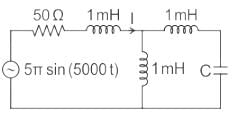
The impedance seen from the voltage source is Zeq (say) which can be calculated as:
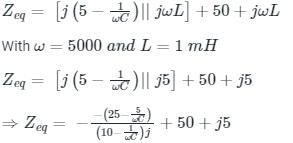
For I = 0, Zeq → ∞ --- (1)
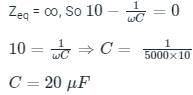
In purely resistive circuit, energy delivered by source is ____________ by resistance.- a)dissipated in the form of heat
- b)stored as electric field
- c)stored as magnetic field
- d)returned to source
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In purely resistive circuit, energy delivered by source is ____________ by resistance.
a)
dissipated in the form of heat
b)
stored as electric field
c)
stored as magnetic field
d)
returned to source

|
Bayshore Academy answered |
In purely resistive circuit, energy delivered by source is dissipated in the form of heat by resistance and is not stored as either electric field or magnetic field.
In the case of a sinusoidal current, the unit of the amplitude is:- a)Radians/second
- b)Hertz
- c)Radians
- d)Amperes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the case of a sinusoidal current, the unit of the amplitude is:
a)
Radians/second
b)
Hertz
c)
Radians
d)
Amperes
|
|
Raghav Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
In the case of a sinusoidal current, the unit of the amplitude is given in Amperes (option D).
Sinusoidal Current:
A sinusoidal current is a current that follows a sinusoidal waveform over time. It can be represented by the equation:
I(t) = I_m sin(ωt + φ)
Where:
- I(t) is the instantaneous value of the current at time 't'
- I_m is the amplitude of the current
- ω is the angular frequency in radians/second
- t is the time in seconds
- φ is the phase angle in radians
Amplitude:
The amplitude of a sinusoidal current is the maximum value of the current waveform. It represents the peak value or the maximum deviation from the average value.
Unit of Amplitude:
The unit of the amplitude of a sinusoidal current is given in Amperes (A). Amperes is the standard unit for measuring electric current.
Alternative Options:
Let's discuss why the other options are not correct:
- Radians/second (option A) is the unit for angular frequency, not the amplitude.
- Hertz (option B) is the unit for frequency, which is the number of cycles per second. It is not the unit for the amplitude.
- Radians (option C) is the unit for the phase angle, not the amplitude.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Amperes, which represents the unit of the amplitude of a sinusoidal current.
In the case of a sinusoidal current, the unit of the amplitude is given in Amperes (option D).
Sinusoidal Current:
A sinusoidal current is a current that follows a sinusoidal waveform over time. It can be represented by the equation:
I(t) = I_m sin(ωt + φ)
Where:
- I(t) is the instantaneous value of the current at time 't'
- I_m is the amplitude of the current
- ω is the angular frequency in radians/second
- t is the time in seconds
- φ is the phase angle in radians
Amplitude:
The amplitude of a sinusoidal current is the maximum value of the current waveform. It represents the peak value or the maximum deviation from the average value.
Unit of Amplitude:
The unit of the amplitude of a sinusoidal current is given in Amperes (A). Amperes is the standard unit for measuring electric current.
Alternative Options:
Let's discuss why the other options are not correct:
- Radians/second (option A) is the unit for angular frequency, not the amplitude.
- Hertz (option B) is the unit for frequency, which is the number of cycles per second. It is not the unit for the amplitude.
- Radians (option C) is the unit for the phase angle, not the amplitude.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Amperes, which represents the unit of the amplitude of a sinusoidal current.
Three 400 Ω resistors are connected in delta and powered by a 400 V (rms), 50 Hz balanced, symmetrical R - Y - B sequence, three-phase three-wire mains. The rms value of the line current (in amperes, rounded off to one decimal place) is
Correct answer is between '1.7,1.8'. Can you explain this answer?
Three 400 Ω resistors are connected in delta and powered by a 400 V (rms), 50 Hz balanced, symmetrical R - Y - B sequence, three-phase three-wire mains. The rms value of the line current (in amperes, rounded off to one decimal place) is
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |

In delta connection, VL = Vph = 400 Ω
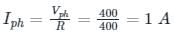
ILine = √3 Iphase = √3 × 1 = 1.732 A
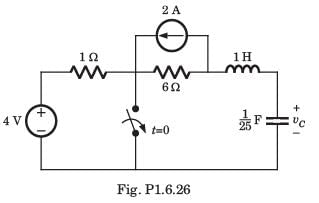
In the circuit shown in the figure, the value of node voltage ��2 is
- a)22 + j2 V
- b)2 + j 22 V
- c)22 – j 2 V
- d)2 – j 22 V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the circuit shown in the figure, the value of node voltage ��2 is

a)
22 + j2 V
b)
2 + j 22 V
c)
22 – j 2 V
d)
2 – j 22 V

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
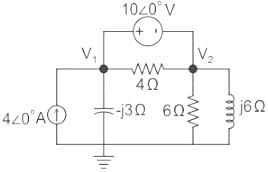
Since there is a voltage source present between the two nodes, the concept of supernode will be applied.
By KCL, using supernode at Node (1) and (2), we can write:
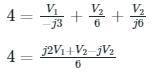
24 = j2 V1 + (1 - j) V2 ---(1)
By KVL, V1 – V2 = 10 ∠0°
V1 = V2 + 10 ---(2)
Substituting (2) in (1), we get:
24 = j2 (V2 + 10) + (1 - j) V2
24 = j2 V2 + j20 + (1 - j) V2
24 = j20 + (1 + j) V2
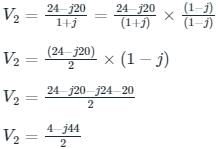
V2 = 2 – j22 V
Three currents i1, i2 and i3 meet at a node as shown in the figure. If i1 = 3 cos (ωt) ampere, i2 = 4 sin (ωt) ampere and i3 = I3 cos (ωt + θ) ampere, the value of I3 in ampere is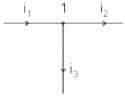
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Three currents i1, i2 and i3 meet at a node as shown in the figure. If i1 = 3 cos (ωt) ampere, i2 = 4 sin (ωt) ampere and i3 = I3 cos (ωt + θ) ampere, the value of I3 in ampere is

|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
By applying KCL at node 1,
i1 = i2 + i3
i3 = i1 – i2
= 3 cos ωt – 4 sin ωt
= 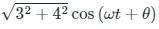
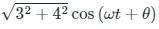
= 5 cos (ωt + θ)
Given that, i3 = I3 cos (ωt + θ)
⇒ I3 = 5A.
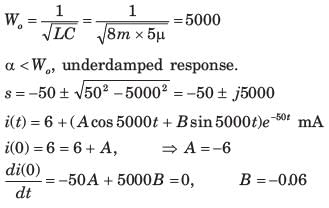
Consider a current source i(t) connected across a 0.5 mH inductor, where i(t) = 0 A for t < 0 and i(t) = (8e-250t - 4e-1000t) A for t ≥ 0. The voltage across the inductor at t = 0 s is- a)0.5 V
- b)1 V
- c)2 V
- d)4 V
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a current source i(t) connected across a 0.5 mH inductor, where i(t) = 0 A for t < 0 and i(t) = (8e-250t - 4e-1000t) A for t ≥ 0. The voltage across the inductor at t = 0 s is
a)
0.5 V
b)
1 V
c)
2 V
d)
4 V
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Concept:
When current source i(t) connected across an inductor(L), then the voltage across the inductor is given as
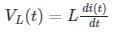
When voltage source v(t) connected across a capacitor(C), then the current across the capacitor is given as
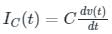
Calculation:
Given i(t) = (8e-250t - 4e-1000t) A for t ≥ 0, L = 0.5 mH
Then the voltage across the inductor is given as
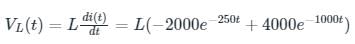
At t = 0 its value is given as
VL = 0.5 × 10-3 × (- 2000 + 4000)
VL = 1 V
Instantaneous power is negative, when the polarities of voltage and current are of __________- a)opposite sign
- b)same sign
- c)voltage is zero
- d)current is zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Instantaneous power is negative, when the polarities of voltage and current are of __________
a)
opposite sign
b)
same sign
c)
voltage is zero
d)
current is zero

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Instantaneous power is negative, when voltage and current have opposite sign that is if voltage is positive, the current is negative and if current is positive, the voltage is negative.
In inductor, the energy delivered by source is ____________ by inductor.- a)stored as magnetic field
- b)dissipated in the form of heat
- c)returned to source
- d)stored as electric field
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In inductor, the energy delivered by source is ____________ by inductor.
a)
stored as magnetic field
b)
dissipated in the form of heat
c)
returned to source
d)
stored as electric field

|
Crack Gate answered |
In inductor, the energy delivered by source is stored as magnetic field by inductor and is not dissipated in the form of heat or stored as electric field.
The time varying part in the equation of instantaneous power has frequency ________________ that of the frequency of voltage or current wave forms.- a)equal to
- b)twice
- c)thrice
- d)four times
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The time varying part in the equation of instantaneous power has frequency ________________ that of the frequency of voltage or current wave forms.
a)
equal to
b)
twice
c)
thrice
d)
four times

|
Machine Experts answered |
The time varying part in the equation of instantaneous power has a frequency twice that of voltage or current wave forms and the other part is a fixed part.
The average value of power if θ = 0⁰ is?- a)VmIm/3
- b)VmIm/2
- c)VmIm/4
- d)VmIm/8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average value of power if θ = 0⁰ is?
a)
VmIm/3
b)
VmIm/2
c)
VmIm/4
d)
VmIm/8

|
EduRev GATE answered |
The average value of power if θ = 0⁰ is VmIm/2. So, average power = VmIm/2 at θ = 0⁰. When phase angle is increased the negative portion of the power cycle increases and lesser power is dissipated.
In capacitor, the energy delivered by source is ____________ by capacitor.- a)returned to source
- b)dissipated in the form of heat
- c)stored as electric field
- d)stored as magnetic field
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In capacitor, the energy delivered by source is ____________ by capacitor.
a)
returned to source
b)
dissipated in the form of heat
c)
stored as electric field
d)
stored as magnetic field

|
Bayshore Academy answered |
In capacitor, the energy delivered by source is stored as electric field by capacitor and is not stored as magnetic field or dissipated in the form of heat.
If there is complex impedance in a circuit, part of energy is ____________ by reactive part and part of its energy is ____________ by the resistance.- a)alternately stored and returned, alternately stored and returned
- b)alternately stored and returned, dissipated
- c)dissipated, alternately stored and returned
- d)dissipated, dissipated
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If there is complex impedance in a circuit, part of energy is ____________ by reactive part and part of its energy is ____________ by the resistance.
a)
alternately stored and returned, alternately stored and returned
b)
alternately stored and returned, dissipated
c)
dissipated, alternately stored and returned
d)
dissipated, dissipated

|
Machine Experts answered |
If there is complex impedance in a circuit, part of energy is alternately stored and returned by reactive part and part of its energy is dissipated by the resistance. The amount of energy dissipated is determined by relative values of resistance and reactance.
Chapter doubts & questions for AC Fundamentals - RRB JE for Electrical Engineering 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of AC Fundamentals - RRB JE for Electrical Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
RRB JE for Electrical Engineering
23 videos|81 docs|32 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily