All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Mechanical Engineering (SSC JE) Tests for Mechanical Engineering Exam
The temperature at which the volume of a gasn becomes zero is called- a)absolute scale of temperature
- b)absolute zero temperature
- c)absolute temperature
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The temperature at which the volume of a gasn becomes zero is called
a)
absolute scale of temperature
b)
absolute zero temperature
c)
absolute temperature
d)
none of these
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
General gas equation
pv=mrt
at absolute zero kelvin temp.
pressure =zero
that means
0×v= mr×0
therefore volume will be zero at absolute zero kelvin temp.
pv=mrt
at absolute zero kelvin temp.
pressure =zero
that means
0×v= mr×0
therefore volume will be zero at absolute zero kelvin temp.
A manometer is used to measure- a)low pressure
- b)moderate pressure
- c)high pressure
- d)atomospheric pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A manometer is used to measure
a)
low pressure
b)
moderate pressure
c)
high pressure
d)
atomospheric pressure
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Manometers are devices in which columns of a suitable liquid are used to measure the difference in pressure between two points or between a certain point and the atmosphere. Manometer is needed for measuring large gauge pressures. It is basically the modified form of the piezometric tube.
Work transfer between the system and the surroundings- a)Is a point function
- b)Is always given by
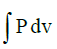
- c)Is a function of pressure only
- d)Depends on the path followed by the system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Work transfer between the system and the surroundings
a)
Is a point function
b)
Is always given by 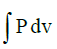
c)
Is a function of pressure only
d)
Depends on the path followed by the system

|
Naroj Boda answered |
The work is the path function so the work transfer between the system and the surrounding depend on the path that followed by tha system.
The Young's modulus of a material is 125 GPa and Poissons ratio is 0.25.The modulus rigidityof the material is- a)30 GPa
- b)50 GPa
- c)80 GPa
- d)100 GPa
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Young's modulus of a material is 125 GPa and Poissons ratio is 0.25.The modulus rigidityof the material is
a)
30 GPa
b)
50 GPa
c)
80 GPa
d)
100 GPa
|
|
Gopal Choudhury answered |
Given parameters:
Young's modulus (E) = 125 GPa
Poisson's ratio (ν) = 0.25
Modulus of rigidity (G) is given by the formula:
G = E/ (2(1+ν))
Calculation:
G = 125/(2(1+0.25))
G = 50 GPa
Therefore, the modulus of rigidity of the material is 50 GPa.
Explanation:
Modulus of rigidity is a measure of a material's resistance to shearing deformation. It is the ratio of the shear stress to the shear strain. It is also known as shear modulus.
Young's modulus is a measure of a material's stiffness or resistance to deformation in response to an applied force. Poisson's ratio is a measure of the ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain when a material is subjected to an applied force.
Using the formula for modulus of rigidity, we can calculate it using Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio. In this case, we were given the values of Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio. Substituting these values in the formula, we get the modulus of rigidity as 50 GPa.
Conclusion:
The correct option for the given question is (B) 50 GPa.
Young's modulus (E) = 125 GPa
Poisson's ratio (ν) = 0.25
Modulus of rigidity (G) is given by the formula:
G = E/ (2(1+ν))
Calculation:
G = 125/(2(1+0.25))
G = 50 GPa
Therefore, the modulus of rigidity of the material is 50 GPa.
Explanation:
Modulus of rigidity is a measure of a material's resistance to shearing deformation. It is the ratio of the shear stress to the shear strain. It is also known as shear modulus.
Young's modulus is a measure of a material's stiffness or resistance to deformation in response to an applied force. Poisson's ratio is a measure of the ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain when a material is subjected to an applied force.
Using the formula for modulus of rigidity, we can calculate it using Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio. In this case, we were given the values of Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio. Substituting these values in the formula, we get the modulus of rigidity as 50 GPa.
Conclusion:
The correct option for the given question is (B) 50 GPa.
In a fillet welded joint, the weakest area of the weld is
- a)toe
- b)root
- c)throat
- d)face
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a fillet welded joint, the weakest area of the weld is
a)
toe
b)
root
c)
throat
d)
face

|
Robot Khan answered |
The fillet welds are subjected to tensile stress. The minimum cross-section of the fillet is at the throat. Therefore the failure due to tensile stress occurs at the throat section. Thus the weakest area of the weld is the throat.
The viscosity of water with respect to air is about:
- a) 50
- b) 55
- c) 60
- d) 65 times
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The viscosity of water with respect to air is about:
a)
50b)
55c)
60d)
65 times|
|
Divya Banerjee answered |
Viscosity of Water with Respect to Air
Viscosity is defined as the measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is a property of fluids that describes the internal frictional forces that cause a fluid to resist flow. The viscosity of a fluid is dependent on the fluid's molecular structure and temperature.
Water and air are both fluids with different molecular structures, and hence, they have different viscosities. The viscosity of water with respect to air is about 55 times.
Explanation:
The viscosity of air at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is approximately 0.0000181 Pa.s, while the viscosity of water at STP is approximately 0.001 Pa.s. This means that water is approximately 55 times more viscous than air.
This difference in viscosity plays a crucial role in many fluid mechanics applications. For example, a fluid such as water will flow more slowly through a pipe than air, even if the pressure difference driving the flow is the same. The higher viscosity of water means that more energy is required to move it through a pipe, and this can result in higher pumping costs.
In summary, the viscosity of water is much higher than the viscosity of air, and this difference has significant implications for fluid mechanics applications.
Viscosity is defined as the measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is a property of fluids that describes the internal frictional forces that cause a fluid to resist flow. The viscosity of a fluid is dependent on the fluid's molecular structure and temperature.
Water and air are both fluids with different molecular structures, and hence, they have different viscosities. The viscosity of water with respect to air is about 55 times.
Explanation:
The viscosity of air at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is approximately 0.0000181 Pa.s, while the viscosity of water at STP is approximately 0.001 Pa.s. This means that water is approximately 55 times more viscous than air.
This difference in viscosity plays a crucial role in many fluid mechanics applications. For example, a fluid such as water will flow more slowly through a pipe than air, even if the pressure difference driving the flow is the same. The higher viscosity of water means that more energy is required to move it through a pipe, and this can result in higher pumping costs.
In summary, the viscosity of water is much higher than the viscosity of air, and this difference has significant implications for fluid mechanics applications.
The dimensions of surface tension are- a)N/m2
- b)J/m
- c)J/m2
- d)W/m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The dimensions of surface tension are
a)
N/m2
b)
J/m
c)
J/m2
d)
W/m
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
surface tension is often expressed as an amount of force exerted in the surface perpendicular to a line of unit length. The unit then is newtons per metre, which is equivalent to joules per square metre.
Measurement of temperature is based on which law of thermo dynamics?- a)Zeroth law of thermo dynamics
- b)First law of thermo dynamics
- c)Second law of thermo dynamics
- d)Third law of thermo dynamics
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Measurement of temperature is based on which law of thermo dynamics?
a)
Zeroth law of thermo dynamics
b)
First law of thermo dynamics
c)
Second law of thermo dynamics
d)
Third law of thermo dynamics

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
law of thermodynamics is the basis for measurement of temperature and setting its scale. In simple word, Zeroth law of thermodynamics says that “When two bodies are separately in thermal equilibrium with the third body, then the two are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.”
In Oxy-acetelene gas welding, for complete combustion, the volume of oxygen required per unit of acetylene is- a)1
- b)1.5
- c)2
- d)2.5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Oxy-acetelene gas welding, for complete combustion, the volume of oxygen required per unit of acetylene is
a)
1
b)
1.5
c)
2
d)
2.5
|
|
Pritam Das answered |
Complete Combustion in Oxy-acetylene Gas Welding
Complete combustion is an essential process in oxy-acetylene gas welding where the fuel gas, Acetylene, burns in the presence of oxygen gas to generate heat. During the process, the acetylene gas is decomposed into carbon and hydrogen, releasing a large amount of heat energy. The heat generated by the exothermic reaction is utilized to melt and join metallic components.
Volume of Oxygen Required for Complete Combustion
The volume of oxygen required for complete combustion in oxy-acetylene gas welding depends on the stoichiometric ratio of acetylene and oxygen. The stoichiometric ratio is the minimum ratio of oxygen required to burn a unit volume of acetylene gas completely.
The stoichiometric ratio for acetylene and oxygen is 1:2.5. It means that for every unit volume of acetylene gas, 2.5 units of oxygen gas are required to burn it completely. Therefore, the correct option for the volume of oxygen required per unit of acetylene is 2.5.
Conclusion
In summary, complete combustion is a critical process in oxy-acetylene gas welding, where the volume of oxygen required for complete combustion depends on the stoichiometric ratio of acetylene and oxygen. The stoichiometric ratio for acetylene and oxygen is 1:2.5, which means that for every unit volume of acetylene gas, 2.5 units of oxygen gas are required to burn it completely.
Complete combustion is an essential process in oxy-acetylene gas welding where the fuel gas, Acetylene, burns in the presence of oxygen gas to generate heat. During the process, the acetylene gas is decomposed into carbon and hydrogen, releasing a large amount of heat energy. The heat generated by the exothermic reaction is utilized to melt and join metallic components.
Volume of Oxygen Required for Complete Combustion
The volume of oxygen required for complete combustion in oxy-acetylene gas welding depends on the stoichiometric ratio of acetylene and oxygen. The stoichiometric ratio is the minimum ratio of oxygen required to burn a unit volume of acetylene gas completely.
The stoichiometric ratio for acetylene and oxygen is 1:2.5. It means that for every unit volume of acetylene gas, 2.5 units of oxygen gas are required to burn it completely. Therefore, the correct option for the volume of oxygen required per unit of acetylene is 2.5.
Conclusion
In summary, complete combustion is a critical process in oxy-acetylene gas welding, where the volume of oxygen required for complete combustion depends on the stoichiometric ratio of acetylene and oxygen. The stoichiometric ratio for acetylene and oxygen is 1:2.5, which means that for every unit volume of acetylene gas, 2.5 units of oxygen gas are required to burn it completely.
The value of 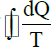 for an irreversible cycle is
for an irreversible cycle is- a)Equal to zero
- b)Greater than zero
- c)Less than zero
- d)Unity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of 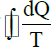 for an irreversible cycle is
for an irreversible cycle is
a)
Equal to zero
b)
Greater than zero
c)
Less than zero
d)
Unity

|
Robot Khan answered |
DQ/T <0 ;="" for="" irreversible="">
dQ/T =0 ; for reversible process
dQ/T =0 ; for reversible process
The liquid used in manometers should have
- a)low density
- b)high surface tension
- c)low surface tension
- d)high density
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The liquid used in manometers should have
a)
low density
b)
high surface tension
c)
low surface tension
d)
high density

|
Vertex Academy answered |
The liquid used in manometers should have high density.To lower the column height, the manometers liquid must have a high density. Making the column height a reasonable limit is critical since manometers are used to measure high pressures.
Which of the following operation is first performed ?- a)Spot
- b)Boring
- c)Tapping
- d)Drilling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following operation is first performed ?
a)
Spot
b)
Boring
c)
Tapping
d)
Drilling
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
Swiss physician Hans Christian Jacobaeus performed the first Laparoscopic surgery on humans. 1916. Austrian surgeon Hermann Schloffer performed boring the first splenectomy operation.
An Otto cycle has a compression ratio of 8. If 250 kJ of work is extracted from the cycle, the heat rejected by the cycle isa)500 kJb)442.69 kJc)331.4 kJd)192.69 kJCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Answer is d) 192.69 kJ
Efficiency η(otto) = 1 - [1/r^(γ - 1)] = W/(W + Q2) = 250/(250 + Q2)
=> 1 - [1/8^0.4] = 250/(250 + Q2)
Q2 = 192.69 kJ
Guest's theory is used for- a)brittle materials
- b)ductile materials
- c)elastic materials
- d)plastic materials
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Guest's theory is used for
a)
brittle materials
b)
ductile materials
c)
elastic materials
d)
plastic materials
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
MAXIMUM SHEAR STRESS THEORY (GUEST's or TRESCA's THEORY)
According to this theory, the elastic failure occurs when the greatest shear stress reaches a value equal to the shear stress at elastic limit in a simple tension test. This is used for ductile material
A process, in which the temperature of the working substance remains constant during itsexpansion or compression, is called- a)isothermal process
- b)hyperbolic process
- c)adiabatic process
- d)polytropic proce
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A process, in which the temperature of the working substance remains constant during itsexpansion or compression, is called
a)
isothermal process
b)
hyperbolic process
c)
adiabatic process
d)
polytropic proce

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Iso- some (constant) where the temperature is constant the process is known as isothermal process.
The phenomenon of pre-ignition- a)always occurs in diesel engines
- b)never occurs in diesel engines
- c)always occurs in petrol engines
- d)increases the power output engines
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomenon of pre-ignition
a)
always occurs in diesel engines
b)
never occurs in diesel engines
c)
always occurs in petrol engines
d)
increases the power output engines
|
|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Pre-ignition (or preignition) in a spark-ignition engine is a technically different phenomenon from engine knocking, and describes the event wherein the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder ignites before the spark plug fires. ... Many engines have suffered such failure where improper fuel delivery is present.
The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is always
- a)equal to one
- b)less than one
- c)greater than one
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is always
a)
equal to one
b)
less than one
c)
greater than one
d)
none of these
|
|
Nishanth Basu answered |
Ratio of Static Friction to Dynamic Friction
Static friction is the force that resists the motion of an object when it is at rest, while dynamic friction is the force that resists the motion of an object when it is in motion. The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction depends on various factors, such as the surface roughness, the weight of the object, and the force applied to the object. However, there is a general rule that can be applied in most cases.
The Ratio Is Greater Than One
The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is greater than one. This means that it takes more force to overcome static friction and start an object moving than it does to keep it moving once it is in motion. This is because static friction is usually stronger than dynamic friction.
Example
For example, imagine trying to push a heavy box across a rough floor. At first, the box will not move because of static friction. You will need to apply a certain amount of force to overcome this static friction and start the box moving. Once the box is in motion, you will need to apply less force to keep it moving, because dynamic friction is weaker than static friction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is always greater than one. This means that it is harder to overcome static friction and start an object moving than it is to keep it moving once it is in motion. Understanding this ratio is important in many applications, such as designing machines and calculating the forces required to move objects.
Static friction is the force that resists the motion of an object when it is at rest, while dynamic friction is the force that resists the motion of an object when it is in motion. The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction depends on various factors, such as the surface roughness, the weight of the object, and the force applied to the object. However, there is a general rule that can be applied in most cases.
The Ratio Is Greater Than One
The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is greater than one. This means that it takes more force to overcome static friction and start an object moving than it does to keep it moving once it is in motion. This is because static friction is usually stronger than dynamic friction.
Example
For example, imagine trying to push a heavy box across a rough floor. At first, the box will not move because of static friction. You will need to apply a certain amount of force to overcome this static friction and start the box moving. Once the box is in motion, you will need to apply less force to keep it moving, because dynamic friction is weaker than static friction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is always greater than one. This means that it is harder to overcome static friction and start an object moving than it is to keep it moving once it is in motion. Understanding this ratio is important in many applications, such as designing machines and calculating the forces required to move objects.
Which of the following component is not subjected to high-pressure high-temperature steam ?- a)Superheaters
- b)Inlet stages of turbine
- c)Condenser
- d)Valves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following component is not subjected to high-pressure high-temperature steam ?
a)
Superheaters
b)
Inlet stages of turbine
c)
Condenser
d)
Valves

|
Abhinash Kodipalli answered |
Function of condenser is to condensate the steam which is expanded in turbine and also maintain the low pressure in the last stages of turbine for better efficiency.So Condenser is designed for low pressure and low temperature.
The critical value of Reynolds number for transition from laminar to turbulent boundary layer in external flows is taken as- a)2300
- b)4000
- c)5 × 105
- d)3 × 106
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The critical value of Reynolds number for transition from laminar to turbulent boundary layer in external flows is taken as
a)
2300
b)
4000
c)
5 × 105
d)
3 × 106
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
For flow over a flat plate, transition from laminar to turbulent boundary layer occurs when Reynolds number at x exceeds Rex,crit ~ 500,000. Transition may occur earlier, but it is dependent especially on the surface roughness.
The fundamental unit of enthalpy is- a)MLT–2
- b)ML2T–1
- c)ML2T–2
- d)ML3T–2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The fundamental unit of enthalpy is
a)
MLT–2
b)
ML2T–1
c)
ML2T–2
d)
ML3T–2
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Enthalapy units and work units are same W = F x S = MLT^-2 x L=ML^2T^-2
In a boiler, the air preheater in invariably located between:- a)Forced draft fan and chimney
- b)Forced draft fan and furnace
- c)Economizer and feed pump
- d)Condenser and feed pump
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a boiler, the air preheater in invariably located between:
a)
Forced draft fan and chimney
b)
Forced draft fan and furnace
c)
Economizer and feed pump
d)
Condenser and feed pump

|
Raghavendra Dasgupta answered |
The air preheater in a boiler is an important component that helps in improving the efficiency of the boiler system. It is responsible for heating the combustion air before it enters the furnace, which results in better fuel combustion and heat transfer.
The correct location of the air preheater in a boiler is between the forced draft fan and the furnace. This placement allows the preheated air to be supplied directly to the furnace for combustion. Let's understand why this is the ideal location:
1. Forced Draft Fan (FDF):
The forced draft fan is responsible for supplying the air required for combustion into the furnace. It creates a positive pressure inside the furnace and ensures the proper airflow. The air preheater is placed before the FDF to preheat the air before it enters the fan.
2. Air Preheater (APH):
The air preheater is a heat exchanger that transfers heat from the flue gases to the incoming combustion air. It consists of a series of tubes or plates through which the flue gases flow. As the hot flue gases pass over these tubes, they transfer their heat to the air flowing through them, thereby preheating it.
3. Furnace:
The furnace is the central combustion chamber where the fuel is burned. The preheated air from the air preheater is supplied to the furnace through the forced draft fan. This preheated air helps in achieving better fuel combustion by providing the required oxygen and temperature for efficient combustion.
Benefits of placing the air preheater between the forced draft fan and furnace:
- Improved Fuel Combustion: Preheating the combustion air results in better fuel combustion as it provides the necessary temperature and oxygen for efficient combustion. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and increased boiler efficiency.
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: The air preheater increases the overall heat transfer in the boiler system by recovering heat from the flue gases. This recovered heat is then utilized to preheat the incoming combustion air, thereby reducing the energy required to heat the air.
- Reduced Flue Gas Temperature: By extracting heat from the flue gases, the air preheater helps in lowering the temperature of the flue gases exiting the boiler. This reduces the heat loss through the chimney and increases the overall efficiency of the boiler system.
- Environmental Benefits: The preheating of combustion air reduces the emission of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO) by improving the combustion efficiency. This contributes to a cleaner and more environmentally friendly operation.
In conclusion, placing the air preheater between the forced draft fan and furnace in a boiler system is essential for achieving better fuel combustion, improved heat transfer, and increased overall efficiency.
The correct location of the air preheater in a boiler is between the forced draft fan and the furnace. This placement allows the preheated air to be supplied directly to the furnace for combustion. Let's understand why this is the ideal location:
1. Forced Draft Fan (FDF):
The forced draft fan is responsible for supplying the air required for combustion into the furnace. It creates a positive pressure inside the furnace and ensures the proper airflow. The air preheater is placed before the FDF to preheat the air before it enters the fan.
2. Air Preheater (APH):
The air preheater is a heat exchanger that transfers heat from the flue gases to the incoming combustion air. It consists of a series of tubes or plates through which the flue gases flow. As the hot flue gases pass over these tubes, they transfer their heat to the air flowing through them, thereby preheating it.
3. Furnace:
The furnace is the central combustion chamber where the fuel is burned. The preheated air from the air preheater is supplied to the furnace through the forced draft fan. This preheated air helps in achieving better fuel combustion by providing the required oxygen and temperature for efficient combustion.
Benefits of placing the air preheater between the forced draft fan and furnace:
- Improved Fuel Combustion: Preheating the combustion air results in better fuel combustion as it provides the necessary temperature and oxygen for efficient combustion. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and increased boiler efficiency.
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: The air preheater increases the overall heat transfer in the boiler system by recovering heat from the flue gases. This recovered heat is then utilized to preheat the incoming combustion air, thereby reducing the energy required to heat the air.
- Reduced Flue Gas Temperature: By extracting heat from the flue gases, the air preheater helps in lowering the temperature of the flue gases exiting the boiler. This reduces the heat loss through the chimney and increases the overall efficiency of the boiler system.
- Environmental Benefits: The preheating of combustion air reduces the emission of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO) by improving the combustion efficiency. This contributes to a cleaner and more environmentally friendly operation.
In conclusion, placing the air preheater between the forced draft fan and furnace in a boiler system is essential for achieving better fuel combustion, improved heat transfer, and increased overall efficiency.
A mandrel is used to hold- a)an eccentric work
- b)a heavy work
- c)a thin work
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A mandrel is used to hold
a)
an eccentric work
b)
a heavy work
c)
a thin work
d)
none of these
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
Mandrel is used to hold a hollow bar or a bar with a bore wen turning between live centre and dead cente of a lathe. A moving mandrel is also used for tube drawing
The C.O.P. of a refrigerator working on a reversed Carnot cycle is where
T1 = Lowest absolute temperature, and
T2 = Highest absolute temperature- a)
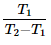
- b)
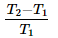
- c)
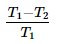
- d)
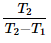
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The C.O.P. of a refrigerator working on a reversed Carnot cycle is where
T1 = Lowest absolute temperature, and
T2 = Highest absolute temperature
T1 = Lowest absolute temperature, and
T2 = Highest absolute temperature
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Jyotindra Chaudhari answered |
Cop of refrigerator is given as desired effect upon work done
A venturi meter is a device based on the bernoulli principle and is used for measuring- a)velocity
- b)pressure drop
- c)total head
- d)flow rate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A venturi meter is a device based on the bernoulli principle and is used for measuring
a)
velocity
b)
pressure drop
c)
total head
d)
flow rate

|
Chandra Prakash Mishra answered |
Flow rate means discharge. as u know venturimeter is a discharge measuring device so correct option is d
Eutectoid reaction occurs ata) 600ºC b) 727ºCc) 114ºCd) 1493ºCCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
In eutectoid reaction, the austenite transforms into a phase mixture of ferrite (containing 0.76% C) and cementite. This phase mixture is known as pearlite. The eutectoid reaction occurs at a constant temperature. This is known as eutectoid temperature and is 723DigreeC
Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowedto reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The temperature is specified by the- a)Zeroth law of thermodynamics
- b)First law of thermodynamics
- c)Second law of thermodynamics
- d)Third law of thermodynamics
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowedto reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The temperature is specified by the
a)
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
b)
First law of thermodynamics
c)
Second law of thermodynamics
d)
Third law of thermodynamics

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
A and C are in thermal equilibrium.
B and C are in thermal equilibrium.
A and B are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
so, final temperature attained is specified by "Zeroth law of thermodynamics."
The metacentric heights of two floating bodies A and B are 1 m and 1.5 m respectively. Select thecorrect statement.- a)The bodies A and B have equal stability
- b)The body A is more stable than body B
- c)The body B is more stable than body A
- d)The bodies A and B are unstable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The metacentric heights of two floating bodies A and B are 1 m and 1.5 m respectively. Select thecorrect statement.
a)
The bodies A and B have equal stability
b)
The body A is more stable than body B
c)
The body B is more stable than body A
d)
The bodies A and B are unstable

|
Thrishna N answered |
Higher the metacentric height ,higher will be the stability of the body
A Hooke's joint is used to connect two- a)Non-Coplanar and nonparallel shaft
- b)Coplanar and nonparallel shaft
- c)Co-planer and parallel shafts
- d)Non- coplaner and parallel shafts
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A Hooke's joint is used to connect two
a)
Non-Coplanar and nonparallel shaft
b)
Coplanar and nonparallel shaft
c)
Co-planer and parallel shafts
d)
Non- coplaner and parallel shafts
|
|
Ashish Pillai answered |
Explanation:
A Hookes joint is a type of universal joint that is used to connect two non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts. It is also known as Cardan joint or universal coupling.
Let's understand the term non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts. Coplanar means lying in the same plane, and parallel means lying in the same direction and never meeting. In the case of shafts, coplanar shafts lie in the same plane, and parallel shafts lie in the same direction. Non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts do not lie in the same plane or direction. They have a misalignment between them.
A Hookes joint is used to transmit torque between two shafts that are not in the same plane or direction. It is used to connect the drive shaft to the driven shaft in automotive applications.
The Hookes joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the spider, which is fitted between them. Each yoke has two arms, and the spider fits between them. The spider has four arms at right angles to each other, and each arm is connected to a yoke. The yokes are connected to the shafts, and the spider connects the two yokes.
When the drive shaft rotates, it causes the yoke to rotate, and the spider transmits the rotation to the driven shaft. The Hookes joint can accommodate a certain amount of misalignment between the two shafts. It can also operate at different angles between the two shafts.
Therefore, a Hookes joint is used to connect two non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts that have a misalignment between them. It can transmit torque between them and accommodate different angles between the shafts.
A Hookes joint is a type of universal joint that is used to connect two non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts. It is also known as Cardan joint or universal coupling.
Let's understand the term non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts. Coplanar means lying in the same plane, and parallel means lying in the same direction and never meeting. In the case of shafts, coplanar shafts lie in the same plane, and parallel shafts lie in the same direction. Non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts do not lie in the same plane or direction. They have a misalignment between them.
A Hookes joint is used to transmit torque between two shafts that are not in the same plane or direction. It is used to connect the drive shaft to the driven shaft in automotive applications.
The Hookes joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the spider, which is fitted between them. Each yoke has two arms, and the spider fits between them. The spider has four arms at right angles to each other, and each arm is connected to a yoke. The yokes are connected to the shafts, and the spider connects the two yokes.
When the drive shaft rotates, it causes the yoke to rotate, and the spider transmits the rotation to the driven shaft. The Hookes joint can accommodate a certain amount of misalignment between the two shafts. It can also operate at different angles between the two shafts.
Therefore, a Hookes joint is used to connect two non-coplanar and nonparallel shafts that have a misalignment between them. It can transmit torque between them and accommodate different angles between the shafts.
The ratio of bulk modulus to Young's modulus for a Poisson's ratio of 0.25 will be- a)1/3
- b)2/3
- c)1
- d)3/2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of bulk modulus to Young's modulus for a Poisson's ratio of 0.25 will be
a)
1/3
b)
2/3
c)
1
d)
3/2
|
|
Dhruv Dasgupta answered |
Bulk modulus and Young's modulus are both measures of a material's elasticity, but they measure different aspects of elasticity.
Bulk modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to compression, while Young's modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to deformation in tension or compression.
Poisson's ratio is a measure of a material's tendency to compress laterally when it is stretched or pulled in one direction.
The relationship between these three measures can be expressed as follows:
Bulk modulus / Young's modulus = 3(1 - 2Poisson's ratio) / (1 + Poisson's ratio)
If Poisson's ratio is 0.25, then:
Bulk modulus / Young's modulus = 3(1 - 2(0.25)) / (1 + 0.25)
= 3(0.5) / 1.25
= 1.2
Therefore, the ratio of bulk modulus to Young's modulus for a Poisson's ratio of 0.25 is 2/3 (option B).
Bulk modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to compression, while Young's modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to deformation in tension or compression.
Poisson's ratio is a measure of a material's tendency to compress laterally when it is stretched or pulled in one direction.
The relationship between these three measures can be expressed as follows:
Bulk modulus / Young's modulus = 3(1 - 2Poisson's ratio) / (1 + Poisson's ratio)
If Poisson's ratio is 0.25, then:
Bulk modulus / Young's modulus = 3(1 - 2(0.25)) / (1 + 0.25)
= 3(0.5) / 1.25
= 1.2
Therefore, the ratio of bulk modulus to Young's modulus for a Poisson's ratio of 0.25 is 2/3 (option B).
Centrifugal tension in belts is- a)useful because it maintains some tension even when no power is transmitted
- b)not harmful because it does not take part in power transmission
- c)harmful because it increases belt tension and reduces the power transmitted
- d)a hypothetical phenomenon and does not actually exist in belts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Centrifugal tension in belts is
a)
useful because it maintains some tension even when no power is transmitted
b)
not harmful because it does not take part in power transmission
c)
harmful because it increases belt tension and reduces the power transmitted
d)
a hypothetical phenomenon and does not actually exist in belts
|
|
Avik Ghosh answered |
Centrifugal tension in belts
Introduction:
In belt drives, there are two types of tensions- initial tension and operating tension. The initial tension is provided to keep the belt in a state of tension when there is no load on the belt. The operating tension is the tension that the belt experiences when power is transmitted. Centrifugal tension is a type of operating tension.
Explanation:
Centrifugal tension is a phenomenon that occurs due to the rotation of the belt. When a belt rotates, the particles on the outer edge of the belt tend to move away from the center of rotation due to centrifugal force. This results in an increase in tension on the outer edge of the belt. This increase in tension is called centrifugal tension.
Effect of centrifugal tension:
Centrifugal tension can be harmful to the belt drive system. This is because it increases the tension in the belt which can lead to excessive wear and tear of the belt. Additionally, centrifugal tension reduces the power transmitted by the belt. This is because the increased tension causes the belt to slip on the pulley, reducing the amount of power transmitted.
Conclusion:
Centrifugal tension is a type of operating tension in belt drives that occurs due to the rotation of the belt. While it can be useful in maintaining some tension when no power is transmitted, it can be harmful when power is transmitted. Centrifugal tension increases the tension in the belt which can lead to excessive wear and tear and reduces the power transmitted by the belt.
Introduction:
In belt drives, there are two types of tensions- initial tension and operating tension. The initial tension is provided to keep the belt in a state of tension when there is no load on the belt. The operating tension is the tension that the belt experiences when power is transmitted. Centrifugal tension is a type of operating tension.
Explanation:
Centrifugal tension is a phenomenon that occurs due to the rotation of the belt. When a belt rotates, the particles on the outer edge of the belt tend to move away from the center of rotation due to centrifugal force. This results in an increase in tension on the outer edge of the belt. This increase in tension is called centrifugal tension.
Effect of centrifugal tension:
Centrifugal tension can be harmful to the belt drive system. This is because it increases the tension in the belt which can lead to excessive wear and tear of the belt. Additionally, centrifugal tension reduces the power transmitted by the belt. This is because the increased tension causes the belt to slip on the pulley, reducing the amount of power transmitted.
Conclusion:
Centrifugal tension is a type of operating tension in belt drives that occurs due to the rotation of the belt. While it can be useful in maintaining some tension when no power is transmitted, it can be harmful when power is transmitted. Centrifugal tension increases the tension in the belt which can lead to excessive wear and tear and reduces the power transmitted by the belt.
A hartnell governor is a- a)dead weight governor
- b)pendulum type governor
- c)spring loaded governor
- d)inertia governor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A hartnell governor is a
a)
dead weight governor
b)
pendulum type governor
c)
spring loaded governor
d)
inertia governor
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In a Porter governor, the balls are attached to the extension of lower links.Porter governor is a modification of Watt's governor, with a central load attached to the sleeve.A Hartnell governor is a spring loaded governor.
The relation between number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l)
- a)l = 2p –2
- b)l = 2p –3
- c)l = 2p –4
- d)l = 2p –5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The relation between number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l)
a)
l = 2p –2
b)
l = 2p –3
c)
l = 2p –4
d)
l = 2p –5
|
|
Stuti Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
A kinematic chain is a set of links connected in such a way that one link is fixed and the other links move relative to it. The number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain can be calculated using the formula:
P = l - 1
where P is the number of pairs and l is the number of links.
The relation between the number of pairs and the number of links can be derived from the above formula as:
l = P + 1
Therefore, the relation between the number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l) is:
l = P + 1
Substituting the value of P from the given options, we get:
a) l = 2P + 2
b) l = 2P + 3
c) l = 2P + 4
d) l = 2P + 5
The correct option is (c) because it satisfies the above relation. Therefore, the relation between the number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l) is:
l = 2P + 4
A kinematic chain is a set of links connected in such a way that one link is fixed and the other links move relative to it. The number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain can be calculated using the formula:
P = l - 1
where P is the number of pairs and l is the number of links.
The relation between the number of pairs and the number of links can be derived from the above formula as:
l = P + 1
Therefore, the relation between the number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l) is:
l = P + 1
Substituting the value of P from the given options, we get:
a) l = 2P + 2
b) l = 2P + 3
c) l = 2P + 4
d) l = 2P + 5
The correct option is (c) because it satisfies the above relation. Therefore, the relation between the number of pairs (P) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links (l) is:
l = 2P + 4
Alcohols are unsuitable at diesel engine fuels because
- a)The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very low which prevents their ignition by compression
- b)The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very high which prevents their ignition bycompression
- c)None of these
- d)The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very low which prevent their ignition by combustion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alcohols are unsuitable at diesel engine fuels because
a)
The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very low which prevents their ignition by compression
b)
The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very high which prevents their ignition bycompression
c)
None of these
d)
The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very low which prevent their ignition by combustion

|
Janhavi Datta answered |
The correct answer is option 'D': The cetane number of alcohol fuels is very low which prevents their ignition by combustion.
Explanation:
Alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, have been considered as potential alternatives to traditional fossil fuels due to their renewable nature and lower carbon emissions. However, they are not suitable as fuels for diesel engines mainly because of their low cetane number.
1. Cetane number: The cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of a fuel. It indicates the ease and speed at which the fuel will ignite in a diesel engine when subjected to compression. A higher cetane number indicates better ignition properties.
2. Diesel combustion process: In a diesel engine, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with the compressed air. The heat of compression causes the fuel to self-ignite and burn, leading to the power stroke. This process is known as compression ignition.
3. Alcohol fuels and cetane number: Alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, have low cetane numbers compared to diesel fuel. Methanol has a cetane number of around 4-7, while ethanol has a cetane number of around 8-15. In contrast, diesel fuel typically has a cetane number of 40-55.
4. Ignition delay: The low cetane number of alcohol fuels leads to a longer ignition delay. Ignition delay refers to the time between the start of fuel injection and the start of combustion. A longer ignition delay can result in poor combustion, incomplete fuel burn, and reduced engine performance.
5. Compression ignition: Alcohol fuels with low cetane numbers require higher compression ratios or higher temperatures to achieve self-ignition. Diesel engines are designed to operate with a specific compression ratio, and altering this ratio for alcohol fuels may not be feasible or efficient.
6. Other factors: In addition to the low cetane number, alcohol fuels also have lower energy content compared to diesel fuel, which can further reduce their efficiency as engine fuels. They also have different physical properties, such as higher volatility and lower lubricity, which may require modifications to engine components and fuel systems.
In conclusion, the low cetane number of alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, prevents their ignition by combustion in diesel engines. This limitation, along with other factors, makes alcohol fuels unsuitable as direct replacements for diesel fuel in diesel engines.
Explanation:
Alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, have been considered as potential alternatives to traditional fossil fuels due to their renewable nature and lower carbon emissions. However, they are not suitable as fuels for diesel engines mainly because of their low cetane number.
1. Cetane number: The cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of a fuel. It indicates the ease and speed at which the fuel will ignite in a diesel engine when subjected to compression. A higher cetane number indicates better ignition properties.
2. Diesel combustion process: In a diesel engine, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with the compressed air. The heat of compression causes the fuel to self-ignite and burn, leading to the power stroke. This process is known as compression ignition.
3. Alcohol fuels and cetane number: Alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, have low cetane numbers compared to diesel fuel. Methanol has a cetane number of around 4-7, while ethanol has a cetane number of around 8-15. In contrast, diesel fuel typically has a cetane number of 40-55.
4. Ignition delay: The low cetane number of alcohol fuels leads to a longer ignition delay. Ignition delay refers to the time between the start of fuel injection and the start of combustion. A longer ignition delay can result in poor combustion, incomplete fuel burn, and reduced engine performance.
5. Compression ignition: Alcohol fuels with low cetane numbers require higher compression ratios or higher temperatures to achieve self-ignition. Diesel engines are designed to operate with a specific compression ratio, and altering this ratio for alcohol fuels may not be feasible or efficient.
6. Other factors: In addition to the low cetane number, alcohol fuels also have lower energy content compared to diesel fuel, which can further reduce their efficiency as engine fuels. They also have different physical properties, such as higher volatility and lower lubricity, which may require modifications to engine components and fuel systems.
In conclusion, the low cetane number of alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, prevents their ignition by combustion in diesel engines. This limitation, along with other factors, makes alcohol fuels unsuitable as direct replacements for diesel fuel in diesel engines.
A spark plug gap is kept froma)0.6 to 1.8 mmb)0.2 to 0.8 mmc)0.4 to 0.9 mmd)0.3 to 0.7 mmCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
A spark plug gap is kept from- 0.3-0.7 mm because 0.3-0.7 is perfect gap for making spark in spark plug.
The Mercury is known as non-wetting liquid because it does not wet the surface. The Mercury posses this property due to- a)Cohesion
- b)Adhesion
- c)Viscosity
- d)Surface tension
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Mercury is known as non-wetting liquid because it does not wet the surface. The Mercury posses this property due to
a)
Cohesion
b)
Adhesion
c)
Viscosity
d)
Surface tension
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Correct Answer :- a
Explanation : Capillarity is the property of both cohesion and adhesion. But surface tension is due to cohesion only it does not involve adhesion. As cohesive force is higher than adhesion in mercury it does not wet the glass.
Wrought iron- a)is a ductile material
- b)can be easily forged or welded
- c)cannot stand suden and excessive shocks
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Wrought iron
a)
is a ductile material
b)
can be easily forged or welded
c)
cannot stand suden and excessive shocks
d)
all of these
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : Wrought iron is an iron alloy with very low carbon content with respect to cast iron. It is soft, ductile, magnetic, and has high elasticity and tensile strength. It can be heated and reheated and worked into various shapes.
A streamlined body is such that :- a)It produces no drag for flow around it
- b)it is symmetrical about the axis along the free stream
- c)Sepration of flow is avoided along its surface
- d)the shape of the body coincides with the stream surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A streamlined body is such that :
a)
It produces no drag for flow around it
b)
it is symmetrical about the axis along the free stream
c)
Sepration of flow is avoided along its surface
d)
the shape of the body coincides with the stream surface
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
A streamlined body
is a shape that lowers the friction drag between a fluid, like air and water, and an object moving through that fluid. It occurs when the fluid closest to the object sticks to its surface, exerting a force that opposes the object's motion.
Which of the following is not a boiler mounting?- a)Blow off cock
- b)Feed check valve
- c)Economiser
- d)Fusible plug
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a boiler mounting?
a)
Blow off cock
b)
Feed check valve
c)
Economiser
d)
Fusible plug
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Economizer is boiler accessory and others are mounting
In arc welding, arc is created between the electrode and work by - a)Contact resistance
- b)Flow of current
- c)Voltage
- d)Material characteristics
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In arc welding, arc is created between the electrode and work by
a)
Contact resistance
b)
Flow of current
c)
Voltage
d)
Material characteristics
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
An arc is generated between two conductors of electricity, cathode and anode (considering direct current, DC), when they are touched to establish the flow of current and then separated by a small distance. An arc is a sustained electric discharge through this ionised gas column called plasma between the two electrodes.
A couple produces- a)translatory motion
- b)Rotational Motion
- c)combined translatory and rotational motion
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A couple produces
a)
translatory motion
b)
Rotational Motion
c)
combined translatory and rotational motion
d)
none of the above
|
|
Om Desai answered |
A couple in mechanics refers to two equal forces that act in opposite direction . The resultant force in a couple is zero, but it does have a moment of force(torque).A couple produces rotational motion in the object it is acting.
In steam and other vapour cycle, the process of removing non-condensable is called- a)dearation process
- b)Scavenging process
- c)Exhaust process
- d)Condensation process
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In steam and other vapour cycle, the process of removing non-condensable is called
a)
dearation process
b)
Scavenging process
c)
Exhaust process
d)
Condensation process

|
Srestha Datta answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', the process of removing non-condensable is called scavenging process. The scavenging process is an important step in the operation of steam and other vapor cycle systems to ensure efficient and effective heat transfer.
Scavenging Process:
The scavenging process involves the removal of non-condensable gases from the vapor cycle system. Non-condensable gases are substances that do not easily condense into a liquid state at the operating temperature and pressure of the system. These gases can accumulate in the system and hinder the heat transfer process, leading to decreased system efficiency and performance.
Reasons for Non-Condensable Gases:
Non-condensable gases can enter the vapor cycle system from various sources, including air leaks, incomplete purging during system startup, or the presence of volatile substances. These gases can include air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases.
Effects of Non-Condensable Gases:
The presence of non-condensable gases in the vapor cycle system can lead to several adverse effects:
1. Reduced Heat Transfer: Non-condensable gases create a barrier between the heat source (such as a boiler or condenser) and the working fluid (such as steam or refrigerant). This barrier hinders the transfer of heat, reducing the overall efficiency of the system.
2. Increased Pressure: Non-condensable gases can accumulate in certain parts of the system, leading to increased pressure. This can cause operational issues and potentially damage system components.
3. Corrosion: Non-condensable gases can react with the working fluid or the materials within the system, leading to corrosion and degradation of system components over time.
Methods of Scavenging:
There are various methods employed to remove non-condensable gases from the vapor cycle system:
1. Purging: Purging involves removing the non-condensable gases from the system by introducing a purge gas (typically steam or an inert gas) and venting the mixture of gases. This process is commonly used during system startup and shutdown.
2. Deaeration: Deaeration is a process that involves removing dissolved gases from the working fluid. This is typically done using deaerator tanks or trays, where the working fluid is heated and exposed to a vacuum to facilitate gas removal.
3. Condenser Air Extraction: In steam power plants, air extraction systems are used to remove non-condensable gases from the condenser. These systems extract air from the condenser and discharge it to the atmosphere.
Importance of Scavenging:
The scavenging process is crucial to maintain the efficiency and performance of vapor cycle systems. By removing non-condensable gases, heat transfer is enhanced, pressure is controlled, and the risk of corrosion is minimized. Regular scavenging helps to ensure optimal system operation and prevents potential issues associated with the presence of non-condensable gases.
In conclusion, the process of removing non-condensable gases from steam and other vapor cycle systems is called the scavenging process. This process is essential for maintaining the efficiency, performance, and longevity of the system by enhancing heat transfer, controlling pressure, and preventing corrosion.
Scavenging Process:
The scavenging process involves the removal of non-condensable gases from the vapor cycle system. Non-condensable gases are substances that do not easily condense into a liquid state at the operating temperature and pressure of the system. These gases can accumulate in the system and hinder the heat transfer process, leading to decreased system efficiency and performance.
Reasons for Non-Condensable Gases:
Non-condensable gases can enter the vapor cycle system from various sources, including air leaks, incomplete purging during system startup, or the presence of volatile substances. These gases can include air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases.
Effects of Non-Condensable Gases:
The presence of non-condensable gases in the vapor cycle system can lead to several adverse effects:
1. Reduced Heat Transfer: Non-condensable gases create a barrier between the heat source (such as a boiler or condenser) and the working fluid (such as steam or refrigerant). This barrier hinders the transfer of heat, reducing the overall efficiency of the system.
2. Increased Pressure: Non-condensable gases can accumulate in certain parts of the system, leading to increased pressure. This can cause operational issues and potentially damage system components.
3. Corrosion: Non-condensable gases can react with the working fluid or the materials within the system, leading to corrosion and degradation of system components over time.
Methods of Scavenging:
There are various methods employed to remove non-condensable gases from the vapor cycle system:
1. Purging: Purging involves removing the non-condensable gases from the system by introducing a purge gas (typically steam or an inert gas) and venting the mixture of gases. This process is commonly used during system startup and shutdown.
2. Deaeration: Deaeration is a process that involves removing dissolved gases from the working fluid. This is typically done using deaerator tanks or trays, where the working fluid is heated and exposed to a vacuum to facilitate gas removal.
3. Condenser Air Extraction: In steam power plants, air extraction systems are used to remove non-condensable gases from the condenser. These systems extract air from the condenser and discharge it to the atmosphere.
Importance of Scavenging:
The scavenging process is crucial to maintain the efficiency and performance of vapor cycle systems. By removing non-condensable gases, heat transfer is enhanced, pressure is controlled, and the risk of corrosion is minimized. Regular scavenging helps to ensure optimal system operation and prevents potential issues associated with the presence of non-condensable gases.
In conclusion, the process of removing non-condensable gases from steam and other vapor cycle systems is called the scavenging process. This process is essential for maintaining the efficiency, performance, and longevity of the system by enhancing heat transfer, controlling pressure, and preventing corrosion.
One Joule (J) is equal to- a)1 N-m
- b)100 N-m
- c)10 N-m/s
- d)10 kN-m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One Joule (J) is equal to
a)
1 N-m
b)
100 N-m
c)
10 N-m/s
d)
10 kN-m/s
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The joule symbol: J) is a derived unit of energy in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy transferred to (or work done on) an object when a force of one newton acts on that object in the direction of its motion through a distance of one metre (1 newton metre or N⋅m).
Chapter doubts & questions for Mechanical Engineering (SSC JE) Tests - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Mechanical Engineering (SSC JE) Tests - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026
3 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup