All Exams >
JEE >
6 Months Preparation for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of General Organic Chemistry (GOC) for JEE Exam
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar - a)The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
- b)In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
- c)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
- d)The most stable conformer is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a)
The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b)
In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d)
The most stable conformer is non-polar
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option D
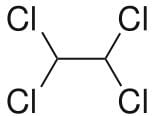
This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°

This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°
Nitration of benzene is:- a)Free radical substitution reaction
- b)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Electrophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitration of benzene is:
a)
Free radical substitution reaction
b)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
c)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Nitration and sulfonation of benzene are two examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution. The nitronium ion (NO2+) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the electrophiles and individually react with benzene to give nitrobenzene and benzenesulfonic acid respectively.
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- a)alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- b)Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
- c)Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
- d)Open chain compounds and closed compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
a)
alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
b)
Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
c)
Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
d)
Open chain compounds and closed compounds

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option D
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?- a)Theoretically infinite conformers exist
- b)Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
- c)Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
- d)By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?
a)
Theoretically infinite conformers exist
b)
Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
c)
Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
d)
By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)- a)Naphthalene
- b)Aniline
- c)Pyridine
- d)Tropolone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)
a)
Naphthalene
b)
Aniline
c)
Pyridine
d)
Tropolone

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Pyridine is heterocyclic aromatic compound. Whereas naphthalene and aniline are benzenoid aromatic compounds and tropolone is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?- a)Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
- b)Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
- c)Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
- d)Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?
a)
Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
b)
Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
c)
Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
d)
Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Correct answer is option D
Chair >Twist boat > Boat > Half-chair
above is the stability order of
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
Aliphatic compound is the other name for- a)Acyclic compounds
- b)Alicyclic compounds
- c)Ring compounds
- d)Closed chain compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aliphatic compound is the other name for
a)
Acyclic compounds
b)
Alicyclic compounds
c)
Ring compounds
d)
Closed chain compounds

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group? - a)Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
- c)Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
- d)Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group?
a)
Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
c)
Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
d)
Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
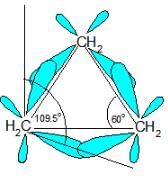
The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.

The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.
The correct IUPAC name of the following compound
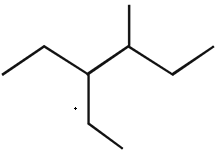
is:- a)4 - methyl - 3 - ethylhexane
- b)3 - ethyl - 4 - methylhexane
- c)3,4 - ethylmethylhexane
- d)4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the following compound

is:

is:
a)
4 - methyl - 3 - ethylhexane
b)
3 - ethyl - 4 - methylhexane
c)
3,4 - ethylmethylhexane
d)
4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhexane

|
Ogu Chukwunyere answered |
The answer is B, the 3rd Carbon atom with the ethyl group, and the methyl group in the 4th Carbon atom because -E- comes before -M-
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:- a)Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
- b)Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
- c)F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
- d)Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:
a)
Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
b)
Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
c)
F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
d)
Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option C
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:- a)Ethanal
- b)Carbocation
- c)Propene
- d)carbanion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:
a)
Ethanal
b)
Carbocation
c)
Propene
d)
carbanion
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Propene, also known as propylene or methyl ethylene, is an unsaturated organic compound having the chemical formula . It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons.
Identify the odd one among the following- a)Indene
- b)Anthracene
- c)o,m,p-xylene
- d)Azulene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the odd one among the following
a)
Indene
b)
Anthracene
c)
o,m,p-xylene
d)
Azulene

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Azulene is a non- benzenoid compound. Whereas, Indene, anthracene, and o,m,p-Xylene are examples of benzenoid aromatic compounds.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?- a)Cl3CCOOH
- b)ClCH2 COOH
- c)Cl2CH COOH
- d)CH3 COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?
a)
Cl3CCOOH
b)
ClCH2 COOH
c)
Cl2CH COOH
d)
CH3 COOH

|
Subhashini Nimashakavi answered |
Because cl3c reacts string than all
The correct statement regarding cyclopropane is/are- a)It has the highest angle strain among cycloalkanes
- b)It has smaller heat of hydrogenation per mole of —CH2— than cyclohexane
- c)It has large torsional strain due to all eclipsed C—H bonds on adjacent carbons
- d)Conformations in cyclopropane is due to flipping of bonds
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement regarding cyclopropane is/are
a)
It has the highest angle strain among cycloalkanes
b)
It has smaller heat of hydrogenation per mole of —CH2— than cyclohexane
c)
It has large torsional strain due to all eclipsed C—H bonds on adjacent carbons
d)
Conformations in cyclopropane is due to flipping of bonds
|
|
Puja Pillai answered |
The correct answers are Options A and C.
In cyclopropane the angle strain is maximum. Hence, it is a highly strained molecule and consequently most unstable.In cyclopropane, the adjacent CH2 groups are also eclipsed. Unlike in ethane, this strain cannot be relieved through rotation (the ring is too rigid). In other words, the CH2 groups are locked in the eclipsed conformation, which results in torsional strain – much like a propeller that has been wound up but held in position.
In cyclopropane the angle strain is maximum. Hence, it is a highly strained molecule and consequently most unstable.In cyclopropane, the adjacent CH2 groups are also eclipsed. Unlike in ethane, this strain cannot be relieved through rotation (the ring is too rigid). In other words, the CH2 groups are locked in the eclipsed conformation, which results in torsional strain – much like a propeller that has been wound up but held in position.
Find the odd one among the following:- a)Alicyclic compounds
- b)Heterogeneous compounds
- c)Branched chain compounds
- d)Aromatic compounds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the odd one among the following:
a)
Alicyclic compounds
b)
Heterogeneous compounds
c)
Branched chain compounds
d)
Aromatic compounds

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Branched chain compound is a classification of open-chain compounds. Whereas, alicyclic, aromatic and heterogeneous compounds are sub-classifications of cyclic compounds.
The correct statement concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol is/are- a)Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer
- b)There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer
- c)The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer
- d) Dissolving, in water lower the percentage of most stable conformer
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol is/are
a)
Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer
b)
There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer
c)
The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer
d)
Dissolving, in water lower the percentage of most stable conformer
|
|
Naveen Chavan answered |
Conformers of 2-Fluoroethanol:
Conformers are different arrangements of atoms that can be achieved by rotating around single bonds. For 2-fluoroethanol, there are three different conformers possible:
1) Anti-conformer
2) Gauche-conformer
3) Syn-conformer
Statement Analysis:
a) Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable conformer of 2-fluoroethanol is the gauche-conformer.
b) There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer - This statement is correct. In the most stable gauche-conformer, there is intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl (-OH) group and the fluorine atom.
c) The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable gauche-conformer has the least steric strain among all three conformers.
d) Dissolving in water lowers the percentage of the most stable conformer - This statement is correct. Dissolving in water disrupts the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the most stable gauche-conformer, leading to a decrease in its percentage.
Therefore, the correct statements concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol are B, C, and D.
Conformers are different arrangements of atoms that can be achieved by rotating around single bonds. For 2-fluoroethanol, there are three different conformers possible:
1) Anti-conformer
2) Gauche-conformer
3) Syn-conformer
Statement Analysis:
a) Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable conformer of 2-fluoroethanol is the gauche-conformer.
b) There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer - This statement is correct. In the most stable gauche-conformer, there is intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl (-OH) group and the fluorine atom.
c) The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable gauche-conformer has the least steric strain among all three conformers.
d) Dissolving in water lowers the percentage of the most stable conformer - This statement is correct. Dissolving in water disrupts the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the most stable gauche-conformer, leading to a decrease in its percentage.
Therefore, the correct statements concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol are B, C, and D.
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds- a)They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
- b)Contain straight chain compounds
- c)Contain branched chain compounds
- d)Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds
a)
They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
b)
Contain straight chain compounds
c)
Contain branched chain compounds
d)
Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups

|
Ruchi Basak answered |
The aromatic compounds (4n+2)pi electrons, which comes under the classification of cyclic compounds and hence they are not associated with aliphatic compounds.
In Friedel crafts alkylation and acylation the attacking reagent is an:- a)Electrophile
- b)Nucleophile
- c)Radical
- d)Ionic species
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Friedel crafts alkylation and acylation the attacking reagent is an:
a)
Electrophile
b)
Nucleophile
c)
Radical
d)
Ionic species

|
Aaditya Ghoshal answered |
A Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction in which a carbocation attacks an aromatic ring with the net result that one of the aromatic protons is replaced by an alkyl group. vinyl and aryl halides cannot be used to form carbocations.
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethane
- c)Cyclopropane
- d)Isobutane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethane
c)
Cyclopropane
d)
Isobutane

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
Cyclopropane is a ring (cyclic) compound and hence it does not come with the examples of open chain compounds.
Halogenation proceeds via:- a)Addition process
- b)Combustion
- c)Termination
- d)Free radical chain mechanism
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Halogenation proceeds via:
a)
Addition process
b)
Combustion
c)
Termination
d)
Free radical chain mechanism
|
|
Puja Pillai answered |
Understanding Halogenation
Halogenation is a chemical reaction where halogens (such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) are added to organic compounds, particularly alkanes and alkenes.
Free Radical Chain Mechanism
The correct answer to how halogenation proceeds is through the free radical chain mechanism. This process can be broken down into three main stages:
Characteristics of Free Radical Mechanism
In summary, halogenation primarily occurs through the free radical chain mechanism, involving initiation, propagation, and termination stages.
Halogenation is a chemical reaction where halogens (such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) are added to organic compounds, particularly alkanes and alkenes.
Free Radical Chain Mechanism
The correct answer to how halogenation proceeds is through the free radical chain mechanism. This process can be broken down into three main stages:
- Initiation: This stage involves the formation of free radicals. For example, when chlorine gas (Cl2) is exposed to heat or light, it dissociates into two chlorine radicals (Cl•). These radicals are highly reactive.
- Propagation: In this stage, the chlorine radicals react with the alkane molecules. A radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from the alkane, forming hydrochloric acid (HCl) and a new alkyl radical. This new radical can further react with another chlorine molecule, generating more chlorine radicals and continuing the chain reaction.
- Termination: This final stage occurs when two radicals combine to form a stable product, effectively stopping the chain reaction. Termination can happen in various ways, such as the combination of two chlorine radicals or the combination of an alkyl radical and a chlorine radical.
Characteristics of Free Radical Mechanism
- Chain Reaction: The process is characterized by a series of reactions that can propagate rapidly.
- Temperature and Light Sensitivity: The initiation phase often requires heat or light, making it sensitive to environmental conditions.
- Radical Stability: The stability of radicals influences the reaction pathway, affecting which products are formed.
In summary, halogenation primarily occurs through the free radical chain mechanism, involving initiation, propagation, and termination stages.
The number of structural isomers for C6H12 is:- a)4
- b)3
- c)6
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of structural isomers for C6H12 is:
a)
4
b)
3
c)
6
d)
5
|
|
Tanvi Iyer answered |
Understanding Structural Isomers of C6H12
The molecular formula C6H12 represents an alkane or a cycloalkane. Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms. For C6H12, we can have various structural isomers based on the type of carbon chain and branching.
Types of Isomers for C6H12
- Straight-chain Alkanes:
- Hexane (n-hexane) is the straight-chain form.
- Branched Alkanes:
- 2-Methylpentane
- 3-Methylpentane
- 2,2-Dimethylbutane
- 2,3-Dimethylbutane
- 3,3-Dimethylbutane
- Cycloalkanes:
- Cyclohexane is another form, which is a cyclic structure.
Total Count of Isomers
- Counting the Isomers:
- There are 5 branched-chain isomers from the straight-chain hexane.
- Adding cyclohexane gives a total of 6 structural isomers.
Conclusion
Thus, the total number of structural isomers for C6H12 is 5 branched isomers plus 1 cyclic isomer, totaling 6 structural isomers. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which states that there are 5 branched isomers.
This comprehensive understanding of structural isomers showcases the diversity of organic compounds even with the same molecular formula.
The molecular formula C6H12 represents an alkane or a cycloalkane. Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms. For C6H12, we can have various structural isomers based on the type of carbon chain and branching.
Types of Isomers for C6H12
- Straight-chain Alkanes:
- Hexane (n-hexane) is the straight-chain form.
- Branched Alkanes:
- 2-Methylpentane
- 3-Methylpentane
- 2,2-Dimethylbutane
- 2,3-Dimethylbutane
- 3,3-Dimethylbutane
- Cycloalkanes:
- Cyclohexane is another form, which is a cyclic structure.
Total Count of Isomers
- Counting the Isomers:
- There are 5 branched-chain isomers from the straight-chain hexane.
- Adding cyclohexane gives a total of 6 structural isomers.
Conclusion
Thus, the total number of structural isomers for C6H12 is 5 branched isomers plus 1 cyclic isomer, totaling 6 structural isomers. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which states that there are 5 branched isomers.
This comprehensive understanding of structural isomers showcases the diversity of organic compounds even with the same molecular formula.
Which among the following is not a class of organic compound- a)Carbonyl compound
- b)Nitro compound
- c)Amides
- d)Electro compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not a class of organic compound
a)
Carbonyl compound
b)
Nitro compound
c)
Amides
d)
Electro compounds

|
Ishani Mehta answered |
Classes of organic compounds are those which involves organic compounds such as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Hence, electro compounds is not a class of organic compounds.
Consider the various conformers possible for meso form and enantiomeric 1,2-dibromo-1,2-dichloroethane and select the correct statement(s).- a)Both have exactly same energy barrier to rotation
- b)The most stable conformer of meso form has lower potential energy than of enantiomeric form
- c)In most stable conformer of an enantiomer, the dihedral angle between bromine atoms is 180°
- d)In the most of the conformation, meso form is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the various conformers possible for meso form and enantiomeric 1,2-dibromo-1,2-dichloroethane and select the correct statement(s).
a)
Both have exactly same energy barrier to rotation
b)
The most stable conformer of meso form has lower potential energy than of enantiomeric form
c)
In most stable conformer of an enantiomer, the dihedral angle between bromine atoms is 180°
d)
In the most of the conformation, meso form is non-polar

|
Gayathri Good answered |
A
The correct statement regarding conformation in butane is/are- a)The two gauche forms, when viewed about C2 - C3 bond, are enantiomer
- b)There is greater barrier to rotation about C1 — C2 bond than to C2 - C3 bond
- c)Its gauche form has higher energy than an eclipsed form when CH3 — and 'H' are eclipsing
- d)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is only 60°
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement regarding conformation in butane is/are
a)
The two gauche forms, when viewed about C2 - C3 bond, are enantiomer
b)
There is greater barrier to rotation about C1 — C2 bond than to C2 - C3 bond
c)
Its gauche form has higher energy than an eclipsed form when CH3 — and 'H' are eclipsing
d)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is only 60°
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
A) For ethane, there exists three conformational isomers or conformers, which are degenerate because they are congruent. They have the same energy and are same, in all respects.
D) Gauche is the most stable form with less repulsion.
D) Gauche is the most stable form with less repulsion.
For the separation of two miscible liquids which method is used?- a)Chromatography
- b)Fractional column
- c)Fractional distillation
- d)Separating funnel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the separation of two miscible liquids which method is used?
a)
Chromatography
b)
Fractional column
c)
Fractional distillation
d)
Separating funnel

|
Simran Gupta answered |
Understanding Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is a crucial method used for separating two miscible liquids based on their differing boiling points. This technique is particularly effective when the boiling points of the components are close to each other.
How Fractional Distillation Works
- Heating the Mixture: The liquid mixture is heated in a distillation flask. As the temperature rises, the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first.
- Vaporization and Cooling: The vapor travels up a fractionating column, where it cools and condenses. The column is designed to provide a large surface area for repeated vaporization and condensation, enhancing separation.
- Collection of Distillate: The condensed vapor is then collected as a distillate in a receiving flask. The process can be repeated to maximize purity.
Advantages of Fractional Distillation
- Efficiency: It allows for the effective separation of liquids with boiling points that are very close together, typically within 25°C.
- Purity: The method can yield highly pure components, which is essential in chemical processes and industries.
Applications
- Petrochemical Industry: Used extensively to separate different hydrocarbons in crude oil.
- Alcohol Production: Employed in distilling alcoholic beverages to separate ethanol from water and other components.
In summary, fractional distillation is the preferred method for separating miscible liquids due to its ability to exploit differences in boiling points efficiently, thereby allowing for the collection of pure substances.
Fractional distillation is a crucial method used for separating two miscible liquids based on their differing boiling points. This technique is particularly effective when the boiling points of the components are close to each other.
How Fractional Distillation Works
- Heating the Mixture: The liquid mixture is heated in a distillation flask. As the temperature rises, the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first.
- Vaporization and Cooling: The vapor travels up a fractionating column, where it cools and condenses. The column is designed to provide a large surface area for repeated vaporization and condensation, enhancing separation.
- Collection of Distillate: The condensed vapor is then collected as a distillate in a receiving flask. The process can be repeated to maximize purity.
Advantages of Fractional Distillation
- Efficiency: It allows for the effective separation of liquids with boiling points that are very close together, typically within 25°C.
- Purity: The method can yield highly pure components, which is essential in chemical processes and industries.
Applications
- Petrochemical Industry: Used extensively to separate different hydrocarbons in crude oil.
- Alcohol Production: Employed in distilling alcoholic beverages to separate ethanol from water and other components.
In summary, fractional distillation is the preferred method for separating miscible liquids due to its ability to exploit differences in boiling points efficiently, thereby allowing for the collection of pure substances.
One molecule of water adds to alkynes on warming with mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid to form:
- a)Carbonyl compound
- b)Propane
- c)Ethyl free radical
- d)Isopropyl free radical
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One molecule of water adds to alkynes on warming with mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid to form:
a)
Carbonyl compound
b)
Propane
c)
Ethyl free radical
d)
Isopropyl free radical
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
When one molecule of alkynes react with mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid at 333 K it result into the formation of carbonyl compounds.
Reaction involved:
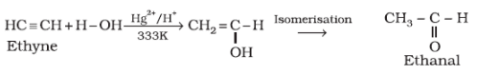
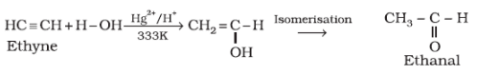
Which of the following cycloalkanes exhibits the greatest molar heat of combustion per —CH2 — group?- a)Methylcyclobutane
- b)Cyclopentane
- c)Cyclobutane
- d)Cyclopropane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cycloalkanes exhibits the greatest molar heat of combustion per —CH2 — group?
a)
Methylcyclobutane
b)
Cyclopentane
c)
Cyclobutane
d)
Cyclopropane

|
Nishanth Verma answered |
Cyclopropane is a cycloalkane molecule with the molecular formula C3H6, consisting of three carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing two hydrogen atoms resulting in D3h molecular symmetry. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Jay Chakraborty answered |
n-pentane, 2-ethylpropane, and 2-methylbutane are the 3 isomeric alkanes of C5H12 (pentane).
The correct statement concerning conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane is- a)it's gauche conformer has higher potential energy than an eclipsed conformer in which H—Cl atoms are eclipsing
- b)syn-periplanar conformer is most stable
- c)increasing temperature decreases dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane
- d)the two gauche conformers are enantiomers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement concerning conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane is
a)
it's gauche conformer has higher potential energy than an eclipsed conformer in which H—Cl atoms are eclipsing
b)
syn-periplanar conformer is most stable
c)
increasing temperature decreases dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane
d)
the two gauche conformers are enantiomers
|
|
Rishabh Malhotra answered |
Option D is correct answer
Which among the following is not an example of alicyclic compound- a)Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexene
- c)Tetrahydrofuran
- d)Acetic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an example of alicyclic compound
a)
Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexene
c)
Tetrahydrofuran
d)
Acetic acid

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Acetic acid is a linear chain compound (acyclic) and hence it is not an example of ring compound (alicyclic).
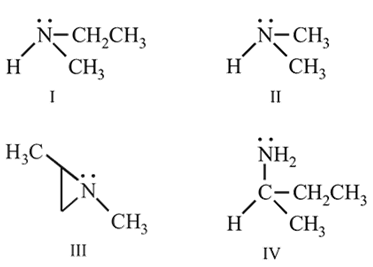
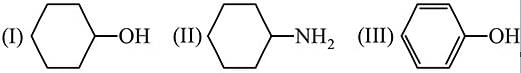
Which of the following amines can be resolved into two enantiomers?
- a)I,IV
- b)I, II
- c)I, III, IV
- d)III, IV
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amines can be resolved into two enantiomers?


a)
I,IV
b)
I, II
c)
I, III, IV
d)
III, IV

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
Most of the simple amines those having smaller alkyl (groups) can't be resolved, although they may contain three different alkyl groups.
Majority of the reactions of alkynes are the examples of:- a)Optical isomerism
- b)Displacement reactions
- c)Homolytic cleavage
- d)Addition reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Majority of the reactions of alkynes are the examples of:
a)
Optical isomerism
b)
Displacement reactions
c)
Homolytic cleavage
d)
Addition reaction

|
Aravind Kapoor answered |
Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds, such as molecules with carbon–carbon double bonds (alkenes), or with triple bonds (alkynes). Two non-polar addition reactions exist as well, called free-radical addition and cycloadditions.
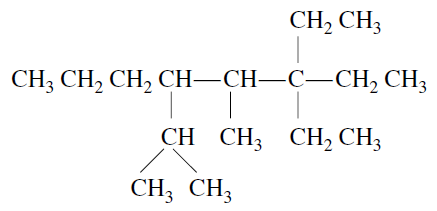
The IUPAC name of the compound
is- a)3,3,-diethyl-4-methyl-5-isopropyloctane
- b)3,3-diethyl-5-isopropyl-4-methyloctane
- c)4-isopropyl-5-methyl-6,6-diethyloctane
- d)6,6-diethyl-4-isopropyl-5-methyloctane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound

is

is
a)
3,3,-diethyl-4-methyl-5-isopropyloctane
b)
3,3-diethyl-5-isopropyl-4-methyloctane
c)
4-isopropyl-5-methyl-6,6-diethyloctane
d)
6,6-diethyl-4-isopropyl-5-methyloctane

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
3,3-diethyl-5-isopropyl-4-methyloctane
Arrange the following free radicals in the correct order of their stability
(i) 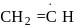
(ii) 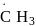
(iii) 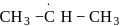
(iv) 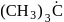
- a)i > ii > iii > iv
- b)iv > iii > ii > i
- c)i > iii > ii > iv
- d)iv >i ii > i > ii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following free radicals in the correct order of their stability
(i)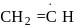
(ii)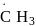
(iii)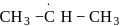
(iv)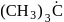
(i)
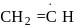
(ii)
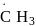
(iii)
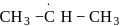
(iv)
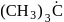
a)
i > ii > iii > iv
b)
iv > iii > ii > i
c)
i > iii > ii > iv
d)
iv >i ii > i > ii

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The stability of free radicals follows the order:-
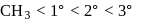
Thus, stability order will be :-
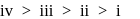
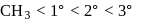
Thus, stability order will be :-
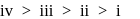
Which of the following structures are aromatic?
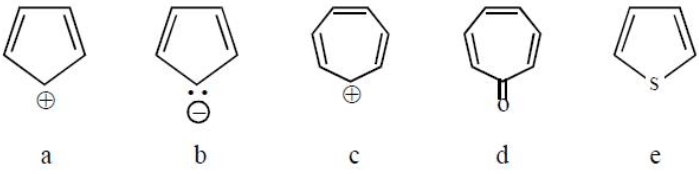
- a)a, c, e
- b)b, c, d, e
- c)a, b, c
- d)b, d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures are aromatic?


a)
a, c, e
b)
b, c, d, e
c)
a, b, c
d)
b, d

|
Learners Habitat answered |
Compounds b, c, d, e all have (4n + 2) pie electrons hence all compounds listed are aromatic.
Select the correct statement(s) regarding conformers of 1,2-dimethyl cyclohexane.- a)In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at both axial and equatorial position
- b)In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at equatorial positions only
- c)In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at axial positions only
- d)In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at equatorial positions only
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) regarding conformers of 1,2-dimethyl cyclohexane.
a)
In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at both axial and equatorial position
b)
In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at equatorial positions only
c)
In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at axial positions only
d)
In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at equatorial positions only
|
|
Ananya Sarkar answered |
Conformers of 1,2-dimethyl cyclohexane:
1,2-dimethyl cyclohexane has two possible conformations: cis and trans.
Cis-isomer:
- In the most stable conformation, the cis-isomer has one methyl group in the axial position and the other in the equatorial position.
- This conformation is more stable because it reduces steric hindrance between the two methyl groups.
- The axial methyl group experiences more steric hindrance than the equatorial methyl group. Therefore, it is preferable to have the axial methyl group to be smaller.
Trans-isomer:
- In the most stable conformation, the trans-isomer has both methyl groups in the equatorial position.
- This conformation is more stable because it reduces steric hindrance between the two methyl groups.
- If both methyl groups were in the axial position, it would result in a high energy conformation due to steric hindrance.
- The equatorial position is preferred because it allows the methyl groups to be farther apart from each other, reducing steric hindrance.
Therefore, the correct statements are:
a) In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at both axial and equatorial position
d) In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at equatorial positions only.
1,2-dimethyl cyclohexane has two possible conformations: cis and trans.
Cis-isomer:
- In the most stable conformation, the cis-isomer has one methyl group in the axial position and the other in the equatorial position.
- This conformation is more stable because it reduces steric hindrance between the two methyl groups.
- The axial methyl group experiences more steric hindrance than the equatorial methyl group. Therefore, it is preferable to have the axial methyl group to be smaller.
Trans-isomer:
- In the most stable conformation, the trans-isomer has both methyl groups in the equatorial position.
- This conformation is more stable because it reduces steric hindrance between the two methyl groups.
- If both methyl groups were in the axial position, it would result in a high energy conformation due to steric hindrance.
- The equatorial position is preferred because it allows the methyl groups to be farther apart from each other, reducing steric hindrance.
Therefore, the correct statements are:
a) In the most stable conformation, cis-isomer has methyl groups at both axial and equatorial position
d) In the most stable conformation, trans-isomer has both methyl groups at equatorial positions only.
Which of the following numberings is correct?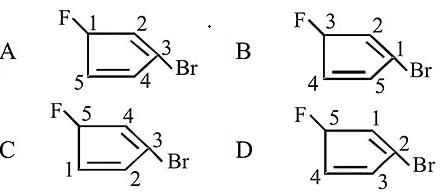
- a)A
- b)B
- c)
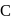
- d)
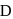
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following numberings is correct?

a)
A
b)
B
c)
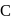
d)
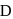

|
Manish Aggarwal answered |
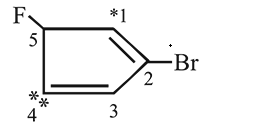
The highest priority functional group is the double bond, and the carbon chain must be numbered such that this functional group is given the lowest number carbon. This is then followed by the lowest numbering of both halogen groups. Therefore, (D) is the correct numbering.
The two compounds given below are
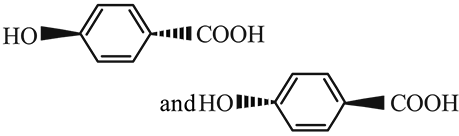
- a)identical
- b)enantiomers
- c)diastereo isomers
- d)regiomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The two compounds given below are
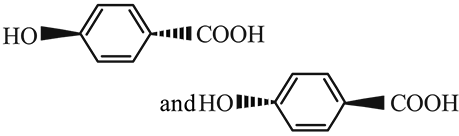
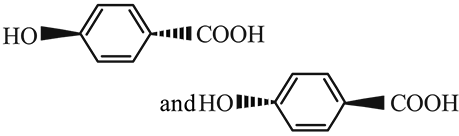
a)
identical
b)
enantiomers
c)
diastereo isomers
d)
regiomers

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
The given compounds are identical
Arrange in the order of increasing acidity.
- a)
- b)
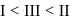
- c)III < II < I
- d)
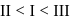
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange in the order of increasing acidity.


a)
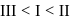
b)
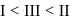
c)
III < II < I
d)
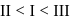

|
EduRev JEE answered |
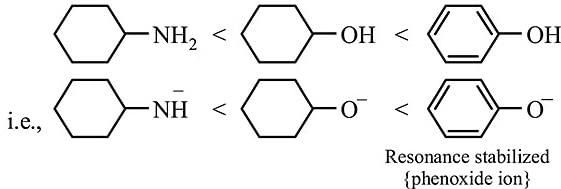
Order of Acidic strength ∝ stability of conjugate base.
Passage I The two major contributors of conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane are anti and gauche. At 32°C in gas phase, the measured dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane is 1.12 D. The dipole moment of a mixture of X and Y is given by the relationship 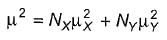 Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D. Q.
Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D. Q.
What is true about percentage of gauche conformer?- a)There is only one gauche conformer in about 12%
- b)There is only one gauche conformer in about 64%
- c)There is racemic mixture, although inseparable, of gauche conformers, about 12%
- d)There is racemic mixture, although inseparable, of gauche conformers, about 64%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The two major contributors of conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane are anti and gauche. At 32°C in gas phase, the measured dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane is 1.12 D. The dipole moment of a mixture of X and Y is given by the relationship
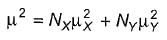
Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D.
Q.
What is true about percentage of gauche conformer?
What is true about percentage of gauche conformer?
a)
There is only one gauche conformer in about 12%
b)
There is only one gauche conformer in about 64%
c)
There is racemic mixture, although inseparable, of gauche conformers, about 12%
d)
There is racemic mixture, although inseparable, of gauche conformers, about 64%
|
|
Rakibul Halsana answered |
CC
Find out the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given following compound: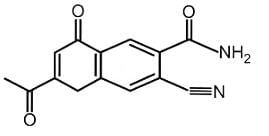
- a)12.00
- b)11.00
- c)13.00
- d)10.00
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given following compound:

a)
12.00
b)
11.00
c)
13.00
d)
10.00

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
The double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given compound is 11
Passage I The two major contributors of conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane are anti and gauche. At 32°C in gas phase, the measured dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane is 1.12 D. The dipole moment of a mixture of X and Y is given by the relationship 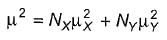 Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D. Q. What happens if temperature if increased to 52°C?
Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D. Q. What happens if temperature if increased to 52°C?- a)Percentage of gauche conformers decreases and that of anti-conformers increases
- b)Percentage of both gauche and anti conformers increases
- c)No change in percentage of anti and gauche conformers occur
- d)Percentage of both anti and gauche conformers decreases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The two major contributors of conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane are anti and gauche. At 32°C in gas phase, the measured dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane is 1.12 D. The dipole moment of a mixture of X and Y is given by the relationship
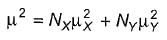
Here, N = mole fraction of each kind of molecule. From bond moment measurement, it has been estimated that gauche conformer of 1,2-dichloroethane should have a dipole moment of about 3.2 D.
Q.
What happens if temperature if increased to 52°C?
a)
Percentage of gauche conformers decreases and that of anti-conformers increases
b)
Percentage of both gauche and anti conformers increases
c)
No change in percentage of anti and gauche conformers occur
d)
Percentage of both anti and gauche conformers decreases
|
|
Rakibul Halsana answered |
D
Passage II
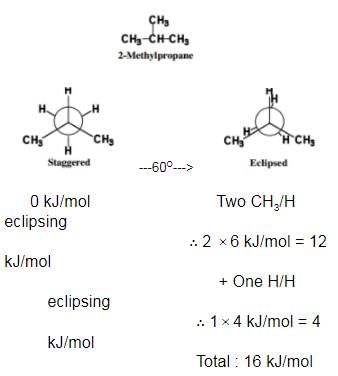
Among conformers, the barrier to rotation originate mainly from torsional strain when atoms or groups eclipse one another. Followings are the costs of energy required to cross the rotational barrier for the indicated pair of groups eclipsing
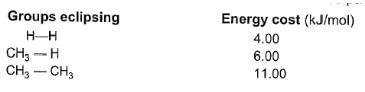 Q.What is the energy barrier to rotation in 2-methyl propane ?
Q.What is the energy barrier to rotation in 2-methyl propane ?- a)10 kJ/mol
- b)12 kJ/mol
- c)14 kJ/mol
- d)16 kJ/mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
Among conformers, the barrier to rotation originate mainly from torsional strain when atoms or groups eclipse one another. Followings are the costs of energy required to cross the rotational barrier for the indicated pair of groups eclipsing
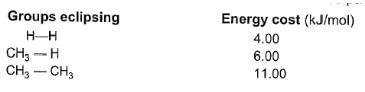
Q.
What is the energy barrier to rotation in 2-methyl propane ?
a)
10 kJ/mol
b)
12 kJ/mol
c)
14 kJ/mol
d)
16 kJ/mol
|
|
Ankita Patel answered |
The correct answer is Option D.

What is relationship between the following Fischer Projections?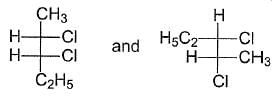
- a)Enantiomers
- b)Conformers
- c)Diastereomers
- d)Structural Isomers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is relationship between the following Fischer Projections?
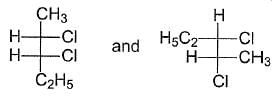
a)
Enantiomers
b)
Conformers
c)
Diastereomers
d)
Structural Isomers

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The Fischer Projections represent different types of stereoisomers. Here’s a breakdown of their relationships:
- Enantiomers: These are mirror images of each other and are not superimposable.
- Conformers: These are different spatial orientations of the same molecule, resulting from rotation around single bonds.
- Diastereomers: These are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another. They have different physical properties.
- Structural Isomers: These differ in the connectivity of their atoms, leading to different compounds.
The correct relationship for the given Fischer Projections is diastereomers.
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)The IUPAC name of
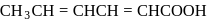 is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid.
is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid. - b)The IUPAC name of the compound
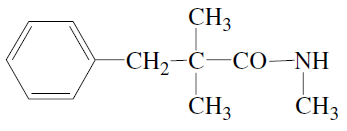 is N-methyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-phenylpropanamide.
is N-methyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-phenylpropanamide. - c)The IUPAC name of the compound
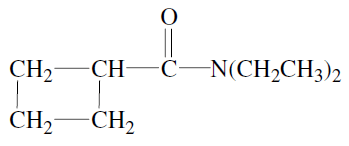 is N-N-diethylcyclobutanecarboxamide.
is N-N-diethylcyclobutanecarboxamide. - d)The IUPAC name of the compound
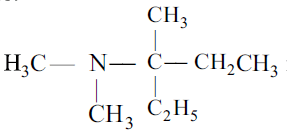 is (N,N-dimethylamino)-3-ethylbutane.
is (N,N-dimethylamino)-3-ethylbutane.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
The IUPAC name of 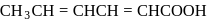 is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid.
is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid.
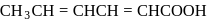 is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid.
is 2,4 -hexadienoic acid.b)
The IUPAC name of the compound
 is N-methyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-phenylpropanamide.
is N-methyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-phenylpropanamide.c)
The IUPAC name of the compound
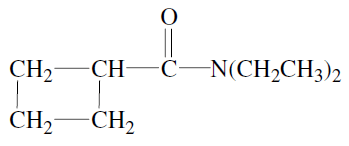 is N-N-diethylcyclobutanecarboxamide.
is N-N-diethylcyclobutanecarboxamide.d)
The IUPAC name of the compound
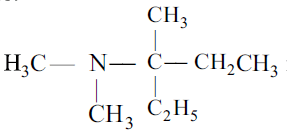 is (N,N-dimethylamino)-3-ethylbutane.
is (N,N-dimethylamino)-3-ethylbutane.

|
EduRev JEE answered |
The correct name is 3-(N, N-dimethylamino)-3-methylpentane
Chapter doubts & questions for General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - 6 Months Preparation for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - 6 Months Preparation for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup



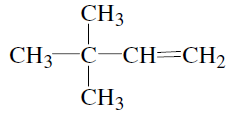
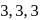 -Trimethylpropane
-Trimethylpropane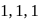 -Trimethylprop-2-ene
-Trimethylprop-2-ene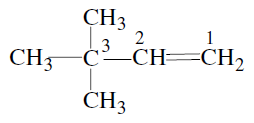
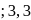 -Dimethylbut-1-ene
-Dimethylbut-1-ene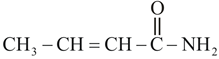 , is :-
, is :-